Biotechnology & Microscopy
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What are the two categories of microscopy?
Optical/ light microscopy and electron microscopy
What are the two types of optical/light microscopy?
Compound microscope: Visible light is focused on a thin slice of the sample→ producing a 2D image
Fluorescence microscopy: Use of fluorescent markers to tag certain structures and assist in visually locating protein expression within a cell
What are the uses and disadvantages of a compound microscope?
Observe a wide variety of cells, tissues, and organisms
Staining can be used for enhanced viewing
Disadvantages
Limited view of living organisms ( only a single cell layer)
Thicker samples require staining, which kills the sample
What are the uses and disadvantages of a fluorescence microscope?
View thin slices of living samples
Can look at protein expression and specific parts of cell (chromosomes during mitosis)
What are the types of electron microscopy?
Scanning Electron Microscopy: Produces a 3D image of a sample’s surface by dehydrating the cell first before viewing.
Transmission Electron Microscopy: Electron beam passes through a very thin section of samples → produces a high magnification. 2D image of the sample
What are the uses and disadvantages of a SEM microscope?
High resolution with surface level detail (texture, shape, etc)
Ideal for viewing external surfaces of cells, tissues, and molecules
Disadvantages
High cost and kill the cell by dehydration
What are the uses and disadvantages of a Transmission Electron microscope?
Allows for high-resolution viewing of the internal surface
Ideal for viewing internal structures of cells, tissue, and organelles
Highest magnification of all microscopes
Disadvantage
Expensive and extensive process to prepare the cell
What is homogenization?
It is a process in cell fractionation where cells are broken apart → cellular homogenate (cell contents without membrane)
List the organelles from first to last that would be separated during a cell fractionation
Nuclei ( Dense + large)
Mitochondria and chloroplast
Ribosomes + viruses ( less dense + smallest)
What are the two types of gene transfers?
Vertical Gene Transfer: Transfer of genes from one generation to the next (Sexual/ asexual reproduction, mitosis)
Horizontal Gene Transfer: Transfer of genes between different organisms
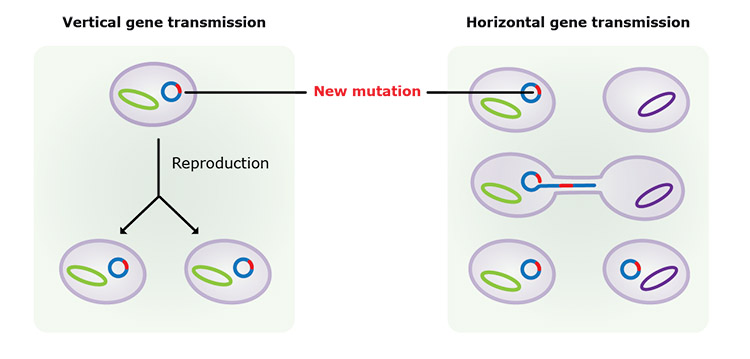
What are the three types of horizontal gene transfer?
Conjugation: Transfer of DNA from a donor cell to a recipient cell ( Utilize a pilus to transfer)
Transduction: DNA is introduced into the genome by a virus
Transformation: Absorb DNA from the surroundings and incorporate it into the genome (Heat shock/electrical)
What is recombinant DNA?
DNA containing different segments from multiple sources. These segments can be transferred via bacterial conjugation, viral transduction, transformation, and artificial recombinant technology
What cuts a specific sequence site in the DNA → palindromic sequence
Restriction enzymes
What are palindromic sequences?
Nucleic acid sequence that reads the same direction in both directions
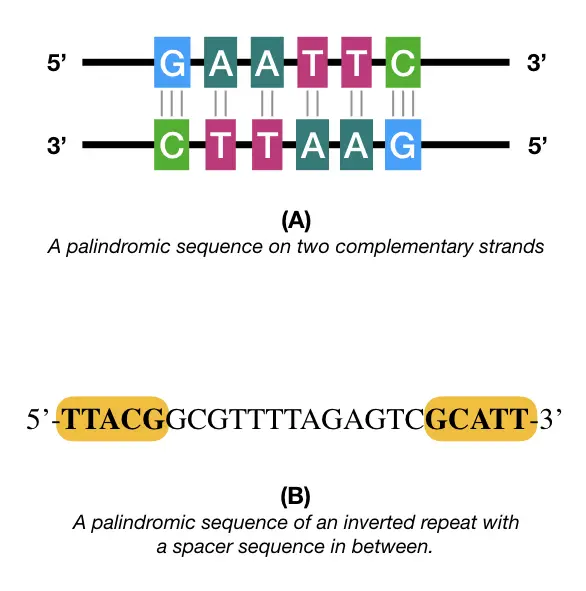
For recombination of DNA, which cut ends are more common?
