Digestion and enzymes
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Digestion order
Ingestion->digestion->absorption->assimilation->egestion
Digestion
Breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules -> smaller, soluble food molecules
Molecules absorbed into the blood stream and delivered to cells for respiration -> energy is released
Excretion
removal of wastes produced by cells
e.g. urea, CO2
Egestion
removal of waste food molecules after digestion
e.g. poop
absorption
uptake of digested food into the bloodstream
mechanical digestion
physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces, chemical structure of food is still the same
increases surface area that enzymes can act on
e.g. mouth and stomach
chemical digestion
Large food molecules -> smaller molecules
change of chemical structure
e.g. stomach
mouth
where food enters the alimentary canal and digestion begins
teeth
chops food into smaller pieces
mechanical digestion
saliva
moistens food so it can be swallowed
contains amylase
chemical digestion
Oesophagus
muscular tube which moves ingested food to stomach
peristalsis
contractions of muscular wall to move food
stomach
muscular walls churn food (mechanical digestion)
also contains stomach acid
gastric juices
contains hydrochloric acid and protease
chemical digestion
hydrochloric acid
drops pH in stomach
kills bacteria
stops digestion of starch
small intestine
produces intestinal juice
contains maltase
duodenum
digestive enzymes are added
bile
made in liver
stored in gall bladder
transported to duodenum via bile duct
neutralises acidity of stomach
emulsification
