Science_T4_2022
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
1
New cards
are light and sound convert-able forms of energy?
yes
2
New cards
light energy can be converted via;
photosynthesis, solar panels
3
New cards
sound energy can be converted via;
microphones
4
New cards
thermal energy (aka heat) is transferred via: (3 things)
conduction, convection, radiation
5
New cards
conduction occurs in
solids
6
New cards
convection occurs in
liquids and gases
7
New cards
radiation occurs in
anywhere! even in a vacuum
8
New cards
heat travels faster when:
moving particles vibrate against more, which vibrate against more, etc.
9
New cards
heat conduction travels at different speeds, depending on the type and state of matter. state the materials, worst to best:
gases are poor
liquids are okay
solids are fastest
within solids, metals tend to be better since they're denser
liquids are okay
solids are fastest
within solids, metals tend to be better since they're denser
10
New cards
sound and light travel as ;
waves
11
New cards
what are the two types of waves
transverse waves, i.e. water waves), and longitudinal waves (aka compression waves), i.e. sound waves
12
New cards
transverse waves work via;
the medium carrying the wave oscillates UP and DOWN PERPENDICULAR to the direction of energy transfer. consists of a series of crests and troughs.
13
New cards
longitudinal waves work via;
the particles move PARALLEL to the propagation direction of the waves. consists of a series of COMPRESSIONS and RAREFACTIONS.
14
New cards
a wavelength is
the distance between two adjacent crests
15
New cards
amplitude is
the maximum distance that each particle moves away from its resting/equilibrium position.
16
New cards
amplitude DETERMINES:
loudness
17
New cards
a period is
the time it takes for one COMPLETE wave to pass a given point, in SECONDS
18
New cards
frequency is
the number of COMPLETE WAVES that pass a point in ONE second. it's measure in waves per second, or HERTZ (Hz).
19
New cards
frequency determines
pitch -- the higher the frequency, the closer the waves are together, and the higher the sound is.
20
New cards
speed is
the horizontal speed of a POINT on a wave as it propagates itself, in meters per second
21
New cards
sound energy is carried
as compression waves; just air particles being pushed together and spread apart
22
New cards
sound can't travel through
empty space
23
New cards
hertz are named after...
heinrich hertz, who first detected radio waves in 1887
24
New cards
sound waves travel faster in mediums whose particles are
closer together, and its slower when the particles are further apart
25
New cards
why do sound waves move faster in warm air?
the particles have more kinetic energy, so they move quicker
26
New cards
sounds with frequencies higher than humans can hear is called
ultrasound. an example of this is dolphins
27
New cards
what are two uses of ultrasound
sending a sound wave through a mother's body to get an image of the child, and sonar along the ocean floor
28
New cards
a cathode ray oscilloscope converts sound energy into
electrical energy, allowing it to be studied
29
New cards
a cathode ray oscilloscope detects sound using what:
the air pressure changes. it produces a graph called a waveform.
30
New cards
the dB (decibel) scale increases by powers of 10 per HOW MANY dB?
10dB. if 0dB is the quietest audible sound, 30 dB is 10^3 (1000) times louder than that, 40 will be 10^4 (10 000) times louder, etc.
31
New cards
any sound above WHAT dB can cause hearing loss:
above 85 dB. you know it's above this if you have to raise your voice to be heard by someone else.
32
New cards
filler card
filler card
33
New cards
epicenter
the point at the surface of the earth directly above the focus
34
New cards
fault
a fracture in the rocks that make up the earth's crust
35
New cards
focus of an earthquake
the point within the earth where an earthquake starts
36
New cards
seismic waves
waves that transmit the energy released by an earthquake
37
New cards
plates
massive rocks that make up the outer layer of earth's surface and whos movement along faults triggers earthquakes
38
New cards
types of plate boundaries
divergent, convergent, transform
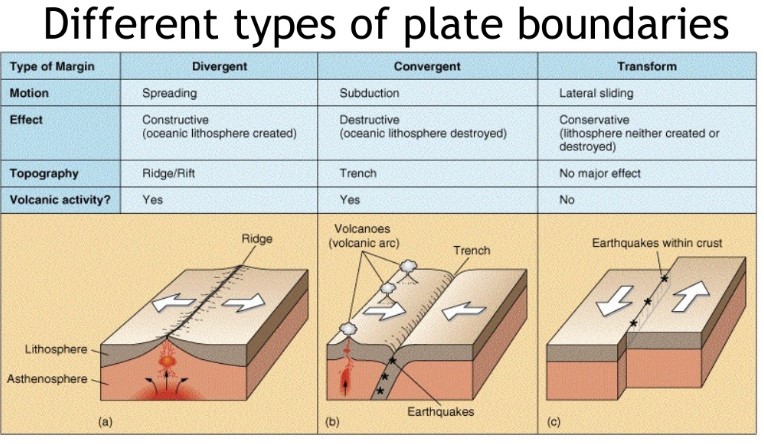
39
New cards
two main categories of seismic waves:
body waves (through the body of the earth) and surface