Health and the Individual
Health, Wellness, and Illness
- Health: a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity
- Wellness: how a person feels about their health
- The seven forms of wellness
- Physical- diet and exercise
- Emotional-ability to understand themselves, how to deal with stress
- Intellectual- able to make informed decisions
- Spiritual- varies from person to person
- Social- the ability to communicate with others
- Environmental- one’s relationship with the environment, being eco friendly
- Occupational- feeling secure, valued, and confident in their workplace
- Illness: the presence of disease; how a person feels about their health
- Disease: a condition with a person’s bodily or mental function which is not normal
- May also describe a group of symptoms
- Remission: no sign of disease
- Disability: deviation from normal function
Health Models
- Medical model
- It emphasizes diagnosis and treatment of disease but may exclude prevention.
- Focusses on the physical process of a disease
- Holistic model
- A concept in medical practice that considers all aspects of a person's needs
- Consists of prevention, treatment, and management of illness or disease
- Traditional health
- Attention aimed at treating symptoms with drugs/surgery.
- The focus is on finding the underlying cause of the symptoms
- Holistic Health
- Personal responsibility patient is given a recommendation and it is up to them that they get better
- Indigenous Wholistic Theory for health
- Considers mental, physical, cultural, and spiritual wellbeing
- East: shows spirit and vision
- South: show the value and importance of relationships
- North: shows healing movement and actions that guide practice
- Wellness model
- Focuses on assuming responsibility for their health and progression over time.
- Not taking self-imposed risks: smoking, drinking, drugs, obesity, and a sedimentary lifestyle
Changing Perceptions of Health and Wellness
- A positive mindset can help a person deal more effectively with stress and fight disease
- Historically, people if they got sick went to the doctor, got medication, and got better without participating in their treatment plan
- Since the 1990s people have had access to information to take control of the treatments
Psychology of Health Behavior
- Transtheoretical
- People who are in the process of change could be
- Pre-contemplation (don’t want to change)
- Contemplation
- Preparation
- Action
- Maintenance
- Relapse
- Termination
- Social-ecological model
- Many influences in one's life shape health (home, family, school, sports, work)
- Protection Motivation Theory
- Fear that they will get sick, so they take action to prevent it
- Health belief model
- If they believe that it will help, they are more prone to do it
- Assuming they do not like the negative outcome
Health Illness Continuum
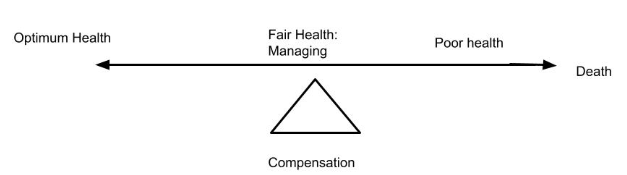
- Continuum: is a method using a straight line with an opposing state at each end
- Ones who society may say have poor health could be closer to optimum health depending on how they view their illness and if they have accepted it yet
- Sick Role Behavior: when people get sick their personality changes
- Remember when dealing with patients this is not who they are
- Be patient with them; they are also tired and frustrated
- Self-Imposed Risk
- Many people participate in risky behavior including:
- Unhealthy diet
- Sunbathing
- Inactivity
- Drug abuse
- Alcohol abuse
- Speeding or driving under the influence of drugs or alcohol
- Driving without a seatbelt
The Health of Canadians Today
- Canadians are living longer now than ever
- The overage life expectancy is 80.7 years
- Currently, the leading cause of death is cancer, and the second is heart disease
- 1 in 2 Canadians are expected to be diagnosed with cancer
