Bio Mini Quiz
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/24
Last updated 8:40 PM on 3/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
replication
DNA copying
2
New cards
transcription
DNA-\>RNA
3
New cards
translation
RNA-\>protein
4
New cards
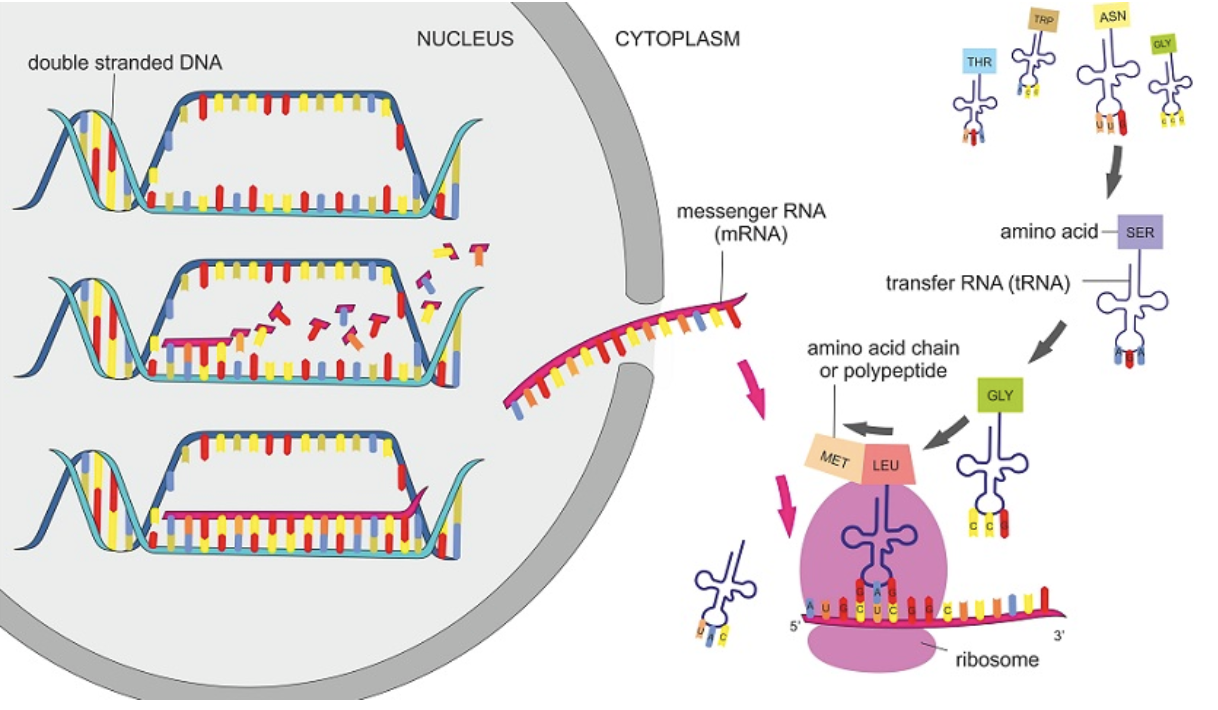
Steps of protein synthesis Advanced
RNA made from DNA as a template
RNA is spliced into mRNA (introns (nonsense RNA) taken out, exons kept)
mRNA is moved outside the nucleus to the ribosome
Codons on mRNA is matched up with anticodons on tRNA
tRNA codons carry an amino acid based on its triplets
The amino acid is added to the growing chain of amino acids creating a protein
When finished the amino acid chain leaves the ribosome and is moved to its target area.
RNA is spliced into mRNA (introns (nonsense RNA) taken out, exons kept)
mRNA is moved outside the nucleus to the ribosome
Codons on mRNA is matched up with anticodons on tRNA
tRNA codons carry an amino acid based on its triplets
The amino acid is added to the growing chain of amino acids creating a protein
When finished the amino acid chain leaves the ribosome and is moved to its target area.
