Health Promotion, Disease Prevention & Cultural Competence
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Health
Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity (WHO)
Healthy People 2030
Healthy people identifies public health priorities to help individuals, organizations, and communities across the united states improve health and well-being. Healthy people 2030, the initiative’s fifth iteration, builds on knowledge gained over the first 4 decades.
(health equity, heath literacy, well being)
How can I use healthy people 2030 in my work?
Healthy people addresses public health priorities by setting national objectives and tracking them over the decade.
Identify needs and priority populations
Browse obj to learn about nationals goals to improve health
see how national goals align with your priorities
consider focusing on groups affected by health disparities
Use this information to make the case for your program, secure resources, and build partnerships
Set your own targets
Find data
Health promotion
the behavior of a person who is motivated by a personal desire to increase- well being and health potential
Health Protection
behavior motivated by a desire to avoid or detect disease or to maintain functioning within the constraints of an illness or disability
Health is measure globally by
Morbidity and mortality
Morbidity
how frequent the disease occurs
Mortality
Number of deaths from a disease
Wellness
an active state of being healthy; living a lifestyle that promotes good physical, mental, and emotional health
Illness
the response of a person to a disease
Acute illness
rapid onset of symptoms and lasts a short time
Chronic Illness
(one or more of the following characteristics)
a permanent change, causes, or is caused by, irreversible alterations in normal anatomy & physiology, requires special patient education for rehab, requires a long period or care or support
Disease
medical term referring to pathologic changes in the structure or function of the body or mind
Illness behaviors
how people cope with altered functioning caused by the disease
Unique to the person and influence by age, biological sex, family values, economic status, culture, educational level, and mental status
