Behavioral Neuroscience Chapter 7
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Taste
- Both taste and smell are stimulated by chemical stimulation/transduction
-Food dissolves in saliva and stimulates taste receptors
Taste Qualities
Basic stimuli is the number of molecules in solution of spit "molar concentration"
Flavor
Dependent on both taste and smell
Six Basic Tastes
Sweet, bitter, saltiness, sour, Umami, Fatty acids
Sweet
Organic molecules with proper H-O-C balance "sugar"
Bitter
Organic molecules with proper H-O-C balance with nitrogen tacked onto it, some are our sot dangerous poisons.
Saltiness
Need Na to keep the sodium- potassium pump and action potential working.
Sour
Organic molecules with excess hydrogen, test for ripeness
Umami "savory"
"MSG" Glutamate ion binds to the glutamate receptor (flavor enhancer)
Fatty acids
Used for insulation and building the myelin sheath
taste buds
- all over the mouth, tongue, roof of mouth, and throat.
-each contains 20-50 receptor cells which live for 10 days
Three types of tasters
average, hard of tasting, super tasters
Taste Receptors
- Fungiform papillae
-Foliate Papillae
-Circumvalate Papillae
-Filliform papillae
Fungiform Papillae
Mushroom shaped, tip of the tongue and front sides
Foliate Papillae
Fold like shape, Primarily found on sides of the tongue
Circumvalate papillae
Hill like shaped, look like bumps, middle and back of the tongue
filliform papillae
File shaped, few in humans
- all over, but mainly front half and middle
Gustatory Pathway
1. Receptor cell s
2. Glossopharyngeal, facial, and vagus nerves
3.Nucleus of the solitary tract in the medulla
4. Thalamus
5. Primary gustatory cortex
6. Secondary gustatory cortex
7. Amygdala, hypothalamus
Factors affecting Taste intensity
- number of taste buds: more taste buds
-Temperature: our body temperature
-Tongue position: front of the tongue
-Olfaction: smell is strongly connected to taste
-Age: increased age = decreased taste buds (decay)
-Cross adaptation: potentiation
Deficits in Taste
Dysgeusia and Ageusia
Dysgeusia
Perception of a taste that is not present
-drugs use can cause this
-nerve damage
Ageusia
Lose the ability to taste substances : specific quality (bitter)
-total ageusia, total loss of tasting anything
-Partial ageusia, very insensitive to taste (can't taste very well)
Olfaction-"smell"
We can detect thousands of odors, but it is difficult to describe them.
- More so than others this sense is linked to the emotional areas of the brain
-Works both dismally and proximally (close and far)
- Compared to other senses we don't know much about this.
Olfactory epithelium (smell skin)
- Produces mucous
-Olfactory rods stick out of it. At the ends of these rods are projection cilia.
-Axons of olfactory nerves come together to form the olfactory nerve. (Must pass through a small opening in sinus cavity)
Factors affecting olfaction
-Flavor
-Number of molecules
-Volatility
-Solubility
-Age
number of molecules
concentration gradient
Volatility
How easily a substance sheds off molecules into the air (evaporate).
Solubility
Ability to dissolve in liquid
Age
We lose our sense of smell when we age
-Asomia: the loss of smell
Pheromones
Chemical detection of smell for communication
- unconscious detection of smell (cranial nerve zero)
-Most of the research done is with insects
Mammal Pheromones
Alpha-androstenal- sexual activity
Human research done on pheromones
-Babies can identify who their mother is and vice versa
-Dormitory Phenomena: females menstruating who live in the same area will often times find their cycles syncing up (if they are not on medication such as birth control).
Audition: three perceptual dimensions of sound
1. Pitch
2. Loudness
3.Timbre
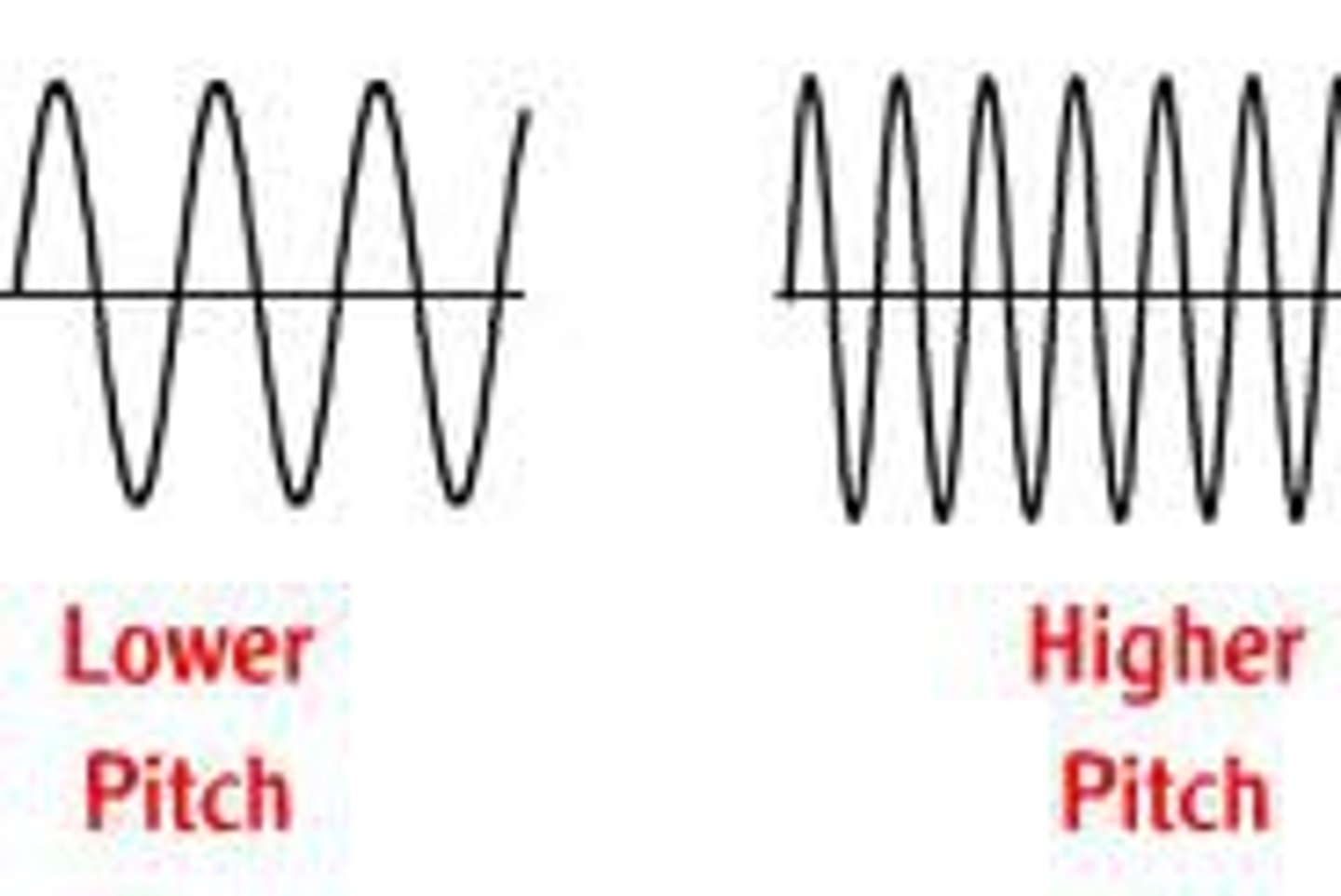
Pitch
- The frequency of vibration (measures in hertz)
-The greater the Hz, the higher the pitch
-Subwoofer is <10 Hz, (rather than hear this you instead feel it)
Loudness
The intensity of a sound

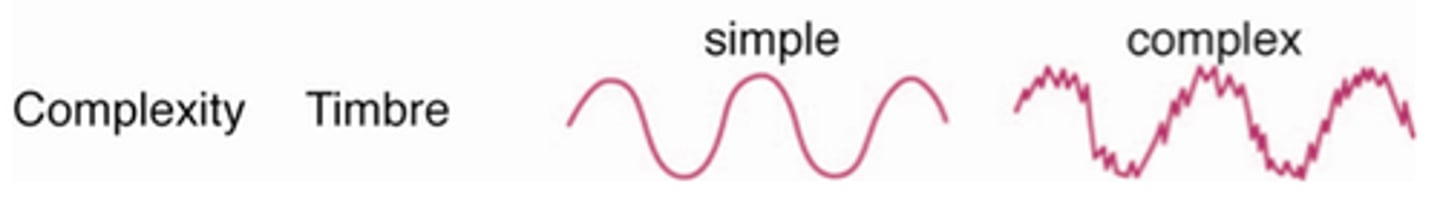
Timbre
- Complexity of sound frequencies, mixtures of frequencies
-In Addition to the note you were aiming for, what else is out there.
