A & P Test 2
1/224
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
225 Terms
pharyngeal cavity (3)
nasopharynx
oropharynx
laryngopharynx
nasopharynx description
extends from soft palate to base of the skull
largest part of the pharyngeal cavity
oropharynx
oropharynx description
extends from hyoid area to the soft palate
laryngopharynx description
extends from laryngeal opening to the level of the hyoid bone
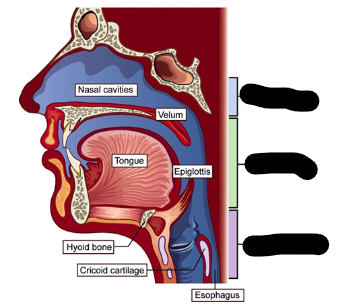
blue
nasopharynx
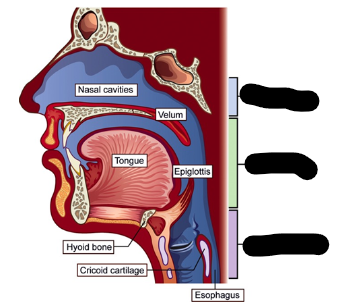
green
oropharynx
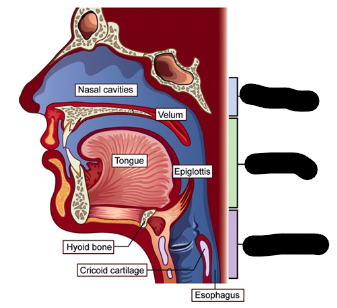
purple
laryngopharynx
oral cavity (5)
anterior and posterior faucial pillars
palatine tonsils
velum/soft palate
hard palate
tongue
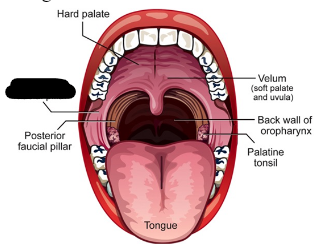
anterior faucial pillars
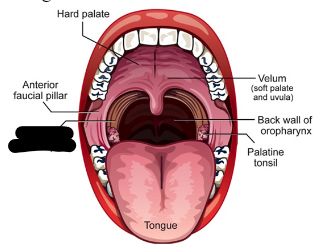
posterior faucial pillars
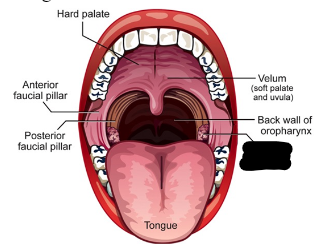
palatine tonsils
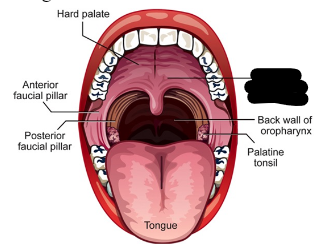
velum/soft palate
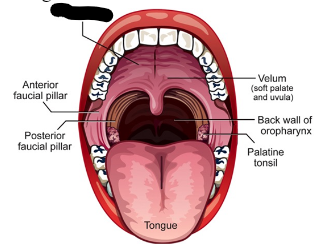
hard palate
how are cavities in nasal cavity separated
nasal septum
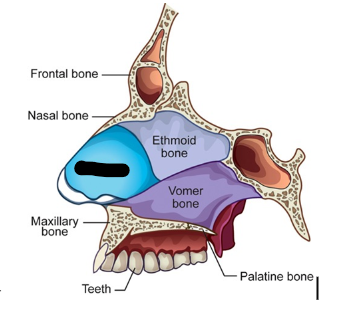
nasal septum parts (3)
cartilage
ethmoid
vomer bones
how many cavities in the nasal cavity
two
roof of nasal cavity
cribiform plate of ethmoid (base of skull)
floor of nasal cavity