Stage 1, Stage 2, Stage 3, Stage 4
Stage 1
experiencing symptoms
Stage 2
Assuming the sick role
Stage 3
assuming a dependent role
Stage 4
Achieving recovery and rehabilitation
Levels of prevention
Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary
Primary
promoting health and preventing the development of disease process or injury
ex: brushing teeth, wearing seatbelt
Secondary
Screening for early detection of disease with prompt diagnosis and treatment
ex: mammogram, identifying early, pap smear
Tertiary
Reducing disability and helping rehabilitate patients to a maximum level of functioning
ex: cardiac rehab, physical therapy
Basic Human needs
Human dimensions
Physical, emotional, intellectual, environmental, sociocultural, spiritual
Self-concept
self-esteem & body image
Risk Factors for illness or injury
modifable vs non- modifable
modifiable
diet, smoking, environmental, health habits
non-modifiable
age, genetic factors
Health Belief Model
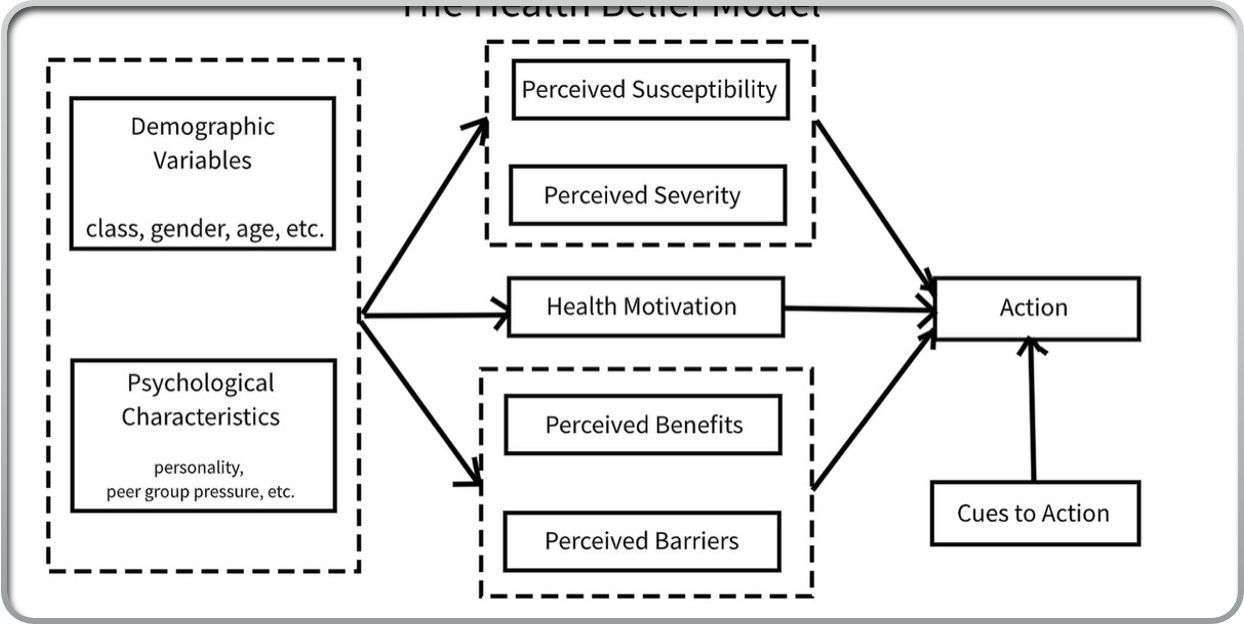
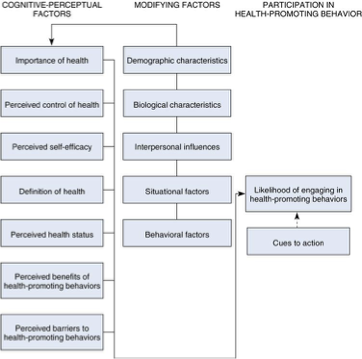
Health Promotion Model
Maslows Hierarchy of Needs
Basic needs: Physiological needs, Safety needs
Psychological needs: Belongingness and love needs, Esteem needs
Self- Fulfillment needs: self actualization
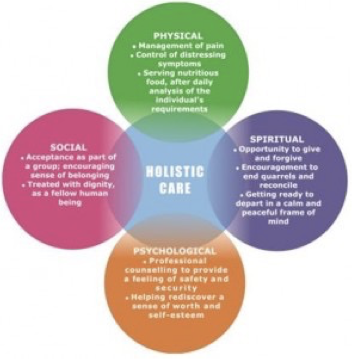
Holistic Health Model
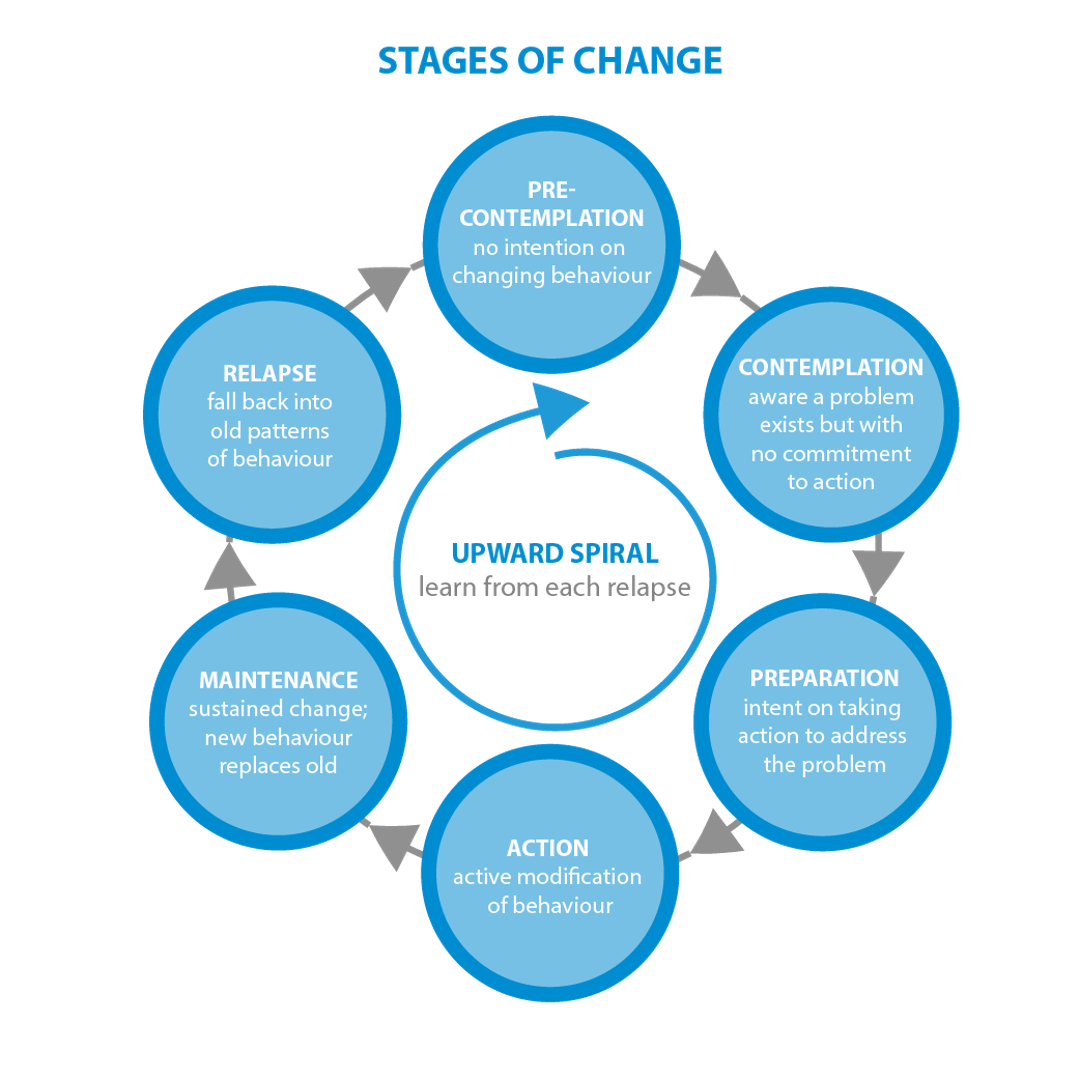
Stages of Change
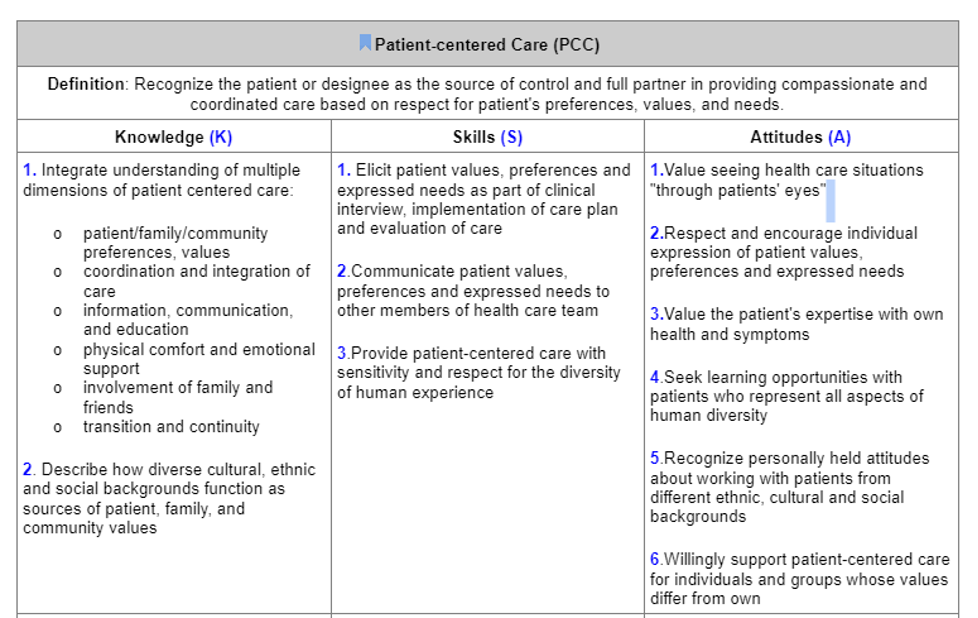
QSEN-Patient_Centered Care
Culture
a shared systems of beliefs, values, and behavioral expectations that provides social structure for daily living.
Cultural Influences on Health & Illness
Physiological Variations
Reactions to Pain
Mental Health
Biological Sex roles
Language and Communication
Orientation to Space and Time
Food and Nutrition
Family support
Socioeconomic Factors
Physiologic variations
racial and ethnic groups may be more prone to certain disease or conditions
Reactions to pain
many of the expressions and behaviors exhibited by people in pain are culturally prescribed
Mental Health
a wide variety of norms and acceptable patterns of behavior for physiological well-being
