Red/Blue/Brown Lesions
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
What is Anemia?
A decrease in volume of RBCs or hemoglobin; often a sign of an underlying disease
What are the general symptoms of anemia?
Tiredness
Headache
Fainting/feeling lightheaded
Pallor/breathlessness
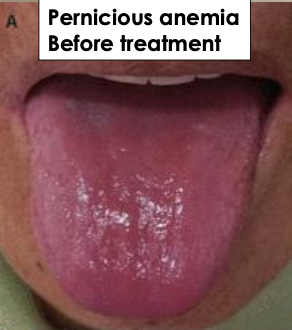
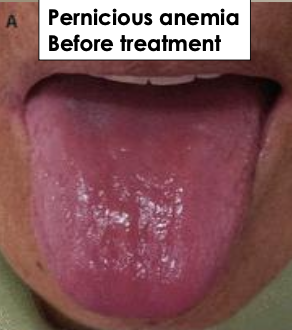
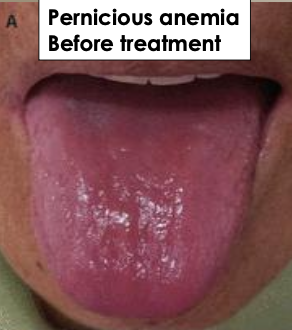
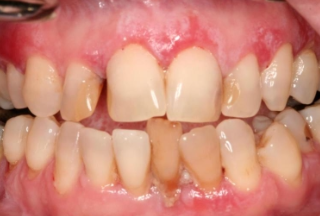
What are some oral mucosal/tongue signs and symptoms of anemia?
Oral mucosa pallor
Smooth and red
Swollen
Pain and tenderness
Reduction or loss of papillae
Difficulty or inability to chew, swallow or speak
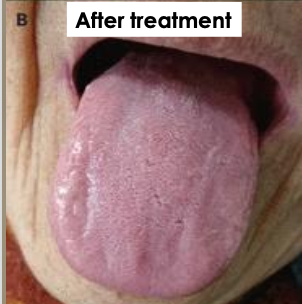
What is the management of anemia?
Treat underlying cause
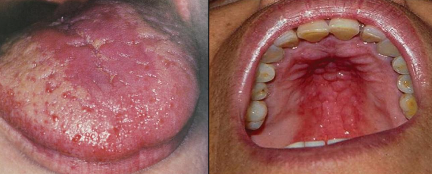
What is acute atrophic candidiasis?
Following a course of antibiotics, burning, painful, red, anywhere; metallic taste, burning sensation
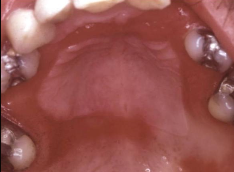
What is denture stomatitis?
Localized to denture-based areas, erythema hemorrhage; metallic taste, burning sensation
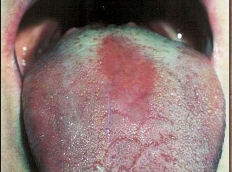
What is median rhomboid glossitis?
Loss of filiform papillae; anterior to circumvallate papilla
What is angular cheilitis?
Due to
Low vertical dimension
excess saliva
candidiasis
staph aureus
Name some erythematous candidiasis conditions
Acute atrophic candidiasis
Denture stomatitis
Median rhomboid glossitis
Angular cheilitis
How would you treat candidasis?
Oral suspension- nystatin
Lozenges- clotrimazole tablet
Tablets (systemic)- diflucan
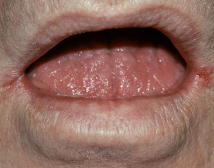
What is erythroplakia?
A clinical term; a red patch that cannot be diagnosed as any other condition that is premalignant
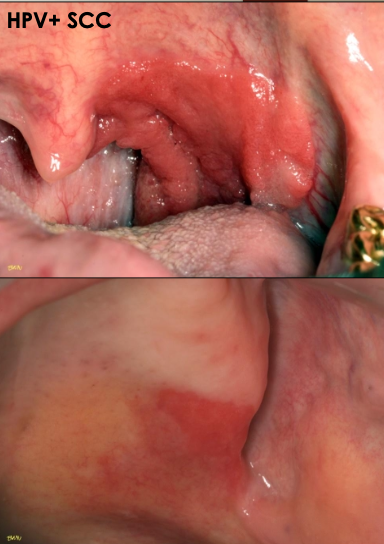
Erythroplakia - key facts
~90% show moderate dysplasia or worse on biopsy
Cause: unknown
Affects middle-aged to older adults
No gender predilection
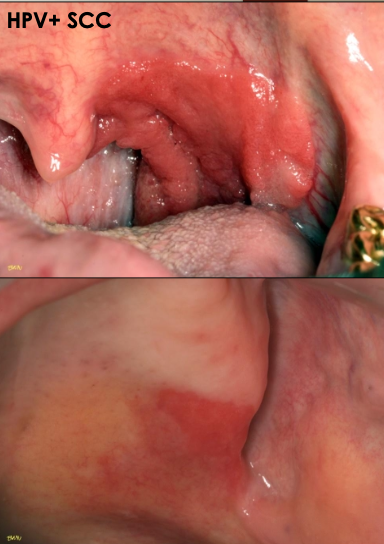
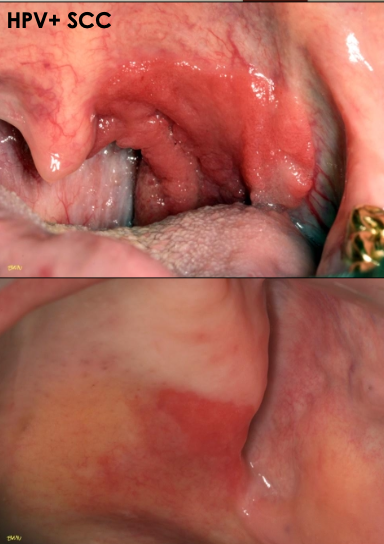
What are some high risk sites for erythroplakia?
Floor of mouth
Lateral ventral tongue
Soft palate
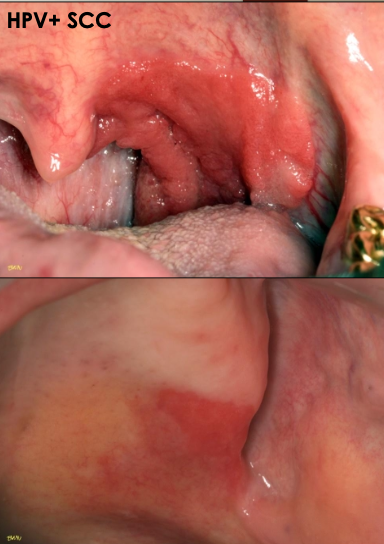
What is the management of erythroplakia?
Incisional biopsy to determine final diagnosis
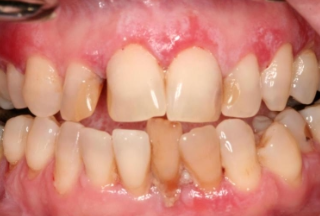
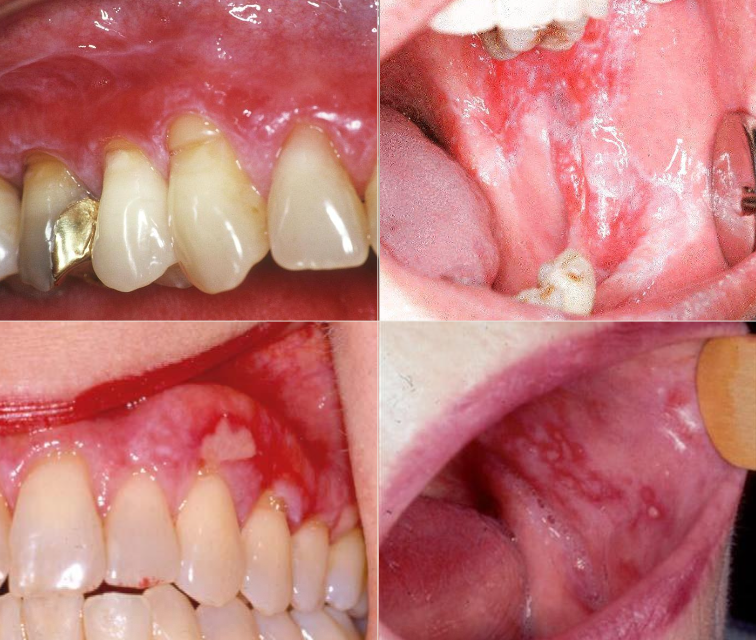
What is erosive lichen planus?