Amplitude (pressure one sound waves)
Measured in decibels (db)
Outer Ear: Pinna
- Gather sound waves in and channel to external auditory canal
-Helps with sound localization alters the shape of sound waves
-Can live without this but would lose a few decibels of hearing
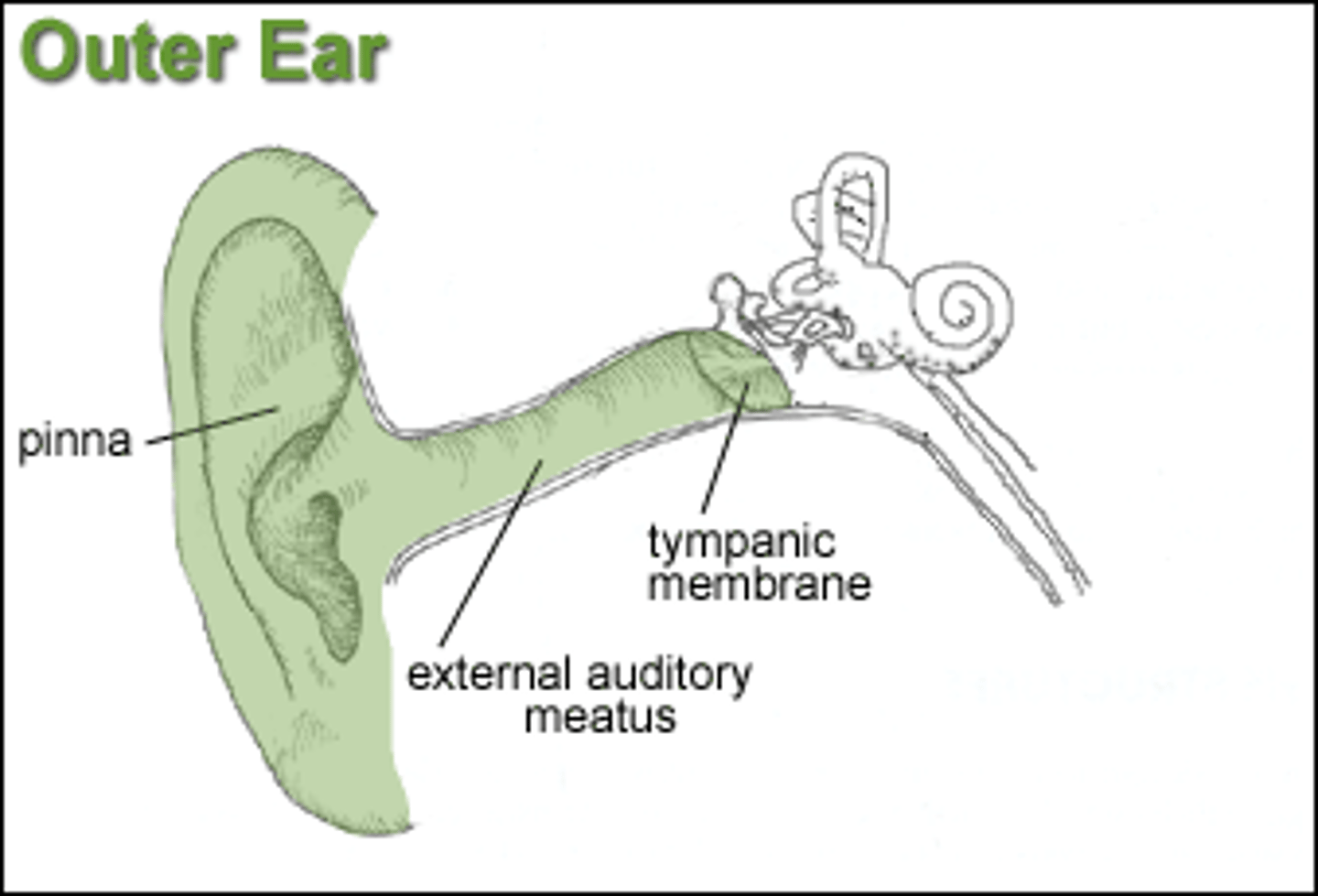
External Auditory Canal
Contains hair and wax glands to prevent dirt from entering deep into the ear
-Acute otitis external (Swimmers ear): Water can get stuck and form the breeding grounds for bacteria
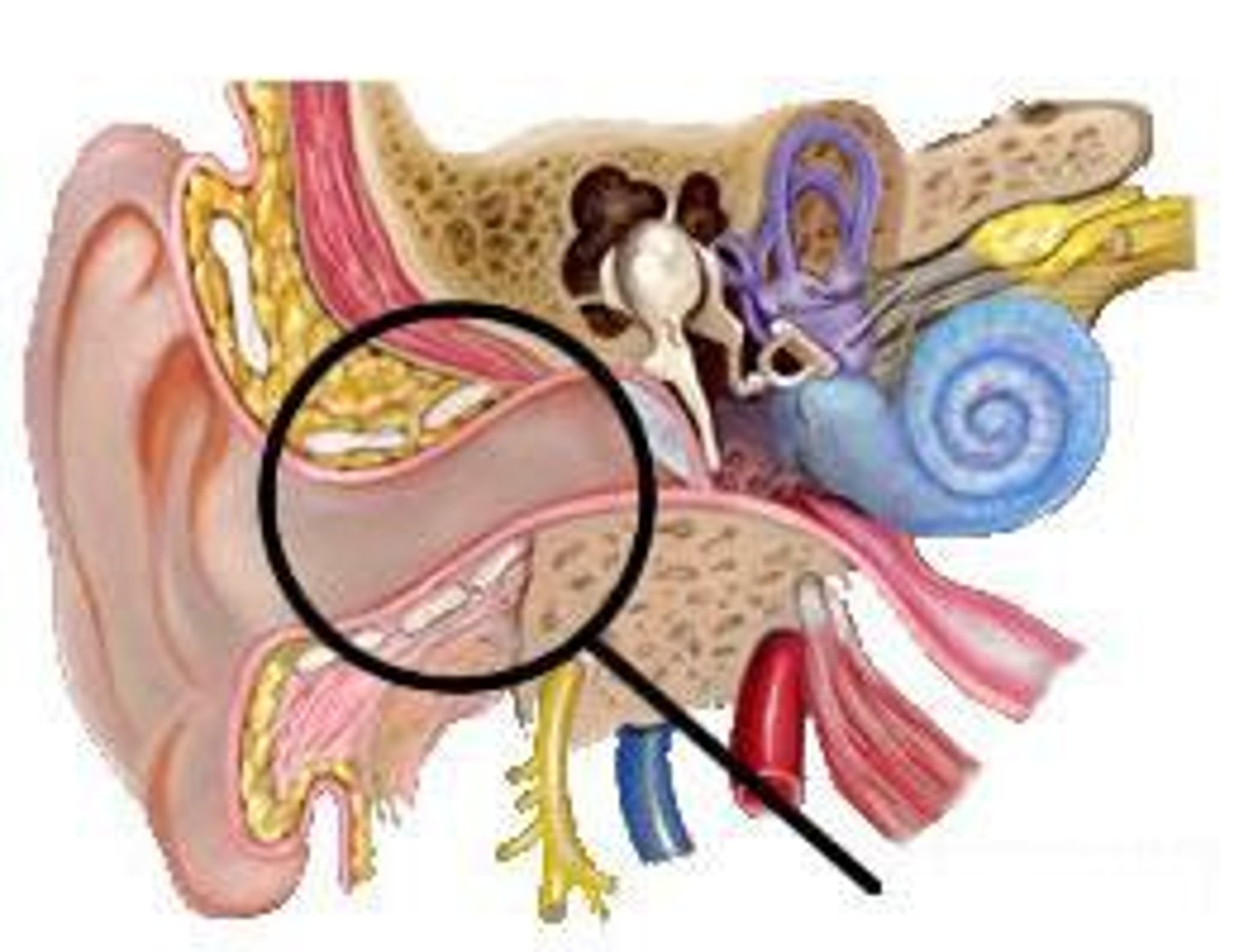
Tympanic Membrane "eardrum"
-Vibrates in and out in correspondence to sound waves hitting it.
