Week 13: Prevention & Off-Loading
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
ounce of prevention is worth
a pound of cure
Chronic wound incidence
5.7-6.5 million
Main comorbidities
• Diabetes
• Obesity
• Vascular disease
Average cost to heal wounds
$3,927
Locations most susceptible to pressure ulcers in supine
heels and sacrum
Toes are susceptible to pressure from
bedsheet
Sidelying locations susceptible to ulcer development
Ear
Elbow
Acromion (shoulder)
Greater trochanter
Top leg medial epicondyle
Bottom leg lateral epicondyle
Heel
Malleoli
Seated locations susceptible to ulcer development
Head
Angles of scapula
Sacrum
Ischial tuberosities
Heel
Toes
3 principles for positioning to prevent pressure ulcers
1. Spread out the pts weight over a larger surface area
2. Position so bony prominences are not in contact with support surface
3. Changes positions regularly
Position change fx while in bed
Minimum of every 2 hrs
Supine locations susceptible to ulcer development
Occiput
Scapula/shoulder
Elbows
Sacrum/buttocks
Heels
Toes
Position change fx while sitting in a chair
every 15 min
position the shoulder for positioning
ER
Why do we change positions?
So that the pressurized area can reprofuse with oxygen
basic seating principles for ulcer prevention
• Thighs horizontal to ground with knees and hips even
• Feet supported so knees are even with hips
• Back supported to keep normal curves
• Ear, shoulder, hip in alignment
• Support surface ends 1.5-2" behind popliteal fossa
Common seated position for ulcer prevention
90/90/90
or
95 hips / 85 knees / 90-95 ankles
Common supine position for ulcer prevention
knees/ hips flexed 25-30 deg
slight turn to take pressure off sacrum
float heels w/ support under entire calf
hip neutral rotation
dorsiflexion to 90 deg to prevent contracture
Common sidelying position to prevent ulcers
Turned to 30 deg
Upper leg position on pillows w/ slight hip/knee flexion
Upper arm 55 deg of abduction with 30 deg horizontal ADD
How do you maintain the 30 deg turn in sidelying?
Entire trunk and pelvis must be supported
Positioning purpose
Comfort
Redistributing a person's BW over large surface area
Contracture prevention