An autoimmune disease with multiple ulcerations
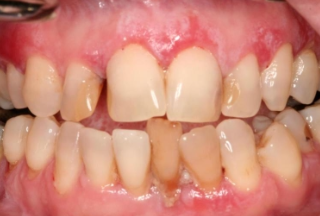
What is the clinical presentation of erosive lichen planus?
Pain
Burning
Erythema with white striations, severity varies
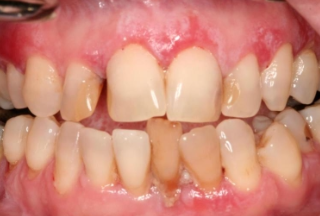
What are common locations for erosive lichen planus?
Buccal mucosa
Gingiva
Tongue
What is the management of erosive lichen planus?
Incisional biopsy for final diagnosis
Rx: prescribe steroid and antifungal
What are some differential diagnoses for desquamative gingivitis?
Lichen planus (erosive)
Lichenoid reaction (hypersensitivity)
Pemphigus vulgaris
Mucous membrane pemphigoid
What are some considerations for autoimmune conditions?
Chronic autoimmune conditions need follow-ups
More common in females
Can have skin lesions
Treated with steroid
Examples of erosive lichen planus
What is one of the most common tumors of infancy, but can also occur in adults?
Hemangioma
Where do majority of hemangiomas occur?
60% in the head and neck
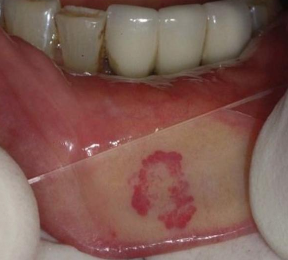
In which populations would you find hemangioma
F > M (3:1)
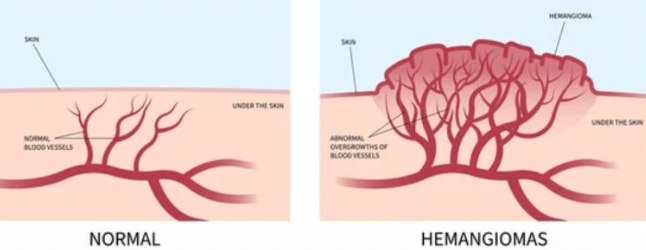
What are the phases of hemangioma?
1st year is rapid growth, faster pace than the infant’s overall growth
Initial phase: proliferative phase lasts 6-12 mo
Intermediate phase: grows proportional
End phase: slow involution, color changes to blue/purple
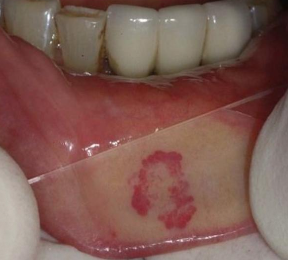
What is the clinical presentation of a hemangioma?
90% regress by age 9, but some had permanent skin changes (scar, wrinkle, atrophy)
Red to blue in color, firm to palpation, may or may not blanch with diascopy
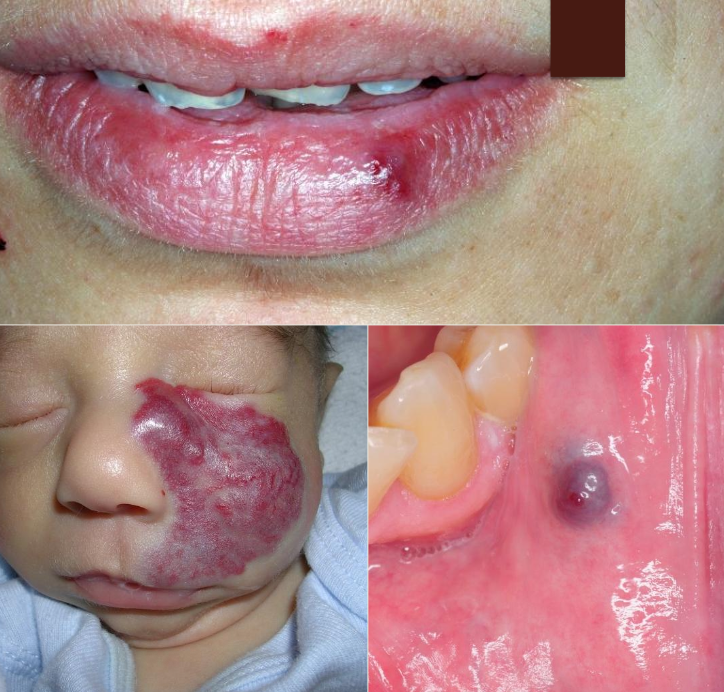
How would you manage hemangioma?
Observation
Beta-blockers (propranolol orally or timolol topically alongside corticosteroids to shrink lesion)
Laser tx
Surgery
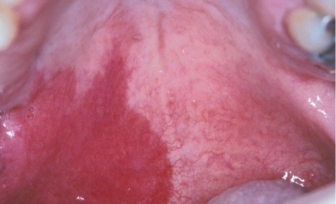
What is Sturge-Weber Angiomatosis (Syndrome)?
A non-hereditary developmental condition (mutation GNAQ on chromosome #9); hamartomatous vascular proliferation involving the brain and face along the distribution of the trigeminal nerve
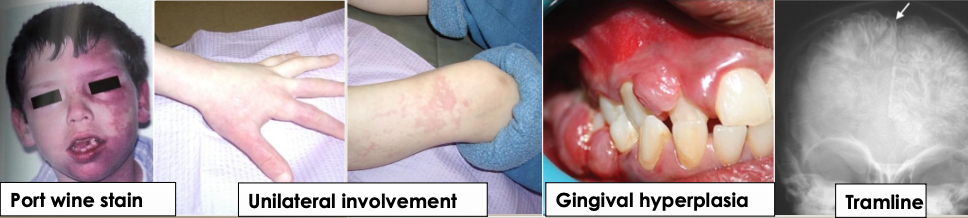
What are the clinical manifestations of sturge-weber angiomatosis?
Facial lesions- port wine stains (nevus flammeus)
Ipsilateral vascular involvement and gingival hyperplasia
Convulsions, stroke, and intellectual disability
Radiographically: “tramline” calcifications in the brain
What are two types of antineoplastic treatment?
Radiation
Chemotherapy
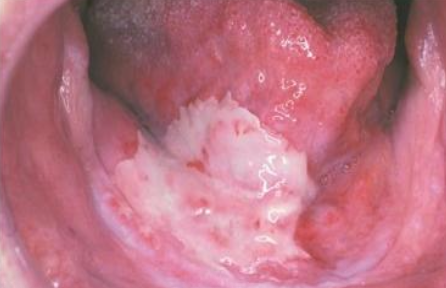
What are the clinical manifestations of radiation treatment (antineoplastic)?