5
New cards
Mutation
A change in the DNA code that changes the protein being made
Can be beneficial, detrimental or neutral
Spontaneous mutations = natural reaction in the organism (no cause)
Induced mutation = due to exposure to UV-light, chemicals or other environmental agent
Are normally permanent
Can be inherited, but not always
Can be beneficial, detrimental or neutral
Spontaneous mutations = natural reaction in the organism (no cause)
Induced mutation = due to exposure to UV-light, chemicals or other environmental agent
Are normally permanent
Can be inherited, but not always
6
New cards
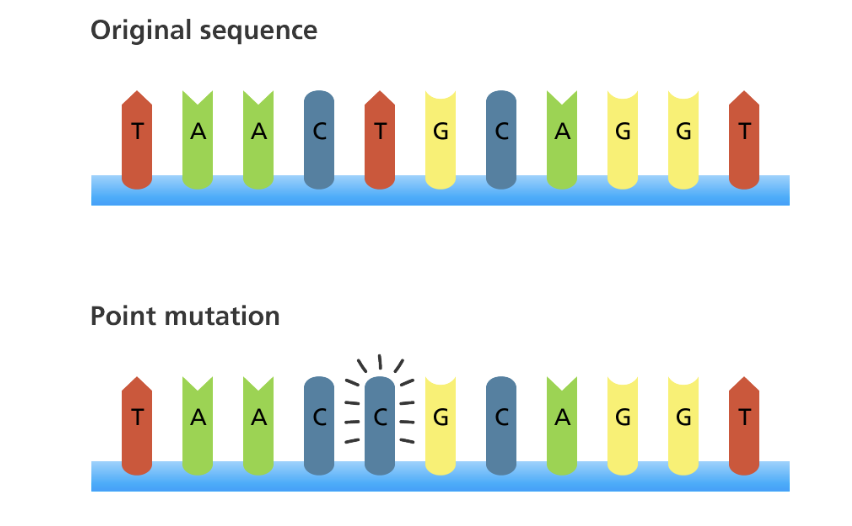
**Point mutation**
Change in one single base in the DNA sequence
Also known as single substitution
mutation
Also known as single substitution
mutation
7
New cards
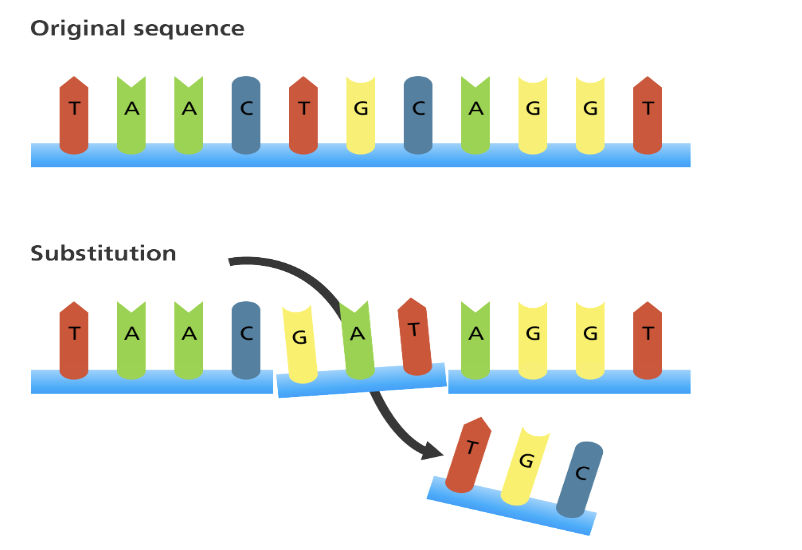
**Substitution mutation**
Can be a single point mutation (previous slide)
Can be several bases
Can be several bases
8
New cards
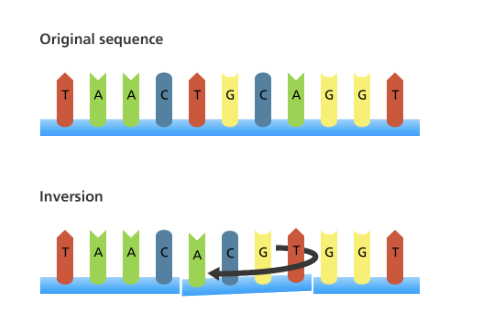
**Inversion**
When a part/segment of a mutation is reversed
9
New cards
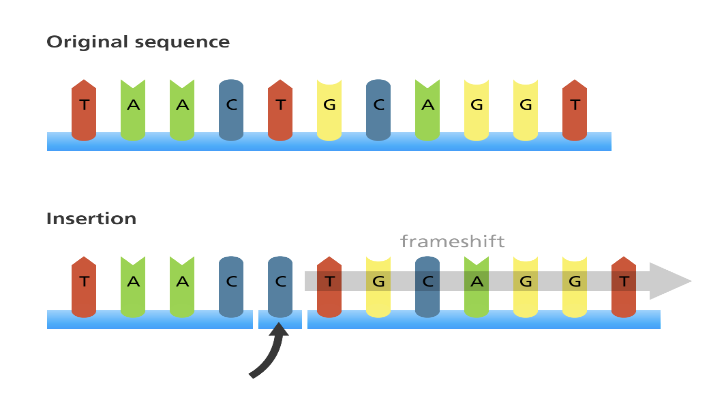
**Insertion**
When a new base or segment is added in
Causes a frameshift, which
makes the protein different
Causes a frameshift, which
makes the protein different
10
New cards
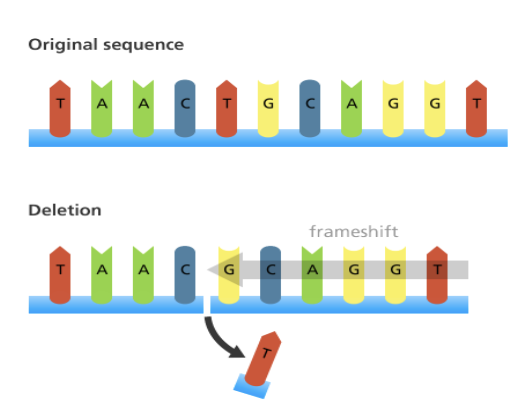
