Metal Bending Assessment - Metals Lecture
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Metal (definition)
a chemical element that is lustrous, hard, malleable, heavy, ductile, tenacious, and usually a good conductor of heat and electricity
Alloy (definition)
combination of elements which exhibits the properties of a metal
alloying used to improve properties such as strength, ductility, hardness, wear resistances and corrosion resistance
All metals are _____.
crystalline
Metals crystallize into a regular arrangement of atoms called________.
space lattices
Cubic System (space lattice)
three contiguous edges of equal length and at right angles
Tetragonal (space lattice)
three contiguous edges, two of equal length, all at right angles
Hexagonal (space lattice)
three parallel sets of equal length horizontal aces at 120 degrees and a vertical axis
In molten form, metals are _________
non-crystalline
the temperature at which atoms begin to crystallize is called __________
its freezing point
Grain
each unit is called a grain
each grain is essentially a single crystal
size of grain depends on the temperature from which the metal is cast, the cooling rate and nature of the metal.
slow cooling - large grain
fast cooling - small grain
Slip planes (below elastic limit)
applied force distorts crystal lattice
remove force, crystal goes back to shape
Slip planes (above elastic limit)
force causes permanent displacement or slip
occurs in lattice on certain specified plane called slip planes (crystal slips without separation, plasticity)
lattice undergoes distortion, becomes highly stressed and hardened
slip planes tend to greatest concentration of atoms and be 45 degrees from applied force
slip is not confined to one set of planes during plastic deformation
Mechanical Properties of Metals
dependent on lattice structure
in general, cubic lattices are more ductile or workable materials
FCC - ductile through a wide temp range
CPH - good hardening by cold working
ability to shape and contour AL and stainless steel depend on plasticity
elasticity governs safe and use as load bearing members
Plasticity
Metals ability to be deformed beyond the range of elasticity without fracture resulting in permanent change in shape
for metals, plastic to elastic ratio is high
100:1
Permanent set as result of slip
further force means that the slip doesn’t happen along original slip plan indefinitely, it gets increased resistance to further motion therefore the slip now occurs along new parallel slip plane
as slip shifts from one slip plane to another progressively higher forces required to cause slip, metal has become work hardened
Actual strength of metals are a ______ of their theoretical strength
fraction
metal strength can be compromised by imperfections like. . .
flaws in regularity of crystal lattice
micro cracks in grains
shrinkage voids
nonmetallic impurities
rough surfaces
notches
Notches are great _______
weakeners
stress raisers and stress complicators, induce stress in many directions
deeper the notch and the sharper its root, the more of a stress problem it is
beware of notches from contouring instruments, grain boundaries
Types of steel and aluminum used in O and P applications
general designations can be misleading
terms don’t accurately describe the material
Carbon Steel
iron as pure as metal - too low strength and hardness for many applications
iron with added carbon
hardness and strength of carbon steel are directly proportional to amount of added carbon
manganese and small amounts of sulfur and phosphorous are also present in carbon steel
Alloy steel
adding other elements to carbon steel to achieve certain properties gives an alloy steel
general characteristics used to describe alloy steel properties
toughness - ability to withstand shock force
hardness - resistance to penetration an abrasion
ductility - ability to undergo permanent changes in shape without rupturing
corrosion resistance - the resistance to chemical attack of a metal under the influence of a moist atmosphere
Characteristics of Specific Alloys
nickel steels - increased toughness, easier heat treating, decreased distortion in quenching, increased corrosion resistance
nickel chromium steels - increased depth hardenability and abrasion resistance
molybendenum steels - greatest hardenability, increased high temp strength and increased corrosion resistance
chromium steel - increased hardening affect (can decrease carbon % and get a steel with high strength and satisfactory ductility)
Steel and Aluminum Alloys
vanadium steel - increaased refinement of internal structure of the alloy