Localized
100% of pts receiving H&N radiation have oral ramifications
Predominant problems mucositis and dermatitis
Xerostomia, hypogeusia, osteoradionecrosis, trismus
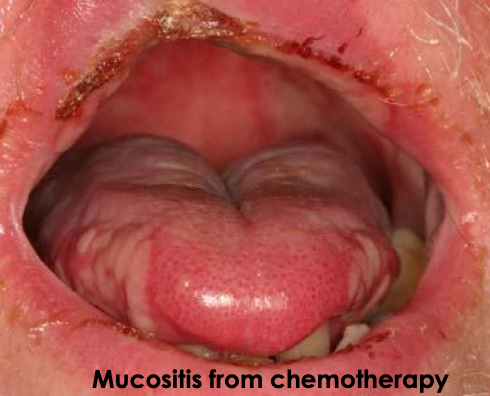
What are the clinical manifestations of chemotherapy treatment (antineoplastic)?
More generalized
Predominant problems = mucositis and hemorrhage
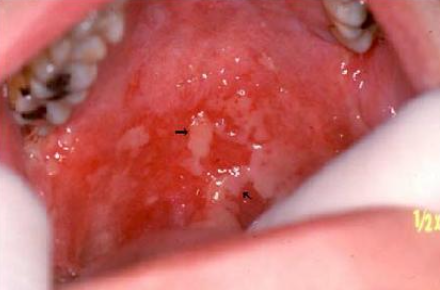
What kind of antineoplastic treatment is this?
Mucositis from radiation treatment nasopharyngeal carcinoma
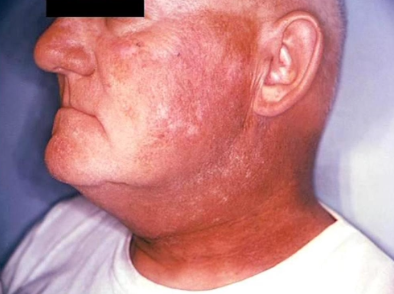
What kind of antineoplastic treatment is this?
Dermatitis from radiation
What treatment would be used for mucositis from antineoplastic tx?
Palliative care:
Meticulous oral hygiene
Dietary adjustments to soft/moist foods
Saline/baking soda rinses with a soft brush
Avoiding alcohol/spicy foods
Prescribed pain relief like topical anesthetics
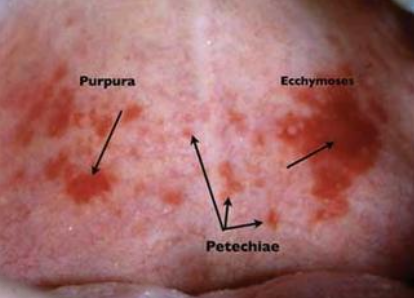
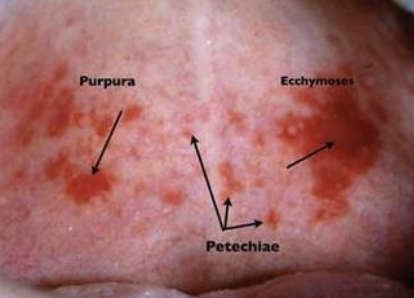
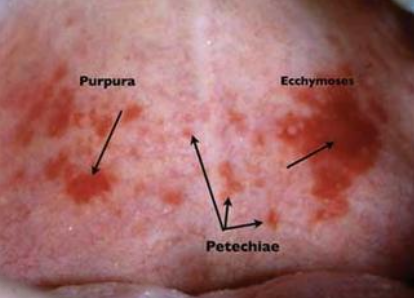
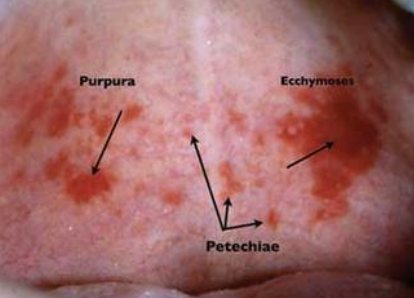
What is petechiae?
Minute hemorrhage below skin
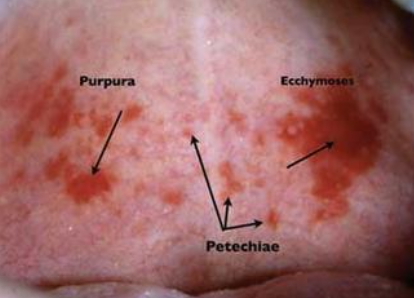
What is purpura?
Slightly larger area is affected by hemorrhage
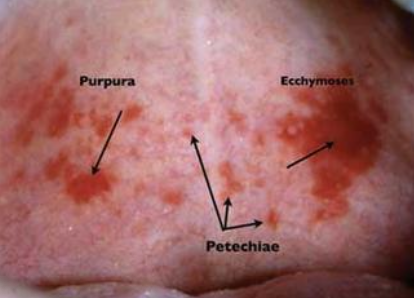
What is ecchymosis?
Accumulation of blood 2 > cm below skin
What is a hematoma?
Accumulation of blood within tissue producing a mass
How would you manage petechiae, purpura, and ecchymosis?
Self-resolving unless there is a root cause
What are some differential diagnoses for multiple red lesions on palate
Trauma - coughing/vomiting/fellatio
Systemic- blood disorders
Infection- mono
POLL EV: All of the following could cause an erythematous tongue with discomfort EXCEPT:
Chewing trauma
POLL EV: Small red dot-like lesions on the palate could be due to all of the following EXCEPT:
Anemia
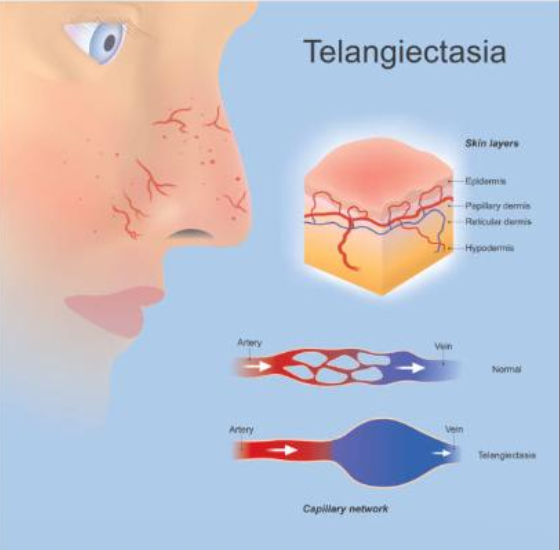
What is telangiectasia?
Dilated small blood vessels near the skin surface —> blanch with pressure (diascopy)
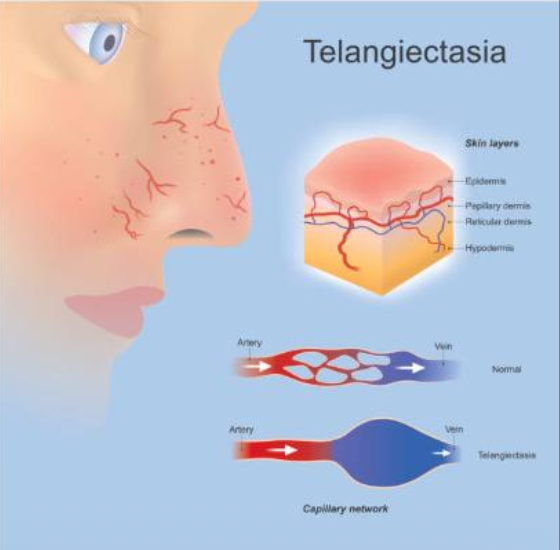
What are some syndromes with telangictasia?