-Mends itself if it gets torn or damaged, but mends with scar tissue so that it isn't as flexible.
-Very sensitive to touch
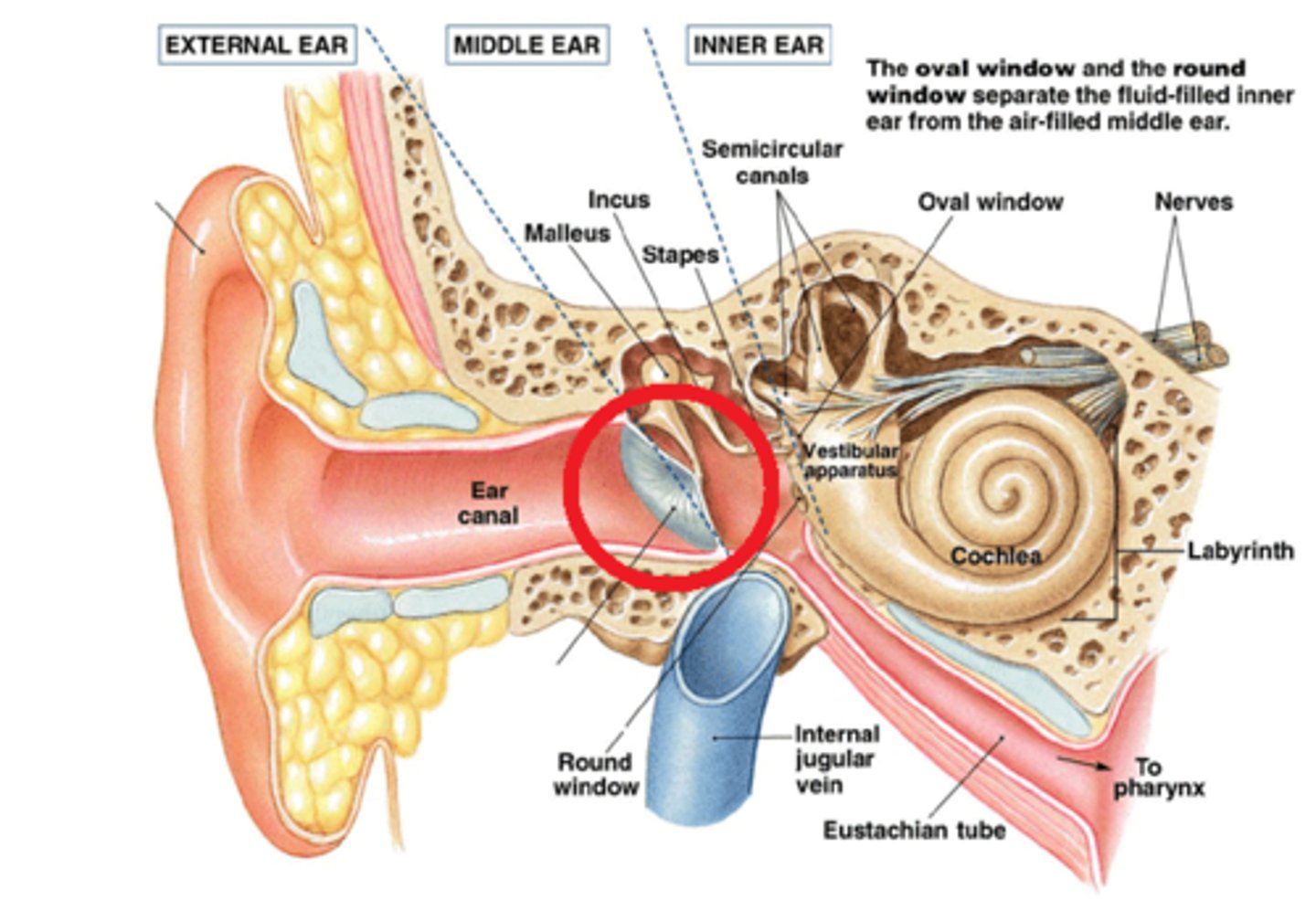
Middle Ear: Eustation Tube
-From middle are, to sinuses, to back of throat with a trap door
-Must equalize pressure between outer and middle ears
-Swallowing or yawning causes the trap door to open and release pressure
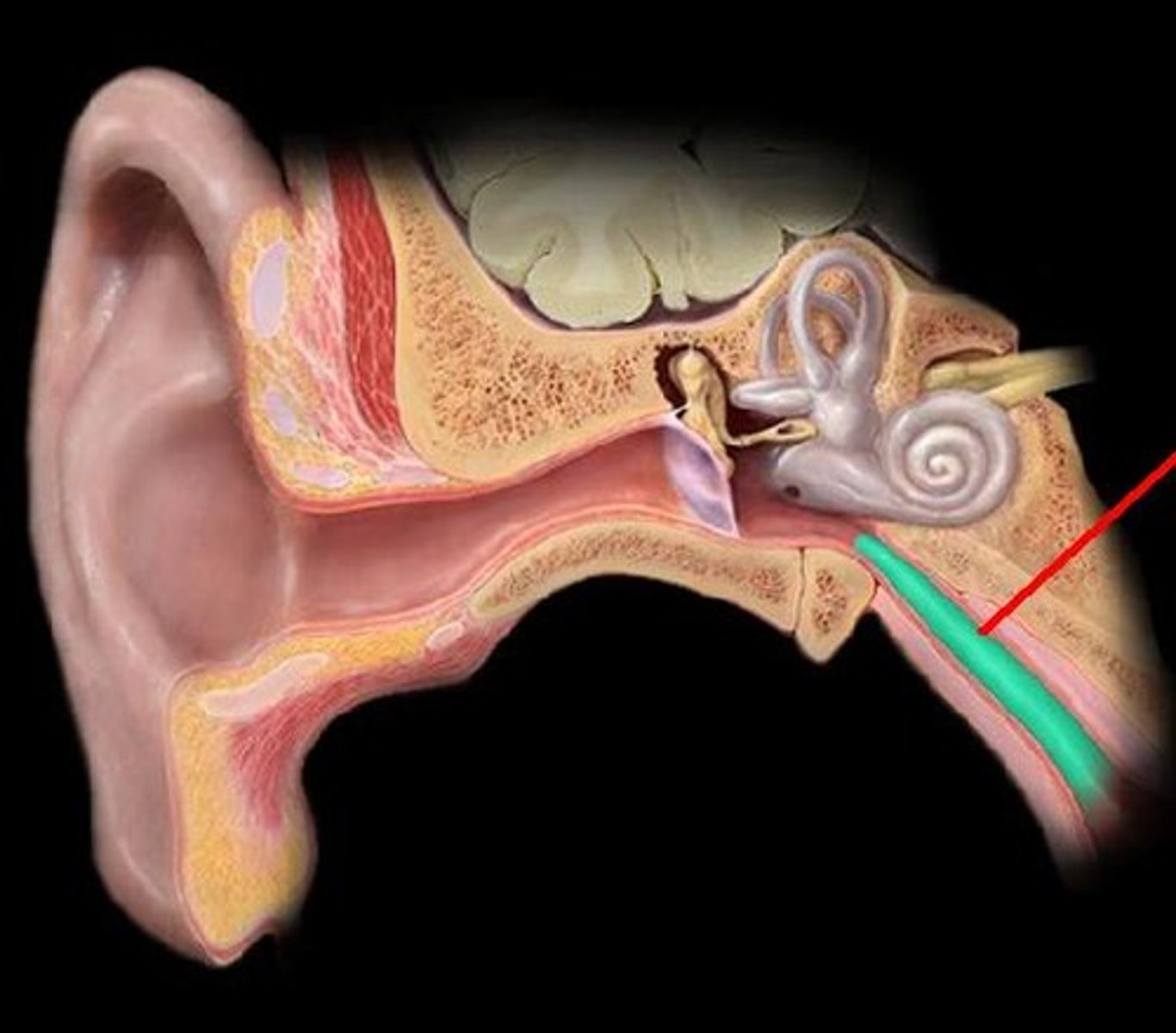
Acute Otitis Media- middle ear infection
