PALAENTOLOGY
TRACE FOSSILS
1) Fugichnia : Escape structure
2) Repichnia : Crawling
3) Cubichnia : resting
4) Domichnia : Dwelling
5) Paschnia : Surface feeder
6) Fodinichinia : Feeding
DIFFERENT TERMS
1) Taphonomy: Study of organism from discovery to final death
2) Necrolysis : Breakup and decay of organism immediately after death
3) Biostratinomy : Study of processes operating after death to final burial
4) Diagenesis : Study of processes after final burial
CHARACTERISTIC FEATURES
Lopophore : Brachiopods
Water vascular system : Echinodermata
Jet propulsion system : Cephalopods
Torsion : Grastropoda
Ecdysis and moulting : Trilobita
Dentition pattern : Pelecypods
Distinct suture lines : Cephalopods
Siphuncle : Cephalopods
Rhabdosome : Graptolites
Neca, Secula : Graptolites
Strepto spiral coiling : Foraminifera
Theca, Epitheca : Corals
Five ray pentameral symmetry : Echinoderamata
Peristome, Periproct, Madreporite plate, Corals : Echinodermata
Ectoderm, Endoderm : Cnidaris
Mesenteries, Dissepiments : Corals
CORALS
Corallite : Cup like or disk like skeletal structure
Corallum : Complete exoskeleton of corals
Apex : Tapering end of solitary corallum by which it is attached to substrate
Calyx : Basal form of cup like depression on which polyp rests
Mesenteries : A radial infolding of fleshy body wall
Fossula : depression at the base of calyx
Dissepiments : curved (Convex inward)
Theca : Outer wall of exoskeleton of corallum and corallite
Epitheca : layer of CaCO3 outside theca
Tabulae : layer of horizontal sheets
Columella: Rod like structure formed from swolen axial end of counter
BRACHIOPODA
Exclusively marine and sessile
Equilateral but inequivalved
Triploblastic coelmate grade with oligomerous body plan
Larger valve : Ventral or Pedicle valve
Smaller valve : Dorsal or Brachial valve - Lopophore attaches to it
Lopophore : Helps in gathering food and respiration, occur in pair with Cilia
MORPHOLOGY
Mantle : all soft part enclosed within a thin skin called mantle , shell is chitinous or calcareous secreted by mantle
Umbo : Posterior protuberanace , Beak : Pointed extreme point of umbo
Auricles : Ear like projections
Delthyrium : Triangular opening on ventral valve
Notothyrium : Similar to delthyrium but located on dorsal side
Deltidium : Delthyrium closed by means of two calcite plates
LIVING FOSSILS OF BRACHIOPODS
Lingula
Trimorella
Discina
Cranida
Terrebratella
PELECYPODA
Also known as Lamillibranchia nad Acephala
Phyllum : Mollucs
Inequivalved and inequilateral
TYPES
Peristracum : outer layer - chitin
Ostracum : middle layer - aragonite and calcite
Hypostracum : Inner layer - alternate chitin and calcite
UMBO- Elevated and protruded part
Prosogyre : beak pointing anteriorly (Arca,Venus)
Opisthogyre : beak pointing posteriorly
Orthogyre/Acline : beak pointing neutrally (Pecten)
TYPES OF DENTITION PATTERN
1) Homodont : Similar size and shaped teeth (Arca)
2) Heterodont : Different size and shaped teeth (Lucina, Glycimeris, Cerastoderma)
3) Taxodont : Numerous subparallel teeth with similar size (Arca, Nucula)
4) Dysodont : small teeth radiate from umbo (Mytillus)
5) Schizodont : Teeth appear to diverge from umbo (Unio, Trigonia)
6) Isodont : Teeth and sockets symmetrical on both valves (Spondyllus)
7) Desmodont : Mya, Ostrea, Gryphea, Exogyra
8) Pachydont : Hippurities
9) Pantodont : Allodesma
10) Anomalodont : Teeths and sockets are absent (Allorisma)
ECOLOGY
Shallow burrower : Cyrena, Venus, Glycimeris
Deep burrower : Mya, solen, ensis
Borer and cavity dwellers: Teredo, Pholas
Swimmer : Pecten, Lima
Byssally attached : Mytillus
Unattached recumbents : Gryphea
Cemented: Ostrea
Normal epifaunal benthic vagile : Arca, Cardita
EXTINCT FOSSILS OF PELECYPODA
Inoceramus
Gryphea
Hippurities
TRILOBITA
Bilateral symmetry
Triplobalstic coelmate grade with metamerous body plan
Phylum: Athropoda
Shows metamorphosis
Have most primitive visual systems
Characteristic feature : Ecdysis and moulting