**Deletion**
When a base or a segment is removed
Causes a frameshift
Causes a frameshift
11
New cards
Silent mutation
No change in the amino acids/proteins being produced
12
New cards
Missense mutation
The amino acid sequence changes
13
New cards
Nonsense mutation
Creates a STOP in the amino acid sequence, which gives a change in function
14
New cards
Frameshift mutations
changes where the reading of the code starts and ends and can change the amino acid chain/protein dramatically
15
New cards
**Steps of Protein synthesis simplified**
Transcription: the DNA sequence/gene is copied, substituting T for U
Translation: the mRNA sequence is matched in the ribosome with tRNA carrying an amino acid. Bases are read as triplets.
Translation: the mRNA sequence is matched in the ribosome with tRNA carrying an amino acid. Bases are read as triplets.
16
New cards
mRNA
Messenger RNA, is the copy of the gene, produced/found in the nucleus, flat shape
17
New cards
tRNA
Transfer RNA, is the link between mRNA and amino acids, carried one amino acid, found in cytoplasm, hairpin shape
18
New cards
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA, found in the ribosome, part of the ribosome’s structure, globular
19
New cards
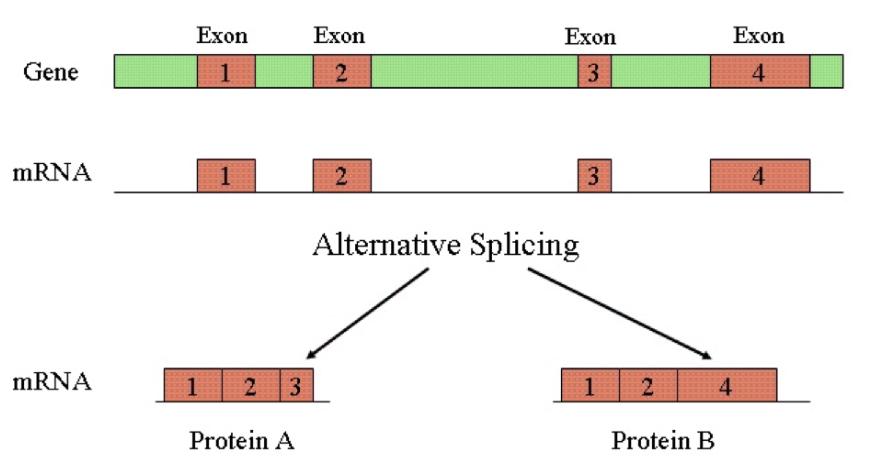
**RNA modification**
Before going on to the ribosome the RNA needs to be modified.
