Introducing Ice
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
A smaller body of ice (less than 50000 km in extent), usually found in mountainous regions
A period of ice advance associated with falling temperatures.
80,000 to 100,000 years
Sometimes caused an ice age
Interglacial
A period of ice retreat associated with rising temperatures.
10,000 to 15,000 years (in the past 2.6M years)
Also called Quarternary warm periods
Climate
Landscapes
Ecosystems
Human Civilisation
Impact of the Last Glacial Period
Earth's Crust: During the last glacial period, huge ice sheets up to 3000 metres thick covered the continents in the northern hemisphere, causing the Earth's crust to sink.
Vast areas of floating sea ice also formed.
Sea Levels: Because so much water was locked in the ice sheets, sea levels dropped by over 100 metres.
Formation of Glaciers
In cold environments and high altitudes, snow falls layer upon layer
Over time, the layers get compacted to ice
If the ice doesn't melt and snow continues to fall, the ice becomes bigger and heavier
When it becomes very heavy, gravity causes it to start moving down very slowly
As the glacier moves, it erodes and changes the landscape
Glacier melts or falls away, evaporates and the cycle repeats
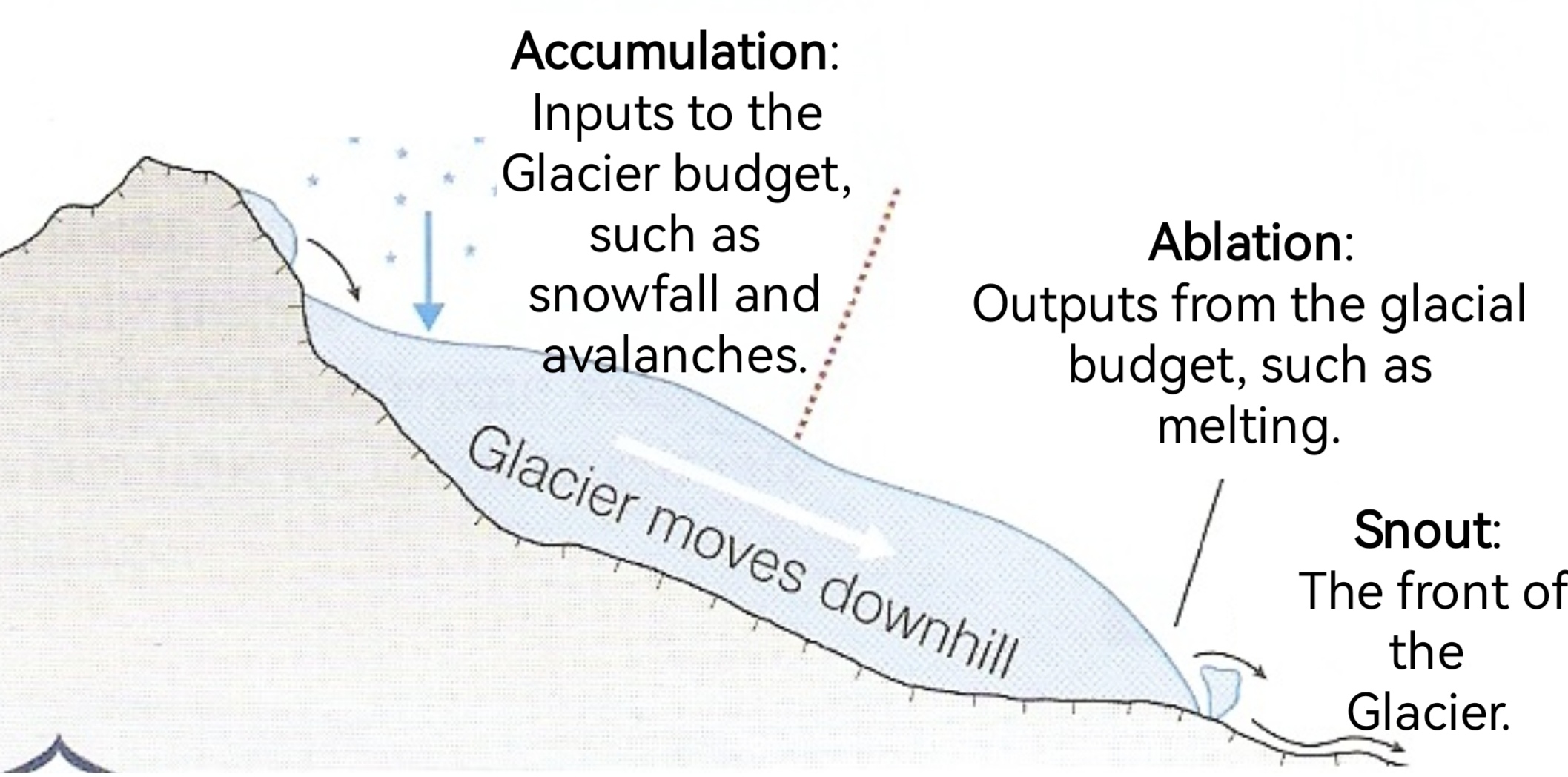
Label the diagram:
Avalanches
Snowfall
Melting
Calving
Evaporation
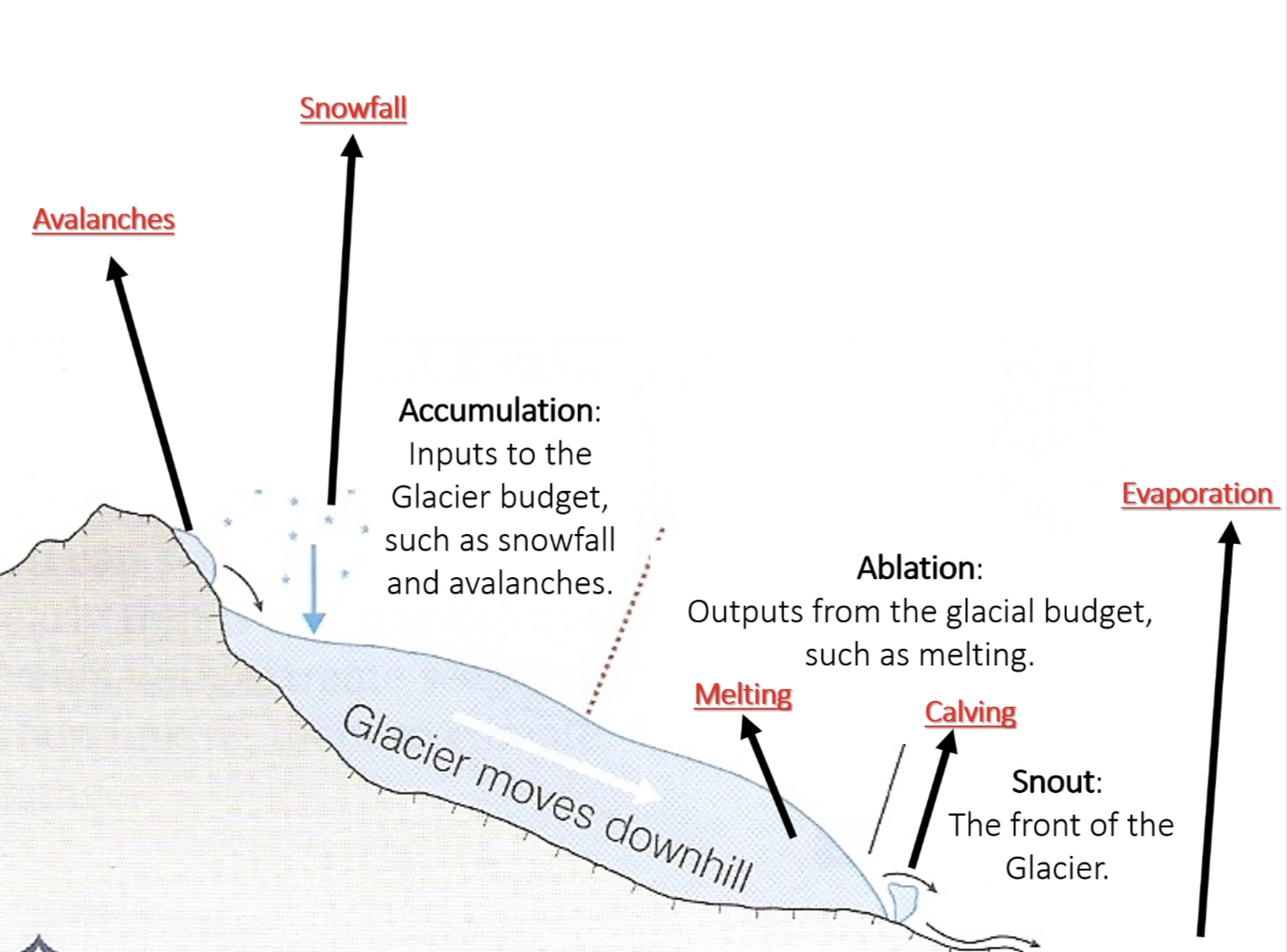
Accumulation
Inputs to the glacial budget, such as snowfall and avalanches
Ablation
Outputs from the glacier budget, such as melting
Temperature change every 100m
1 degree celsius
Which part of the glacier is the 'snout’?
The end
What accumulates to form a glacier?
Snowfall
As a glacier advances, what does it do to the landscape?
Erodes/carves
How long ago did the last ice age finish?
