NURS 3108 - Exam #1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/239
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:48 PM on 9/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
240 Terms
1
New cards
Health assessment information (database)
•History (Subjective Data-70%)
• Physical Examination (Objective Data-20%)
• Laboratory/Imaging Studies (Objective data-10%)
• Physical Examination (Objective Data-20%)
• Laboratory/Imaging Studies (Objective data-10%)
2
New cards
subjective
symptom: what the patient feels/ communicates
3
New cards
objective
Sign: clinical findings collected during physical examination
4
New cards
Clinical manifestations
signs/ symptoms collected
5
New cards
Three levels of health promotion
1. Primary= promotion of healthy lifestyle
2. Secondary= screening efforts to detect disease
3. Tertiary= minimizing disability from illness/ injury to allow for most productive life within limitations
2. Secondary= screening efforts to detect disease
3. Tertiary= minimizing disability from illness/ injury to allow for most productive life within limitations
6
New cards
Purpose of health history
subjective: picture into past and present
1. comprehensive
2. problem based
3. follow- up
4. screening
1. comprehensive
2. problem based
3. follow- up
4. screening
7
New cards
Therapeutic communication
most important skill: is communication.
-active listening
-clarifying
- reflecting
- open-ended questions
-active listening
-clarifying
- reflecting
- open-ended questions
8
New cards
Non-therapeutic communication
- using medical terminology w no explanation
- interrupting
- disagreeing
- interrupting
- disagreeing
9
New cards
Health illiteracy
patient does not understand, so help them understand with handouts, video, etc. Help patient understand
10
New cards
Professional nursing behavior
calm, organized, competent, professional
11
New cards
Health history: biographic information
name, age, gender, occupation
12
New cards
CC (Chief Complaint)
presenting problem; why seeking care
13
New cards
HPI (History of Present Illness)
History of present illness - brief history of as to what is wrong with the patient at the present time. chronological record onset- current
14
New cards
HPI: presenting symptoms
-Start with "presenting" symptoms
- Description of symptoms in patient's own words
->last time felt well, overall health before, previous episodes of similarity
- Description of symptoms in patient's own words
->last time felt well, overall health before, previous episodes of similarity
15
New cards
LOCSTAAM
Location, Onset, Character, Severity, Timing, Associated factors, Aggravating/Alleviating factors, Meaning to the patient
16
New cards
OLDCARTS
Onset, Location, Duration, Character, Aggravating/ relieving factors, Related symptoms, Treatment, Severity
17
New cards
Location
-Point to spot where it hurts or describe
- Is it localized or generalized?
- Does it radiate (or move toward or away from)?
- Ex. stomachache: patient c/o pain in the RUQ that radiates towards the umbilicus
- Is it localized or generalized?
- Does it radiate (or move toward or away from)?
- Ex. stomachache: patient c/o pain in the RUQ that radiates towards the umbilicus
18
New cards
Onset
-When did symptoms first start?
-Precipiatating factors?
-Setting in which symptom occured?
-What were you doing at the onset of symptoms?
-Where were you during the onset of symptoms?
-Patient c/o pain in the RUQ that radiates toward the umbilicus x 2 weeks. Pain occurs after eating fatty foods
-Precipiatating factors?
-Setting in which symptom occured?
-What were you doing at the onset of symptoms?
-Where were you during the onset of symptoms?
-Patient c/o pain in the RUQ that radiates toward the umbilicus x 2 weeks. Pain occurs after eating fatty foods
19
New cards
Character
-What the patient feels or symptoms look like
-Describe sensation or appearance to the best of the patients ability
-Patient c/o stabbing pain in the RUQ thay radiates toward the umbilicus x 2 weeks. Pain occurs after eating fatty food
Specific descriptive terms such as... burning, sharp/dull, aching, gnawing, throbbing, shooting, stabbing, crushing, cramping
-Describe sensation or appearance to the best of the patients ability
-Patient c/o stabbing pain in the RUQ thay radiates toward the umbilicus x 2 weeks. Pain occurs after eating fatty food
Specific descriptive terms such as... burning, sharp/dull, aching, gnawing, throbbing, shooting, stabbing, crushing, cramping
20
New cards
Severity
-Size, extent, number amount
-Measure if possible
-Grade on scale 1-10 (for A&O pts)
-Better, worse, same?
-How limiting are symptoms?
-Patient c/o stabbing pain in the RUQ that radiates toward the umbilicus x 2 weeks. Pain= 5/10, occurs after eating fatty foods. No changes in level of pain since onset.
For PEDS use: FACES
-Measure if possible
-Grade on scale 1-10 (for A&O pts)
-Better, worse, same?
-How limiting are symptoms?
-Patient c/o stabbing pain in the RUQ that radiates toward the umbilicus x 2 weeks. Pain= 5/10, occurs after eating fatty foods. No changes in level of pain since onset.
