Science_T4_2022
1 movement of heat energy
explain processes underlying convection and conduction of heat energy and identify situations where waves transfer energy (eg radiation)
- light and sound are convert-able forms of energy
- light energy can be converted to other forms with photosynthesis and solar panels
- sound energy can be transformed into electric energy via microphones
- thermal energy (aka heat) is transferred from a region of high temperature to a region of cold temperature through either conduction, convection, or radiation.
- conduction is mainly in solids
- convection is mainly through liquids and gases
- radiation can be anywhere, even in a vacuum
conduction
- heat travels when fast moving particles vibrate against some more particles which vibrate against more particles, etc.
- can go through objects or from one to another e.g. cooktop to saucepan
- heat can travel by conduction at different speeds, depending on the type of material and state of matter
- gases are poor, liquids are okay, and solids are the fastest
- metals are generally better conductors than
2 waves and energy
- sound and light travel as waves which transfer or propagate energy
- two types of waves:
- transverse waves e.g. water waves. the medium or material carrying the wave oscillates up and down perpendicular to the direction of the energy transfer. they consist of a series of crests and troughs.
- longitudinal waves aka compression waves e.g. sound waves. the particles move parallel to the propagation of the wave. contains compressions and rarefactions.
- wavelength = distance between two adjacent crests.
- amplitude = maximum distance that each particle moves away from its resting/equilibrium position. determines loudness.
- period = the time it takes from one complete wave to pass a given point (in secs)
- frequency = number of complete waves that pass a point in one sec. measured in waves/second, or Hertz (Hz). determines pitch. the higher, the closer together—and vice versa.
- speed = horizontal speed of a point on a wave as it propagates itself, in meters/second
- also compression waves, e.g. sound waves. outcome three goes into more detail on this.
3 sound energy
- it’s carried as compression waves. sound is essentially just air particles being pushed together then spread apart, bumping into each other and creating a series of compressions and rarefactions.
- sound can’t travel through empty space, because there are no particles to vibrate, unlike light.
- Hertz (Hz) are named after Heinrich Hertz, the German physicist who first detected radio waves in 1887.
- sound waves travel faster in mediums whose particles are closer together - so solid, then water, then air
- air = 343
- sea water = 1533
- rubber = 1600
- copper = 3560
- iron = 5130
- diamond = 12 000
- dolphins send out high frequency sound (ultrasound) to locate food and communicate.
- sound moves faster in warm air due to the particles having more kinetic energy, moving quicker.
- sound with frequencies higher than humans can hear is called ultrasound.
- e.g. sending a sound wave through a mother’s body, some sound is reflected back from the baby, and can be translated into an image.
- sonar is another word for ultrasound along the ocean floor.
- a cathode ray oscilloscope converts sound energy into electrical energy, allowing it to be studied. it uses air pressure changes to detect it, and produces a graph called a waveform.
- the decibel (dB) scale measures the loudness of sound. it increases by powers of 10 per 10dB; if 0dB is the quietest audible sound, 30 dB is 10^3 (1000) times that, and 40 is 10 000 times that.
- any sound above 85 dB can cause hearing loss. you know it’s above this if you have to raise your voice to be heard by someone else.
4 properties of light
describe the occurrence and some applications of absorption, reflection, and refraction in everyday situations
light is an electromagnetic wave. it’s transverse.
electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum and travel through air at 300 000 kilometers per second.
the line used to show the path light takes are called rays.
individual light rays aren’t visible, but can be seen when the light is scattered through a material, e.g. car headlights on a foggy night, or party lights through smoke.
light reflection from curved mirrors - they can be concave (curved inwards) or convex (curved outwards). parallel rays of light are reflected to a focal point; this is outside the mirror for concave, and inside it for convex.
transparent = object on the other side visible translucent = light scattered so much object is not clearly visible opaque = can’t see it at all

light normally goes in straight lines. light can be made to bend by passing it through different transparent media, called refraction—the change in the speed of light when it moves from one substance to another.
