Data Visualization, Data Wrangling, and Risk Management in Business Analytics
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Preattentive attributes
Features that can be used in a data visualization to reduce the cognitive load required to interpret it.
color
Size
shape
length
Data-ink
The ink used in a table or chart that is necessary to convey the meaning of the data to the audience.
Data-ink ratio
The proportion of ink used for data to the total amount of ink in a table or chart.
- It measures how much of the ink (or pixels) in a chart actually shows real data, versus how much is just decoration.
Decluttering
The process of increasing the data-ink ratio in a chart.
Crosstabulation
A useful approach to describing a tabular summary of data for two variables.
- another word for pivot
-a simple way to compare two sets of information in a table.
Scatter chart
A graphical presentation of the relationship between two quantitative variables.
- is a simple graph that shows how two things are related.
Pivot Tables
quickly summarize and organize large amounts of data.
Table Design Principles
-Keep the data-ink ratio high.
-Use lines only to separate labels from data and calculated fields.
-Labels should be left-aligned.
-Values should be right-aligned.
-Center vertical labels.
line chart
a useful representation of time series data
multiple line chart
Bar charts
use horizontal bars to display the magnitude of the quantitative variable
Column Charts
use vertical bars to display the magnitude of the quantitative variable.
Types: stacked-column chart or a clustered-column chart
stacked-column chart
clustered-column chart

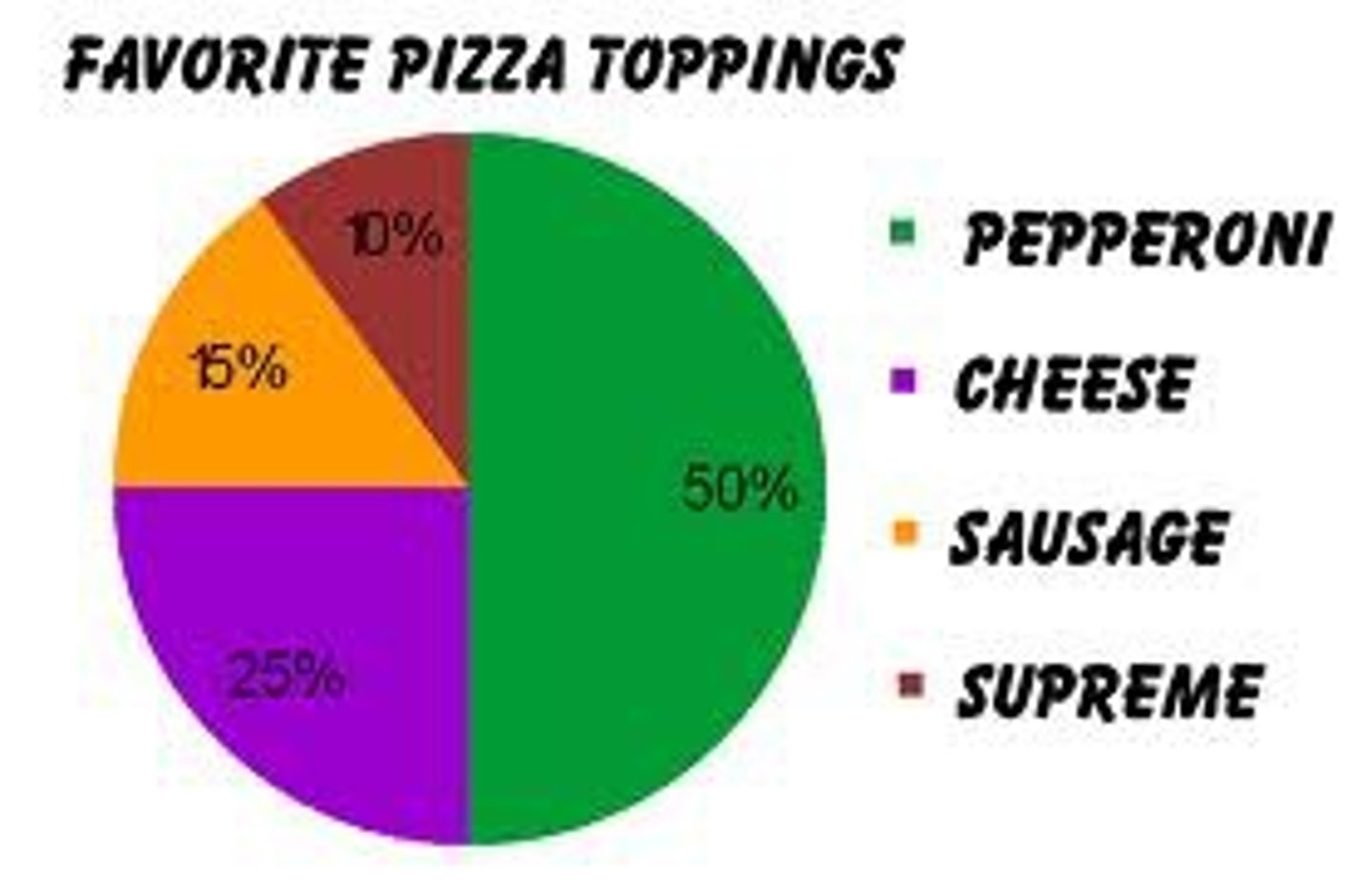
Pie Charts
are a common form of chart used to compare categorical data
Data dashboards
data visualization tool that illustrates multiple KPIs and automatically updates as new data becomes available
What to know about Data dashboards...
