Psychology 100 Exam 1 Study Guide
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:40 PM on 9/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
1
New cards
Perspective which focuses on how bodily events affect behavior, feelings, and thoughts.
Biological Perspective
2
New cards
Perspective which focuses on how our mental processes work, such as how we reason, remember, understand language, and problem solve.
Cognitive Perspective
3
New cards
Perspective which focuses on how the environment and our experiences affect a person or animal's actions.
Learning Perspective
4
New cards
Perspective which focuses on the impact of other people and cultural roles on behavior, attitude, and beliefs.
Sociocultural Perspective
5
New cards
Perspective which focuses on how the unconscious can influence us.
Psychodynamic Perspective
6
New cards
Field of professional activity in which psychologists typically hold a doctorate and work at universities and colleges and instruct courses and conduct studies on behavioral and mental processes. (Professors)
Teaching and Conducting Research
7
New cards
Field of professional activity in which psychologists typically hold a masters or doctorate and work in the private sector to improve the physical and mental health of individuals. (Private practice, hospitals, schools, etc.)
Psychological Practice
8
New cards
Field of professional activity in which psychologists hold various degrees and work in Industry, Law, and other community settings. (Sports, advertising, animal behavior, etc.)
Private Sector Research or Consultation
9
New cards
The study of natural relationships between variables (associations).
Correlational Research
10
New cards
Examining if a change in one variable causes, or leads to, a change in a second variable, all while controlling for other variables.
Experimental Research
11
New cards
Maximum and minimum value correlation can have (max\#, min\#)
1, -1
12
New cards
The relationship between two variables in which one variable increases as the other variable decreases.
Negative coorelation
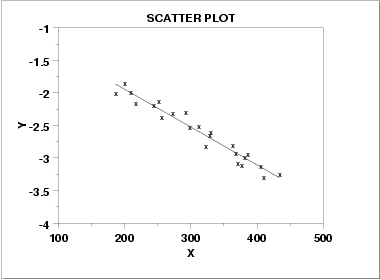
13
New cards
If both the independent variable and the dependent variable change in the same directions
Positive correlation
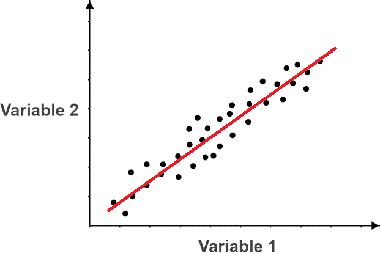
14
New cards
Determined by the difference in data points
Strength of Correlation
15
New cards
Determined by the direction of the line on the graph, or by the increase or decrease of both variables
Type of Correlation
16
New cards
A third variable that is related to both variables, and as a result, makes it appear that both variables are related when in truth they are not (reason why casual statements can't be fully based off correlation).
Covariate
17
New cards
Using a random method to select participants for your study, typically from the entire population (Sample system used to generalize a population)
Random Sampling
18
New cards
The process of placing participants into groups using a random method (Sample system used to equalize two groups)
Random Assignment
19
New cards
What is being manipulated by the researcher; has different levels
Independent Variable
20
New cards
What is being measured by the researcher; the behavior or response
Dependent Variable
21
New cards
Any variable that inadvertently influences the data; time, gender, age, etc.