bile breaking fat into small droplets
increases surface area for lipase
ileum
further digestion occurs
absorption of molecules
long with large surface area to absorb molecules, folds and villi
thin lining on the wall so molecules pass through easily
dense capillary network and lacteal
absorption method
end products absorbed by passive diffusion until equilibrium
moves by active transport to accumulate
blood capillaries
transport glucose, amino acids, minerals, water-soluble vitamins from ileum to liver
lacteal
transport fatty acids, glycerol, fat-soluble vitamins from ileum to lymphatic system
large intestine
water absorbed and material becomes solid
peristalsis moves solid matter into rectum
egested through anus
metabolic reaction
chemical reactions that occur in cells, controlled by enzymes
enzymes
biological catalysts (speeds up reaction without being used up)
group of proteins
specific and only react with particular substrates
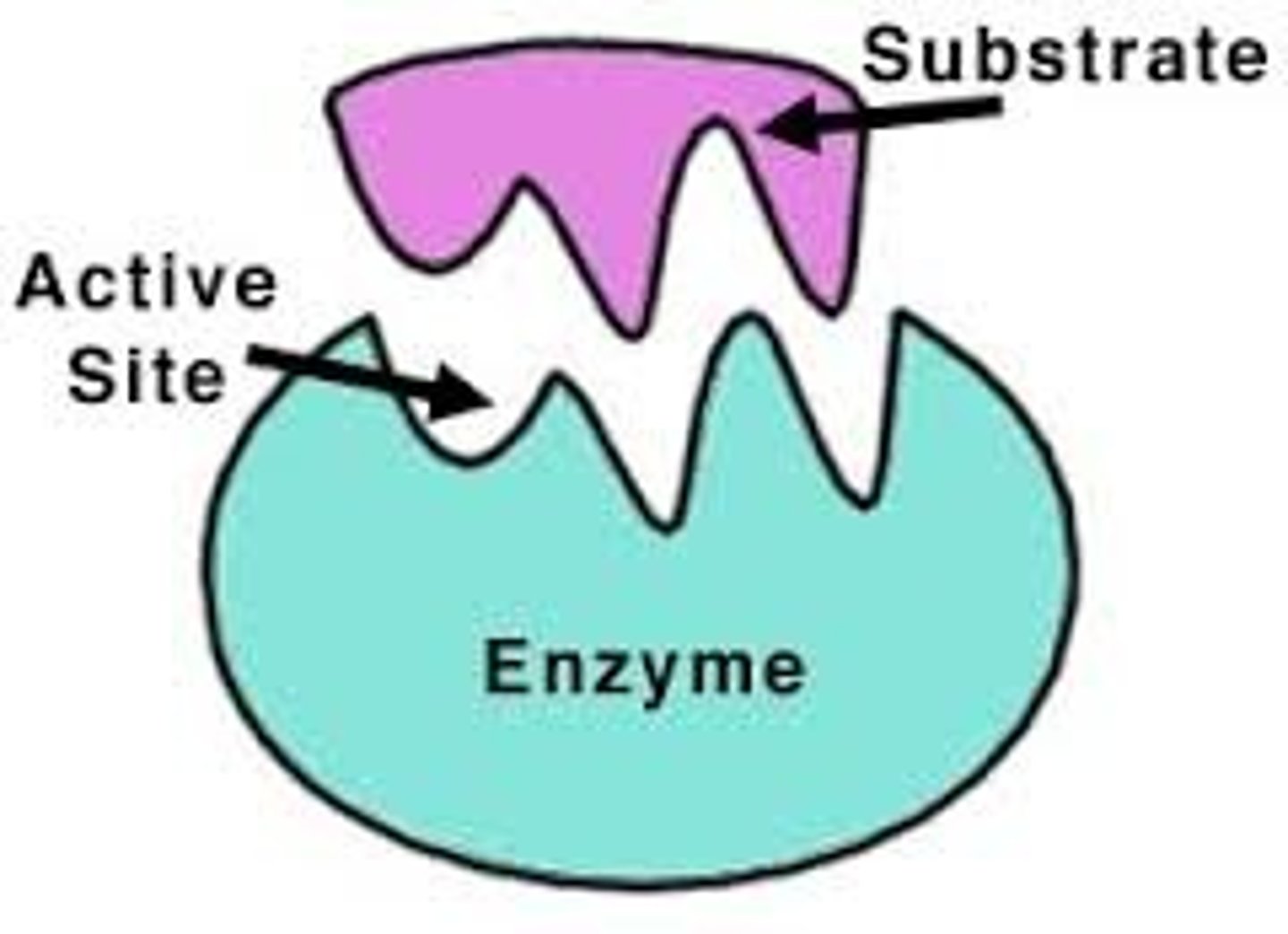
substrate
molecules an enzyme acts on
active site
where substrate attaches to and forms an enzyme substrate complex
reactions
Starch + amylase = maltose
Maltose + maltase = glucose
Protein + pepsin = amino acids
Lipids + lipase = fatty acids + glycerol
temperature
enzymes are temp sensitive
first temp rises and enzymes have more kinetic energy
if temp too high, enzyme is denatured and reaction stops
fastest rate of reaction is at the optimum temp
denatured
active site loses shape
Temperature graph
1. low temp, less kinetic energy, rate is low
2. optimum temp (37 for humans) max rate
3. high temp, enzyme denatures, active site loses shape, rate is 0