For PEDS use: FACES
21
New cards
Timing
- Chronological (when started?)
- Duration (how long have you had them & how long do they last?)
- Frequency (constant, intermittent?)
- Pattern (# times per day, week, month, after meals, at bedtime, etc)
- Patient c/o stabbing pain in the RUQ that radiates toward the umbilicus x 2 weeks. Pain= 5/10, occurs 1-2 times per day after eating fatty foods and lasts 1 hour. No changes in level of pain since onset.
- Duration (how long have you had them & how long do they last?)
- Frequency (constant, intermittent?)
- Pattern (# times per day, week, month, after meals, at bedtime, etc)
- Patient c/o stabbing pain in the RUQ that radiates toward the umbilicus x 2 weeks. Pain= 5/10, occurs 1-2 times per day after eating fatty foods and lasts 1 hour. No changes in level of pain since onset.
22
New cards
Aggravating and Alleviating symptoms
-What makes the symptoms worse or better?
-What aggravates them- weather, activity, food, medication, standing, bending over, fatigue, time of day, season, etc
-What relieves symptoms? (rest, medication, ice, etc)
What have you tried to do or take to relieve symptoms
-What aggravates them- weather, activity, food, medication, standing, bending over, fatigue, time of day, season, etc
-What relieves symptoms? (rest, medication, ice, etc)
What have you tried to do or take to relieve symptoms
23
New cards
Meaning of symptoms to patient
What are you most worries about
Did the pain wake you up from sleep
How does it affect daily activities
How they have been coping
Did the pain wake you up from sleep
How does it affect daily activities
How they have been coping
24
New cards
past medical history
Childhood Illnesses, adult illnesses, Accidents or Injuries,
hospitalization, immunization, health examination, screening tests
hospitalization, immunization, health examination, screening tests
25
New cards
Family history
genogram, age currently, each persons state of health
26
New cards
Screening tools
- substance abuse screening (CAGE, TACE, CRAFFT)
- domestic violence screening
- eating disorder screening
- adolescent screening for general issues HEADSS
- domestic violence screening
- eating disorder screening
- adolescent screening for general issues HEADSS
27
New cards
CAGE
cut down, annoyed, guilty, eye opener
28
New cards
TACE
Take you to get high (how many drinks), Annoyance (who criticizes your drinking), Cut down on your drinking (should you cut down on your drinking?), Eye-opener (have you ever had an eye-opener drink to wake you up in the AM)
29
New cards
CRAFFT
screening tool for substance abuse in adolescents
Car, Relax, Alone, Forget, Friends, Trouble
Car, Relax, Alone, Forget, Friends, Trouble
30
New cards
HITS (DV)
Hurt you physically, Insult or talk down to you, Threaten you with physical harm, Scream or curse at you
31
New cards
HEADSS
Adolescent screening for general issues HEADSS(home life, education, substance use, emotional, sexuality)
32
New cards
Present health status
current health condition, current medication, allergies
33
New cards
General survey
- 1 step of assessment
- observation/ inspection
- baseline of info
- every day use
- observation/ inspection
- baseline of info
- every day use
34
New cards
SENSES to observe
only senses:
visual- see/ look
auditory- hear/ listen
olfactory- smell
tactile- tocuh/ feel
visual- see/ look
auditory- hear/ listen
olfactory- smell
tactile- tocuh/ feel
35
New cards
Assessment done head to toe? Why do we do this?
cephalocaudal; clean to dirty
36
New cards
key concept is to assess for:
symmetry
37
New cards
Initial observation
mental status?
Where did you find pt?
General appearance?
Overall development and nutrition Noticeable odor
dress/ grooming hygiene appropriate
Where did you find pt?
General appearance?