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT)
CREST syndrome
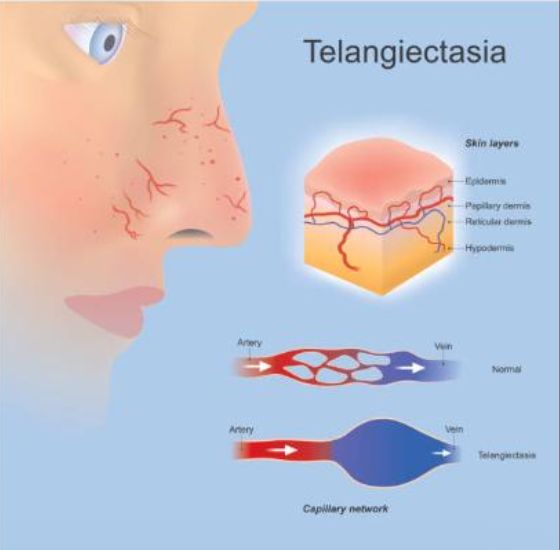
What is the management of telangiectasia?
Laser therapy
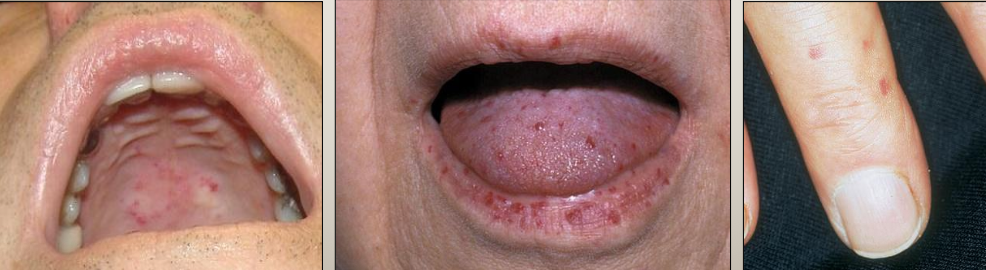
What is Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)?
An autosomal dominant mucocutaneous disorder with frequent episodes of epistaxis —> blanch with pressure (diascopy)
What are the clinical manifestations of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)?
Telangiectasia on
lips
tongue
buccal mucosa
hands
feet
GI
lungs
What is another name for CREST syndrome?
Limited scleroderma
What are the manifestations of CREST syndrome?
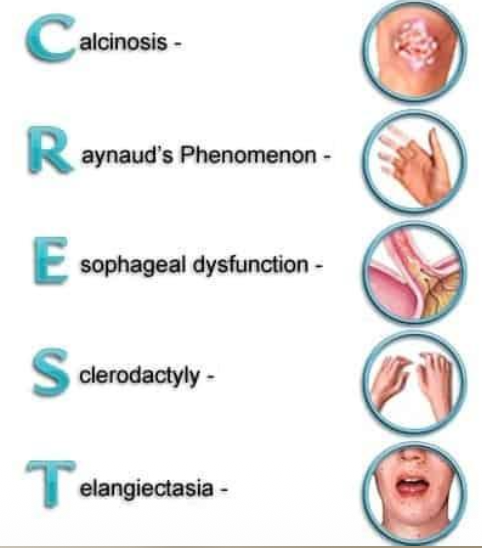
C- Calcinosis
R- Raynaud’s Phenomenon
E- Esophageal dysfunction
S- Sclerodactyly
T- Telangiectasia
Calcinosis seen in CREST syndrome
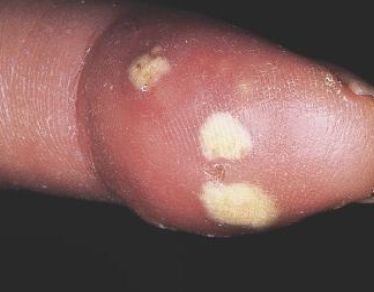
Raynaud’s phenomenon seen in CREST syndrome
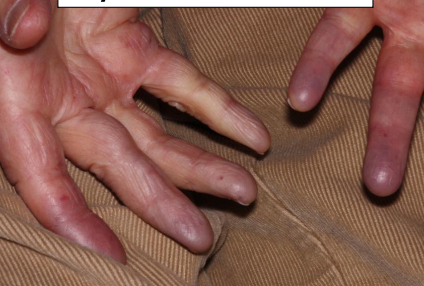
Sclerodactyly seen in CREST syndrome
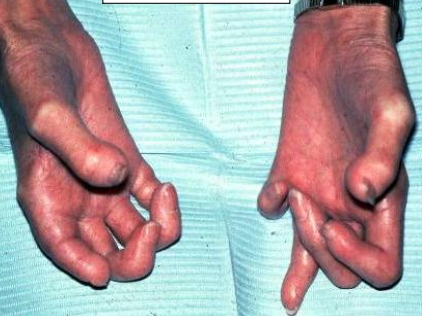
Telangiectasia seen in CREST syndrome
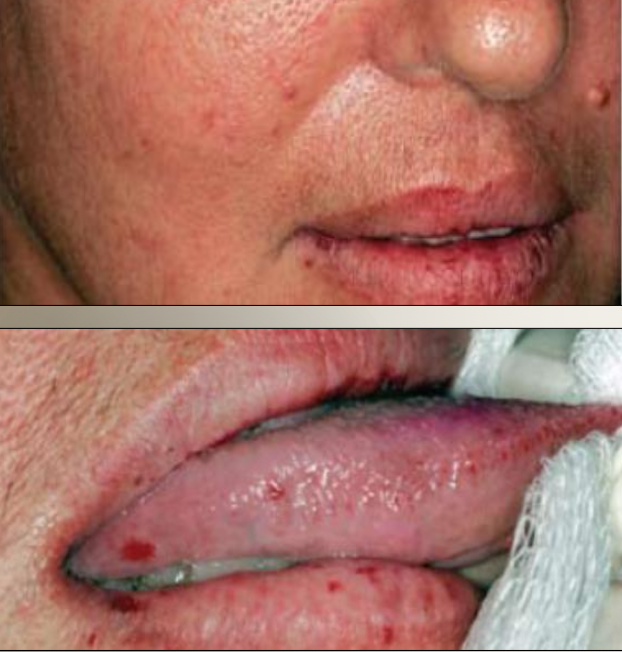
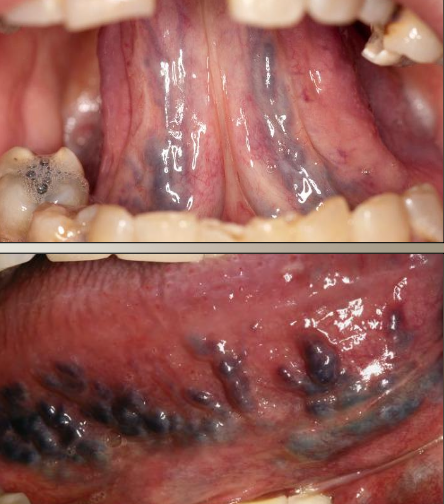
What are varicose veins (varix)?
Asymptomatic abnormally dilated and tortuous veins in older adults that can present as multiple or single
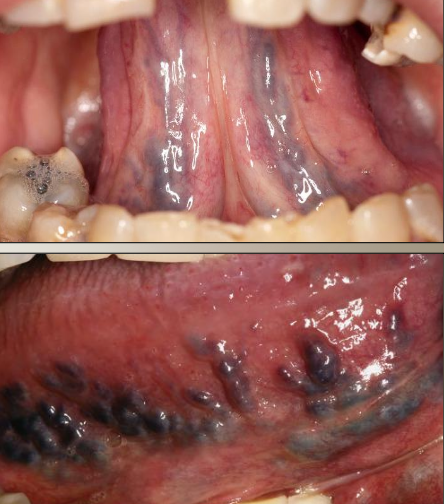
What is the most common sublingual varix?