bones of hard palate (maxillary and palatine bones)
function of nasal conchae/turbinates
heat
humidify
filter
cartilage
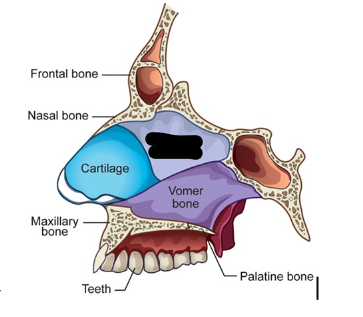
ethmoid bone
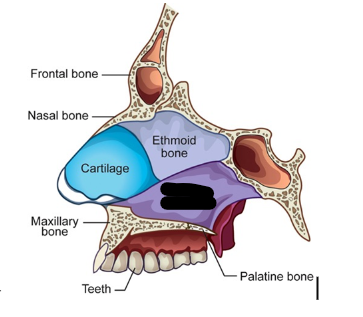
vomer bone
nasal conchae/turbinates
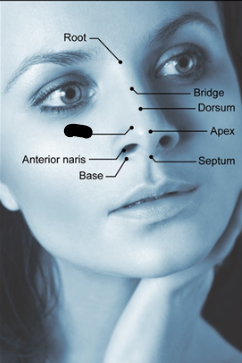
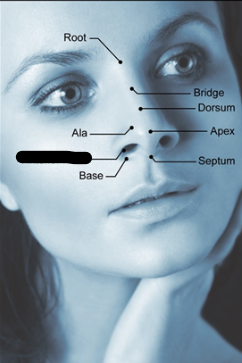
outer nose parts (3)
septum
naris/nostril
ala
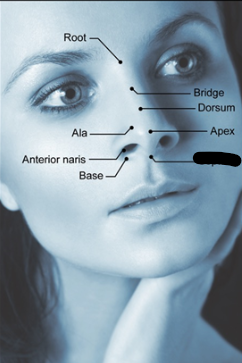
septum
ala
naris/nostril
sphenoid bone forms
roof of pharyngeal and nasal cavities
parts of sphenoid bone
lateral pterygoid plates
medial pterygoid plate
hamulus of pterygoid
hamulus of pterygoid description
upper attachment for pterygomandibular ligament
hamulus of pterygoid function
pulley for a tendon that stretches soft palate
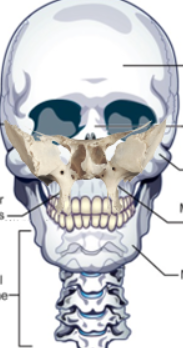
sphenoid bone
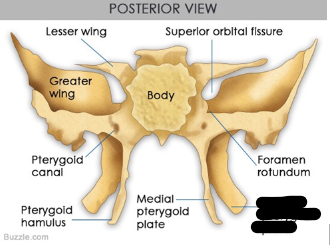
lateral pterygoid plates
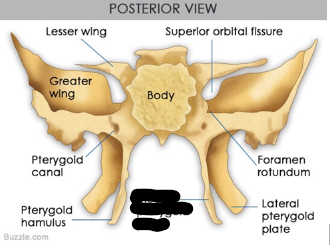
medial pterygoid plates
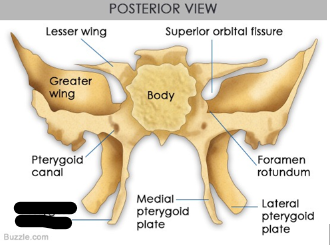
hamulus of pterygoid
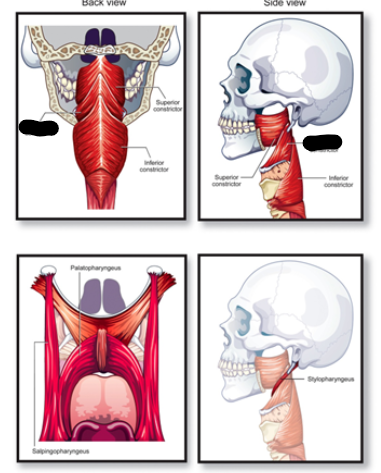
superior constrictor muscle origin
medial pterygoid plate of sphenoid
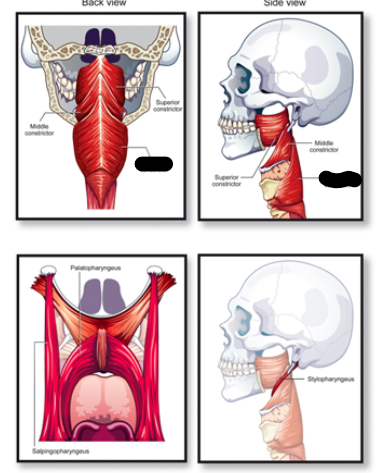
middle constrictor muscle origin
horns of hyoid bone
superior constrictor description
wraps around upper portion of pharynx
middle constrictor muscle description
