AP World History: Byzantine Empire, Orthodox Christianity, and Medieval Europe
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What was the capital of the Byzantine Empire?
Constantinople
What language was primarily used in the Byzantine Empire?
Greek
Who was the notable emperor that rebuilt Constantinople and codified Roman law?
Justinian I

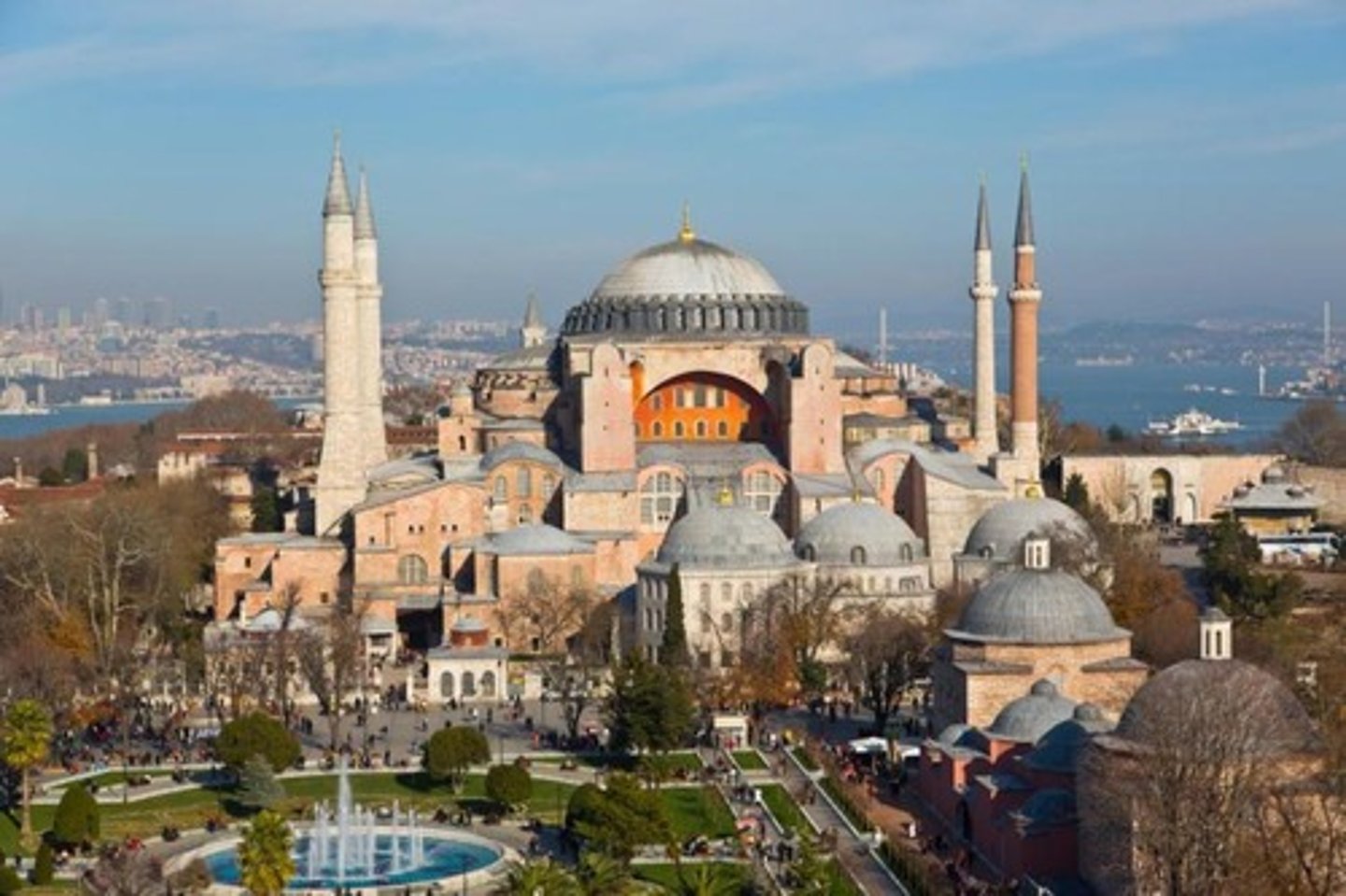
What architectural masterpiece was built during Justinian's reign?
Hagia Sophia

What major conflict contributed to the decline of the Byzantine Empire?
The Seljuk Turks' invasions
What was the significance of the Schism of 1054?
It divided Christianity into the Catholic Church in the West and the Orthodox Church in the East.
