1.6 Growth & evolution
Introduction
- Scale of operation: maximum output that can be achieved using the available inputs (resources) - this scale can only be increased in the long term by employing more of all inputs.
Increasing the scale of operations
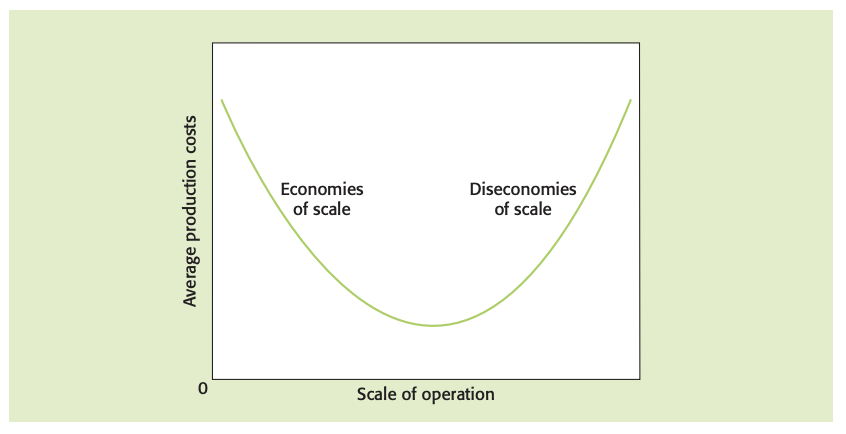
Economies of scale: reductions in a firm’s unit (average) costs of production that result from an increase in the scale of operations.
- Reasons for the cost benefits to arise:
- Purchasing economies
- Technical economies
- Financial economies
- Marketing economies
- Managerial economies
Diseconomies of scale: factors that cause average costs of production to rise when the scale of operation is increased.
- Causes of management problems:
- Communication problems
- Alienation of the workforce
- Poor coordination and slow decision-making
Large-scale production - unit costs
Merits of small and large organizations
Potential advantages of small and large businesses
- Small businesses:
- Can be managed and controlled by the owner(s)
- Often able to adapt quickly to meet changing customer needs
- Offer personal service to customers
- Find it easier to know each worker and many staff prefer to work for a smaller, more “human” business
- Average costs may be low due to no diseconomies of scale and low overheads
- Easier communication with workers and customers
- Large businesses:
- Can afford to employ specialist professional managers
- Benefit from cost reductions associated with large-scale production
- May be able to set prices that other firms have to follow
- Have access to several different sources of finance
- May be diversified in several markets and products, so risks are spread
- More likely to be able to afford research and development into new products and processes
Potential disadvantages of small and large businesses
- Small businesses:
- May have limited access to sources of finance
- May find the owner(s) has to carry a large burden of responsibility if unable to afford to employ specialist managers
- May not be diversified, so there are greater risks of negative impact of external change
- Unlikely to benefit from economies of scale
- Large businesses:
- May be difficult to manage, especially if geographically spread
- May have potential cost increases associated with large-scale production
- May suffer from slow decision-making and poor communication due to the structure of the large organization
- May often suffer from i divorce between ownership and control that can lead to conflicting objectives
What is an appropriate scale of operation?
- Business owners must weigh up and assess:
- Owners’ objectives
- Capital available
- Size of the market the firm operates in
- Number of competitors
- Scope for economies of scale
Business growth
Internal growth: expansion of a business by means of opening new branches, shops or factories (also known as organic growth).
External growth: business expansion achieved by means of merging with or taking over another business, from either the same or a different industry.
Merger: agreement by shareholders and managers of two businesses to bring both firms together under a common board of directors with shareholders in both businesses owning shares in the newly merged business.
Takeover: when a company buys over 50% of the shares of another company and becomes the controlling owner often referred to as “acquisition”.
Horizontal integration: integration with a firm in the same industry and at the same stage of production.
Forward vertical integration: integration with a business in the same industry but a customer of the existing business.
Backward vertical integration: integration with a business in the same industry but a supplier of the existing business.
Conglomerate integration: merger with or takeover of a business in a different industry.
Joint ventures, strategic alliances and franchising
Joint venture: two or more businesses agree to work closely together on a particular project and create a separate business division to do so.
Strategic alliances: agreements between firms in which each agrees to commit resources to achieve an agreed set of objectives.
Franchise: business that uses the name, logo and trading systems of an existing successful business.
Globalization: growing integration of countries through increased freedom of global movement of goods, capital and people.
Free trade: no restrictions or trade barriers exist that might prevent or limit trade between countries.
Protectionism: using barriers to free trade, such as tariffs and quotas, to protect a country's own domestic industries.
Multinational businesses
Multinational company/business: business organization that has its headquarters in one country, but with operating branches, factories and assembly plants in other countries.
Why become a multinational?
- Closer to main markets
- Lower costs of production
- Avoid import restrictions
- Access to local natural resources