Keys to pressure ulcer prevention
Education
Positioning
Mobility
Nutrition
Managing incontinence
What should you perform every time when working with a pt in the hospital?
Skin inspection
if someone develops a pressure ulcer in the hospital
• the facility will not get paid to heal it
Turning schedule
Every 2 hrs in bed
Every 15 min in chair
Every hr if dependent on a support system
pressure in sitting vs supine
sitting is more in a smaller area when sitting vs supine
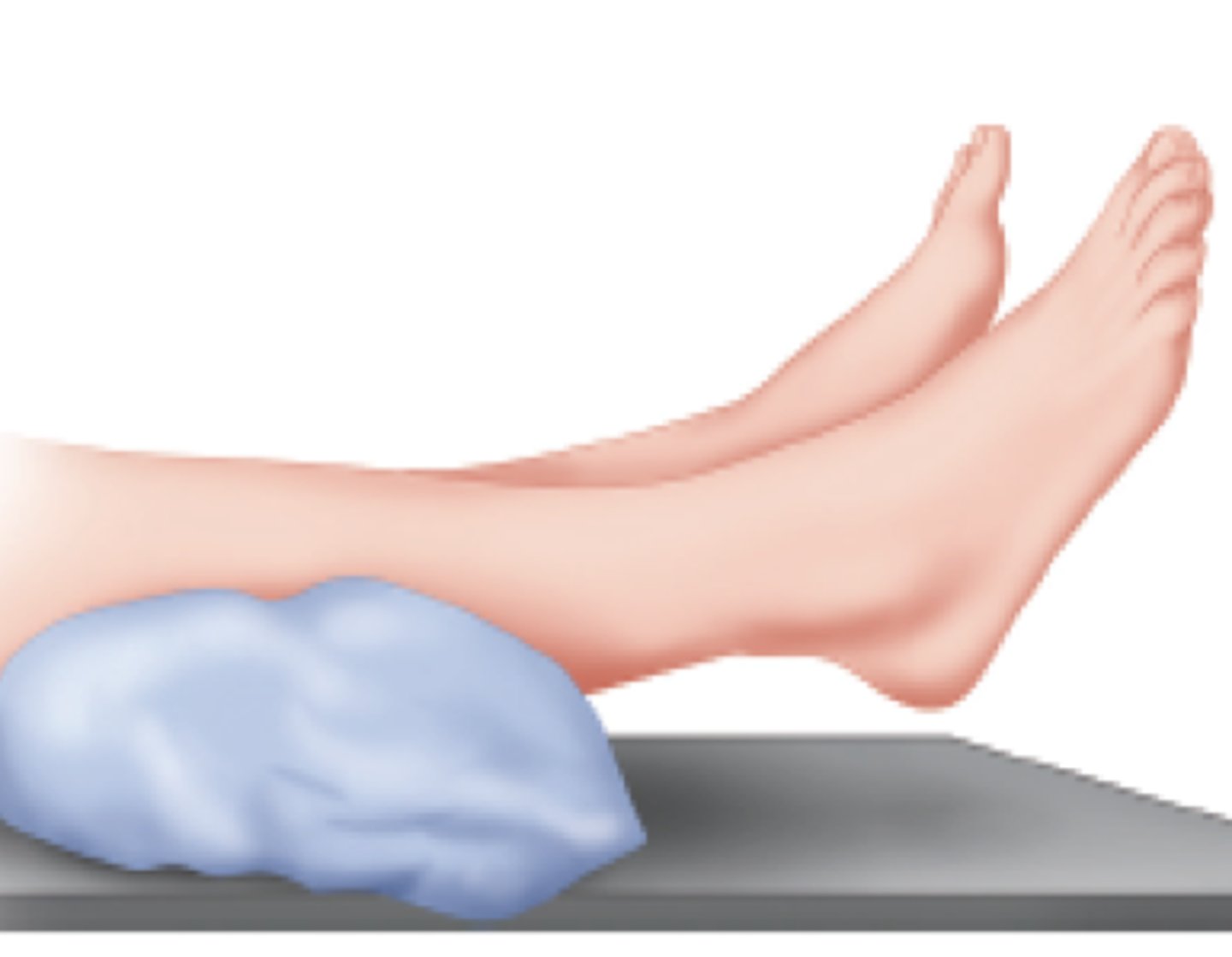
Floating heels
pillow is placed under ankle to allow the heel to hang over the pillow
Trapeze uses can assist with
pressure relief
Trapeze negatives
• people may want to take them home instead of learning how to properly use their legs
How do you identify at risk pts?
Braden scale
Braden scale
Pressure ulcer grading scale ranging from 6-23
Lower score Braden scale
Greater impairment and a higher risk for developing a pressure ulcer
Braden score <18
Pt at risk for developing pressure ucler
Braden score 15-18
mild risk
Braden score 13-14
moderate risk
Braden score <13
High risk
Footcare guidelines
1. Inspect feet daily
2. Do on walk barefoot
3. Do not soak feet
4. Moisturize feet but not b/w toes
5. Toenails cut straight across
6. Seek medical attention if callus forms
7. Control DM/stop smoking
why no moisturizer between the toes
fungal growth
calluses can cause
skin breakdown beneath the,
What should you educate a diabetic pt on?
Footcare guidelines
loss of sensation
diabetic nails should only be cut by a
podiatrist
Duration required to restore oxygen levels to unloaded levels
1-2min of complete relief
What should you recommend prior to surgery?
ABI
Support surface
anything we are sitting or lying on
Types of surfaces
Seat cushions
Mattresses
Mattress overlays
Mattress replacements
integrated bed systems
Factors to consider of the pts status
Body structure
BW
Continence
Risk of development
Dependency/mobility
Factors to consider of the pts needs
pressure redistribution
shear reduction
temperature control
moisture control
when getting a patient out of bed
Lift, don't drag
What happens to the temperature of an area that is pressurized?