Peoples values and beliefs about health, illness, and health care are influenced by cultural and ethnic groups
Natural (cold air, impurities in air/water/food) vs Unnatural illness (punishment for failing to follow God’s rules)
Folk/traditional healers (divine intervention; often more understanding of cultural practices) vs allopathic health care providers
Culturally Respectful Nursing Care- Elements of cultural Competence:
Develop an awareness of one’s own “culture” to prevent from having undue influence
demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the patients’s culture, health-related needs, and culturally specific meanings of health and illness
Accept and respect cultural differences
Do not assume the health care providers beliefs and values are the same as the patient
Resist Judgmental attitudes such as “different is not as good”
Being open to and comfortable with cultural encounters
Accept responsibility for one’s own education in cultural competence
Health Disparities
health differences between groups of people
Health equity
the attainment of the highest level of health for all people
Social Determinants of Health
the conditions in the environments in which people are born, live, learn, work, play, worship, and age that affect a wide range of health, functioning and quality of life outcomes and risks
Cultural Diversity
Coexistence of different ethnic, biological sex, racial and socioeconomic groups within one social unit
Cultural Respect
Enables nurses to deliver care that is respectful and responsive to health beliefs, practices, and linguistic needs of diverse patients.
Cultural Assessment
Enhance understanding of:
Beliefs, values, traditions and practices of a culture
culturally defined, health -related needs of individuals, families, and communities
Culturally based belief systems of the etiology of illness and disease and those related to health and healing
Attitudes toward seeking help from health care providers
Cultural Assessment
Culturally respectful nurse has the knowledge and skills to adapt nursing care to cultural similarities and differences
accommodate cultural practices
respect family roles
avoid mandating change
seek assistance