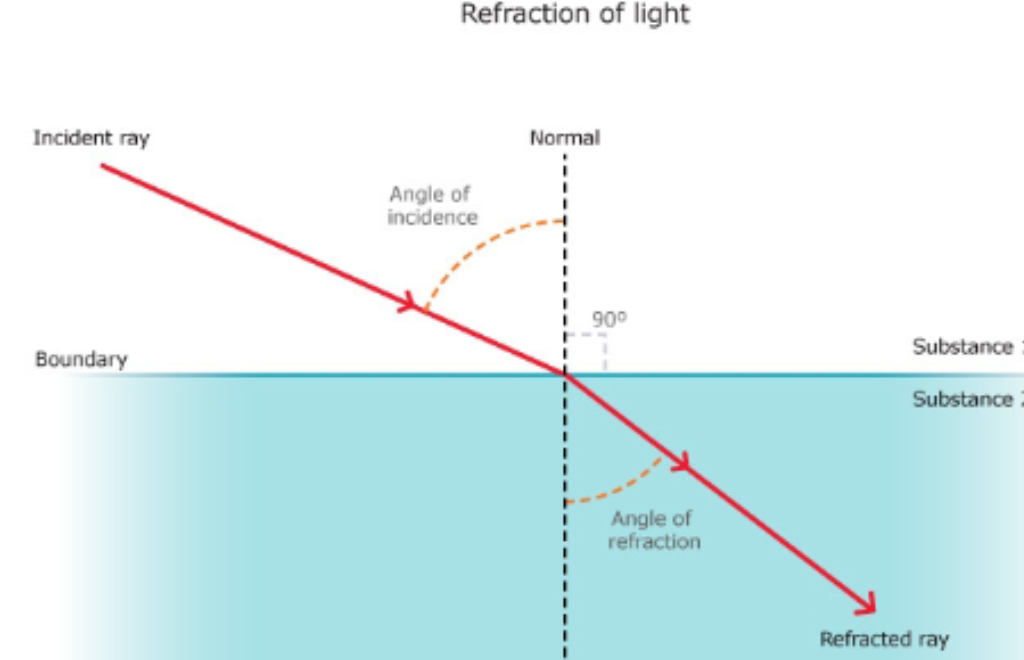
- refraction:
- convex versus concave lenses:
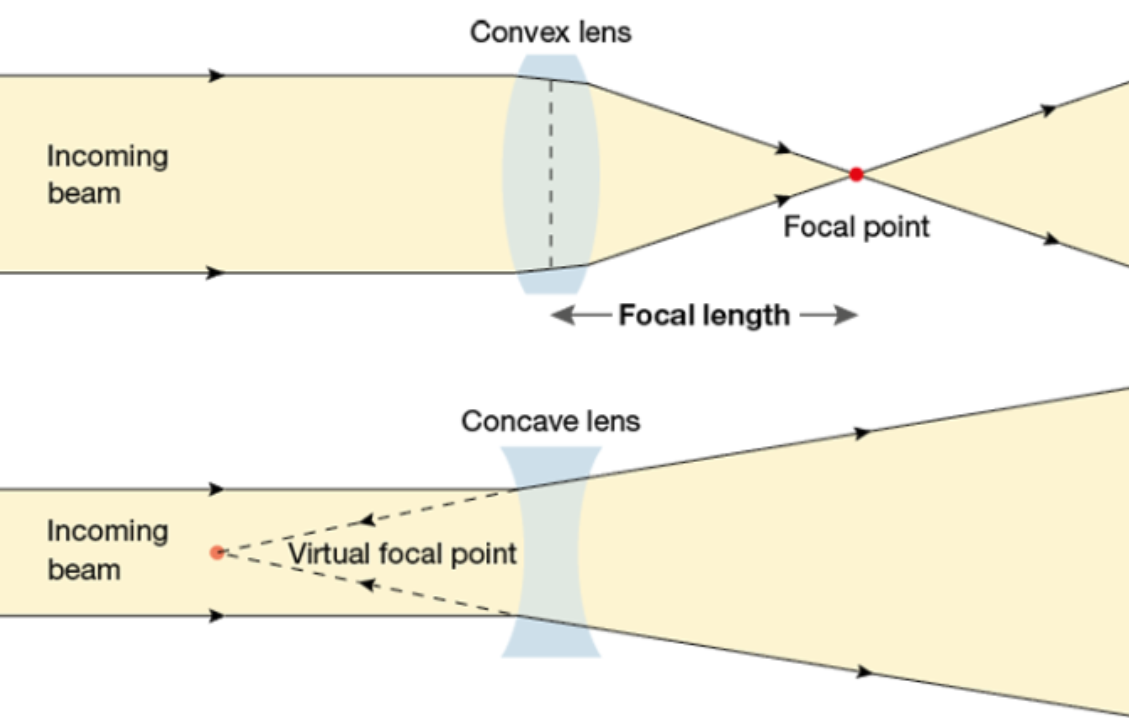
- convex are called converging lenses because the light rays are refracted towards each other. concave are called diverging lenses because the rays are refracted away from each other. observed in the diagram
- dispersion = separation of colours that make up white light; each one is bent out differently when entering or leaving a glass prism.