Common in children, may have been born with genetically smaller or thinner eustation tubes
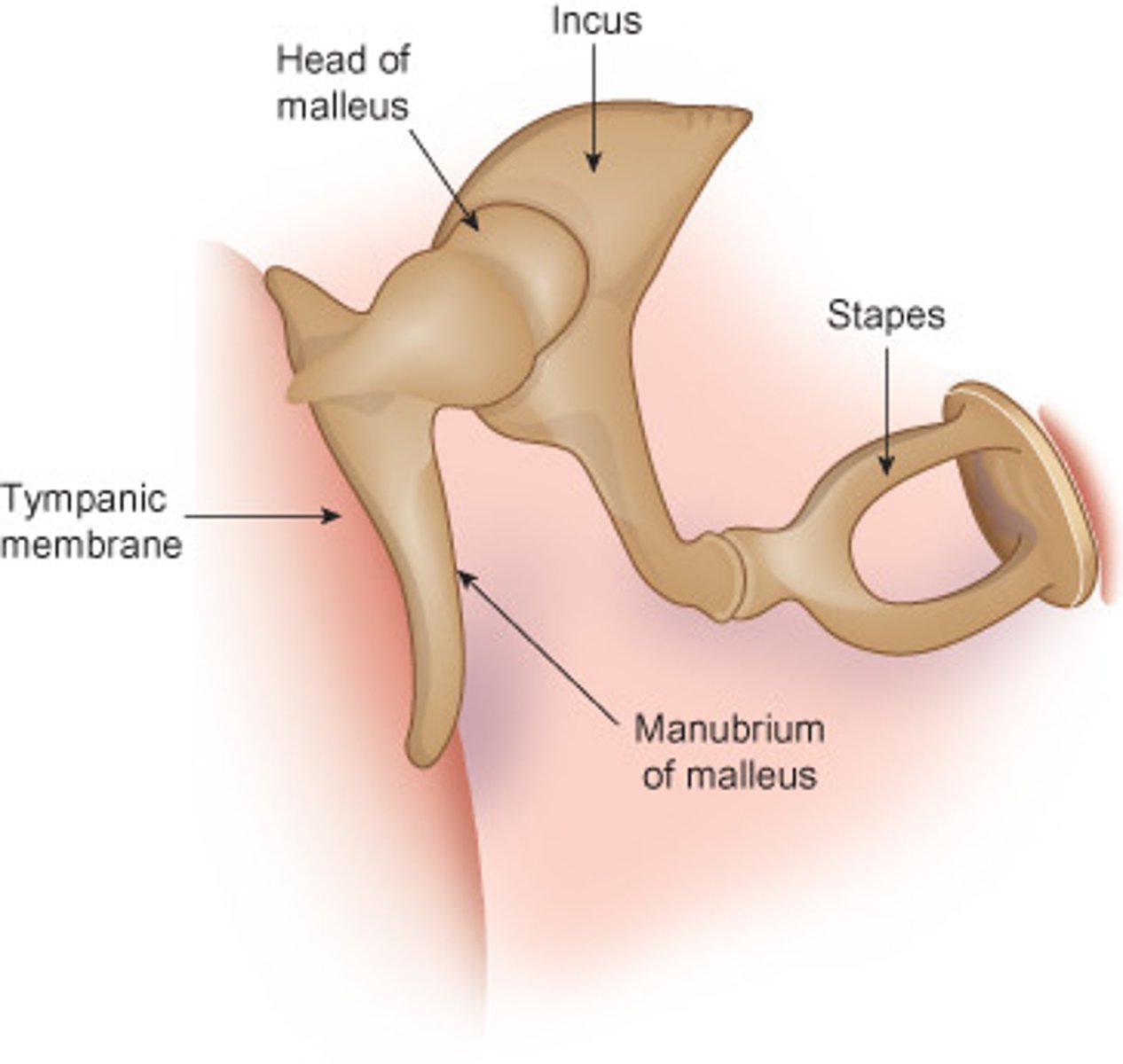
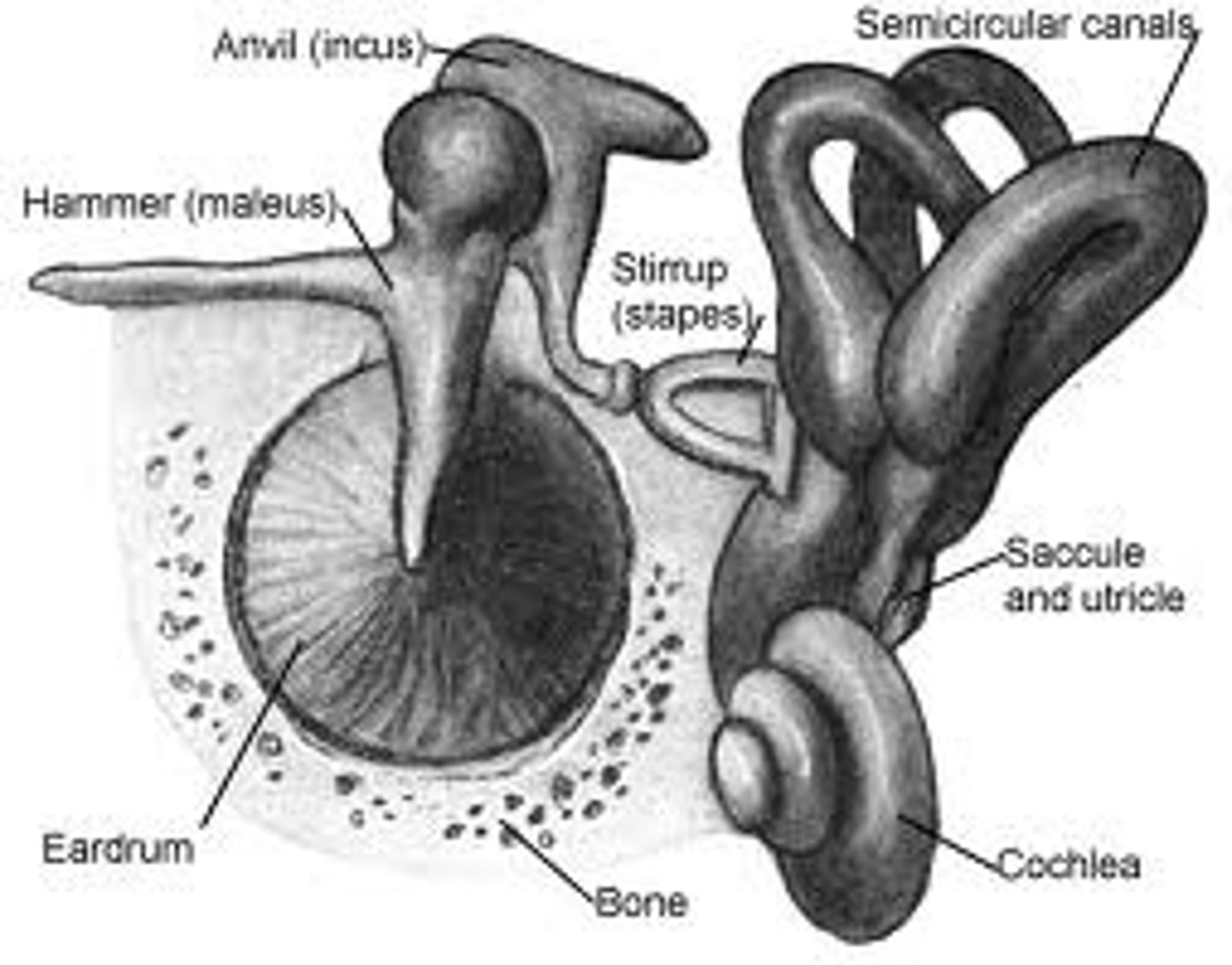
Ossicles
Three bones which transfers vibrations
-Malleus (hammer): connected to eardrum, pushes down on the incus
-incus (anvil): pivots on the stapes
-Stapes (stirrup): connected to the oval window of the cochlea (inner ear)
All three act like a lever system to amplify the force
Oval Window
Another membrane