Extraneous Variable
22
New cards
Group(s) of participants who receive a particular treatment
Experimental group
23
New cards
Group(s) of participants who do not receive the treatment, or who receive the current standard of care
Control group
24
New cards
The study of behavior and mental processes
Psychology
25
New cards
An agreed upon statement of what we observe (People can conserve water)
Fact
26
New cards
An idea that explains or predicts a fact (Limiting showers to 5 minutes helps to conserve water)
Theory
27
New cards
A testable statement describing a relationship that may occur between events (people who limit showers to 5 minutes have a lower water bill than those who shower for more than 5 minutes)
Hypothesis
28
New cards
Freud's term for the psychic energy that drives all behavior and motivates us to strive for self-preservation and survival
The Libido
29
New cards
Seeks immediate satisfaction, particularly sexual and aggressive instincts; contains the libido ("it")
The Id
30
New cards
Mediator; represents reason and guides the Id ("I")
The Ego
31
New cards
The conscience; represents morality ("Above I")
The Superego
32
New cards
The extent to which someone is curious and imaginative, or conformal and predictable (versus resistance to new experiences)
Openness to Experience
33
New cards
The extent to which someone is responsible, steadfast, and self-disciplined, or undependable, fickle, and impulsive (versus impulsiveness)
Conscientiousness
34
New cards
The extent to which people are outgoing, or shy (versus introversion)
Extroversion
35
New cards
The extent to which someone is good natured, cooperative, and secure, or irritable, abrasive and jealous (versus antagonism)
Agreeableness
36
New cards
The extent to which someone experiences anxiety, negative emotions, and resentment (versus emotionally stable)
Neuroticism
37
New cards
Gender identity is due to natural selection, the brain, and other physiological differences
Biological perspective
38
New cards
Gender develops based on the identification with a same sex parent or care taker
Psychoanalytic Perspective
39
New cards
Gender roles are learned through observations of others
Social Learning Perspective
40
New cards
Gender is based on mental "rules" for how men and women are supposed to act
Cognitive Perspective
41
New cards
Location where the predominant belief is that parents play a large role in the development of a child's personality (this is not supported by any of the research findings)
The Western World
42
New cards
Has little influence on personality; siblings often have very different personalities
"Shared" Environments
43
New cards
Will often change due to many factors, such as mood
Child Rearing
44
New cards
The influence of parents on personality is best captured when we look at both how the parents raised the child, and how the child responds to the parents
A Dynamic Relationship
45
New cards
A distinctive and relatively stable pattern of behavior, thoughts, motives, and emotions that characterizes an individual
Personality
46
New cards
A characteristic of an individual describing a habitual way of behaving, thinking, or feeling.
Personality Trait
47
New cards
Theories that explain behavior and personality in terms of the movement unconscious, phycological energy within a person
Psychodynamic Theories
48
New cards
Measures and defines personality in terms of specific traits (more modern approach)
Core Trait Theories
49
New cards
Blocking from memory
Repression
50
New cards
Repressed and then attributed to someone else
Projection
51
New cards
Directing uncomfortable or conflicted emotions toward someone or something else
Displacement
52
New cards
Reverting to a previous stage of development
Regression
53
New cards
A refusal to admit that something unpleasant is happening
Denial
54
New cards
Methods used by the ego to prevent anxiety or threatening thoughts from entering the conscious
Defense Mechanisms
55
New cards
Values, beliefs, and attitudes shared by most of a particular community; highly elated to personality
Culture
56
New cards
The self is regarded as autonomous, and individual needs and goals are generally placed ahead of the group's
Individualistic Cultures
57
New cards
The self is regarded as part of the group, and group needs and goals are generally placed ahead of an individual's needs and goals
Collectivist Cultures
58
New cards
Most commonly can cause deafness
Rubella (German measles)
59
New cards
Can cause fetal deformities and cognitive abnormalities
Radiation (Including x-rays)
60
New cards
Increases chance of miscarriages, premature birth, and low birthweight
Cigarette smoking
61
New cards
Associated with low birthweight, smaller brain size, facial deformities, and mental impairments
Alcohol consumption
62
New cards
Can cause mental impairments or blindness; HIV may be passed from mother to baby
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
63
New cards
Can cause various associated outcomes during child development
Numerous Legal and illegal drugs
64
New cards
A universal capacity of all primates and is essential to good health and survival