silicon manganese steels - increased strength and hardness
Double and triple alloys have some characteristics of each
chromium molybendenum steels - excellent hardenability and satisfactory ductility
chromium nickel steels - good hardenability and satisfactory ductility
Stainless Steels
steel alloys with >3.99% chromium
AISI 3 digit grading system for types of stainless steels
austenitic - most common, cannot be heat treated, cold working increased properties, high nickel and chromium content, rapidly work harden (use sharp tools), highest corrosion resistance
martinistic - can be head treated to improve properties
ferritic - non hardenable by heat treatment and only slightly by cold working
SAE Number
4 digits
1st digit - type of steel
2nd digit - approximately % alloying element
3rd and 4th digits - % of carbon in 1/100’s of a percent
Comparison of Steel and Aluminum
Size, weight, and strength comparisons
aluminum 1/3 modulus of steel
aluminum ~ 1/3 weight of steel
AL more subject to fatigue failure than steel
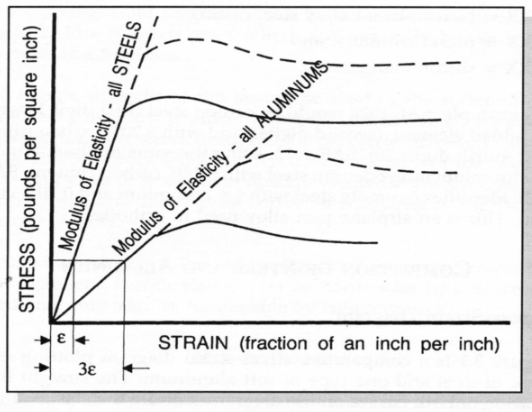
Strengthening Aluminum and Steel
AL can be stronger than some steels (proper alloying, heat treatement or cold working)
still more subject to fatigue
Heat Treatment Purposes
increase or decrease hardness or tensile strength
relieve internal stresses due to hot or cold working
improve machinability
increase toughness
Techniques for steel
steel heated above critical range undergoes definite internal changes
if steel is slowly cooled from this elevated temp, internal changes will have to reverse themselves
if steel is cooled more rapidly, structure will be modified and mechanical characteristics altered
Heat treat cycle
normalized steel - returns to its original or normal internal structure
will have increased strength and hardness but decreased ductility than same piece annealed
annealed steel - relieve internal stresses and lower yield point for max ductility
Strengthening Aluminum and Steel
tempering - often follows quenching. Heat treated steel can be too brittle and hard. Tempering can make it softer more ductile and tougher
aluminum alloy - large increased in both yield and ultimate strengths when heat treated
steel alloy - effects of hot and cold working and heat treating
carbon steel - the difference between a carbon steel and a high carbon steel that has been heat treated and tempered
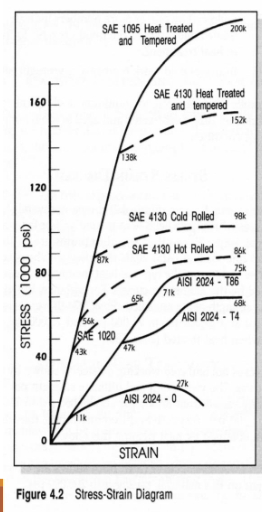
Strengthening Aluminum
tempering aluminum alloys is the major determinant of its strength, hardness, ductility, and other properties
some are tempered with heat treating, and others by cold working
temper designations are added to the four identifying digits
Preventing Failure
fatigue stress - fluctuating stressed lower than the ultimate stress of the material, but will cause after a number of cycles
this is called fatigue failure
Comparison of Fatigue in Aluminum and Steel
steel curve levels of at about 50% of its original stress
aluminum does not level off, more subject to fatigue failure
adding alloying elements can increase yield and ultimate stress but doesn’t change fatigue strength much
heat treating also doesnt’t change fatigue strength a lot
Minimizing Stress Concentraion
following practices help minimize stress concentrations in orthoses:
remove nicks and scratches by polishing
cap vice jaws that are checkered before clamping your workpiece
make sure contouring instruments have smooth curved surfaces
do not shape orthotic stirrups, uprights with a metal hammer
avoid abrupt changes in cross section
Overall what is the best way to minimize stress concentration due to bending?
avoid sharp bends
Orthotic bars are designed to be more _____________ (with knee locked) than M-L direction.
rigid in flexion
Titanium
titanium has strength comparable to steel while having a density of 56% steel but 60% greater than aluminum
double the strength of aluminum
better strength than steel, steel has better fatigue resistance
good biological compatibility
very resistant to corrosion
more expensive
Metals are highly __________ and crystallize into ______________.
crystalline, space lattices
Alloying steel is done to improve properties such as _____, __________, ________, ________________
toughness, hardenability, ductility, corrosion resistance
_______ is the major determinant of strength, hardness, and ductility for AL alloys.
Tempering
Aluminum is _____ density of steel, while steel has _______ the modulus of AL
1/3, 3x
Steel has a better _______ _________ than AL.
fatigue resistance
The best way to minimize stress concentrations in orthotic fabrication are:
prevent nicks, notches, large drilled holes, sharp contours