-Show on a single screen all KPIs related to one aspect of the operations.
-Create multiple dashboards of related KPIs to prevent scrolling.
-The KPIs should convey clear meaning and be related to decisions.
-Dashboards must adhere to the principles of effective data visualization.
-Use color to call attention and differentiate between categorical variables.
Key performance indicators
are metrics indicative of current operating characteristics
- the most important numbers or measurements that show how well something is doing.
- If youre on track to reach your goals
Raw data
is data that has not been processed or prepared for analysis.
- Also called source data or primary data
Data Wrangling
The process of cleaning, transforming, and managing raw data so that it is more reliable and can be more easily accessed and used for analysis.
- Also called data munging or data remediation
What is data wrangling objective?
to produce a final dataset that is accurate, reliable, and accessible
What is the format of Data wrangling?
determines how the data are wrangled
- Each data point is a group of characteristics for particular observation
What is the activities of Data wrangling?
- Merging multiple data sources into a single data set.
- Identifying missing values in data and either filling or deleting the record or observation.
- Identifying erroneous values in data and replacing them with the correct values.
-Identifying and deleting duplicate observations or records in data.
-Identifying extreme values in data, determining whether they are legitimate, and taking appropriate action.
-Subsetting data to facilitate analyses and comparisons of subgroups of the raw data.