- each colour is a slightly different speed, so is refracted at a slightly different angle.
- the colour of an object depends on which parts of the spectrum are reflected off it towards your eyes. e.g. a red surface absorbs all colours but red.
- the brain only has three colour sensitive cells—blue, green, and red. colours are just mixes of those. colours that are equal mixes of these colours are called secondary colours, i.e. yellow, magenta, cyan.
5 electromagnetic spectrum
- relate the properties of different types of radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum to their uses in everyday life, including communications technology
- the frequency of electromagnetic waves is the number of pulses of electric/magnetic fields generated per second.
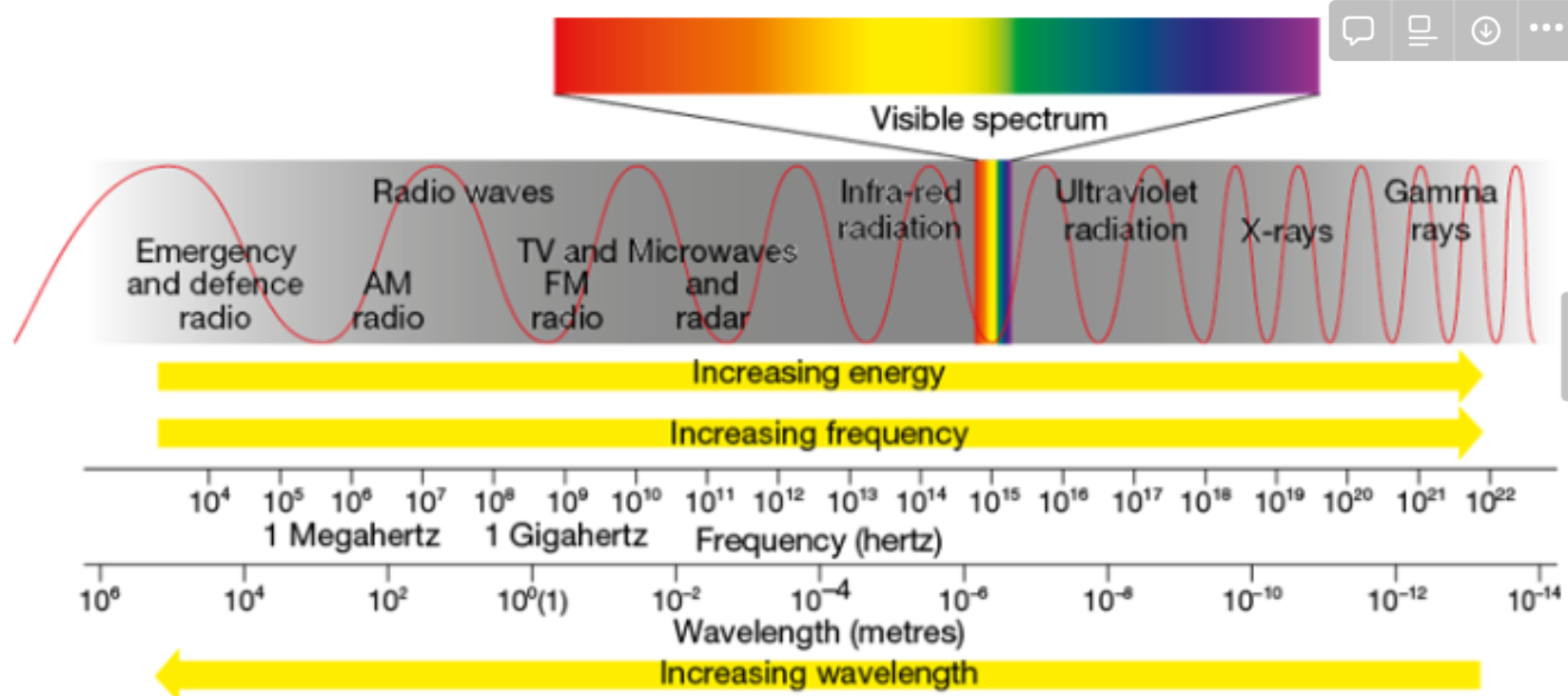
- gamma waves: radioactive
x-rays: medical uses
ultraviolet: sunburns you
visible spectrum: thank god you’re not blind!
infrared: heat maps
microwaves: heat your food. satellites.
radio waves: transfer information. thank god for mobile data. - might need to go through the rest of 4.5 in textbook, but this is all the classwork.
