Chapter 4 & 5: Ecology
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Ecology
study of interactions between organisms and their relationship with their environment
Ecosystem
Consists of a community of organisms and their environment
Biosphere
Parth of the earth in which life can exist
Community
Populations of different species of organisms in an environment
Habitat
Where an organism lives and to which it is adapted
Abiotic
non-living features of an ecosystem that affect the community
Examples of Abiotic Environmental Factors
temperature, pH, light intensity, altitude,humidity
Biotic
living features of an ecosystem that affect the community
Examples of Biotic Environmental Factors
predators, prey, parasites, pathogens, competitors
Climatic
elements of climate that influence life and distribution of the organisms that live in a particular environment
Examples of Climatic Environmental Factors
temperature, rainfall, humidity, wind, day length
Edaphic
characteristics of soil that influence the community
Examples of Edaphic Environmental Factors
soil type, soil pH, available water, humus
Examples of Aquatic Factors
light penetration, currents, wave action
Energy Flow
pathway of energy transfer from one organism to the next in an ecosystem due to feeding
Food Chain
flow diagram that begins with a plant and shows how energy is passed through a series of organisms in a community
Grazing Food Chain
food chain where the initial plant is living
Detritus Food Chain
food chain that begins with dead organic matter and animal waste
Food Web
two or more interlinked food chains which show the feeding connections in a habitat/ecosystem
Producers
organisms capable of making their own food by photosynthesis
Consumer
organisms that feed on other organisms
Trophic Level
position of an organism in a food chain
Limited Size of Food Chains
due to 90% of energy lost as heat between organisms
Pyramid of Numbers
represents number of organisms at each trophic level in a food chain
Niche
functional role of an organism in an ecosystem
Nutrient Recycling
nutrients that make up bodies of living things are recycled and used time and time again
Carbon Cycle
CO2 in atmoshpere → photosynthesised by plants → eaten by animals → excreted and respired by animals → decay of animals releases CO2
Nitrogen Cycle
nitrogen in atmosphere → nitrogen fixation into nitrates → absorbed by plants → consumed, urea excreted by animals, death of plants and animals → ammonification into ammonia → nitrification into nitrites and then nitrates → denitrification by denitrifying bacteria back into nitrogen in atmosphere
Pollution
any harmful addition to the environment
Types of Pollution
air, water/river, domestic, agricultural
Agricultural Pollutant
slurry and fertiliser
Agricultural Pollutant Source
washed from land
Agricultural Pollutant Effects
algal blooms and eutrophication
Industrial Pollutant
sulphur dioxide
Industrial Pollutant Source
burning fossil fuels
Industrial Pollutant Effects
acid rain
Domestic Pollutant
plastic bags
Domestic Pollutant Source
shopping
Domestic Pollutant Effects
suffocate small animals, litter
Eutrophication
where lakes become over-enriched with nutrients and cause a rapid increase of algae as they use up the nutrients
Control of Agricultural Pollutants
avoid spreading on wet, water logged, frozen, or steeply sloping land, or within 1.5m of any watercourse
Control of Industrial Pollutants
use catalytic scrubbers in factory chimneys
Control of Domestic Pollutants
bag levy and reusable bags
Conservation
protection and management of organisms and their environment
Agricultural Conservation Practices
mixed farming, crop rotation, biological controls, gene banks
Fishing Conservation Practices
fishing net size, quotas, re-stocking
Forestry Conservation Practices
re-planting, broadleaf/conifer mix
Fishing Net Size
size of openings enclosed by threads of net
Fishing Quotas
fixed proportion of the total allowable catch allocated to each fishing nation
Restocking
translocation of species where they have naturally occurred which achieves permanent increase in a sustainable population of a species
Waste Management
collection, transport, processing, recycling or disposal of waste materials produced by human activity in an effort to reduce their effect on human health or local aesthetics or amenity
Role of Micro-Organisms in Waste Management
micro-organisms decompose organic matter into a stable substance called compost which recycles all the nutrients required for plant growth
Problems Associated with Waste Disposal
availability of suitable landfill sites, the toxic or pollution content of fumes from incineration, decaying waste produces methane gas which contributes to the greenhouse gases, harmful substances may leak into groundwater supplies, plants and animals in rivers and lakes are killed through direct poisoning or eutrophication
Waste Minimisation
reduce, reuse, recycle
Factors That Control a Population
competition, predation, parasitism, symbiosis
Competition
when organisms struggle for a limited resource
Types of Competition
intra-specific, inter-specific, contest, scramble
Intra-specific Competition
occurs between members of the same species
Inter-specific Competition
occurs between members of different species
Contest Competition
only one organism gets the resource
Scramble Competition
all competing individuals get some of the resource
Predation
catching, killing and eating of another organism
Predator
organism carries out predation
Prey
organism eaten by predator
Adaptations of Predators
hawks have excellent eyesight, ladybirds have strong mouth parts, cheetahs can run at 60km/h
Adaptations of Prey
plants may have thorns, spines or stings, nasty taste when eaten, faster than their predator, staying in herds or flock, camouflage
Parasitism
occurs when one organism feeds off of a living host and causes harm to the host
Ecto-Parasites
live on outside of the host
Endo-Parasites
live on inside of the host
Symbiosis
occurs when two organisms of different species live in harmony and at least one benefits
Examples of Symbiosis
nitrogen fixing bacteria in the nodules of legumes, bacteria in colon
Predator-Prey Dynamics
prey population increases, predators have more food and their population increases, number of prey being killed increases so predators have less food and their population decreases, prey population increases as a result
Predator-Prey Graph
prey numbers are larger then predators
waves are out of sync
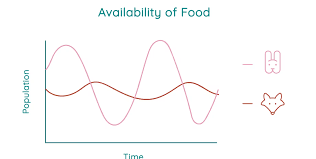
Factors that Affect Predator-Prey Relationships
food supply, concealment
Food Supply
greater food supply, greater population increase, movement of predators
Concealment
prey can conceal themselves which allows their numbers to increase again
Movement of Predators
too few prey will lead to the predators moving out of the area
Factors Affecting Human Population Growth
famine, war, disease, contraception
Famine
famine leads to malnutrition which leads to death and low birth rates
War
war reduces population numbers through deaths and partners separating
Disease
advances in modern medicine has lead to population increase
Contraception
increased contraception has lead to a decrease in population growth