Localized temperature increases
increased temperature causes
• metabolic demands of the tissue also increase
3º drop in skin temperature results in a
• 14% reduction in interface pressure
wicking quality
• Takes fluid off skin and redistributes to environment
• Important for incontinence
Devices and support surfaces NOT a substitute for
turning and pressure relief
Breakdown pressure
32 mm Hg
Pressure reducing technologies
lower tissue interface b/w 23-32mmHg
Pressure relieving technologies
lower tissue interface pressure to <23mmHg
Static support surfaces
used to prevent wounds from forming
static support surfaces are used
prophylactically
Static support surface types
Foam
Foam/air
Foam/water
Foam/gel
• mattress replacements or mattress overlays or cushions
Dynamic support surface types
motorized or nonmotorized
Motorized dynamic support system
Electric device that uses air or fluid flow to redistribute pressure more equally across the body
Dynamic support surfaces
electric devices that use currents of air or fluid to redistribute pressure across the body
Nonmotorized dynamic support surfaces
use valve system to redistribute pressure
Immersion
depth of penetration into a support surface
Pressure relief via immersion
air filled cushions that sink down and allow pt to immerse into them
Consideration for immersion techniques
make sure pt doesnt bottom out and hit a hard surface
Pressure relief via envelopment
support surface conforms to body's structure
Materials used in support surface technology
Gel
Foam