Varicose vein (verix)
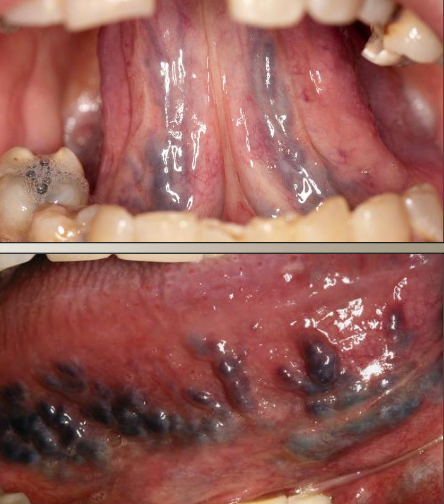
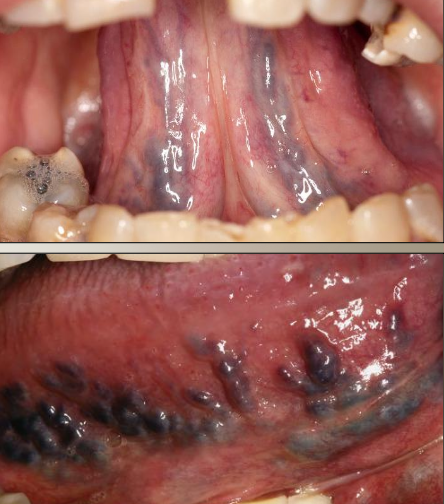
Where are the most common locations for varicose veins (varix)?
Ventral tongue
Lips
Buccal mucosa
Floor of mouth
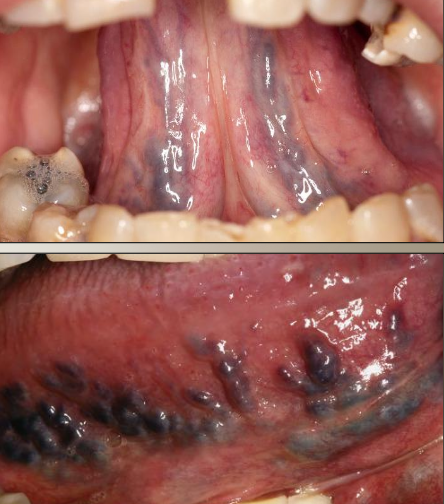
If varicose veins are calcified, what is that called?
Phlebolith
What is the treatment for varicose veins (varix)?
None, except for esthetic reasons
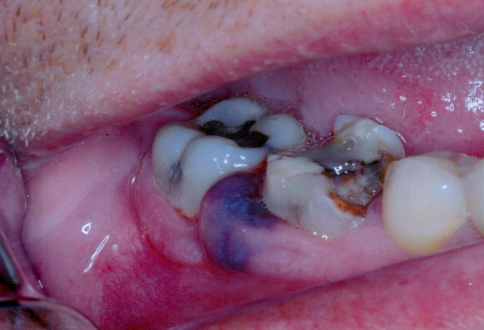
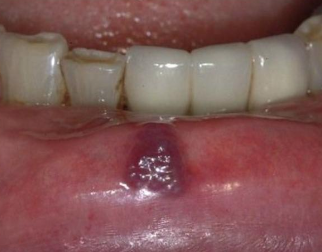
What is this an example of?
Hematoma- accumulation of blood within the tissue producing a mass
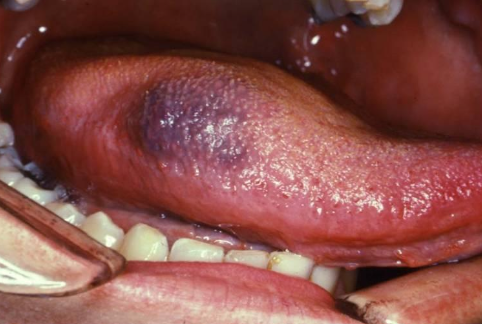
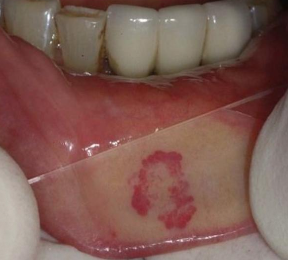
What is this an example of?
Hemangioma- benign tumor of blood vessel
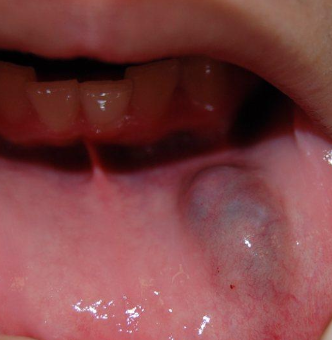
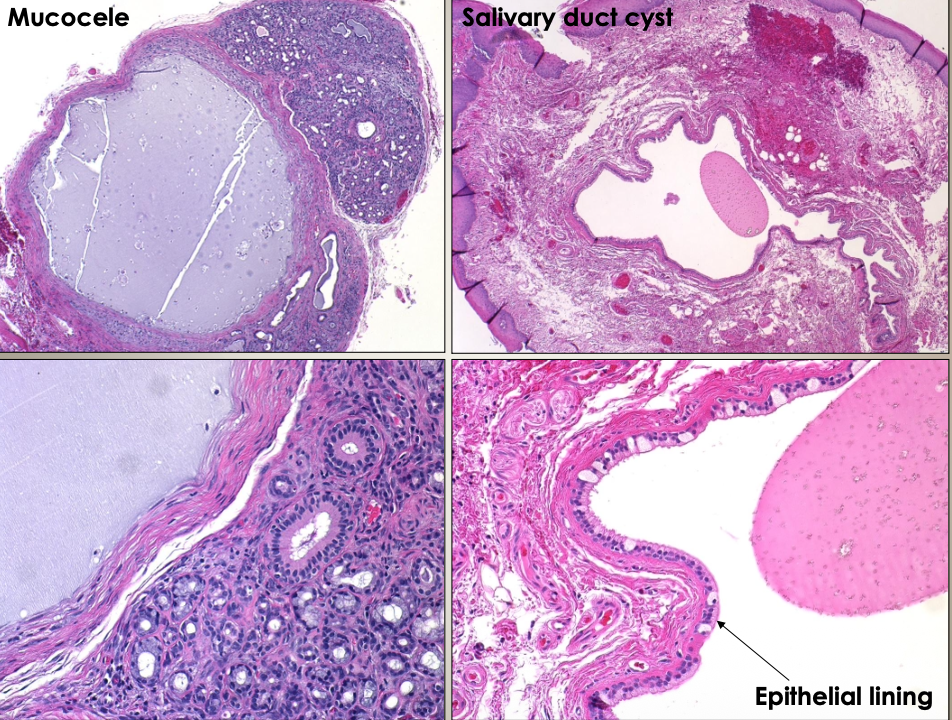
What is a mucocele?
Due to trauma to minor salivary gland, usually in kids with painless swelling
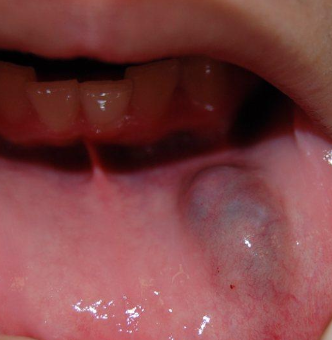
What is the most common location of a mucocele?
Lower lip
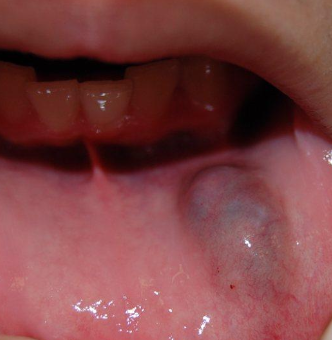
What is the management of a mucocele?
Surgical removal of lesion and minor salivary glands
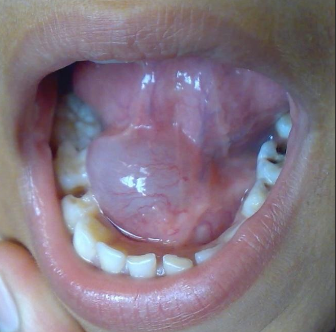
Where would you find a ranula?