Introns are being spliced out, exons are expressed so they are kept.
Spliceosome is responsible for splicing.
Alternative splicing: gives a single gene an option to make several different proteins.
Introns are being spliced out, exons are expressed so they are kept.
Spliceosome is responsible for splicing.
Alternative splicing: gives a single gene an option to make several different proteins.
20
New cards
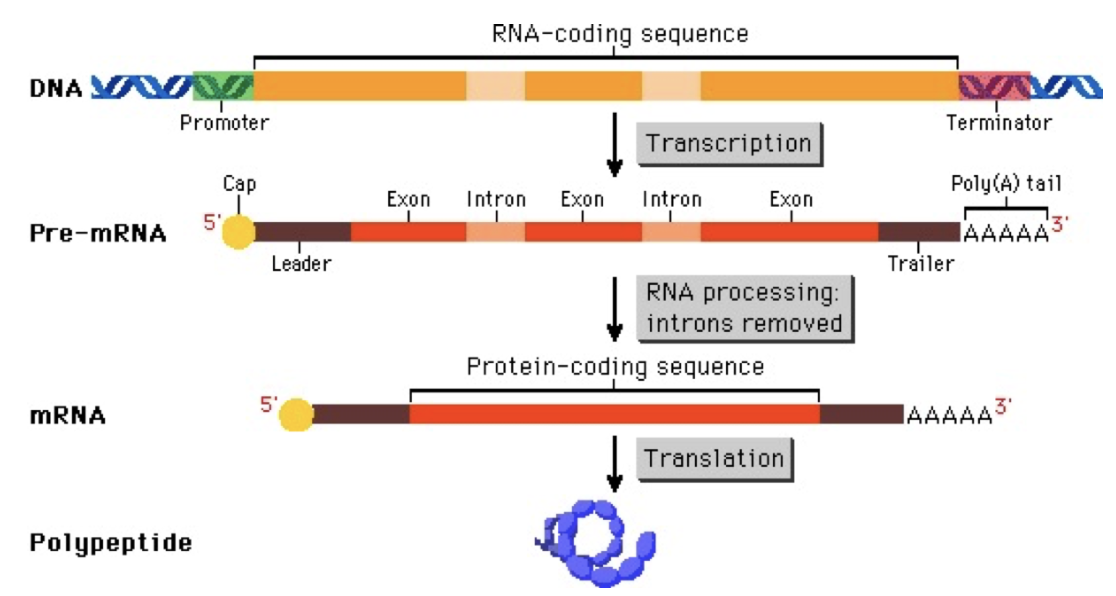
mRNA Protection
The mRNA has to be protected from digestive enzymes in the cytoplasm. Does this in two ways:
Capping: addition of modified guanine, protects from digestive enzymes, helps attach to the ribosome
Capping: addition of modified guanine, protects from digestive enzymes, helps attach to the ribosome
21
New cards
**RNA Messaging Key**
Introns removed- REFINES MESSAGE!
Alternative Splicing -MAXIMIZE MESSAGE -to create different protein recipes from same mRNA.
Capping and Tailing – PROTECTS THE MESSAGE!
Alternative Splicing -MAXIMIZE MESSAGE -to create different protein recipes from same mRNA.
Capping and Tailing – PROTECTS THE MESSAGE!