Fluid/air-filled bladders
Gel in support surface tech
able to conform in proportion to the load applied to it
Gel disadvantages
affected by temperature
gel cushions in a cold environment
cold and firm
gel cushions in a hot environment
soft and moisture retentive
Gel advantages
doesn't require much maintenance
Key to using foam
thick enough so person doesnt bottom out while sitting on it
With foams we need to ensure
it's not too stiff or dense to limit the ability to envelop or immerse a patient
Fluid/air-filled bladders
fluid moves in chambers in response to pts movement

Features of support surfaces
air fluidized
alternating pressure
lateral rotation
low air loss
Air-fluidized bed
contains collection of tiny beads with a mattress cover-beads are blown upward on warm air.
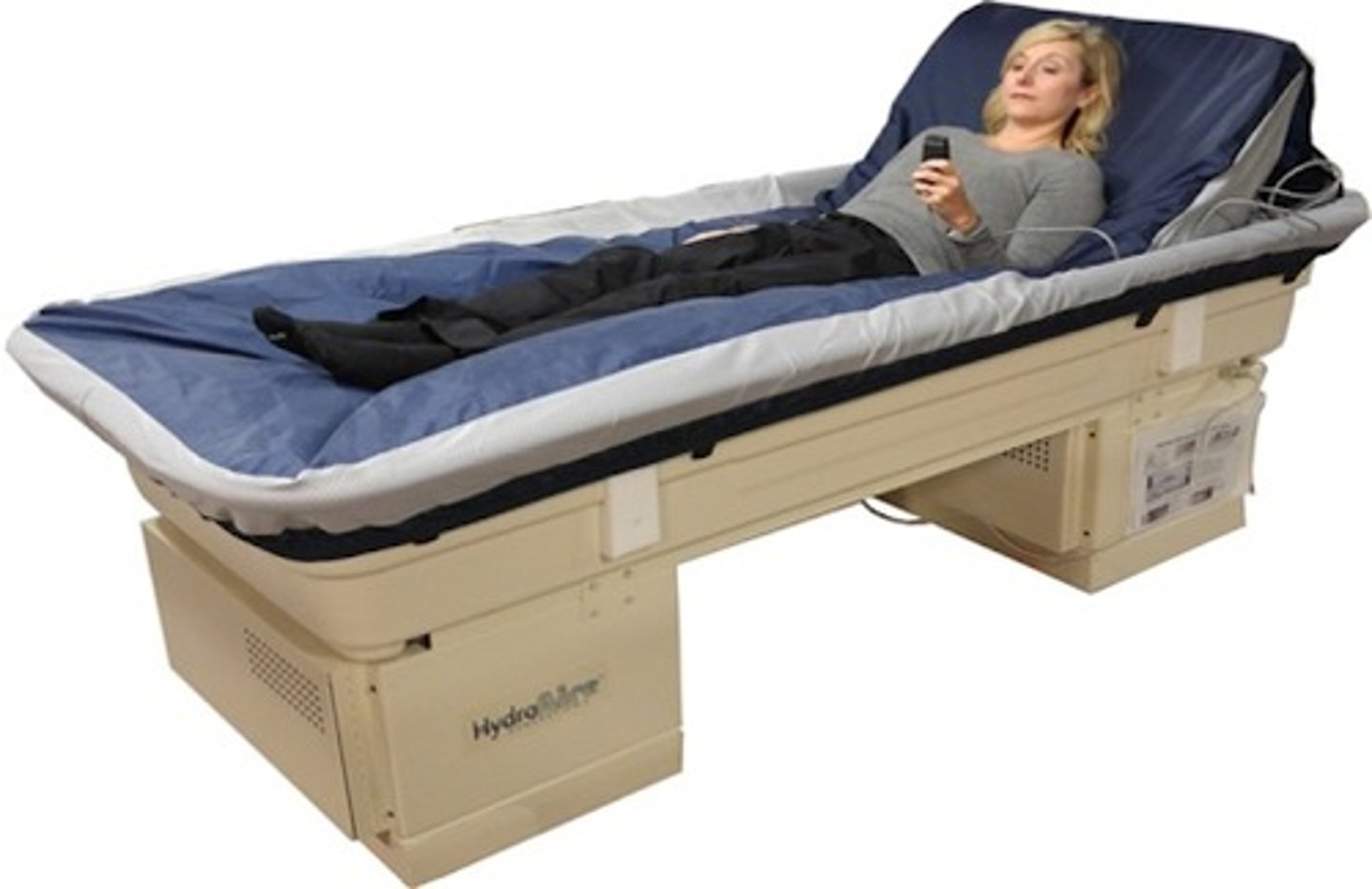

What population is air-fluidized bed used for?
large burns
large skin grafts
Low-air-loss bed
mattress placed directly on existing bed frame or as overly on other mattress, pressure redistribution and air flow to manage heat/moisture of skin
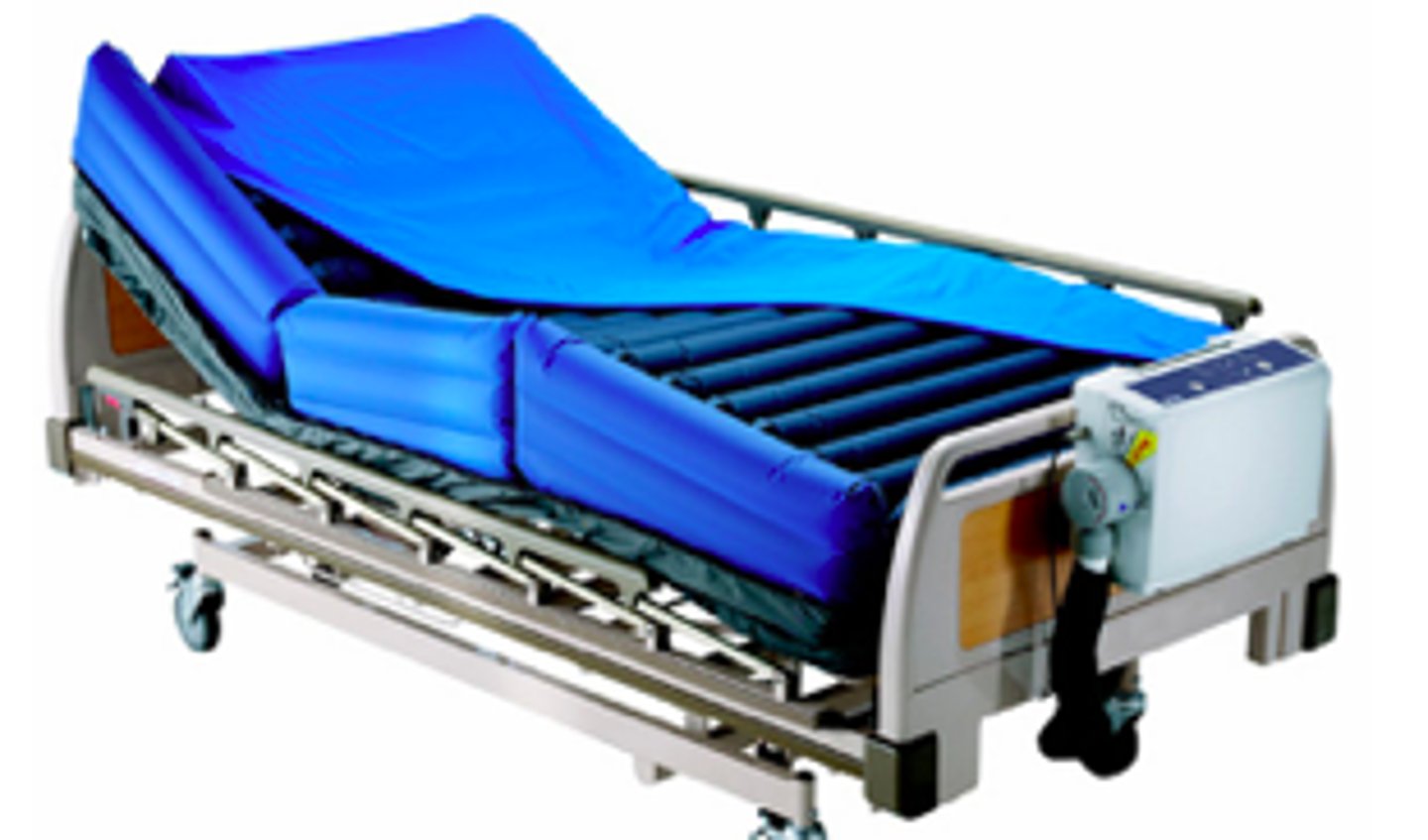

How does the low-air-loss bed decrease maceration?
Porus fabric for wicking
Blower to get heat/moisture out
Alternating pressure bed
supports the person on a series of compartments that fill with air and then deflate on a rotating basis
Lateral rotation bed
passively move Pt side to side
improve circulation
good for pulmonary Pt and spinal fractures
still need to adjust Pt position
Population common for lateral rotation/roto bed