6 theory of continental drift
- describe the theory of continental drift
- identify and explain the evidence for this theory
- outline how the theory of plate tectonics changed ideas about the structure of the earth and continental movement over geological time
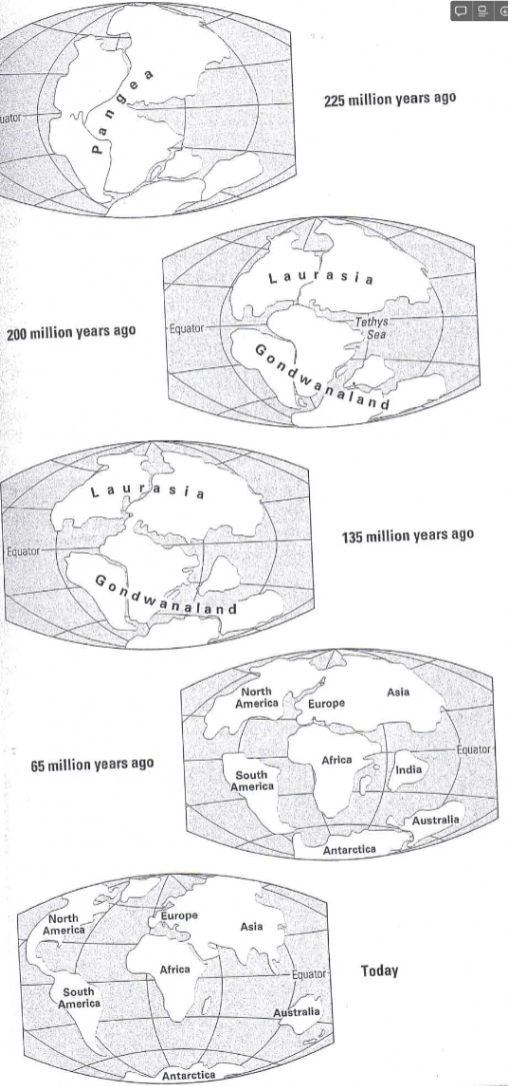
- in 1910, German scientist Alfred Wegener hypothesised all the continents use to be joined together and have since drifted apart. He named the supercontinent Pangea, and it existed about 280 million years ago—it drifting apart is called the continental drift.
- He used things like land features (ie mountains), fossils, and climate change, that all connected from different areas of the world.
- he was initially rejected because there was no explanation to how the continents could move.
- Sea floor spreading occurs when magma oozes up from inside the earth along oceanic ridges, and creates new sea floor, which spreads away from its origin (the ridge) and eventually sinks into deep ocean trenches, where it’s destroyed.