- smaller than the tympanic membrane
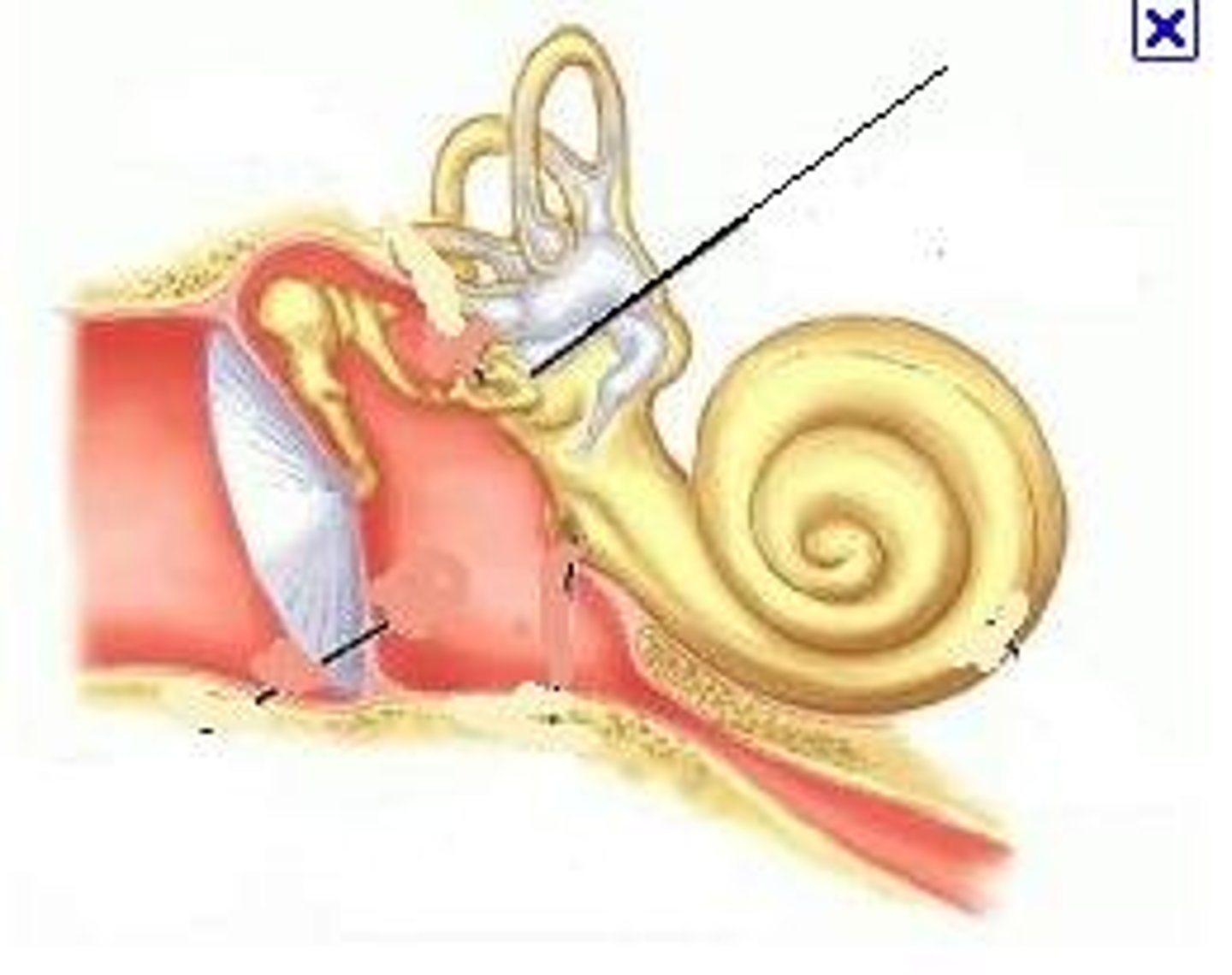
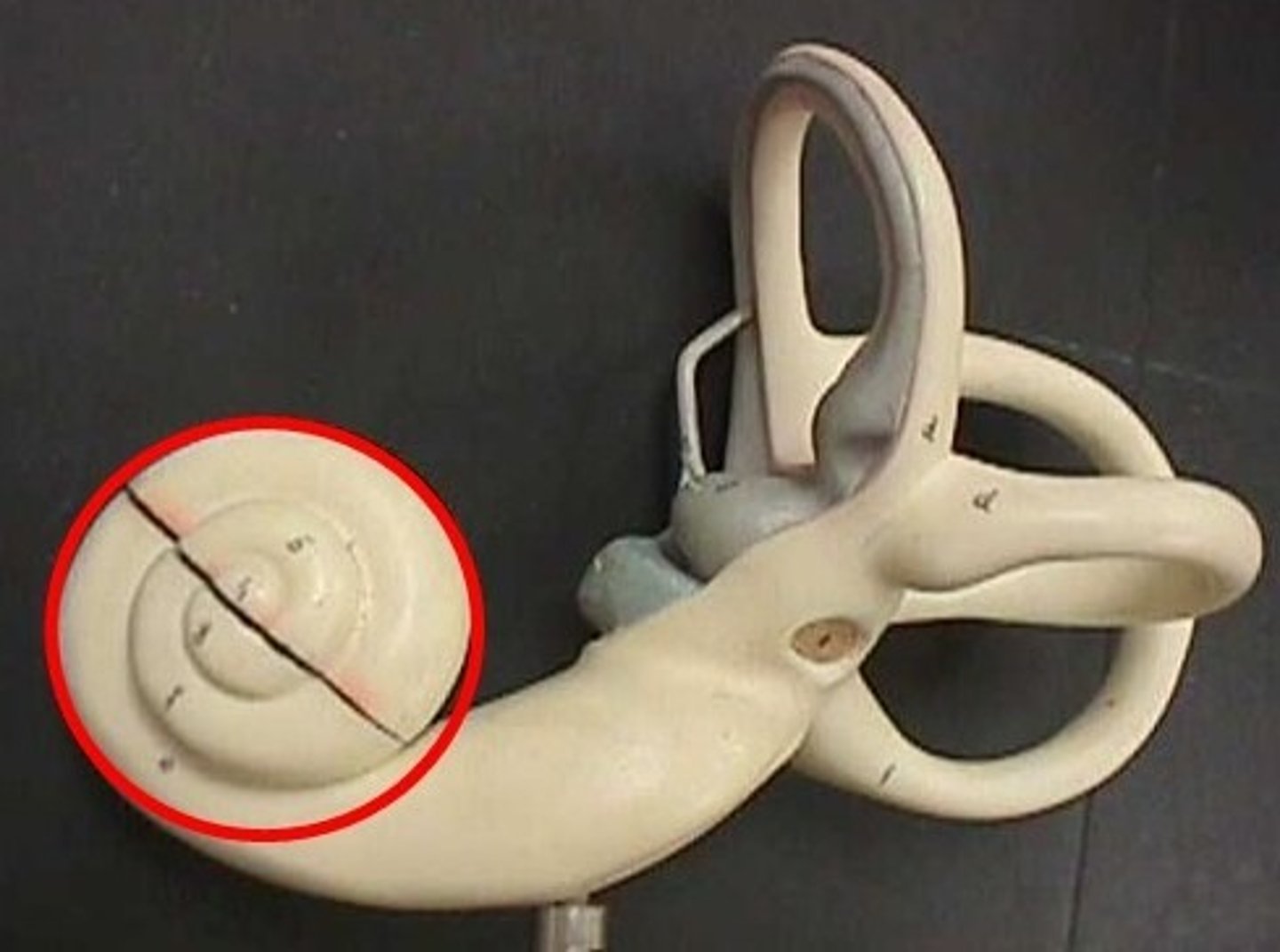
Inner ear: Cochlea
Fluid-filled chamber
- spiral shaped like a seashell
-Contains receptor cell for sound detection: transfers sound from air to fluid
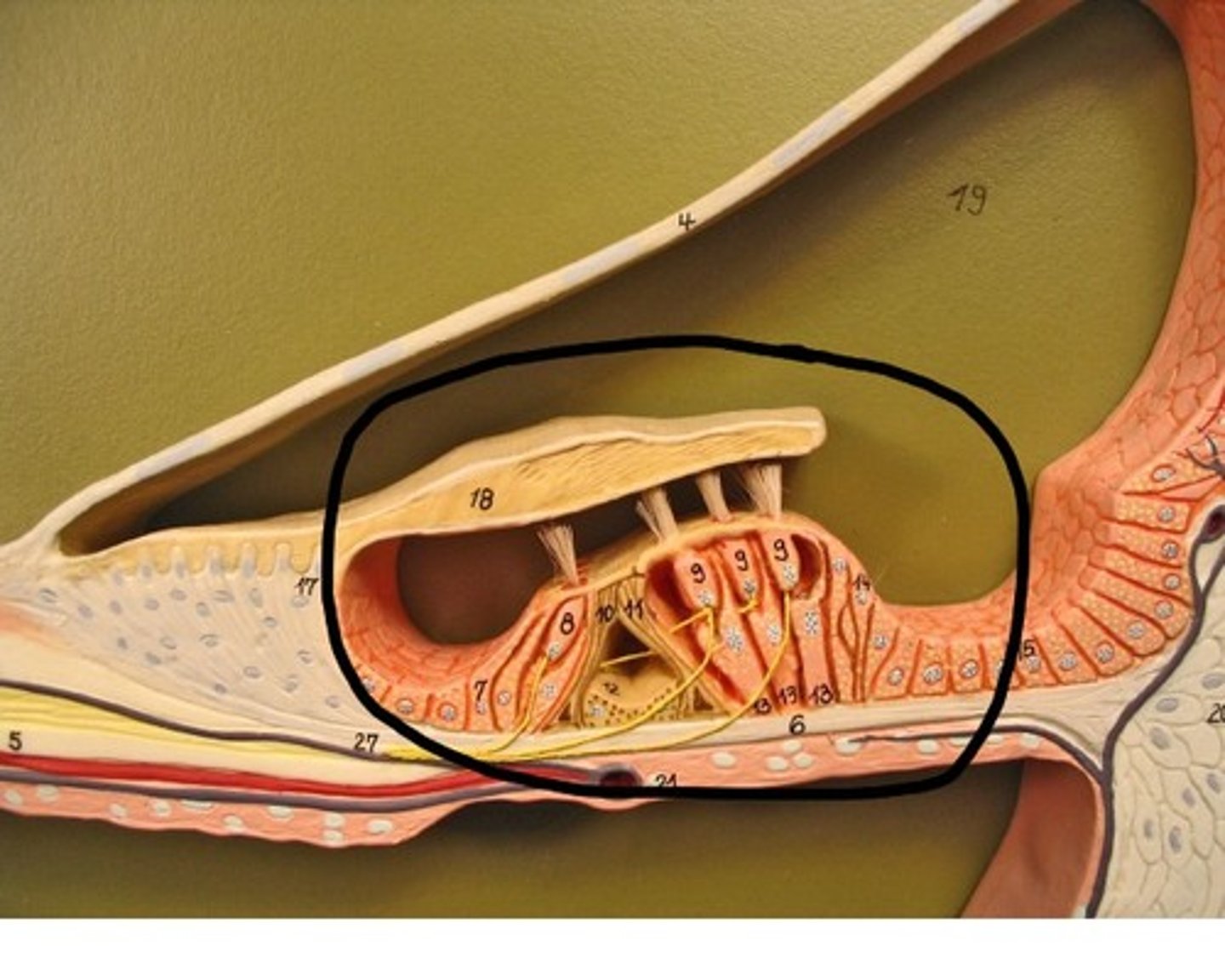
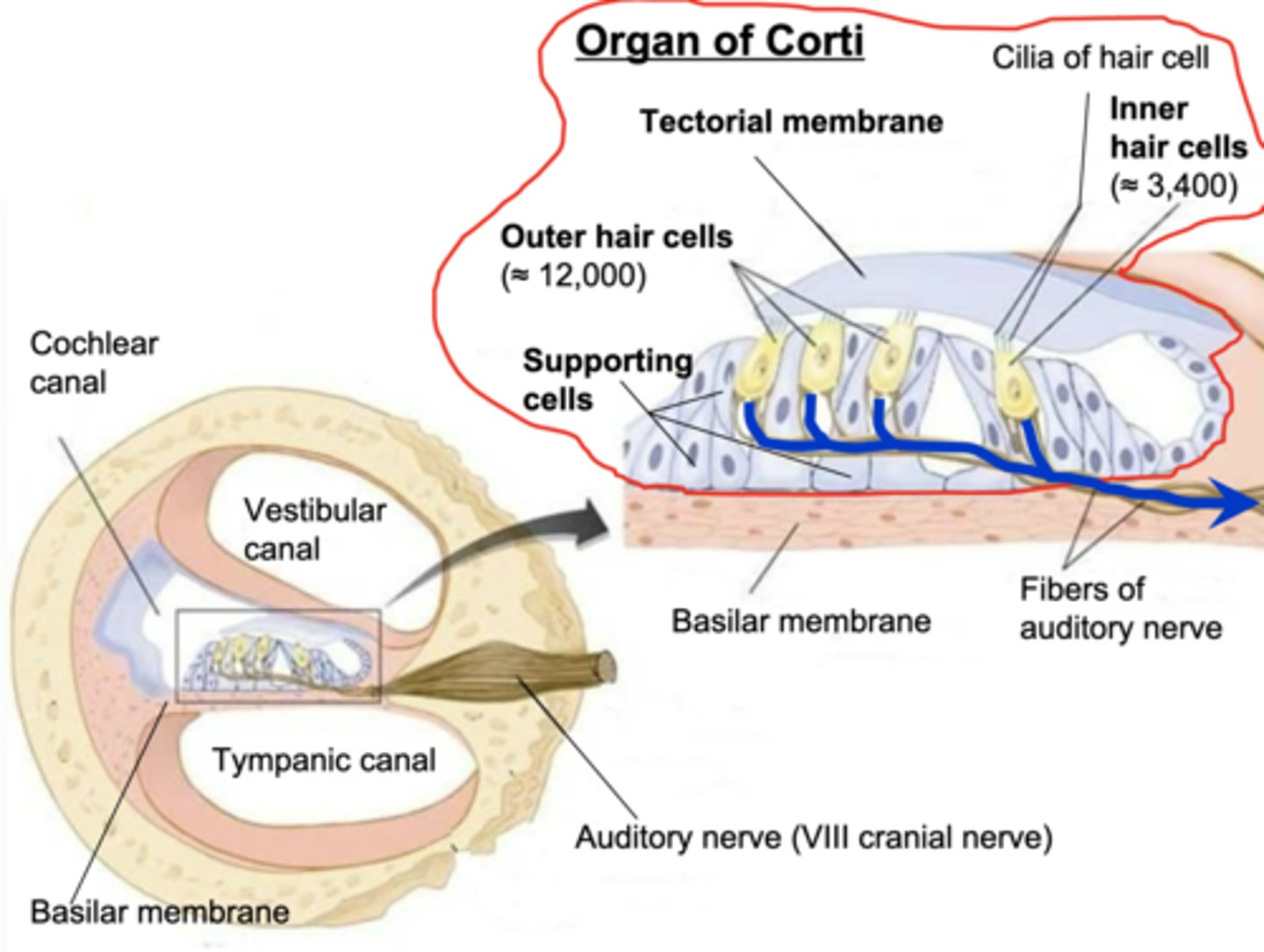
Organ of Corti
The actual receptive organ that contains:
-auditory receptor cell s
-basilar membrane
-hair cell cilia
Basilar membrane