Overall development and nutrition Noticeable odor
dress/ grooming hygiene appropriate
38
New cards
first impression
speech
Facial expressions & affect
Behavior
Breathing
Age
Response to questions
Tremors/tics
Eye contact
skin color
family
posture
Facial expressions & affect
Behavior
Breathing
Age
Response to questions
Tremors/tics
Eye contact
skin color
family
posture
39
New cards
assessment techniques
1. Inspection
2. Palpation
3. Percussion
4. Auscultation
2. Palpation
3. Percussion
4. Auscultation
40
New cards
inspection 1
what do you see
41
New cards
palpation 2
hands to detect tenderness/ painful areas
- temp
- texture
- moisture
- masses
- temp
- texture
- moisture
- masses
42
New cards
Light palpation
one hand
1/2 in deep (1 cm)
RN's use
1/2 in deep (1 cm)
RN's use
43
New cards
deep palpation
two hands
1 1/2 in (4 cm)
- organ size
- advanced practice
1 1/2 in (4 cm)
- organ size
- advanced practice
44
New cards
bimanual palpation
two hands to assess the kidneys and uterus
- advanced practice
- advanced practice
45
New cards
percussion 3
striking, tapping of body to produce sound/ vibration
46
New cards
Palpating technique
-finger pads are most sensitive part of the body
- dorsal to assess temp
- warm hands, short nails
- tell pt
- dorsal to assess temp
- warm hands, short nails
- tell pt
47
New cards
direct percussion
involves striking a finger or hand directly against the patient's body
48
New cards
indirect percussion
tapping a finger on another finger help against chest wall/ abdomen
49
New cards
Auscultation 4
listening with stethoscope-- amplifies sound in body cavities/ blocks room sounds
- must have diaphragm and bell
- must have diaphragm and bell
50
New cards
Diaphragm
high-pitched sounds like breath, bowel, and normal heart sounds
- hold firmly on skin
- hold firmly on skin
51
New cards
Bell
best for low pitched sounds like extra heart sounds, murmurs
- lightly against skin
- lightly against skin
52
New cards
Culturally competent care
delivered when nurses value health or illness through patient's eyes
53
New cards
Diverse cultural example
Native Indians emphasize spirituality
- nurse touching someone has spiritual power
- honor includes components of appreciation and respect
- nurse touching someone has spiritual power
- honor includes components of appreciation and respect
54
New cards
"Melting pot"
U.S. has many cultures and religions
- 20% speak other language than english at home
- 20% speak other language than english at home
55
New cards
Diversity can create challenges when caring for a patient but
do not force compliance but work with beliefs and value systems
56
New cards
cultural competence
Learning process:
- self-awareness
- reflective practice
- knowledge or core cultural issues
- self-awareness
- reflective practice
- knowledge or core cultural issues
57
New cards
cultural competence
- recognizing ones own culture, values, biases, and using patient-centered communication skills
- required acceptance
- required acceptance
58
New cards
Cultural competence requires healthcare providers to be sensitive towards__________
Patients Heritage, sexual orientation, socioeconomic situation, ethnicity, cultural background
59
New cards
You are not responsible for knowing ______a____, practices, and values of all groups. You ARE responsible for asking about ___b____
a) health beliefs
b) beliefs
b) beliefs
60
New cards
Culture
All the socially transmitted behavioral patterns, arts, beliefs, knowledge, values, morals, customs, lifeways, and characteristics that influence a worldview.
61
New cards
Ethnicity
Social group within a cultural and social system that share common cultural and social heritage including:
Ex. language, history, religion, symbols, folklore
Ex. language, history, religion, symbols, folklore
62
New cards
Race
is genetic in origin and includes physical characteristics
Ex. skin color, bone structure, eye color, hair color
Ex. skin color, bone structure, eye color, hair color
63
New cards
religion
An organized system of beliefs, rituals, and practices with individual participants
64
New cards
spirituality
broader concept:
Prayer
Meditation
Listening to music
Intentional appreciation of beauty
Being present in the world with others
Prayer
Meditation
Listening to music
Intentional appreciation of beauty
Being present in the world with others
65
New cards
Impact of culture
influences way patients seek medical care and clinicians provide care
66
New cards
1 become culturally competent
respect pt by assessing individuals
- beliefs, values, preferences, needs
- beliefs, values, preferences, needs
67
New cards
2 do not stereotype
recognize uniqueness
68
New cards
3. Develop a Template for Assessment
Direct the assessment of patient's health beliefs and practices that reflect his/her cultural heritage.
69
New cards
Personal and psychosocial open ended questions
allow for the patient to give own response and elaborate
70
New cards
open ended question examples
1. roles in family
2. special dietary practices
3. note patients surroundings
1. roles in family
2. special dietary practices
3. note patients surroundings
1. who makes decisions in your family
2. are there any foods forbidden by your culture
3. any religious symbols
2. are there any foods forbidden by your culture
3. any religious symbols
71
New cards
VS: Temperature
-regulated by hypothalamus
body generates heat by shivering and vasoconstriction
& cools by vasodilation
body generates heat by shivering and vasoconstriction
& cools by vasodilation
72
New cards
vasoconstriction
Reduces blood flow and heat transfer by decreasing the diameter of superficial blood vessels.
