Biology 12 Unit 2: Cell Structure & Function (CYTOLOGY)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What is the Cell Theory?
1. All living organisms are made up of one or more cells
2. Cells are the basic unit of life
3. All cells come from pre-existing cells
What is a prokaryotic cell?
- Includes bacteria, blue-green algae (Monera).
- Single Cell organisms that lack both a true nucleus and other membrane bounded substructures.
- Prokaryotic DNA is typically circular.
The Fluid Mosaic Model
- Membrane has properties of solids and liquids.
- Forms a "fluid sea" where proteins and lipids etc. form a thin membrane around the cell
Fluid part - contains phospholipids forming phospholipid bilayer.
Solid part - proteins
Nuclear Envelopes
Double membrane (2 Phospholipid Bilayer) that is a continuation of ER
Chromatin
Combination of DNA and Histone Proteins
Chromosomes
Packages DNA during nuclear division, controls gene expression
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
What are our knowledge of cells built on?
Work done with microscopes
What is an eukaryotic cell?
- Plants, animals, protozoa, fungi
- Contains nucleus and membrane bound organelles
- Genetic Material organized into chromosomes
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
1. Cell membrane: thin layer containing cell contents. - Plant cells also have a cell wall surrounding the membrane
2. Nucleus: specialized structure within cell containing DNA. Controls cell function and reproduction
Cell Membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell (Transportation). Homeostasis, recognition, communication.
Selectively permeable (allows some substances but not others)
Plant Cells - Cell Wall
- Surrounds cell membrane
- Made up of cellulose fibers
- Selectively permeable
Nucleus
- Control center of the cell
- Determines metabolism, growth, differentiation, structure, reproduction
Nuclear Pores
holes in the nuclear envelope that allow materials to pass in and out of the nucleus
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Increases Surface Area where reactions occur. Channels = storage.
Protein leaving ER goes into Golgi for further processing
Ribosomes = Rough, No ribosomes = Smooth
Ribosomes
Protein Synthesis
Golgi Body
"Quality control", Modifies, Processes and Packages proteins made by the cell that are later packaged into vesicles.
Looks like a flattened stack of hollow tubes.
Like FedEx
Vacuole & Vesicles
Storage depots.
PEETS
P - Pinching off from Golgi
E - Endocytosis of the cell membrane
E - Extension of the ER membrane
T- Transport and storage of materials
Vacuoles in Plants
Plant cells usually have one large central vacuole that stores water, food, waste, cell support and help plants photosynthesize.
Lysosomes
Cellular stomachs - special vesicles animals cells only (sometimes plants) formed by the golgi apparatus.
- Hydrolytic enzymes functioning in:
digestion, disposal, breakdown
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell.
2 membranes, inner and outer.
Inner - cristine
Outer - matrix
Function: AEROBIC ENERGY METABOLISM
Chloroplast
Double-membrane bound structures containing pigments found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs. Makes food.
Most prominent plastid.
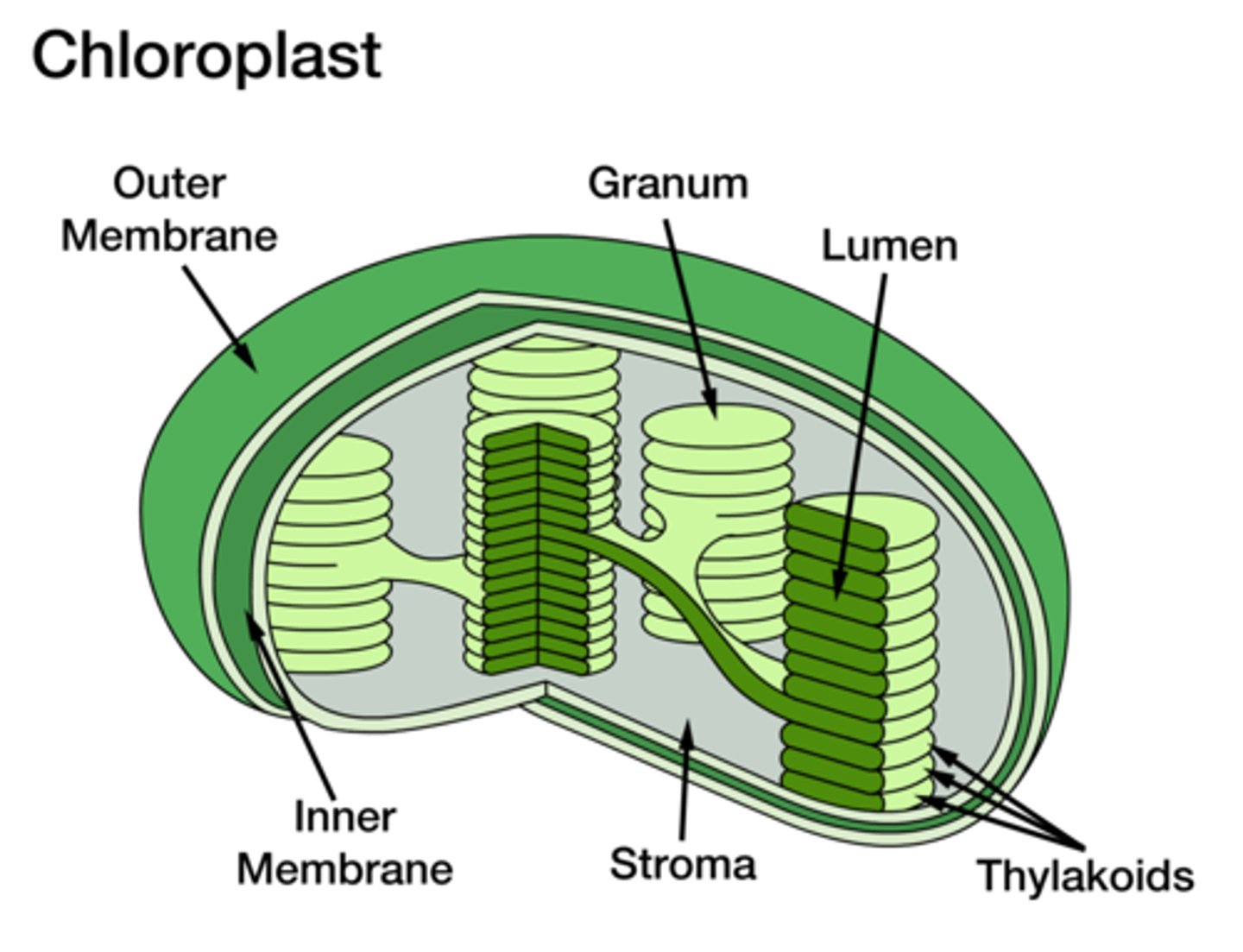
Grana
Looks like pancakes, chlorophyll is located inside.
Chlorophyll is needed to photosynthesize.
Thylakoid
Each pancake (within the stack) is called a thylakoid
Centrioles