Imbedded in this are thousands of auditory nerves
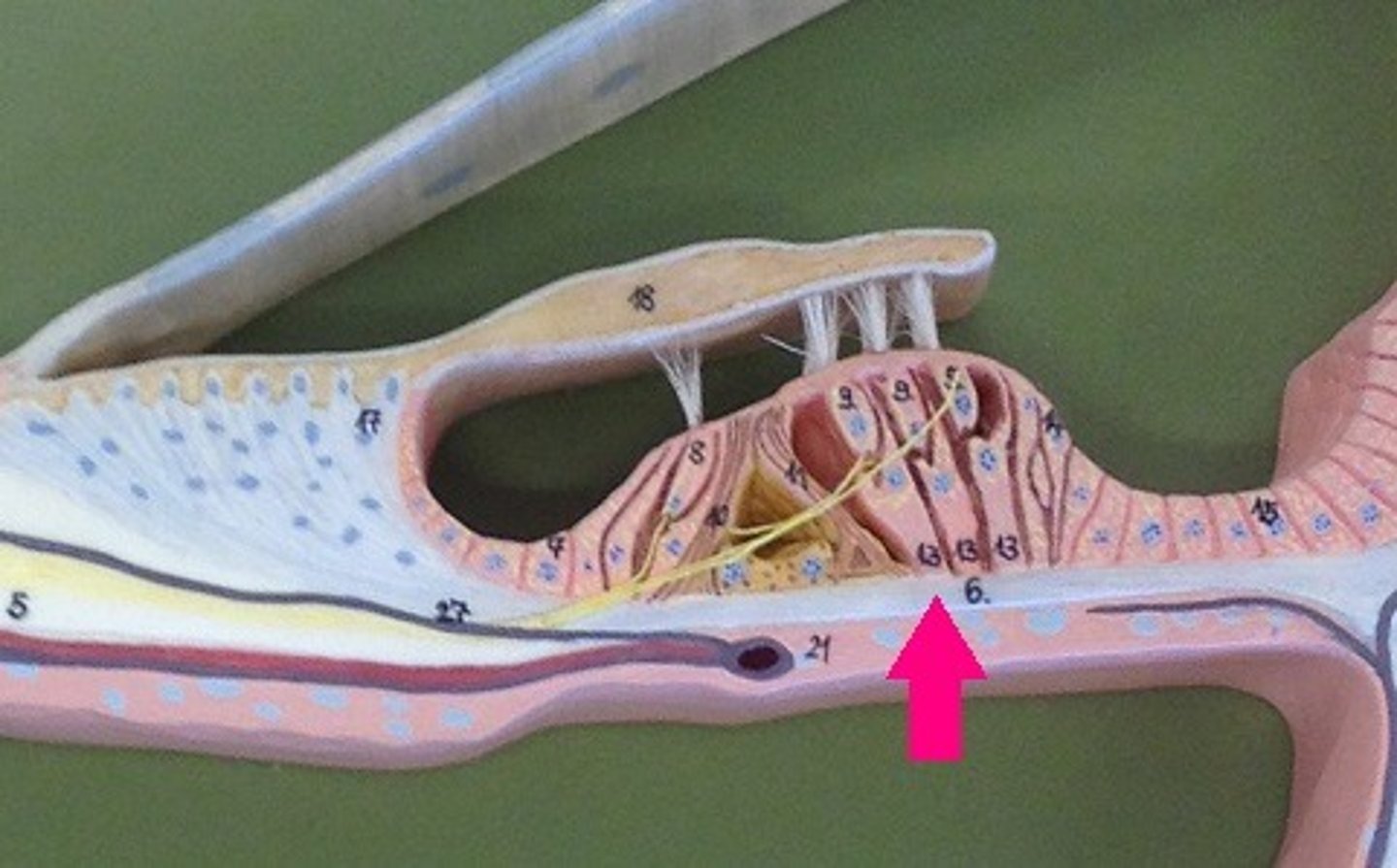
Auditory receptors
The hair cells in your ear
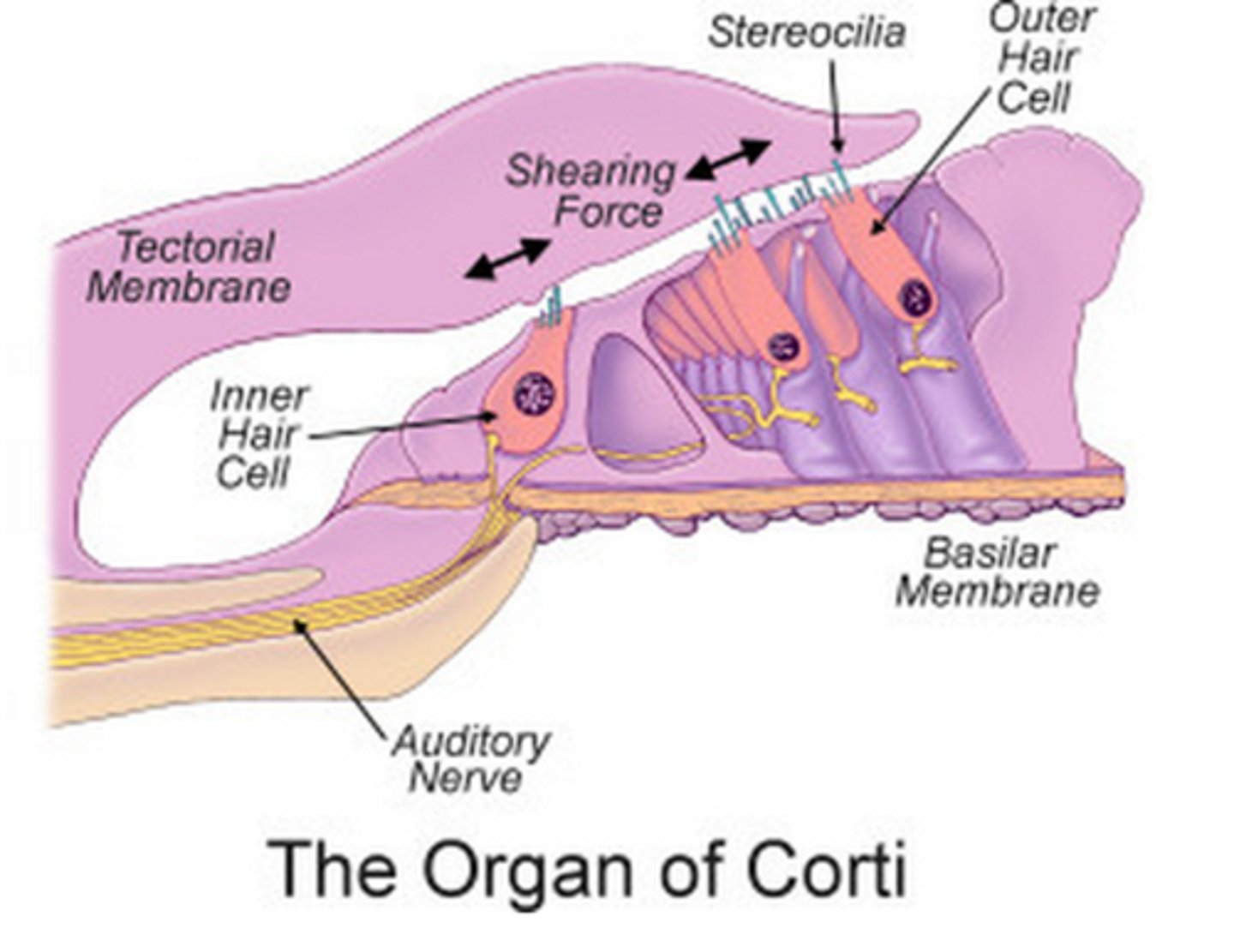
Hair cell cilia
Tiny hairs
Cochlear nerve
A branch of the auditory nerve
-bipolar cells (afferent) with cell bodies in the cochlear nerve ganglion; the axons make up the cochlear nerve
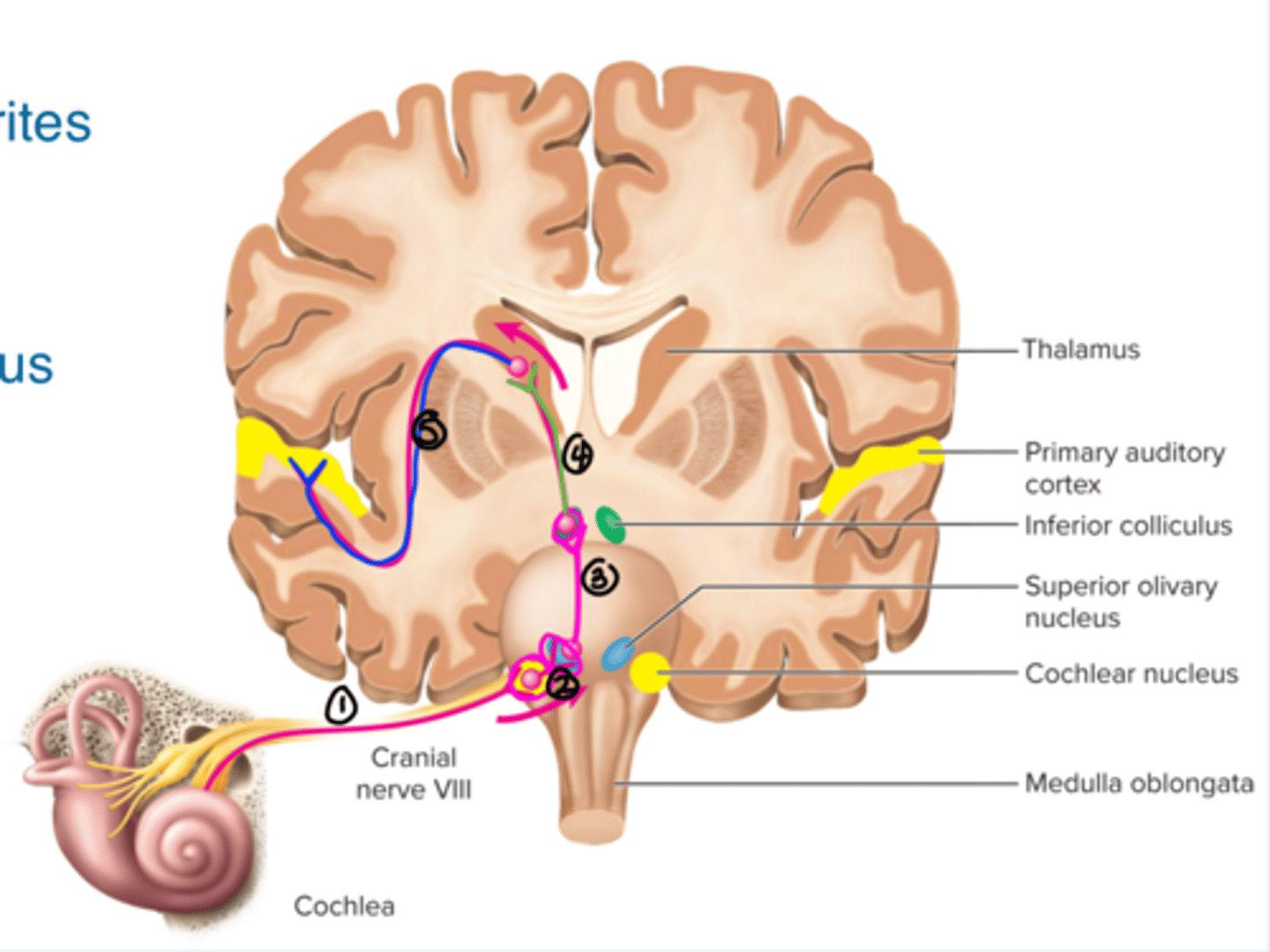
Auditory Pathway within the brain
1. Axons enter cochlear nucleus of the medulla
2.Superior Oliver's complex
3.Lateral Lemniscus
4.Inferior colliculi
5.Medial geniculate nucleus of the thalamus
5.Primary auditory cortex
6.Auditory association cortex
Auditory perception: perception of spatial location
-Phase difference's for low frequencies: difference of arrival times of sound waves at each ear
-intensity differences for high frequencies: difference in intensity of sound waves in each ear
-Analysis of timbre: determines if sound is in front or behind.