spinal cord injury
Donut cutouts are not so good because
• the area around the cutout breaks down from higher pressure
NO ULCERS
Nutrition and fluid status
Observation of skin
Up and walking or assist with position changes
Lift, don't drag
Clean skin and continence care
Elevate heels
Risk Assessment
Support surfaces
SKIN
Surface selection
Keep turning
Incontinence management
Nutrition
How to prevent shear during transfers?
Lift, don't drag
• Avoid shear when raising HOB
• Can cause shear to sacral area and low back
policy for lifting patients
• 50lbs per clinician when moving people
floating the heels
• Pillow longitudinally, not sheepskin heel cups
Recumbent position
lying down in any position
Sitting position for <90 deg hip flexion
Cushion for stabilization
Open seat to back angle for accommodation
Sitting position for <90 deg knee flexion
Adjustable/elevating leg rests to accommodate for ROM
A cushion to prevent sliding
calf support
Sitting position for flexible scoliosis
build up the lower side
Cushion w/ pressure elimination at ischials
Pelvic obliquity
one side of the pelvis is lower than the other side, named by the lower side
fixed scoliosis
can't get pelvis level
Adjustable soliosis
able to get pelvis level
Sitting position for fixed scoliosis
build up higher side (bring support surface to meet higher side)
Sitting position for kyphosis
Tilt chair back so head and trunk align
Pillow/support under dowagers hump and head
Sitting position for below knee amputee
Stump board
cushion under legs