What was the primary economic activity in the Byzantine Empire?
Trade, heavily regulated by the state.
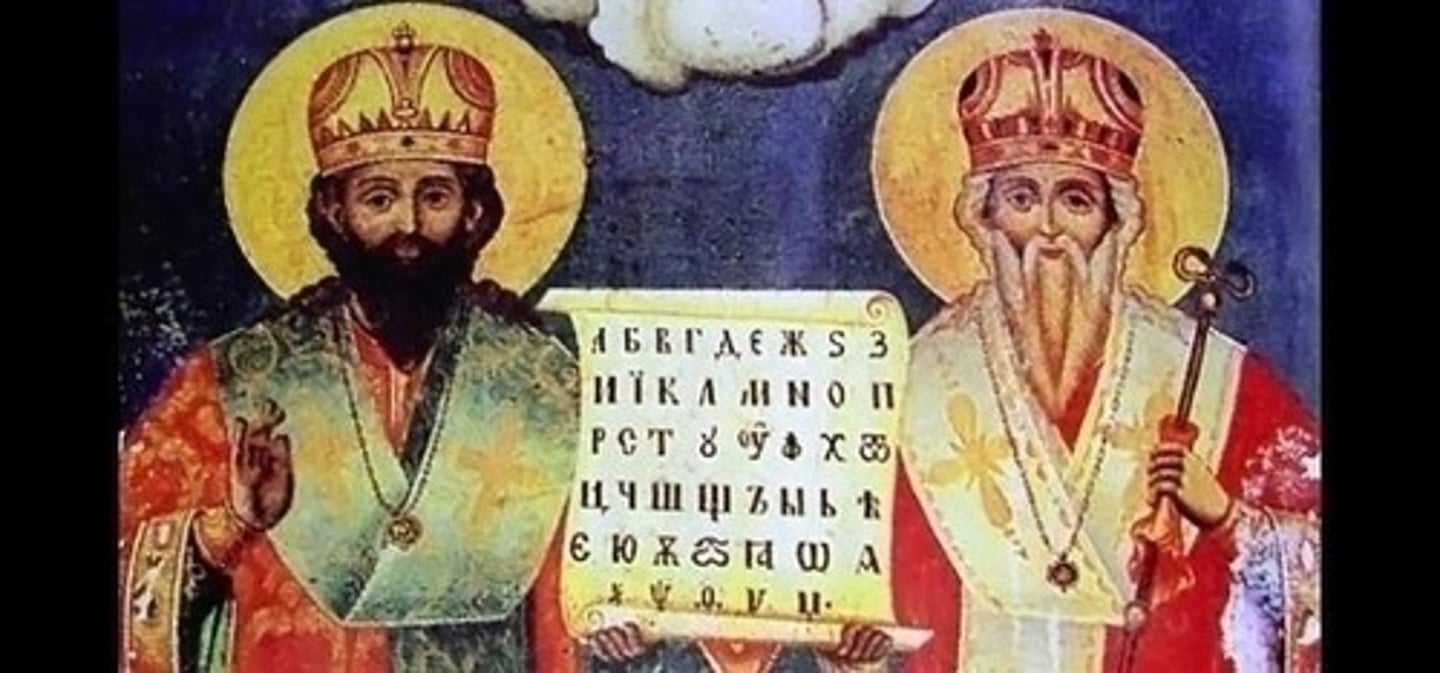
Which two missionaries created the Cyrillic script for Slavic languages?
Cyril and Methodius

What was the Kievan Rus' initial religious belief system before conversion?
Animism
Who was the first king of Kievan Rus?
Rurik
What was the role of Vladimir I in Kievan Rus?
He converted the region to Orthodox Christianity and established formal law codes.
What were the boyars in Kievan Rus society?
Aristocrats with limited political power.
What major event led to the decline of Kievan Rus?
The Mongol invasion (1237-1241).
What cultural influences did Kievan Rus adopt from the Byzantine Empire?
Art, literature, and religious practices, including illuminated manuscripts and icons.