Sound processing in brain
Auditory cortex is responsible for pattern recognition
Hearing Problems
-Bilateral lesions of auditory cortex
-Lesions of left auditory cortex
-lesions of auditory association cortex
Bilateral lesions of auditor cortex
Problems with localization: trouble locating where a sound is coming from.
Lesions of left auditory cortex
Problems with discrimination of vocalizations: trouble knowing who is talking to you because you can't discriminate between voices.
Lesions of auditory association cortex
-auditory agnosia: inability to comprehend the making of sounds
-amusia: can't appreciate characteristics of music
Auditory fatigue
Overexposure to loud noises=some suppression of ability to hear for a given time
Age-related hearing loss
Damage to cilia from repeated use
Vestibular sense
Main parts are the vestibular sacs and semicircular canals of the inner ear
Vestibular sacs- utricles and saccules
-respond to the force of gravity
-information on head orientation
Semicircular canals
Respond to natural acceleration (rotation of the head)
-weak response to change in position and inner acceleration
ex- car sickness
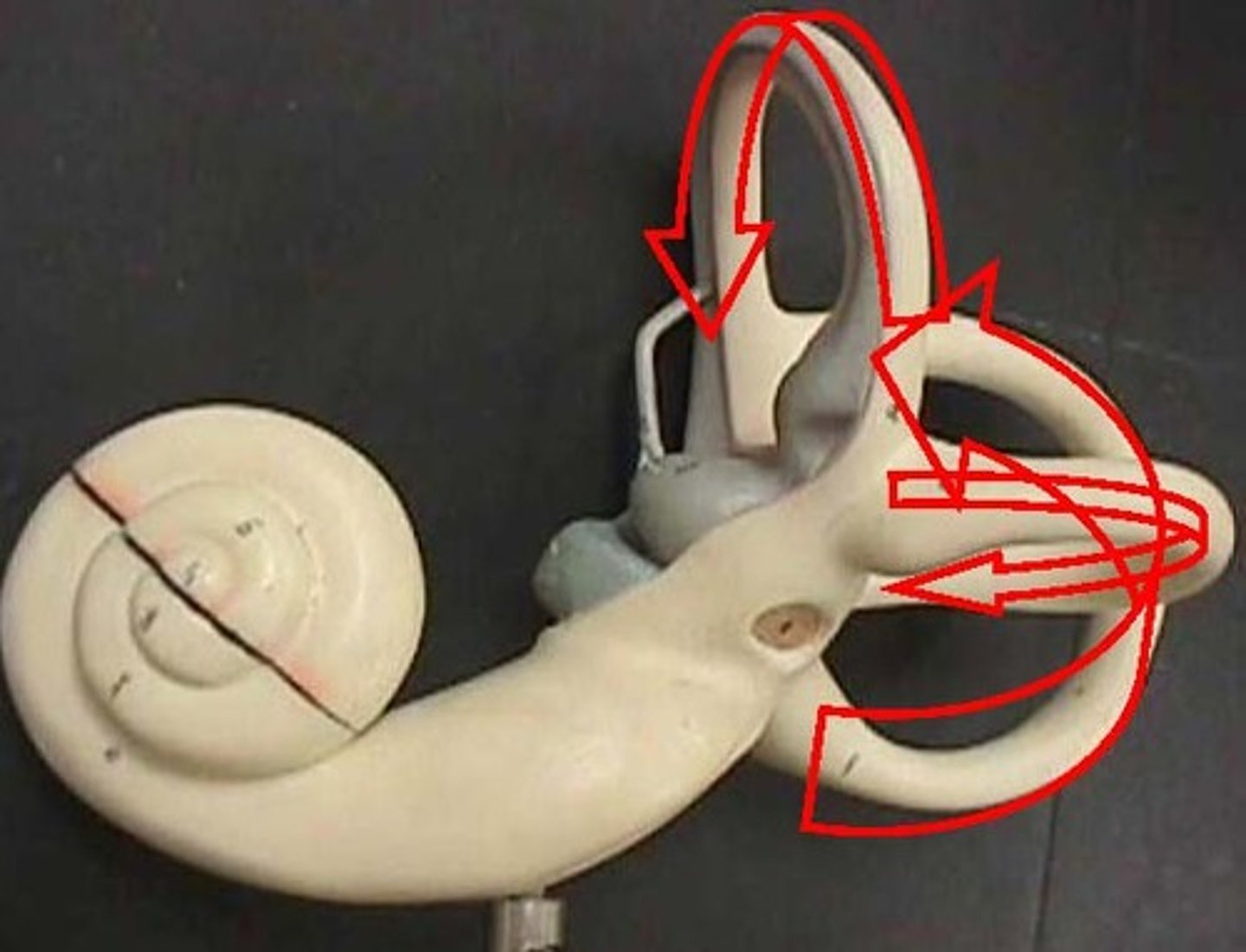
vestibular nerve
Vestibular nerve axons project to the:
-vestibular nuclei in the medulla
-cerebellum, pons, and spinal cord
Somatosenses
Information for what is happening on the skin surface and inside the body.
cutaneous senses
Sense of touch
kinesthesia
position and movement
- receptors in joints, muscles, and tendons
Organic sense
-pleasurable and unpleasurable experiences
-receptors in internal organs
Types of stimuli
pressure, heating, cooling, pain, vibration
Receptors of the skin
-Ruffini corpuscles
-Pacinian corpuscles
-Meissner's corpuscles
-Merkel's disks
Ruffini corpuscles
Association with hair and detect low frequency vibrations, indentations
Pacinian corpuscles
Touch, high frequency vibrations
Meissner's corpuscles
low frequency vibrations
Merkel's disks
Skin indentations
Perception of stimulation
Touch- pressure and vibration caused by movement of skin
Temperature- have both warm and cold receptors in skin
Pain- pain receptors can detect
1. Intense pressure, heat and acids, and tissue damage
2. anterior cingulate cortex of the limbic cortex: emotional reaction to pain
3. Primary somatosensory cortex- pain perception
Somatosensory agnosia
Cannot Know the making of objects placed in hand despite normal somatosensory functioning
-can't identity by tactile exposure
-can't recognize shape, size, or other qualities by exposure only