Pharmacology of the neuromuscular system
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
what is the motor unit
motor nerve + muscle fibres it controls
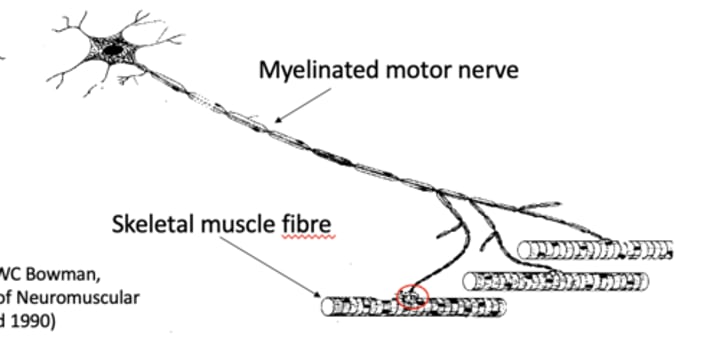
how big is the gap between the nerve and the muscle?
60nm
what cell forms 'lids' over the junctional cleft?
Schwarnn cells
what are the 5 things drugs can interfere to modify synaptic transmission?
synthesis, storage, release, receptors, removal mechanism of NTs
what is the role of Ca2+ in neurotransmission?
Triggers release of synaptic vesicles (acetylcholine)
what causes calcium channels to open?
action potentials
what is CAT?
Choline Acetyl Transferase
what is the function of CAT?
synthesises acetylcholine (ACh)
what 2 compounds is ACh synthesised from?
choline + acetylchoenzyme A (AcCoA)
What does hemicholinium inhibit?
blocks uptake of choline (stops synthesis)
what does AH5183 (vesamicol) do?
blocks uptake of Ach into vesicles (prevents storage)
how can Mg2+ stop neuromuscular transmission?
they block voltage gated calcium ions
how does Botox (botulinum toxin) work?
blocks the process of exocytosis (prevents release)
Clostridium botulinum gives what drug?
botulinum toxin
if botox is ingested it can cause death, how?
stops contraction of diaphragm and intercostal muscles- breathing stops
What is blepharospasm? how is it treated?
involuntary tight closure of the eyelids- treated with small amounts pf botox
what is hyperhidrosis?
excessive sweating
what type of receptors to ACh activate after they diffuse across the junctional gap?
NAChR- nicotinic ACh receptors
Acetylcholine is the only NT in neuromuscular transmission, true or false?
true
in the synapse, an enzyme hydrolyses ACh, what is it called?
AChE- acetylcholinesterase
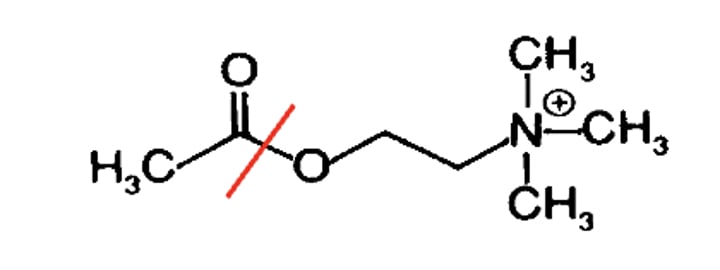
how long is an action potential?
2ms (0.02sec)
nicotinic receptors are what type of receptors?
ionotropic/ ion channel
Describe nicotinic receptors (3)
-5 subunits
-non-selective cation channel
-permeable to Na+ and K+
what is epp?
end plate potential- depolarisation of muscle membrane after NAChR activation
reversible competitive antagonist can act on NAChR to stop ACh binding and activating, T or F
true
what is tubocurarine?
competitive antagonist at NAChR
what is the clinical use of reversible competitive antagonists?
muscle relaxants
What does neostigmine do?
reverses the effect of general anaesthesia
why must patients be artificially ventilated when administered muscle relaxants?
they cannot breathe- diaphragm and intercostal muscle contraction is inhibited by muscle relaxant
Suxamethonium (succinylcholine) is an ______________ at NAChR
agonist
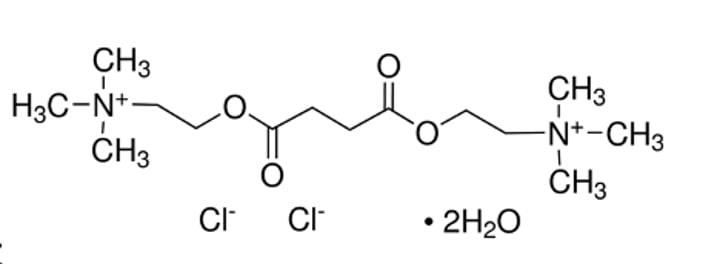
describe the structure of suxamethonium
2 molecules of ACh joined
How does suxamethonium prolong transmission?
it cannot be hydrolysed by AChE
how quick does suxamethonium take effect?
few sec
how does suxamethonium relax skeletal muscle?
refractory/recovery period is not allowed to occur- only one action potential goes through then no more