Sticky ends (overhangs of nucleotides)!
There is another one call blunt ends ( no overhanging)
What is restriction mapping?
It’s a map that creates known restriction enzyme cut-sites within a sequence of DNA
What is used to link an individual's DNA to a crime scene? Why?
Restriction Fragment Polymorphisms because they create unique fragments of different sizes between individuals
What are single-nucleotide polymorphisms?
It’s a difference of a single nucleotide in the human genome. May be found near disease-associated alleles → used as genetic markers for certain diseases
What does gel electrophoresis do?
Can be used to separate DNA/RNA/proteins based on charge and size
In gel electrophoresis, where are the samples added? At the negative or positive?
Negative
Shorter DNA molecules move? Than larger DNA molecules
Further
What makes gel electrophoresis of proteins different?
The addition of SDS helps fold the protein into a linear form + negative charge
What is nucleic acid hybridization?
A nucleic acid of one strand ( DNA or RNA) forms base pairs with complementary nucleic acids on a different strand
What is in-situ hybridization?
Tests the expression of a specific mRNA using a nucleic acid probe (Fluorescent dye) where in a tissue
What is DNA sequencing?
It is used to determine the # of base pairs in a DNA or RNA molecule and their sequence
What are the reagents to synthesize DNA?
DNA, DNA polymerase, Deoxyribonucleotide, and a fluorescent Dideoxyribonucleotide
Why are ddNTPs different from dNTP
lack a 3’ -OH
What is reverse transcriptase? Does it include introns?
When an mRNA template is reverse-transcribed back to a DNA molecule. It is used in lab procedures to create complementary DNA (cDNA) from an mRNA template
Due to the template being RNA, there are no introns.
What do some viruses use to replicate their genome and proliferate in a host?
Reverse transcription
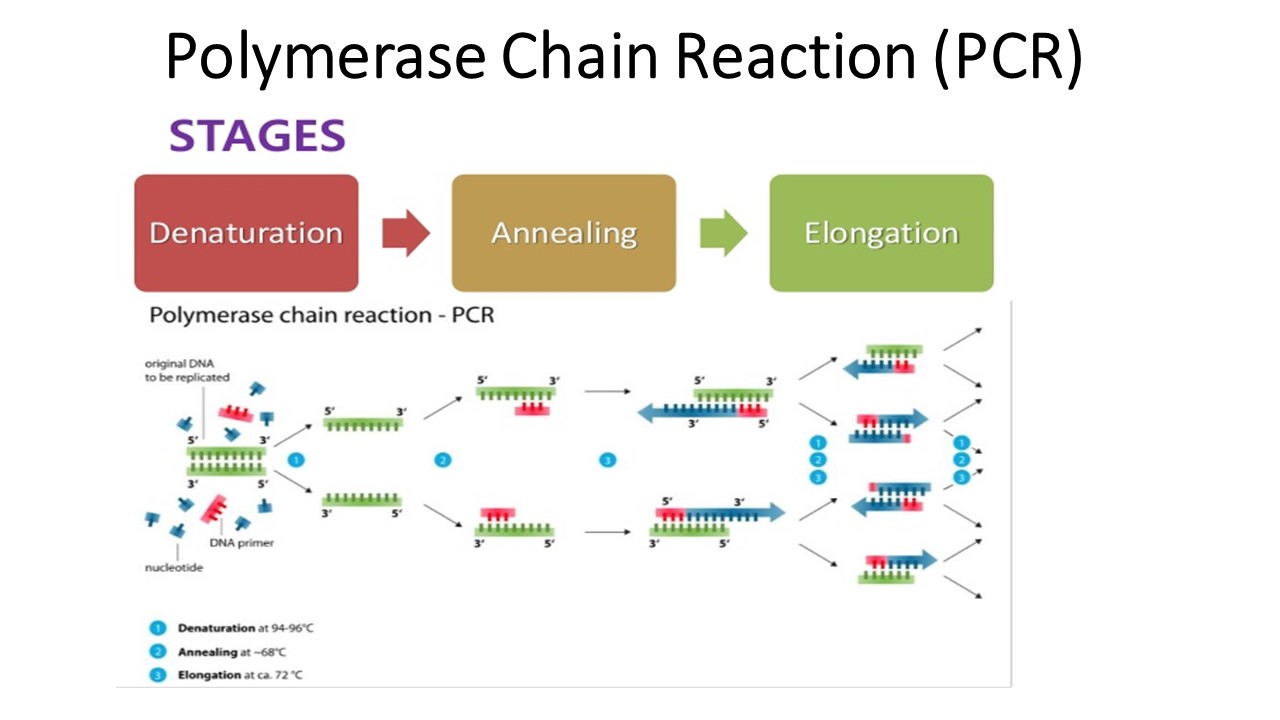
What is Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)? What are the necessary ingredients?