Cell organelle that aids in cell division in animal cells (and plant).
Two cylindrical bodies.
The Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
Microtubules
Within Cytoskeleton, hollow, cylindrical aggregates of tubelike structures that help give cell shape and form.
Microfilaments
Long, thin fibers that function in the movement and support of the cell
Formula for Cellular Respiration
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H20 + ENERGY (ATP)
Formula for Photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O + LIGHT → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Glycolipids
Glycogen attatched to a phospholipid, which are associated with cell membranes. Cellular adhesion.
Glycoproteins
Glycogen attatched to a protein. Cellular recognition.
What criteria is used by cell membrane to determine which molecules can enter?
Shape, size, polarity, charged/non-charged macromolecules
What are the two means which substances can enter and exit cells?
1. Passive Transport - No energy required
2. Active Transport - Energy required
Diffusion
The movement of molecules from higher concentration to lower concentration. Can be slowed through increase temperature, increase concentration gradient, decrease in size of molecules.
PASSIVE TRANSPORT
Facilitated Transport
a process by which material moves down a concentration gradient (from high to low concentration). Carriers in cell membrane control passage of molecules.
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane driven by a difference in the concentration of solutes on either side of the membrane.
Osmotic Pressure
pressure that must be applied to prevent osmotic movement across a selectively permeable membrane
Tonicity
When placed in a solution, the concentration outside of the cell may be different than the inside
Isotonic Solution
Equal concentration inside and outside of the cell
Hypertonic Solution
Greater concentration of the solute outside the cell than inside
Hypotonic Solution
Lesser concentration of the solute outside the cell than inside
Turgor Pressure
The pressure inside of a cell as a cell pushes itself against the cell wall.
Why doesn't a plant cell burst from turgor pressure when placed in a hypotonic solution? How does it help photosynthesis?
Cell wall prevents cell from absorbing more H20, keeping plants erect and providing more surface area towards the sun.
Active Transport
Moves molecule against the concentration gradient from lower to higher concentration. Opposite of diffusion. Important in maintaining homeostasis.
Endocytosis
Cell membrane forms a vesicle around the substance to be taken in.
Phagocytosis
Cell eating, (eg. amoebas engulfing bacteria)
Pinocytosis
Cell drinking (eg. Amino Acids, Glucose, ions)
Exocytosis
Reverse of endocystosis. Vacuole within cell fuses with cell membrane and the vacuole contents are deposited on the outside. Taken OUT of cells.
Surface Area to Volume Ratio & Cell Size
When cells get to large, they must divide because cell volume changes with respect to surface area. As Size of the cell increases, SA:V decreases. Becomes less efficient.
Why is this ratio important?
Cells rely on difusion for material to enter/exit cell. Diffusion is not a highly efficient mean of distributing materials over long distances.
How do cells get around the limits of the SA:V ratio?
1. Divide
2. Slow down metabolism - eg. unfertilized chicken eggs
3. Long and thin shape rather than round and fat
4. Folds in membrane
5. Branch out