73
New cards
vasodilation
increase heat loss through skin; evaporation of perspiration. Widening of blood vessels
74
New cards
pyrexia
fever response
75
New cards
Temperature range
97.2 F- 99.9 F (36.2 C-37.7 C)
fever is T>100.4 (38 C)
oral, rectal, axillary, tympanic, forehead
fever is T>100.4 (38 C)
oral, rectal, axillary, tympanic, forehead
76
New cards
VS: Pulse
heart rate. ventricular heart contraction pushes a pressure wave of blood throughout arterial system
77
New cards
Pulse range
60-100 bpm
carotid, brachial, radial, femoral, popliteal, dorsalis
carotid, brachial, radial, femoral, popliteal, dorsalis
78
New cards
VS: Respiratory rate
inspiration: diaphagram moves downward, external intercostal muscles increase
expiration:
internal intercostal muscles decrease diameter
expiration:
internal intercostal muscles decrease diameter
79
New cards
Respiratory rate range
12-20 breaths/ min
80
New cards
tachypnea
faster than normal respiratory rate
81
New cards
bradypnea
slower than normal respiratory rate
82
New cards
VS: blood pressure
force of the blood against the wall of an artery as the ventricles contract and relax
83
New cards
blood pressure range
120/80 (systolic: 120-139) (diastolic: 60-89)
84
New cards
VS: Pain
common, uncomfortable sensation and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage
85
New cards
Acute pain
is sudden, of short duration, and usually associated with surgery, injury, or acute illnes
86
New cards
Chronic pain
is persistent, lasting weeks, or months, or longer; usually sustained by a pathophysiologic process
87
New cards
Neuropathic pain
pain is long-term, associated with damage or dysfunction of the CNS or PNS.
88
New cards
Pain in infants/ children
-Increased pulse and respiratory rate
-Lower blood pressure than adults
-Behavioral cues
-Less able to modify pain impulses
-Easily distracted but still have pain
-Different pain scales
-Lower blood pressure than adults
-Behavioral cues
-Less able to modify pain impulses
-Easily distracted but still have pain
-Different pain scales
89
New cards
pain in older adults
-No diminished perception of pain
-Decreased pain threshold
-Pain from chronic conditions
-Decreased pain threshold
-Pain from chronic conditions
90
New cards
Pain is subjective or objective?
subjective!
91
New cards
Pain scales
OLDCARTS or LOCSTAAM
- numeric: 0-10
-descriptive: none-worst
-visual: point to an area on scale
- children, Under sedation: wong/baker FACES
-infants: observe the behavior
- numeric: 0-10
-descriptive: none-worst
-visual: point to an area on scale
- children, Under sedation: wong/baker FACES
-infants: observe the behavior
92
New cards
To assess pain you inspect:
body movements, facial expressions, vocal, vitals, pupils, attention span, palpate skin
93
New cards
Pain control measures
Distraction, relaxation, ice, heat, massage, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENs), acupuncture
94
New cards
Alert and orientated x 4 (A&Ox4)
-most important indication of neurological status
-test in order: time, place, situation, and person
-pt becoming disorientated will lose in that order
-test in order: time, place, situation, and person
-pt becoming disorientated will lose in that order
95
New cards
A&O X4 steps
1. Time
2. Place
3. Situation
4. Person
2. Place
3. Situation
4. Person
96
New cards
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
a scale used to assess the consciousness of a patient upon physical examination, typically in patients with neurological concerns or complaints (higher the better -- best 15)
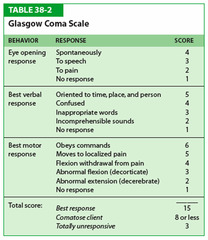
97
New cards
cerebral functioning
1. judgement
2. abstract thinking and reasoning
3. memory
4. communication skills
5. calculation
6. Vs
7. Eyes
2. abstract thinking and reasoning
3. memory
4. communication skills
5. calculation
6. Vs
7. Eyes
98
New cards
Nutrition: Subjective Assessment
Questions explore dietary intake and perceived nutrition-related problems
99
New cards
Tools for nutrition assessment
•24-hour Dietary Recall
•Typical Day
•Use of food diary
•Food frequency questionnaire
•Comprehensive diet history (more often done by nutritionist)
•Use of tools: 'My Plate'
•Assessment of diet in terms of variety of foods, serving sizes, disease specific, etc.
•Typical Day
•Use of food diary
•Food frequency questionnaire
•Comprehensive diet history (more often done by nutritionist)
•Use of tools: 'My Plate'
•Assessment of diet in terms of variety of foods, serving sizes, disease specific, etc.
100
New cards
Nutrition: Physical Assessment (Objective)
•Height & Weight (BMI)
•Waist Circumference
•General appearance & orientation
•Skin (hydration, vitamins)
•Hair & nails (protein, iron)
•Eyes (vitamin deficiencies [A])
•Oral Cavity (ability to eat, vitamin deficiency [B])
•Extremities (size, shape, movement, strength)
•Waist Circumference
•General appearance & orientation
•Skin (hydration, vitamins)
•Hair & nails (protein, iron)
•Eyes (vitamin deficiencies [A])
•Oral Cavity (ability to eat, vitamin deficiency [B])
•Extremities (size, shape, movement, strength)