10,000 to 15,000 years
Cycle that affects the Earth's climate causing glacial and interglacial periods
Milankovich Cycles
Countries with glaciers
France, China, India, Pakistan, Chile, etc.
Define:
Erosion
Transportation
Deposition
Wearing away of the land
Moving or carrying something
Putting something down
Plucking
When ice freezes around rocks under the glacier and then the glacier tugs them out
Freeze- thaw weathering
When water freezes in cracks expanding them so the crack becomes bigger
Striations
The indentation the glacier makes as it scratches the rock beneath it
Abrasion
When rocks grind against other rocks wearing it away like sand paper
Corrie
Glaciers form a hollow on the mountain where they've been forming
The hollow deepens through plucking, abrasion and freeze-thaw weathering
Carries are revealed whne the glacier melts, often with a lake in them
Tarn
The corrie fills with water, forming a tarn.
Arete
Corries sometimes form side by side, forming an Arete
Pyramidal Peak
Three/four corries around a mountain lead to the formation of a pyramidal peak.
U-Shaped Valleys
Glaciers erode V-shaped valleys, making them less steep and forming U-shaped valleys
Truncated Spurs
As glaciers flow, they erode the valleys and bulldoze the interlocking spurs, truncating them.
Misfit Streams
A narrow river in a wide valley
Ribbon Lakes
Ice erodes the valley floor unevenly
This is because of different rock types
As the glacier melts, meltwater fills the valley, forming ribbon lakes
Hanging Valley
A hanging valley is a smaller side valley left 'hanging' above the main U-shaped valley formed by a tributary glacier.
Erosion
Freeze-thaw weathering
Abrasion
Plucking
Erratics
Large rocks or boulders
Found on their own
Unusual shapes and sizes
Not native to the area they've been dumped
Drumlins
Elongated hills of glacial deposits
1km long and almost 500m wide
group: Drumlin swarm or basket of eggs
Part of the sediment acccumulated by the glacier until it was overloaded
they then got deposited
Moraine
Created when a glacier deposits the till it's been carrying
Made of unsorted angular rocks
Types:
Lateral
Medial
Terminal
Ground
Link between CO2 Levels and Atmospheric Temperature
Evidenced by ice core
Increased burning of fossil fuels and methane released from permafrost has contributed to higher CO2 levels.
Increase in CO Particles per Million
Gradual increase from 1800
106 particles per million from 1800 to 2008
Biggest increase: 1980 to 2008 (49 ppm)
Which end of a glacier points in the direction of glacial advance?
Elongated end
Alps: Location
Span 1200km across Europe
They span France, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Liechtenstein, Austria, Germany, and Slovenia.
The highest point is Mont Blanc which is situated on the France/ Italy border and is 4808 metres above sea level.
Rivers like the Rhine, the Rhône, the Inn, and the Po originate here.
They flow into the North Sea, the Mediterranean Sea, the Adriatic Sea and the Black Sea.
Alpine Lifestyle
Traditionally: farming and agriculture.
Because of the fertile land in the lower regions caused by factors associated with glaciation.
Good supply of fresh water as well as minerals eroded from the mountain by the glaciers themselves.
Positive Social Impact: Alpine Toursim
Young people stay in villages because of increased oppurtunities
Negative Social Impact
Traditional culture is eventually lost
Residents may become hostile towards tourists
Positive Economic Impact
Tourists put money into the economy by spending
Extra money can be reinvested into the infrastructure
Jobs are created in the summer months as well
Jobs are created in the lower slopes
Jobs other than the service sector are created
Positive Environmental Impact
Money generated can be reinvested to help improve biodiversity
Negative Environmental Impact
Large amounts of energy used
Noise from machinery scares away wildlife
Increase in vehicles= Increase in CO2
Skiing over thin ice damages vegetation and land
Deforestation
Vegetation is destroyed
Extreme Tourists
Young (late 20s to early 30s): have the time, energy and motivation
Often Unmarried: no commitments or attachments = more freedom
Both have good jobs: high income helps fund expensive trips
DINKS: noone to look after, more time, more freedom
Why is Antarctica extreme?
Located on the South Pole
Continent about 5M square miles wide
Emptiness: uninhabited until 1897, now about 200-1000 people
Temperatures -30 to 0 degrees Celsius
Wilderness: Few people and buildings, limited wildlife
Reasons for visiting Antarctica
Comfort: easier than in the past
Ease of access: more tour each year
Wilderness: Antarctica is still unspoilt
Ecotourism: people want to visit places with as little environmental impact as possible
Financial: young people with big incomes + recently retired people
Things to do in Antarctica
Fly over the ice
Climb rock and ice faces
Visit research stations
Hike
Go underwater in underwater vehicles