BOOTH - SPACE
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
space
a cavity/gap between solid elements
invisible void filled w air that exist between objects
space in a landscape is aka
“outdoor room”
why is space important in landscape architecture
what la’s mold/shape when they organize objects such as pavement, plants, walls, etc
the creation of space is the “architecture” in la
interior space
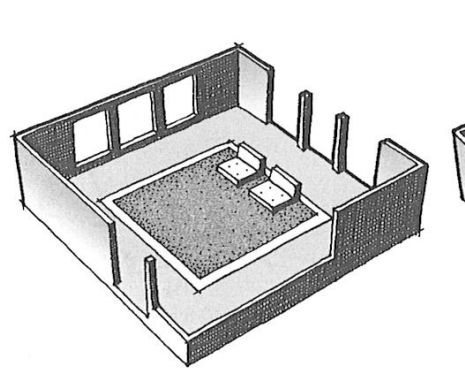
exterior space
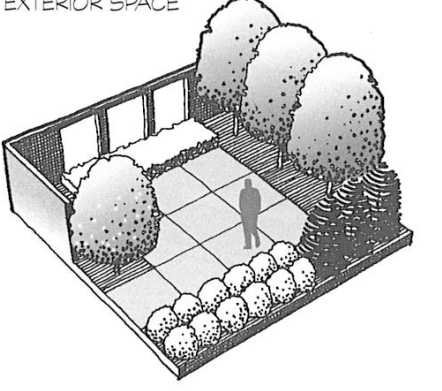
what are the 3 planes of spatial enclosure that forge the mutual relationship between solid and void
base plane
vertical plane
overhead plane
base plane
the floor of the exterior space
defined by: bare earth, grasses, lawn, pavement, water
ground may be level, sloped, rolling, etc in contour
the base plane represents
spiritual earth and symbolize where all plants grow
everything in the landscape must connect to the..
base plane
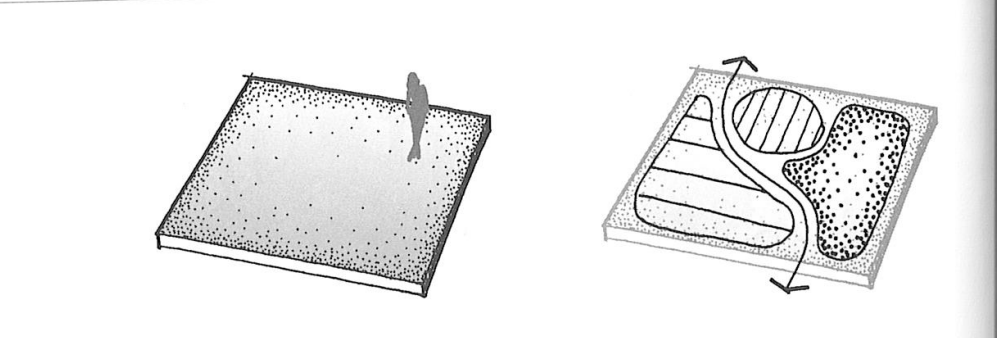
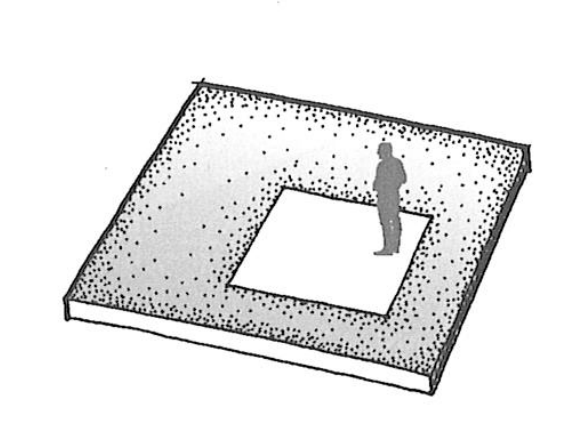
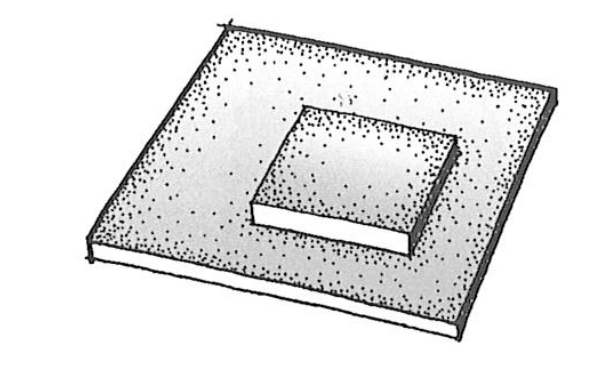
types of space in the base plane
material change
excavation into
elevation above
material change
excavation into
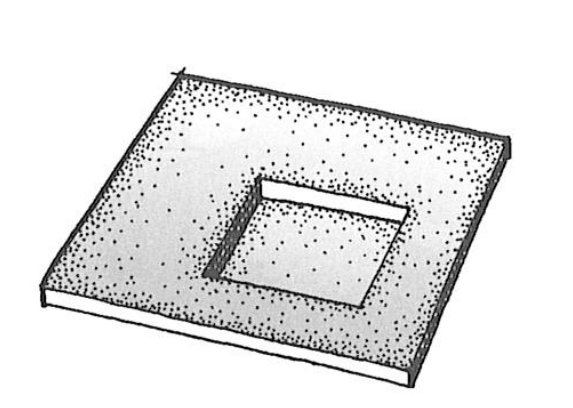
elevation above
vertical planes
walls of an outdoor space
ex. walls, fences, plant material, anything that extends up from ground plane

vertical planes purpose
control views
sense of privacy
prove backgrounds
structural support
spatial enclosure by the vertical planes is affected by
position, height, solidity
overhead plane
the ceiling of the outdoor plane
awnings, umbrellas, pergolas, tree canopies
low overhead plane
provides a personal, intimate atmosphere
high ceiling
establishes a more communal setting
spatial types
physical envelope, landscape setting, descriptive experience
physical envelope
built space includes
public spaces, courtyards, walled gardens
spatial sequence
every space is preceded and followed by another
how form and space interact
extruded forms
multiple forms
independent forms
extruded forms
extending ground floor edges upward to enclose space
design process steps
acceptance, analysis, definition, ideation, ideation selection, implementation, evalutation
what comes from this process
project acceptance, master plan, construction documents
analysis stage
gain as much knowledge as possible about a site and its context
gathering physical, environmental, social, cultural, historical ingo and then evaluating it
physical factors analysis
regional character, site context, and the macro patterns/features
site context
natural and human factors in the immediate surroundings of a site tht can be drawn upon to suggest design form
natural features
topography, adjoining streets and roads, footprint and orientation of nearby buildings
macro patterns
the configurations established by edges, distribution, and general shape of topography, geological formations, vegetation, water bodies, infrastructure
envisioning
to foresee what the design solution should be
aka definition, problem definition, and ideation
parti
theme or big idea
overriding concept that governs all aspects of design
controls the overall organization, character, appearance and meaning of a project
parti of a la site design can be based on
site context
site
client
users
program
site designs based on metaphor
moonscape, winding river, groove
design program
to identify + list all the spaces and elements required in a design
determine function of space, size, form and proportion
“form follows function”
factors that influence design form in the landscape
uses, parti, spatial quality, environmental factors, site, creativity, material budget