Floor of the mouth from the sublingual gland
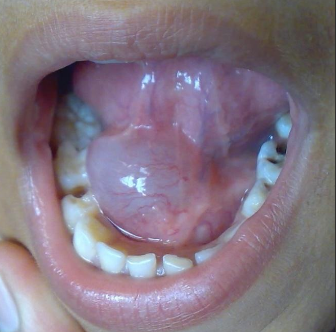
How would you manage a ranula?
Surgical removal
Marsupialization
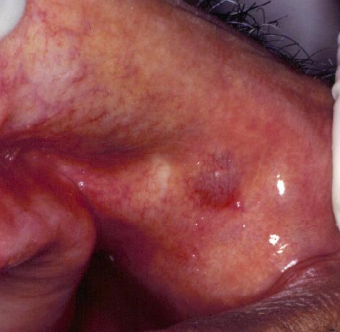
Where would you find a salivary duct cyst?
Usually in adults; more common in upper lip
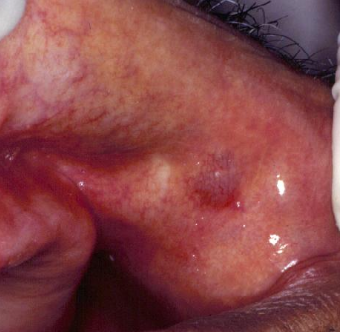
How would you manage a salivary duct cyst?
Surgical removal
How would you distinguish between a salivary duct cyst and mucocele?
Microscopically. A salivary duct cyst has an epithelial lining
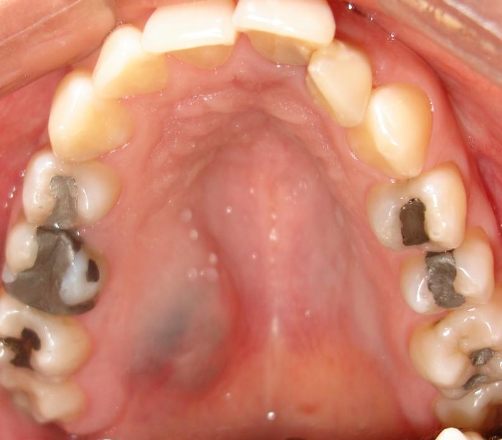
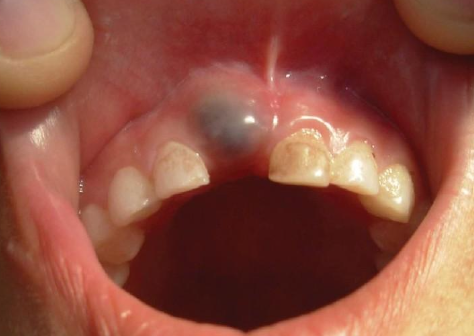
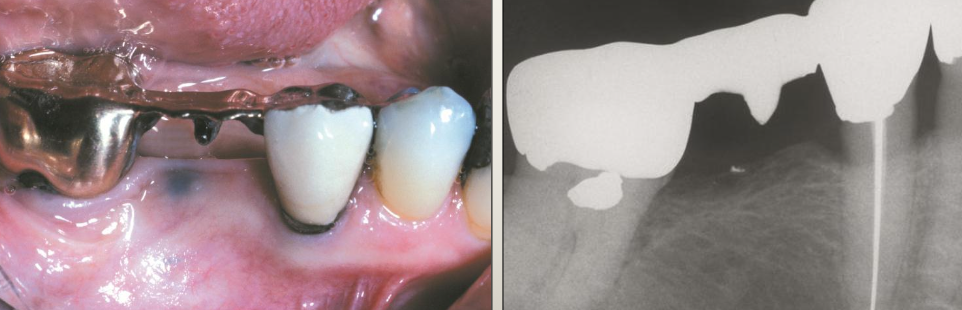
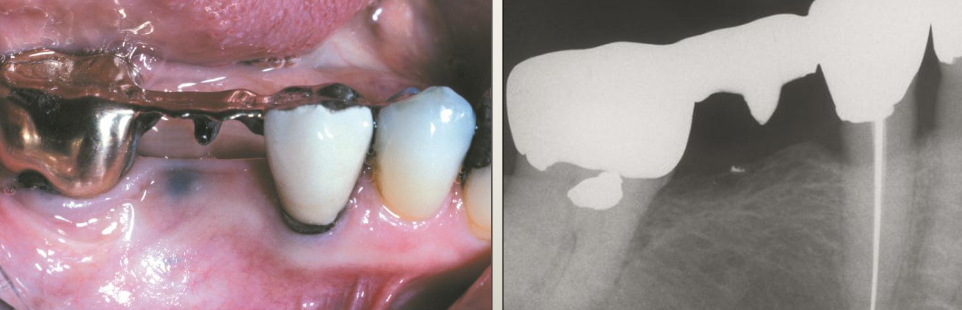
What is another name for a salivary gland neoplasm?
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
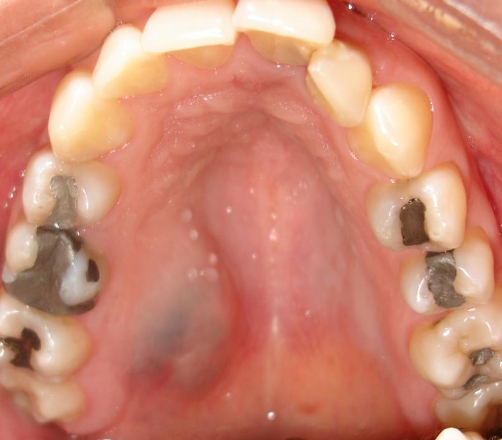
What is the clinical presentation of mucoepidermoid carcinoma?
Blueish color
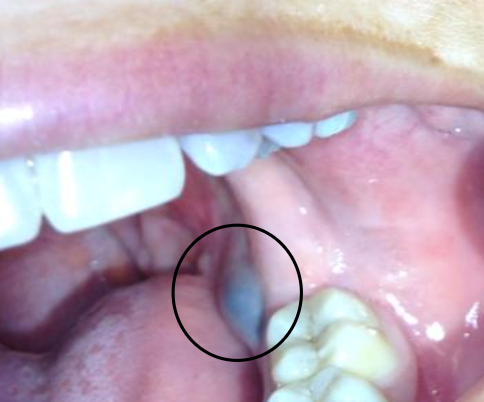
What is the management of mucoepidermoid carcinoma?
Incisional biopsy for definitive diagnosis
What is an eruption cyst?
Children, overlying the crown of erupting deciduous or permanent tooth, subsides when tooth erupts
What is a gingival cyst?
Adults, most common location is between mandibular canine & PM, surgical excision
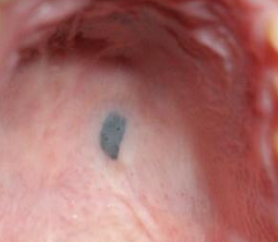
What is an amalgam tattoo?
Appear as macules or (rarely) as raised lesions which are blue, black, or gray in color
May have ill defined borders
PA x-rays are usually negative but sometimes small particles can be seen
What is the management of amalgam tattoos?
No tx, incisional bx, excisional surgery (depends)
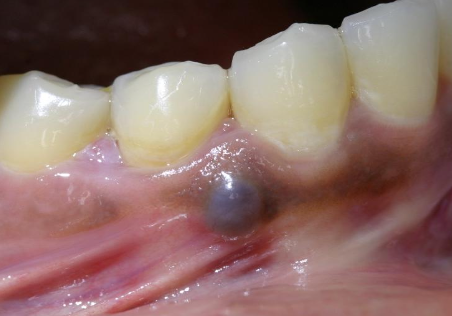
What is this?