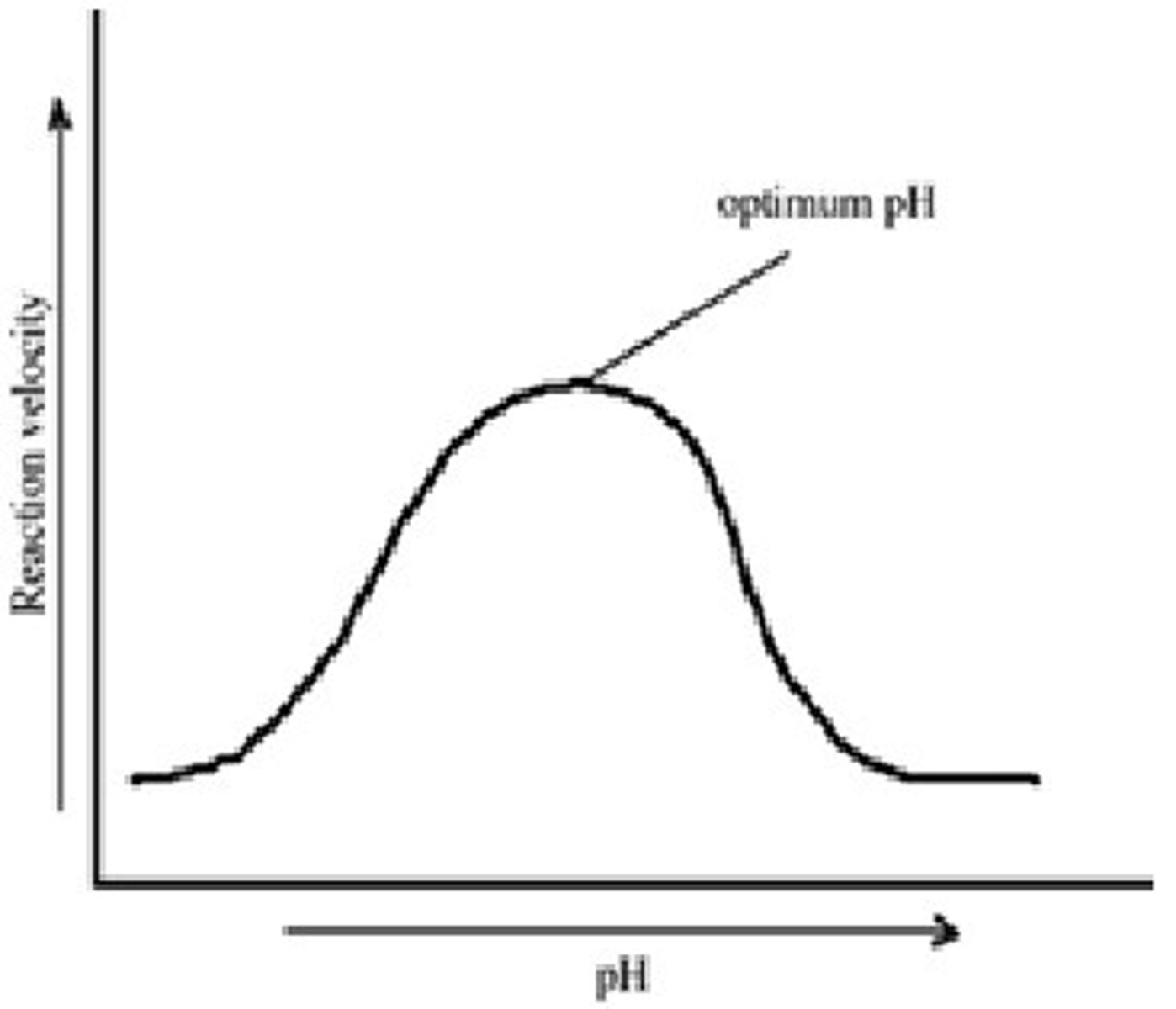
pH
most enzymes work best in neutral conditions (pH7)
extreme pH leads to enzyme being denatured
fastest rate of reaction is at the optimum pH
pH graph reaction
1. low pH denatures the enzyme, reduces rate
2. optimum pH, maximum rate
3. high pH denatures the enzyme, reduce rate
enzyme/substrate concentration
rate of reaction increases by adding more enzyme/substrate
this increases initial rate of reaction until maximum initial rate is reached
egg experiment
Heat & egg: egg goes colourless liquid -> white solid
pH & egg: colourless liquid -> white solid
both change the structure of the protein
liver experiment
A metabolically active organ
Liver & hydrogen peroxide: bubbles of oxygen, a bit exothermic
Manganese IV oxide & hydrogen peroxide: few bubbles of oxygen, exothermic
Liver & heat: liver's structure changed, doesn't react with hydrogen peroxide anymore
Manganese IV oxide & heat: no effect on it, still reacts
Amylase
made in salivary glands
works in the mouth/duodenum
acts on starch
end products maltose
protease
made in stomach/pancreas
works in stomach/duodenum
act on protein
end products amino acids
lipase
made in pancreas
works in duodenum
acts on lipids
end products glycerol and fatty acids
maltase
made in the wall of small intestine
works in ileum
acts on maltose
end products glucose
experiment temp & amylase
4 diff temps 10, 20, 40, 80
Presence of starch, iodine from yellow -> blue/black
Dimple tile, water baths, stopwatch
experiment pH & enzymes
cellulase breaks down cellulose in plant cell wall
more juice can move out of the cytoplasm/vacuole
measuring cylinder, apple, funnel