- This explains why there is no more than 300 million years worth of sediment or fossils on the ocean floor.
7 mechanism of plate movement
- relate movements of the earth’s plates to mantle convection currents and gravitational forces
- we’re not entirely sure how they move. we think it’s convection currents in the lithosphere (asthenosphere).
- the convection currents are the most plausible, but may only be part of the reason they move.
- three main types of boundaries: divergent (away from each other), convergent (one goes under one goes over), transform (they slide past in opposite directions)
- subduction in convergent boundaries is caused by 3 methods: ridge-push, gravity-slide, slab-pull
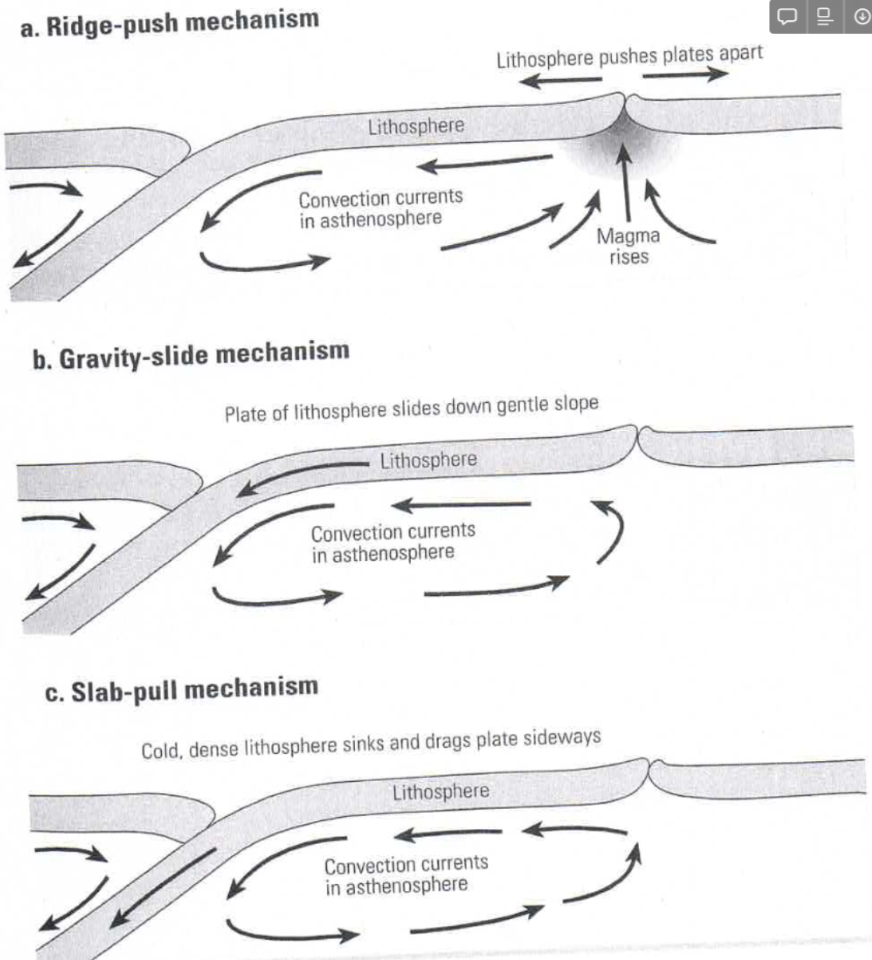
- the whole mechanism of plate movements involves all three of these, together with convection currents. a lot of it still isn’t finalised with a proper model.
8 plate tectonics and landforms
- outline how the theory of plate tectonics explains earthquakes, volcanic activity, and formation of new landforms
- \
9 impacts of natural events
- describe some impacts of natural events, including volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and tsunamis on the earth’s spheres
10 technology, global patterns, and geological activity
- describe how some technological developments have increased scientific understanding of global patterns in geological activity, including in the asia-pacific region
- this was the bit we did on japan + america + chile i think
- \