Blue nevus
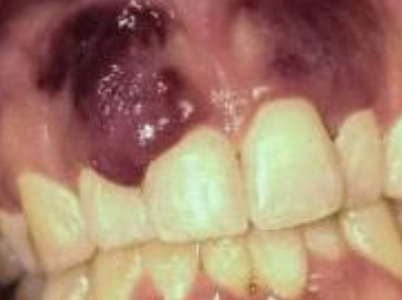
What is kaposi’s sarcoma?
An AIDS related vascular malignant neoplasm caused by HHV-8
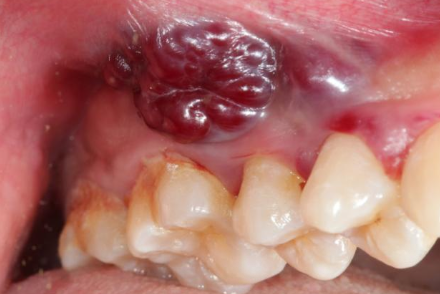
What is the clinical presentation of kaposi’s sarcoma?
Multiple vascular neoplasms on skin and intra oral
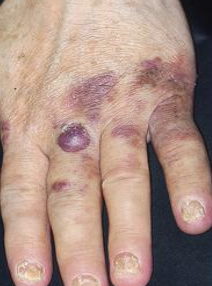
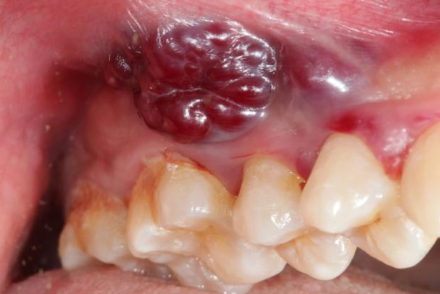
What is the management of kaposi’s sarcoma?
Incisional biopsy for definitive diagnosis then surgery and adjunct therapy
POLL EV: Which of the following exhibits a large (3cm) bluish mass on the palate?
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
POLL EV: A 36-year-old male with a blue lesion that appears flat or plaque-like on his palate that has been present for years. Which of the following is in the differential diagnosis?
Blue nevus and amalgam tattoo
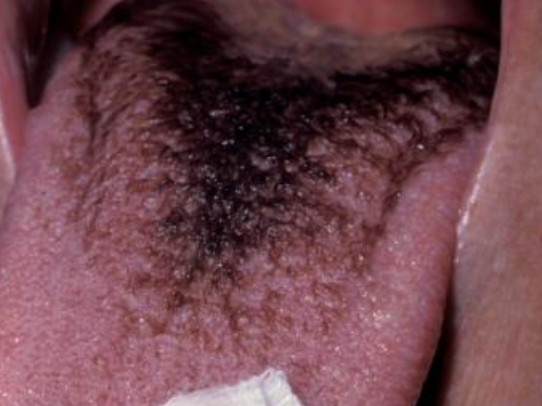
What is hairy tongue?
Excess keratin on surface of filiform papillae
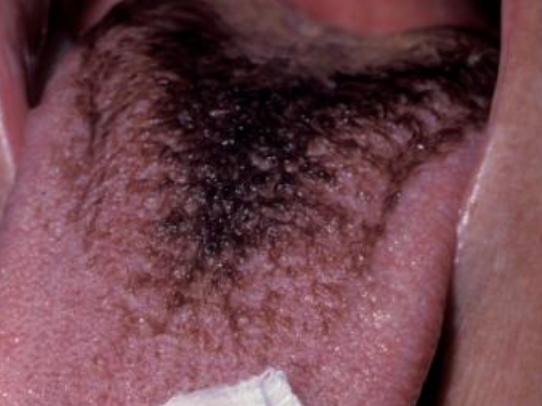
What is the cause of hairy tongue?
Uncertain but can be due to smoking, drugs, xerostomia, hx of radiotherapy to H&N, poor oral hygiene —> halitosis
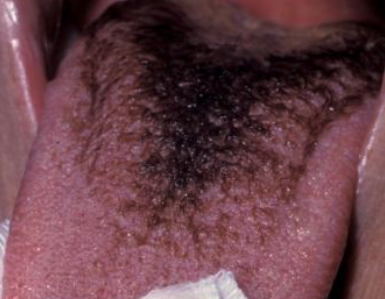
What is the clinical presentation of hairy tongue?
Starts white, may become black, brown, orange, green, yellow. The stain is from food/drink stains, chromogenic bacteria
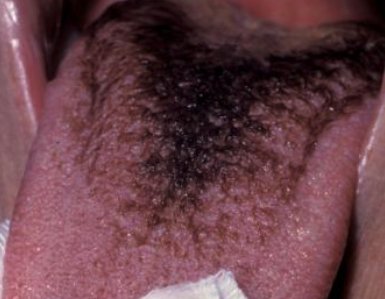
What is the treatment for hairy tongue?
Remove offending agent
Brushing tongue
Scrape the tongue with floss
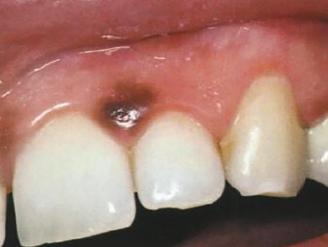
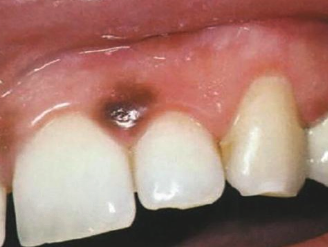
When does acquired melanocytic nevus develop?
During childhood and young adults
Where does acquired melanocytic nevus develop?
Skin above the waist most common; most common on hard palate or gingiva but can occur anywhere
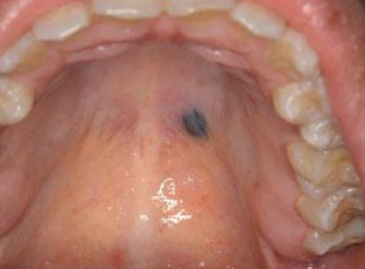
What are the different types of acquired melanocytic nevus?
Intradermal
Intramucosal
Blue nevus
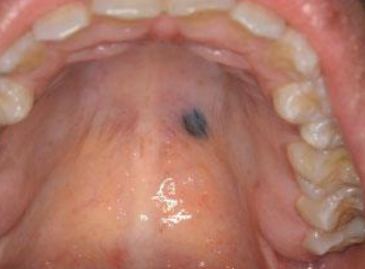
What is the treatment for acquired melanocytic nevus?
Observation
Excise for definitive diagnosis
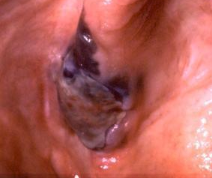
What is Melanoma?
A malignant proliferation of melanocytes
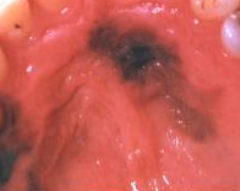
What is the cause of melanoma?
On skin = UV exposure
In mouth = unknown (no tobacco)
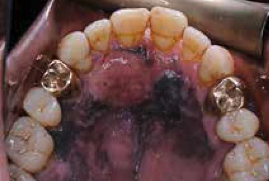
Where would you find melanoma?
Back for men, leg for women, eye, nails, scalp, intraoral —> ABCDE
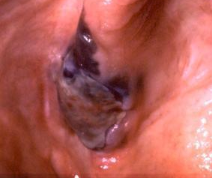
What is the management for melanoma?