Attachment
65
New cards
The innate pleasure derived from close physical contact
Contact comfort
66
New cards
Once attached to a caretaker, most infants display distress when their primary caregivers leave them with strangers (typically begins around 6 to 8 months)
Separation anxiety
67
New cards
Experiment devised by researcher Mary Ainsworth to study attachment
Strange Situation
68
New cards
Baby cried or protested when mother left and were happy to play with mother again when she returned
Secure Attachment
69
New cards
Baby treated the stranger the same as the mother and did not seem to care if the mother was there or not
Insecure Avoidant Attachment
70
New cards
Baby protested loudly when the mother left, but when she returns baby resisted contact with her
Insecure Anxious-Ambivalent
71
New cards
Abandonment or deprivation in the first 1 to 2 years of life
Promotes insecure attachment
72
New cards
Abusive or neglectful parenting, or erratic parenting due to chronic irresponsibility or clinical depression
Promotes insecure attachment
73
New cards
The child's own genetically influenced temperament, especially when combined with nonresponsive parenting
Promotes insecure attachment
74
New cards
Stressful circumstances within the family
Promotes insecure attachment
75
New cards
The understanding that something exists even when you can't see it
Object Permanence
76
New cards
The understanding that the properties of objects can remain the same even when their form or appearance changes
Conservation
77
New cards
Focuses on the progression of changing patterns of thought and action interactions (comparing objects and ideas) (Piaget's stages)
Cognitive Development
78
New cards
Each stage of development is defined by the focus of the libido at that time (Freud's stages)
Psychosexual Development
79
New cards
Focuses on a series of conflicts that people face throughout the lifespan (Erickson's stages)
Psychosocial Development
80
New cards
Infants use their senses and motor actions to explore the world; begin to use symbolic thought through images or words (Piaget: Cognitive Development)
Sensorimotor Stage
81
New cards
Preschoolers use symbolic thought to develop language, engage in pretend play, and solve problems; thinking is egocentric and not yet logical (Piaget: Cognitive Development)
Preoperational Stage
82
New cards
School-aged children acquire logical operations allowing them to mentally classify concrete objects ("real world"); problem solve using trial-and-error approach (Piaget: Cognitive Development)
Concrete Operations Stage
83
New cards
Adolescents can think about abstract concepts and hypothetical possibilities; can track long-term consequences of behavior (Piaget: Cognitive Development)
Formal Operations Stage
84
New cards
Libido is focused on mouth as source of pleasure; breast feeding (Freud: Psychosexual Development)
Oral Stage (Stage: 1)
85
New cards
Libido is focused on the anus; toilet training (Freud: Psychosexual Development)
Anal Stage (Stage: 2)
86
New cards
Libido is focused on genitals; notices genital differences between mom and dad (Freud: Psychosexual Development)
Phallic Stage (Stage: 3)
87
New cards
Libido is inactive; child focuses on school work and same sex friendships
Latency Period (Stage: 4)
88
New cards
Libido is focused on sexual relationships and reproduction; puberty, parenting (Freud: Psychosexual Development)
Genital Stage (Stage: 5)
89
New cards
Infants need to learn how to trust their caregiver(s) to meet their needs; if not, child will have difficulty with trust in relationships in future relationships (Erikson: Psychosocial Development)
Trust vs. Mistrust
90
New cards
Children must learn how to assert their wills and do things for themselves; if not, children doubt their abilities (Erikson: Psychosocial Development)
Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
91
New cards
Preschoolers must develop and carry out bold plans, but also learn to respect the rights of others (Erikson: Psychosocial Development)
Initiative vs. Guilt
92
New cards
Children must develop social and academic skills and keep up with their peers; if not, children will feel inferior (Erikson: Psychosocial Development)
Competence vs. Inferiority
93
New cards
Adolescents must establish social and vocational goals; if not, adolescents will be confused about their roles as adults (Erikson: Psychosocial Development)
Identity vs. Role confusion
94
New cards
Young adults must seek to form a shared identity with another person; if not, they will fear intimacy and experience loneliness (Erikson: Psychosocial Development)
Intimacy vs. Isolation
95
New cards
Middle-aged adults must feel they are producing something; if not, they may become stagnant and self-centered (Erikson: Psychosocial Development)
Generativity vs. Stagnation
96
New cards
Older adults must feel their lives as meaningful; if not, they will fear death with worries and regret (Erikson: Psychosocial Development)
Integrity vs. Despair
97
New cards
All humans are believed to be born with the \_____________________________
Innate capacity for language