It is an important technique that amplifies the DNA
Necessary Ingredients: nucleotides, primers, and heat-resistant polymerase (Taq)
What are the steps of PCR?
Denaturation: Raise the temperature
Annealing: As the temperature cools down, the primers can attach to separate strands
Elongation: The temperature is raised → heat-resistant polymerase synthesizes complementary strands
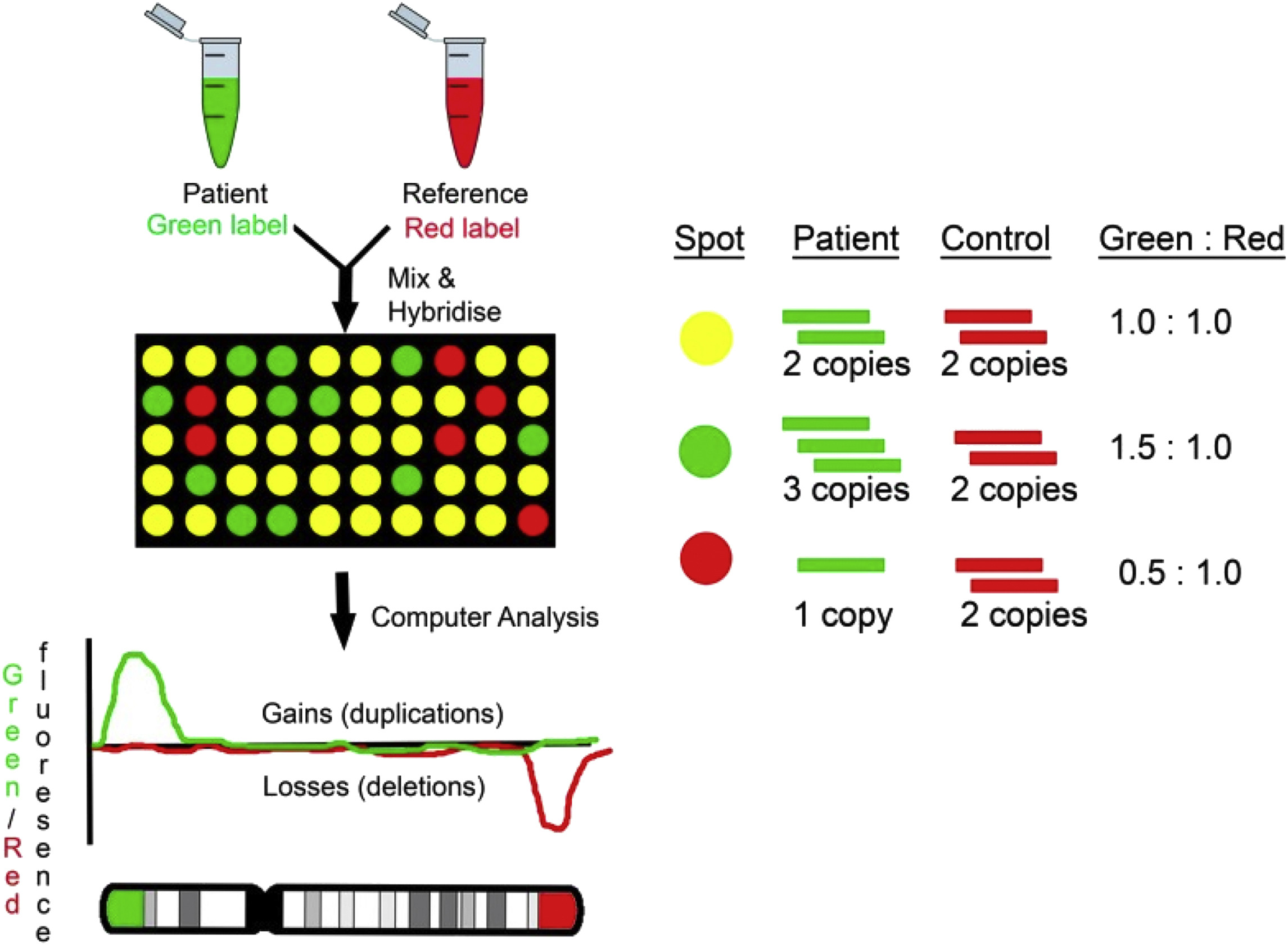
What is DNA microarray assay? Why is it useful?