6 steps of data wrangling
1. Discovery: become familiar with the raw data and conceptualize its use.
2. Structuring: arrange the raw data to be more readily analyzed.
3. Cleaning: find and correct errors in the raw data that might distort the ensuing analyses.
4. Enriching: incorporate values from other data sets and/or apply transformations to portions of the existing data.
5. Validating: verify that the wrangled data are accurate, reliable, and ready for the ensuing analyses.
6. Publishing: create a file containing the wrangled data and documentation and make it available to its intended users.
Structured Data
refers to data arrayed in a predetermined pattern to make them easy to manage and search
Unstructured data
data not arranged in a predetermined pattern
Semi-structured data
not organized as structured data but contains elements that allow for isolating some raw data elements
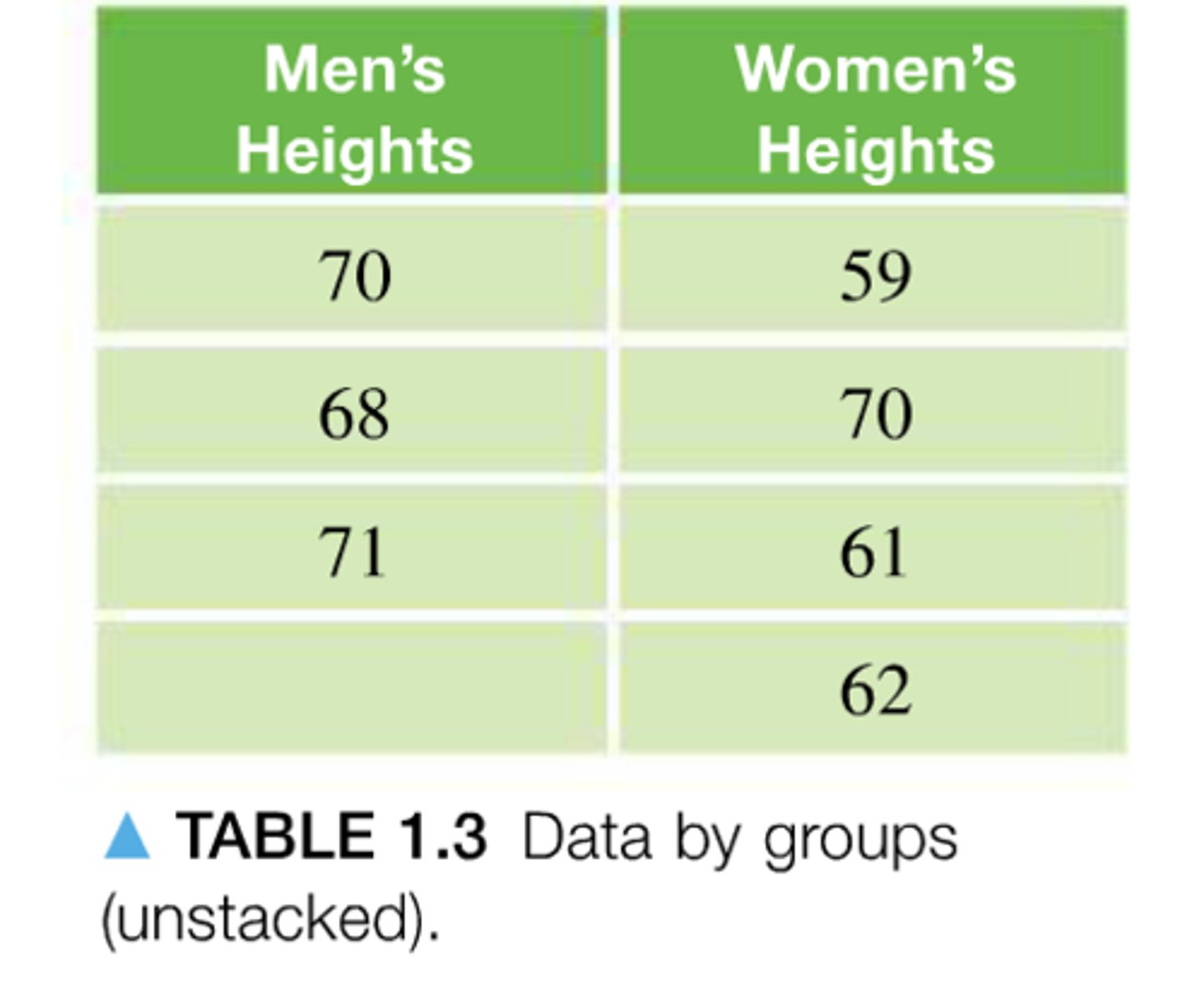
Stacked data
are organized so that the values for each variable are stored in a single field.
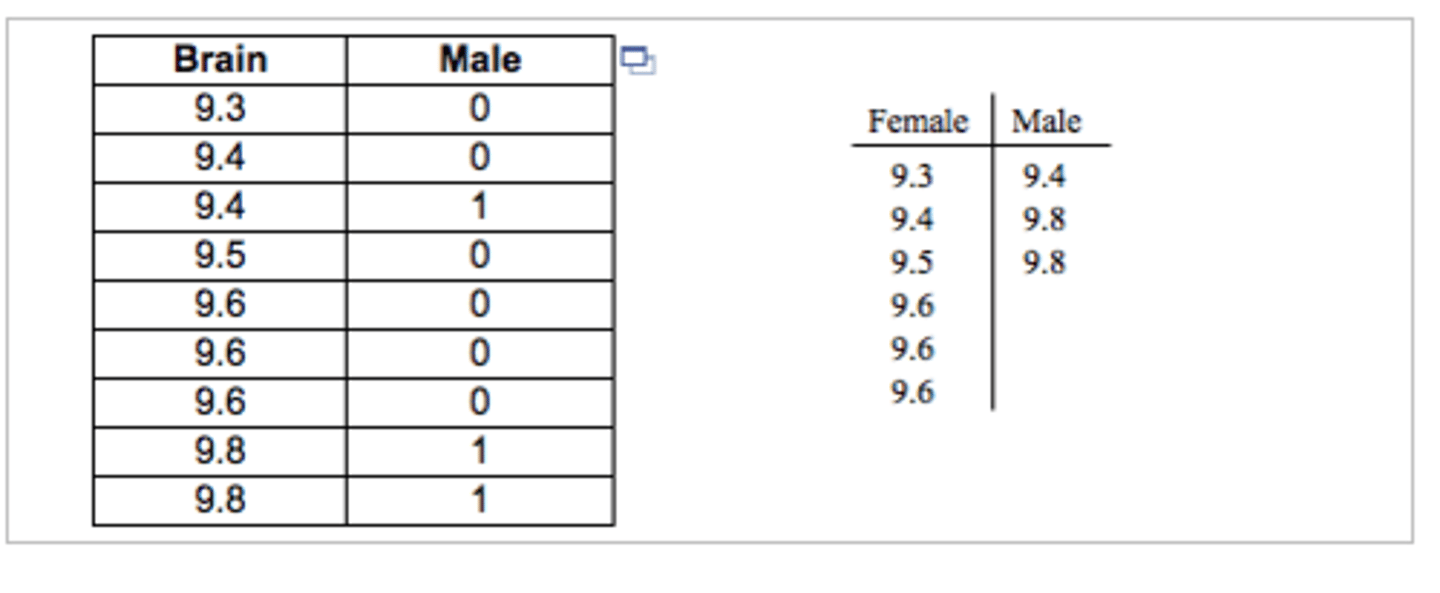
unstacked data
are organized so that the values for one variable correspond to separate fields
Legitimately missing data
if a value of a field is missing because of an appropriate reason
ex: a survey question asking whether a male respondent is pregnant
Illegitimately missing data
everything else
- Remedial action is considered for illegitimately missing data only
Data Dictionary
documenting several attributes should also be included
- names, definitions, and units of measure used in the fields, the raw data sources and relationship(s) with other data, and miscellaneous attributes.
