1) Electric Charges & Fields
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CBSE Class12 Chapter 1- Electric charges and Fields flashcards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Electric Charge & its SI unit
Intrinsic Property of elementary particles of matter due to which it produces electric force b/w various objects. Its S.I. unit is coulomb (C)
Electric charge has three basic properties:
Quantisation, Additivity and Conservation.
Properties of charge:
Charge is scalar quantity
2 types (+ve and -ve)
Charge is quantized.
Charge is conserved
Charge is additive; total charge is the algebraic sum of individual charges
Charge is invariant, doesn’t change with speed, motion of charged body or observer
Quantization
Charge of an object is always an integral multiple of electronic charge and never its fraction.
Q = ±ne (n∈ I & e= 1.6 × 10-19 )
Conservation of Charge
Charge can neither be created nor destroyed. It can be transferred from one body to another.
Net charge of an isolated system always remains constant.
Additivity of charge
Total charge of a system is the algebraic sum of all individual charges of the system
Conductors and insulators
Those substances which readily allow the passage of electricity through them are called conductors, they contain a large no. of free electrons. e.g. metals, the earth.
Those substances which offer high resistance to the passage of electricity due to absence of free electrons are called insulators.
1mC=
1μC =
10-3 C
10-6 C
Coulomb’s Law states that the electrostatic force of interaction or repulsion acting between two stationary point charges is given by
F = (k Q1 Q2)/ r2 (k= 1/4𝛑ε∘ =9 × 109 Nm2/C2)
Coulomb’s law in vector form
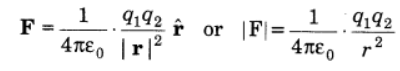
Electric Field Intensity (E)
The electric field intensity at any point due to source charge is defined as the force experienced per unit positive test charge placed at that point without disturbing the source charge. It is expressed as —>
SI unit of E is N/C and it’s a vector quantity

Electric Field
Space around a source charge in which its influence can be experienced. Defined as force on a unit +ve test charge at a point.
Electric field lines
Imaginary lines or curves drawn through a region such tht the tangent at which gives the direction of electric field.These lines start on positive charge and end on negative charge.
properties of field lines are
Field lines are continuous curves without any breaks.
Two field lines cannot cross each other.
Electrostatic field lines start at positive charges and end at negative charges —they cannot form closed loops.
Electric Dipole
An electric dipole is a pair of equal and opposite charges q and –q separated by some distance 2a.
dipole moment
strength of an electric dipole is measured by vector known as electric dipole moment (p) has magnitude 2qa and is in the direction of the dipole axis from –q to q.
Unit: C m
Electric Field due to a Dipole
Space around the dipole in which the electric effect of the dipole can be experienced.
Electric dipole in a uniform electric field has resultant electric force
qE-qE=0
The flux ∆ɸ of electric field E through a small area element ∆S is given by
∆ɸ = E . ∆S
Gauss’s law
The flux of electric field through any closed surface S is 1/e∘ times the total charge enclosed by S.