CLASSIFICATION
Longitudinal : Pleural (on each side) and Axial lobes ( down the centre)
Transverse : Cephalon, Thorax and Pygididium
MORPHOLOGY
Cephalon : Anterior most part
Glabella : Cephalic portion of the axial lobe
Fixed cheeks (Fixigena) : Inner portion of each cheek fixed with glabella
Free cheeks (Librigena) : Outer portion of cheek which is movable
Hypostome : A plate on ventral side of cephalon in front of mouth
Rostrum : A small shield like elevated portion in front of hypostome
FACIAL SUTURES
Potoparian : Suture marginal to cephalon. eg: Olenellus
Proparian : Suture originating from anterior and ending in front of genal angle
eg: Dalmanites, Phacops
Opisthoparian : Suture like proparian but ending posterior to the genal angle
eg: Isotelus, Paradoxides
Gonatoparian : Facial suture ending at genal angle , eg: Calymene
Hypoparian : Marginal but on ventral side without eyes, eg: Paraherpes
PYGIDIUM
Micropygous : Very small sized Pygidiyum, eg: Paradoxides
Heteropygous : Large but smaller than Cephalon , eg: Calymene
Isopygous : Pygidium and Cephalon are of equal size, eg: Isotelus
Macropygous : Pygidium is larger than Cephalon, eg:Anisopyge
GASTROPODS
Include snail and slugs
Marine, Freshwater and terrestrial
Characteristic feature : Torsion - Helps in rotation of Visecera
MORPHOLOGY
Whorl : a complete revolution (360) of shell around the axis
Whorl profile : whorl outline as appeared in the axial plane
Spire : all whorl except the last one
Body whorl : last whorl of the shell (usually the last one)
Columella : pillar or rod like structure along the axis of coiling
COILING PATTERNS
Sinistral : anticlockwise coiling, eg: Physa, Planorbis
Dextral : Clockwise coiling, eg:voluta
Planispiral : coiling around axis in a single plane
Conispiral : coiling like a screw
Evolute : loosely coiled, whorls not in contact eg: Ecculiompalus
Advolute: whorls are just contact but not embracing , eg: Planorbis
Involute : Natica
Convolute : Cyphrea
CEPHALOPODS
Exclusively marine
Triplobalstic coelmate grade with amerous body plan
Well known fossils
Ammonites : extinct in K/T boundary
Belemnites : extinct in K/T boundary
Nautilus : Triassic to recent
Characteristic feature : Jet propulsion system
MORPHOLOGY
Siphuncle : tube like structure and is connected by fleshy talk
Jet propulsion : during swimming, a natuilus floods the mantle cavity with water, then closes off the entrances and forces the water out the nozzle like hyponome
COILING TYPES
Planispiral : coiling around an axis in single plane, eg: Perisphincts
Conispiral : coiling around an axis in different planes, eg: Turrilites
Evolute : coiled shell but whorls are not touching, eg: Gyroceras
Advolute: Coined shell, whorls just touching and all whorls visible, eg: Centroceras
Involute: Coiled shell in which earlier whorls seen partly enveloped by
later whorls. eg: Macrocephalites-
Convolute: Coiled shell in which last whorl concealing the preceding whorls.
eg: Nautilus
SUTURAL TYPES
Orthoceratitic : Uncoiled, straight suture line , eg: Orthoceras

Nautilitic : Undulating suture with both lobes and saddles are rounded, eg: Nautilus
Lobes : Rounded
Saddle : Rounded

Goniatitic : Lobes are angular but saddles are rounded
Lobes : Angular
Saddles : Rounded
Ceratitic : Lobes are crenulated but saddles are still rounded
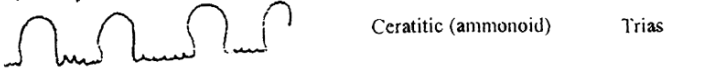
Ammonitic : Lobes are saddles are crenulated, complex structure

ECHINODERMATA
Exclusively Marine
Water vascular system
Triploblastic Coelomate grade with oligomerous body plan
Extinct fossils : Blastoids and Cystoids
Characteristic feature : Five ray pentameral system
MORPHOLOGY
Regularia : radial symmetry
Irregularia : bilateral symmetry
Peristome : a circular area enclosing mouth surrounded by soft plates
Periproct : circular area enclosing anal aperture
Corona : part of test excluding periproct, peristome and occutogenital ring
Ambitus: peripheral outline of corona, that outline-shape of the test