Internal Controls Definition
A process, implemented and managed by an entity's board of directors, management, and other personnel, designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of objectives in the following categories:
-effectiveness and efficiency of operations
-reliability of financial reporting
-compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Risk
the potential for loss, damage or destruction of an asset as a result of a threat exploiting a vulnerability
Risk is associated with...
Likelihood and impact
Likelihood: How likely is the event to happen?
Impact: Assuming it happens, how bad is it?
4 Purposes of Internal Controls
1. Safeguard assets
2. Ensure reliable financial reporting
3. Promote operating efficiency
4. Encourage compliance with management directives (and the law)
example of Safeguard assets
Ex: Ray's auto parts sells high value parts (alternators, radios, air bags, etc.). The store is located in a high crime area and fears burglary
example of ensure reliable financial reporting
Ex: Joe is an accounting manager for a publicly traded firm. The CEO pressures Joe to record revenue for deals that haven't actually closed
Example of Promote operating efficiency
Ex: Becky Lynn's is a retail store. They've always staffed their store with 3 clerks. However, in the early morning and late evening they sell very little
Example of Encourage compliance with management directives (and the law)
Ex: XYZ, Inc. has a set of policies governing ethical conduct. Managers, however, rarely communicate or emphasize these
4 categories of risk
1. Financial Risk
2. Operational risk
3. Strategic risk
4. hazard risk
Risk can "fit" into multiple categories
Financial risk
- are related to monetary activities
- market risk: refers to changes in a company's stock prices, investment values, and interest rates
- credit risk: is associated with customers' unwillingness or inability to pay amounts owed to the organization
- liquidity risk: involves the possibility that a company will not have sufficient cash and near-cash assets available to meet its short-term obligations
operational risk
- Risks concern the people, assets, and technologies used to create value for the organization's customers
-systems risk: relates directly to information technology. As a business becomes more reliant on IT procedures, there is a chance that IT will fail at a crucial moment
-human error risk: recognizes the possibility that people in the organization may make mistakes
Strategic Risk
- Relate to the entity's decision-making process at the senior management and board of directors level
- legal and regulatory risk is concerned with the chance that those parties might break laws that result in financial, legal, or operation sanctions
- business strategy risk comprises poor decision-making related to a company's basis for competing in its markets
Hazard risk
- Directors' and officers' liability
- These individuals have a risk of litigation if leading the company wrong.
Examples pf Controls
1. Adequate documentation
2. Background Checks
3. Segregation of duties
4. User training
5. Computer Backup
6. Backup of power supply
7. Bank reconciliation
8. Batch control totals
9. Data encryption
10. Document matching
Who is Drew Love
WireMaster: CEO
What does Wiremasters not do?
Production
Wiremasters info
- ERP System: Rubicon
- Military Contractor & Commercial (50/50)
- Own Developers in House
- Wires are curated for aerospace (lightweight)
- Gulfstream is their biggest account & they provide every wire for every plane
- Work with SpaceX
- All data is about how quickly a data set answers a question that I have.
- Most of their business is done entirely through email
- What WireMasters does not do: Production
What is a Column
is a field
Row is what
a record or observation
Internal Control has 4 main purposes
1. Safeguard assets
2. Ensure reliable financial reporting
3. Promote operating efficiency
4. Encourage compliance with management directives (and the law)