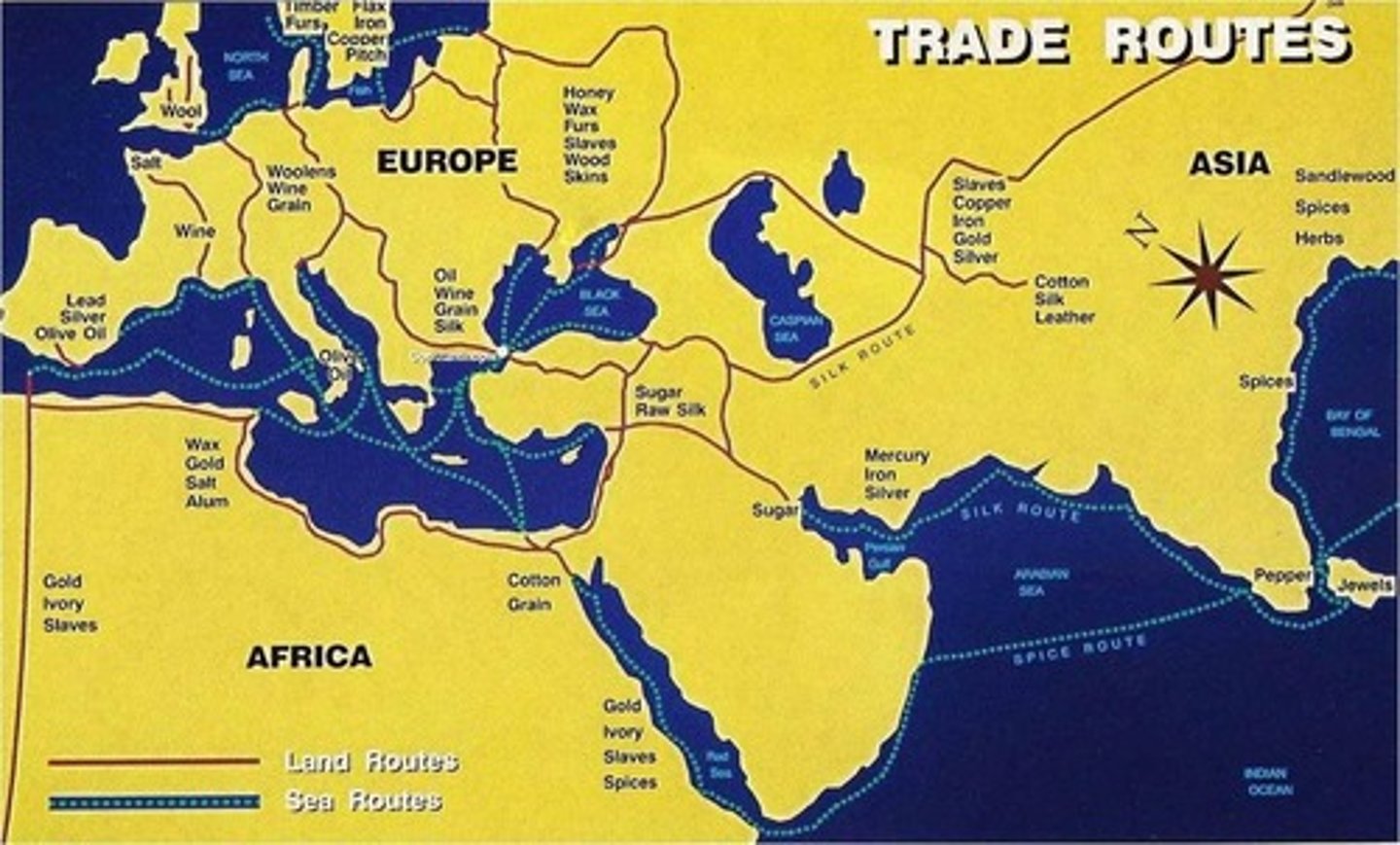
What was the impact of the fall of Constantinople on Russia?
It marked the rise of Russia as the 'Third Rome.'
What was the primary difference between Catholicism and Orthodox Christianity?
Catholicism was centered in the West, while Orthodox Christianity was centered in the East, with different practices and leadership structures.
What was the significance of the Byzantine Empire in terms of classical learning?
It maintained and preserved classical knowledge and learning through trade and cultural exchanges.
What was the role of the Byzantine military in society?
Military leaders could gain political and economic power through service, often recruiting from land offers.
What was the economic structure of Byzantine society?
It was hands-on, with controlled food prices and heavily regulated trade.
What was the Byzantine approach to religious art?
It focused on religious themes, often using mosaics and icons.
What was the impact of the Black Death on Europe?
It caused significant population decline and social upheaval, affecting economies and labor systems.
What was the significance of the 3-field system in medieval agriculture?
It improved agricultural productivity by rotating crops and allowing land to rest.
What was the role of trade in the Byzantine Empire?
Trade was crucial for economic prosperity and cultural exchange, linking Europe and Asia.
What was the Byzantine Empire's self-image?
They viewed themselves as the continuation of the Roman Empire.