wraps around middle portions of pharynx
inferior constrictor muscle origin
sides of thyroid cartilage
inferior constrictor muscle description
wraps around lower-mid portions of pharynx
insertion of all constrictor muscles of pharynx
raphe of posterior pharyngeal wall
contraction of all pharynx constrictor muscles
narrow/constrict the pharynx
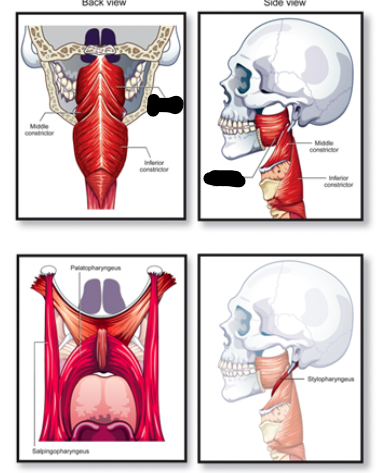
superior constrictor muscle
middle constrictor muscle
inferior constrictor muscle
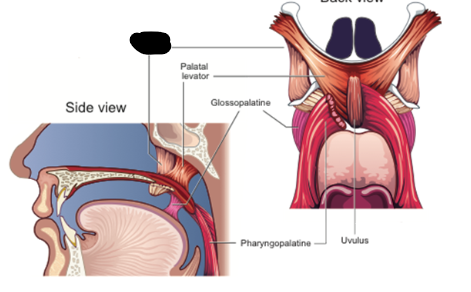
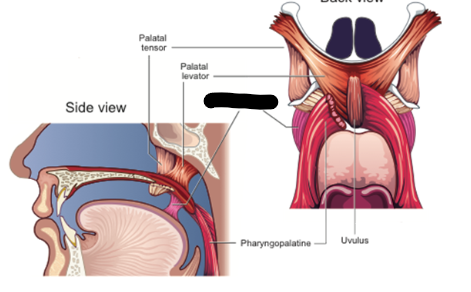
palatal levator description
between medial pterygoid place and palatine aponeurosis
palatal levator contraction
elevates velum and pulls it posteriorly
what muscle is a major part of velopharyngeal closure
palatal levator
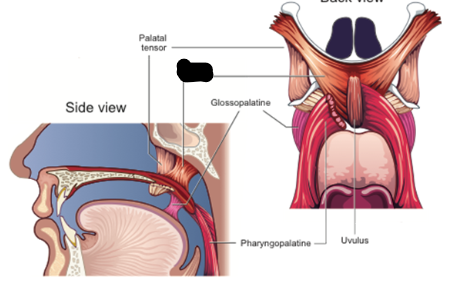
palatal tensor description
starts at medial pterygoid plate
hooks around hamulus and flattens out to form palatine aponeurosis
palatal tensor contraction (1)
tenses velum and opens eustachian tube
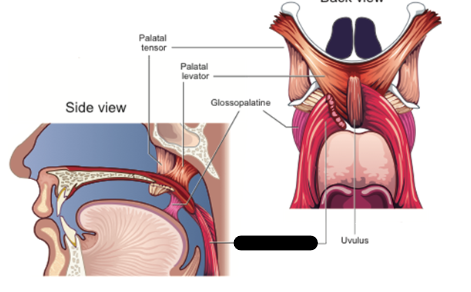
glossopalatine description
between palatine aponeurosis and tongue
another name for glossopalatine
anterior faucial pillar
palatal tensor contraction
lowers the velum
pharyngopalatine description
palatine aponeurosis and pharyngeal wall
another name for pharyngopalatine