Incisional biopsy
Surgery + adjunct therapy if needed
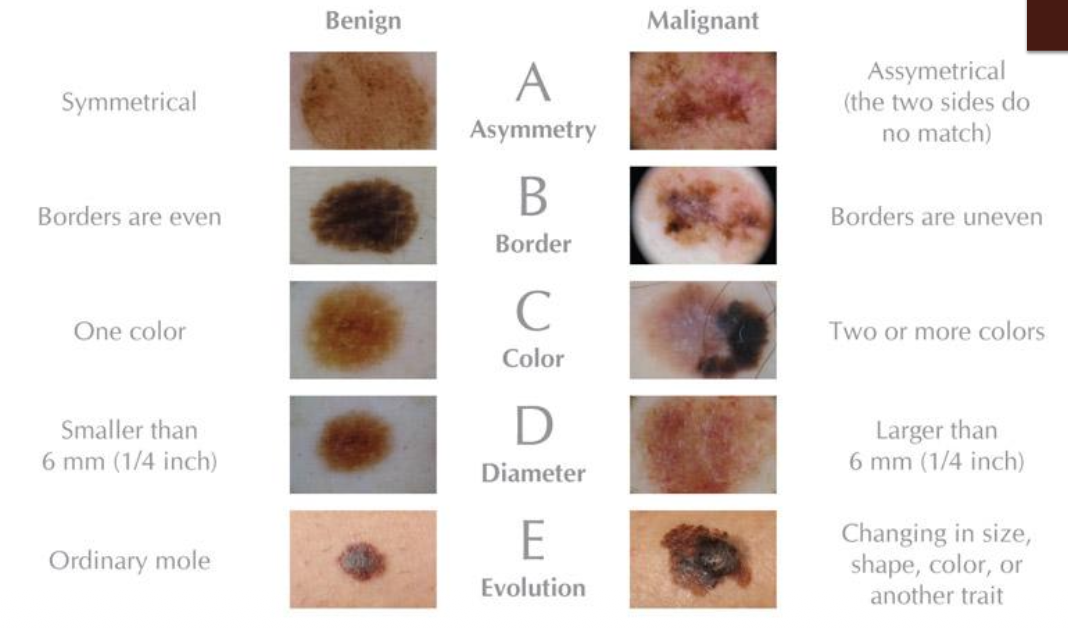
What does ABCDE stand for in Melanoma?
A = Asymmetry
B = Border
C = Color
D = Diameter
E = Evolution
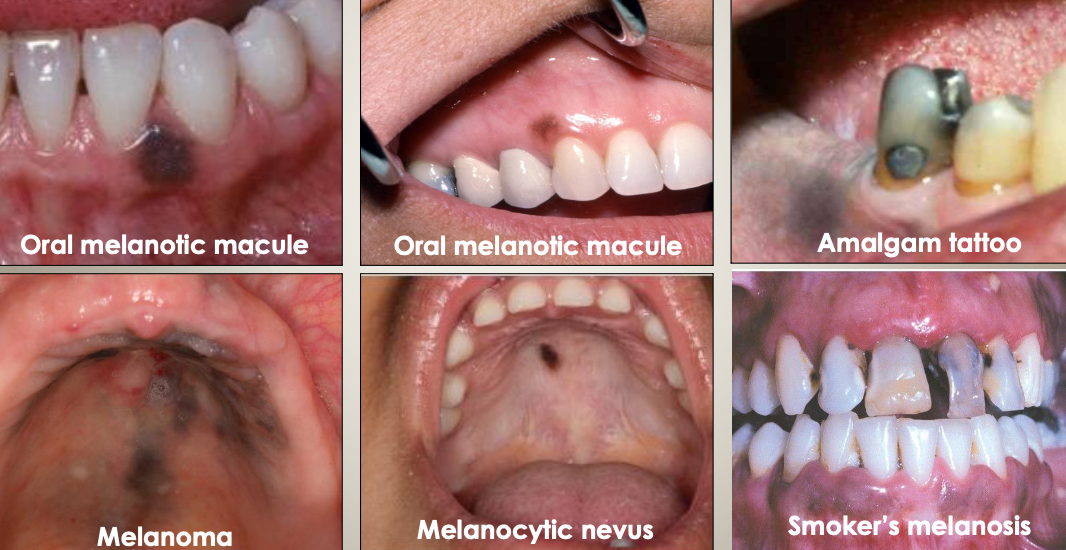
What should be included in the differential diagnoses for brown/black pigmentations?
Oral melanotic macule
Amalgam tattoo
Melanoma
Melanocytic nevus
Smoker’s melanosis
Comparison chart of distinguishing a benign vs. malignant lesion for melanoma (ABCDE)
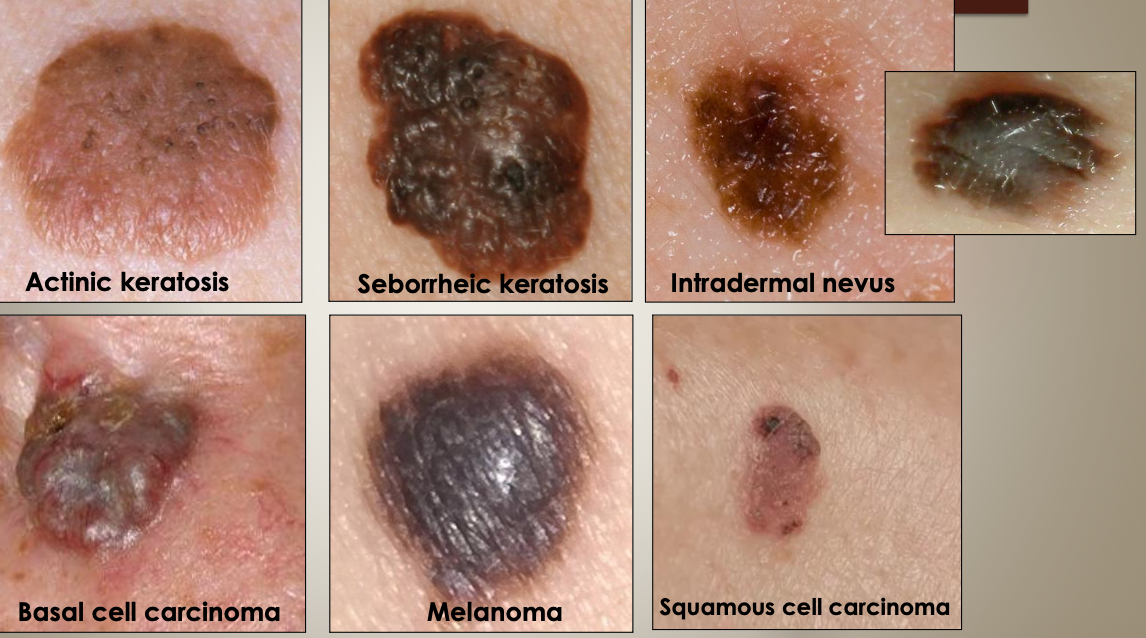
What should be included in the differential diagnoses for pigmented skin lesions?
Actinic keratosis
Seborrheic keratosis
Intradermal nevus
Basal cell carcinoma
Melanoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
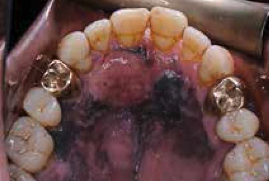
What does oral pigmentation look like if a patient is taking medication?
AZT pigmentation
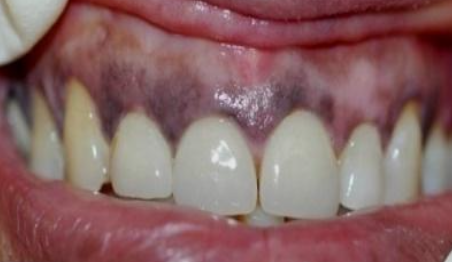
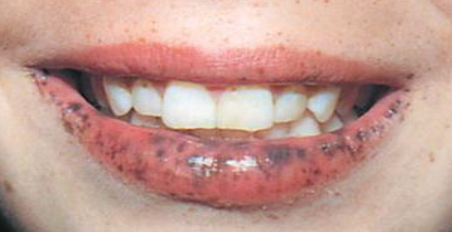
What does oral pigmentation look like if a patient has Peutz-Jeghers Systemic or syndrome?