22
New cards
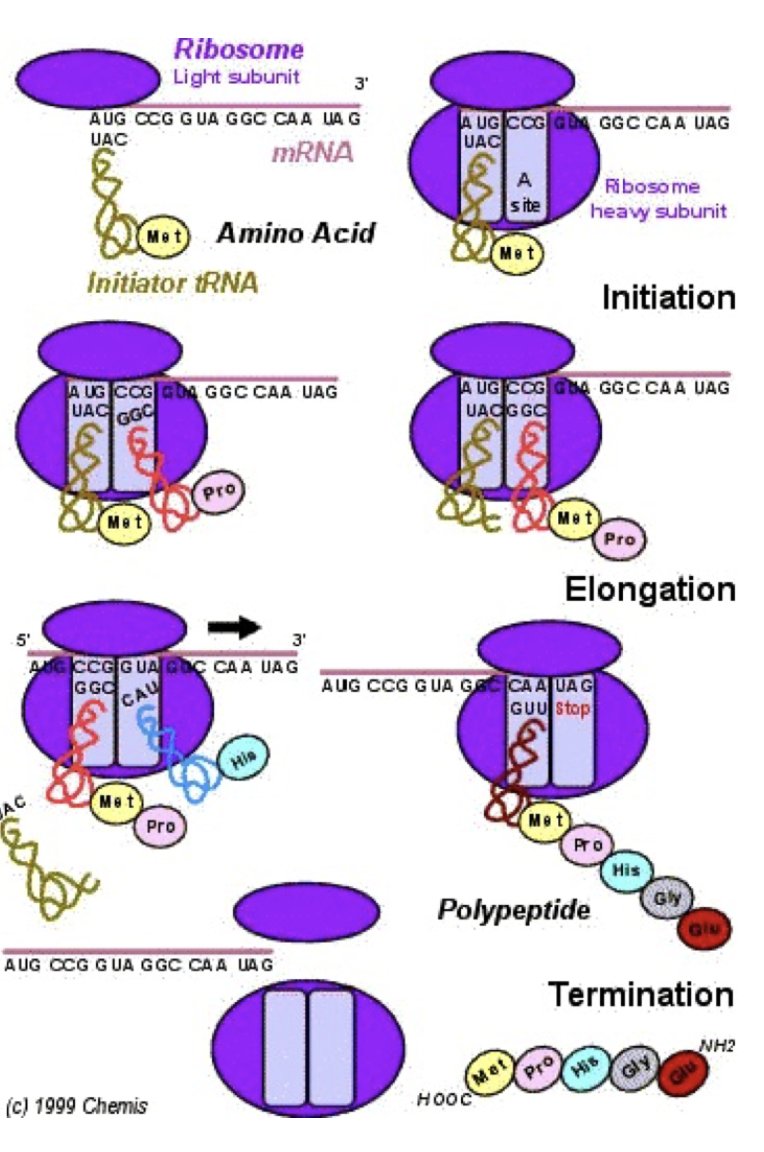
**Translation Stages**
Initiation: tRNA starts the coding based on the start codon - AUG
Elongation: amino acids are joined together one-by-one with covalent bonds
Termination: a stop signal is reached on the mRNA and the new polypeptide chain detaches.
Stop codons: UAA, UAG, UGA
Codes that starts with a U it is most likely a stop codon
Elongation: amino acids are joined together one-by-one with covalent bonds
Termination: a stop signal is reached on the mRNA and the new polypeptide chain detaches.
Stop codons: UAA, UAG, UGA
Codes that starts with a U it is most likely a stop codon
23
New cards
Codons
a mechanism where the message is read in triplets – what we call “codons”
Codon – the triplet of bases on the mRNA that correspond to a particular amino acid
Anti-codon – the complimentary triplet of bases on tRNA that brings a specific amino acid to the ribosome
Codon – the triplet of bases on the mRNA that correspond to a particular amino acid
Anti-codon – the complimentary triplet of bases on tRNA that brings a specific amino acid to the ribosome
24
New cards
**Gene Regulation**
Only 2% of the human genome actually codes for something, as far as we know
A lot of DNA seems to have come from viruses
This explains the need for splicing
A lot of DNA seems to have come from viruses
This explains the need for splicing
25
New cards
**Promoters and enhancers**
Promoter sequences: non-coding DNA, longer
“Shows” where transcription for RNA starts
Very often known as the TATA box
Located 25-35 bases away from the start of the actual gene
\n
Enhancer sequence: non-coding DNA, shorter
Enhances the rate of transcription = makes transcription faster
“Shows” where transcription for RNA starts
Very often known as the TATA box
Located 25-35 bases away from the start of the actual gene
\n
Enhancer sequence: non-coding DNA, shorter
Enhances the rate of transcription = makes transcription faster