posterior faucial pillar
pharyngopalatine contraction
lowers the velum (opens velopharyngeal port)
palatal levator
palatal tensor
glossopalatine
pharyngopalatine
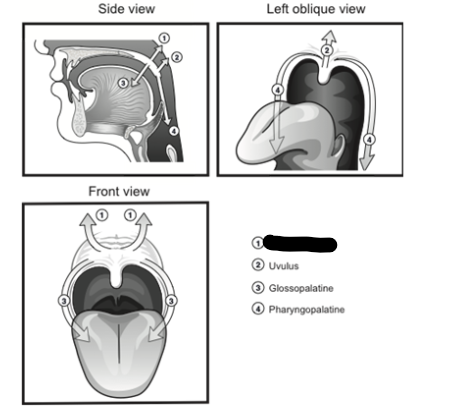
palatal levator
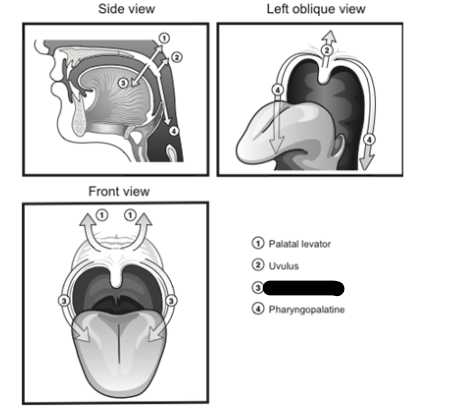
glossopalatine
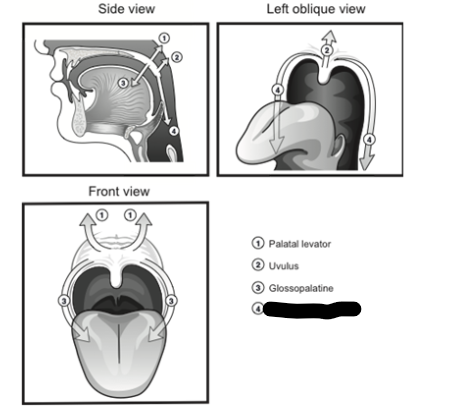
pharyngopalatine
velopharyngeal closure involves contribution from what two things
velum and pharyngeal walls
True/False: pattern of closure is the same for everyone
false
sphincteric closure
idea that everything constricts inward
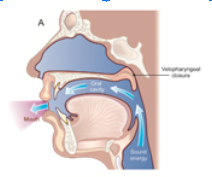
velopharyngeal port is _____
closed
for most phonemes air goes through
oral cavity ONLY
for most phonemes velopharyngeal port is
closed
for nasal sounds velopharyngeal port is _____ and oral cavity is _____
open
obstructed
for nasal sounds air is
directed through nasal cavity
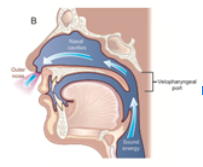
air flow for nasal sound production
velopharyngeal incompetence
air and sound are directed through the oral and nasal cavity
sound energy is _______ anytime it travels through nasal cavity
damped/muffled
velopharyngeal incompetence makes it hard to
build intraoral pressure for production of pressure sounds
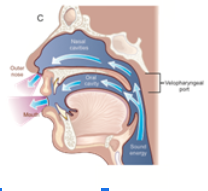
velopharyngeal incompetence
nasopharyngeal tonsil/adenoid _______ with age