It is a process that monitors the expression of large groups of genes across the entire genome
It is useful in seeing which genes are transcribed in different tissues or at different stages of development
What is the blotting technique?
It allows for the identification of target fragments of DNA,RNA, or protein
What are the three types of blotting techniques?
Southern Blotting: Identification of DNA Fragments
Northern Blotting: Identification of RNA molecules
Western Blotting Identification of Proteins
SNOW DROP → Southern Northen O Western - DNA RNA O Protein
What are the steps for blotting?
Extract DNA with the gene of interest ( DNA is extracted from a biological sample of blood or tissue, They are cut into fragments via restriction enzymes)
Separate DNA fragments by size
Fragments transferred to nitrocellulose paper ( Nucleic acids separated by electrophoresis)
Nitrocellulose paper exposed to labelled DNA probe
Allows DNA fragments to be visualized
What is immunofluorescent staining?
It is a staining technique that allows for the visual identification of proteins
What are the steps for immunofluorescent staining?
Addition of Primary Antibody: The primary antibody binds to the protein of interest
Addition of secondary antibody: Secondary antibody contains a fluorescent tag and binds to the primary antibody
Visualization of the protein of interest: Using a microscope, the fluorescent tag can be visually located to detect the protein of interest w/o killing the cell
What is in vivo mutagenesis?
Helps determine the function of a gene. This occurs by introducing a specific mutation into a gene to observe for any phenotypic difference.
A frequently used example → knockout mice
What is in-vitro?
It is a similar process to in vivo, but only studies the effect of the mutation outside of a living organism (a cell in culture)
What is genome annotation?
It is using a computer database to compare a known sequence
What is gene therapy?
It is the introduction of genes into an afflicted individual for therapeutic purposes
using a retroviral vector to insert genome material into chromosomal DNA
What is transgenic animals?
Animals that have a gene introduced from the genome of another individual, often another species
What is a genomic library? And what are its seven steps?
A collection of cloned DNA pieces from a genome
can locate a gene of interest
Isolate the genome of interest
Cut the genome with restriction enzymes
Cut the plasmid with the same restriction enzymes
Ligate genes into a plasmid
Insertion of plasmid into bacteria (transformation)
allows bacteria to multiply and replicate their genomes
DNA isolation as needed
What helps to verify which bacteria were successful in accepting the plasmid?
By performing an antibody resistance test
What are the six steps of mammalian reproductive cloning?
Isolate the donor cell with the nucleus ( in a somatic cell)
Isolate an unfertilized enucleated egg (From a female; The nucleus is removed)
Transplant the nucleus into an enucleated egg ( using an electric shock)
Embryo formation
Transfer the embryo into the surrogate mother
Deliver a baby clone
What did Pasteur’s swan-neck flask experiment prove?
It proved spontaneous life generation was invalid → life cannot be created from non-living, only existing living organisms
What did Griffith’s experiment show?
It showed that genetic traits could be transferred between different bacterial strains
What did the Avery-Macleod-McCarty experiment show?
It demonstrates that DNA was the heritable substance causing bacterial transformation (DNAase added is important because it does not affect s and r strain)
What is the Hershey-Chase experiment?
It shows that the DNA, not protein, is the genetic material of phage T2 ( a viruse)
Why is sulfur important?
Sulfur is specific to proteins
What did Meselson & Stahl's experiment prove?
It proves that the semiconservative replication was a valid DNA model
What did Gordon’s nucleic acid transfer experiment prove?
It proves that fully differentiated cell do not lose their genetic information- they retain the full genome