diminishes
in childhood what do the nasopharyngeal tonsils do
help with velopharyngeal closure
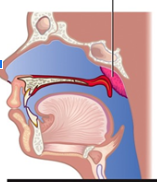
nasopharyngeal tonsil
maxilla forms
upper jaw and most of hard palate
hard palate is comprised of (2)
two palatine processes of maxilla (left and right)
two horizontal processes of palatine bone
alveolar process of maxilla contains
tooth sockets for upper teeth
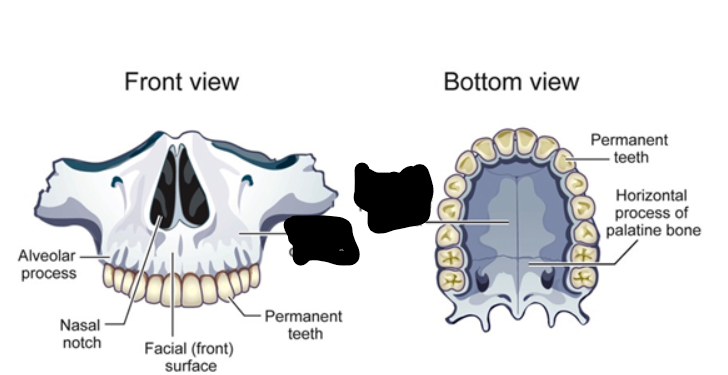
maxilla
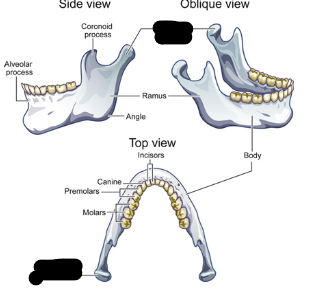
mandible parts
ramus
body
alveolar
ramus description
vertical portion
condylar process attachment
attaches jaw to skull at TMJ
coronoid process attachment
attachment for muscles that raise jaw
mandible body description
horizontal portion
mandible body contains
teeth sockets
mandible body is the
skeletal framework for floor of mouth
alveolar process contains
sockets for lower teeth
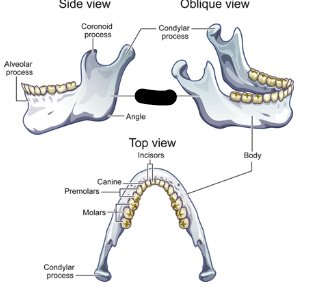
ramus
condylar process
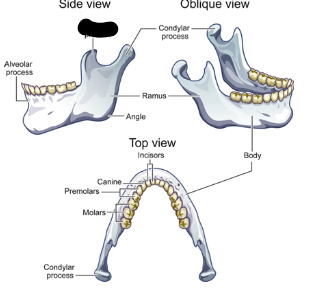
coronoid process
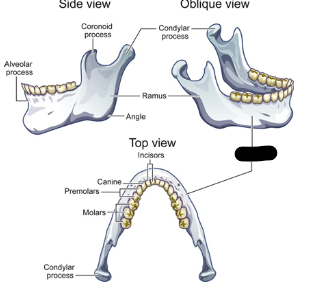
mandible body
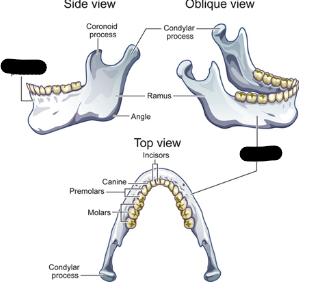
alveolar process
what makes up portions of the brain case
frontal
parietal
temporal
occipital
styloid and mastoid processes are
attachment point for muscles (ie sternocleidomastoid and syloglossus)