Microbial Diversity: EUKARYOTIC MICROBES
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
LEARNING OUTCOMES
compare and contrast the differences between ALGAE, PROTOZOA, and FUNGI
explain what is meant by a “RED TIDE” and its MEDICAL SIGNIFICANCE
list the four major categories of PROTOZOA and their most important DIFFERENTIATING CHARACTERISTICS
define the term PELLICLE, CYTOSTOME, and STIGMA
list five major infectious diseases of humans that are caused by PROTOZOA and five that are caused by FUNGI
define and state the importance of PHYCOTOXINS and MYCOTOXINS
explain the differences between AERIAL and VEGETATIVE HYPHAE, SEPTATE and ASEPTATE HYPHAE, and SEXUAL and ASEXUAL SPORES
Explain the major DIFFERENCE between a LICHEN and a SLIME MOULD
Eukaryotic Microbes: ALGAE
singular alga
photosynthetic microorganisms
protist, classified under the kingdom PROTISTA
contain double-membrane cell organelles
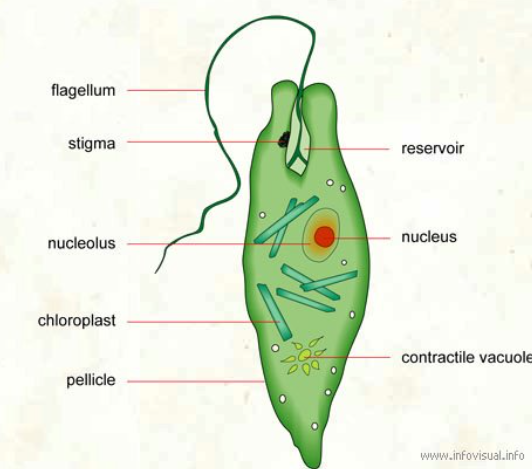
pellicle, a thickened cell membrane
stigma or eyespot, a light-sensing organelle
flagella for locomotion
pellicle
a thickened cell membrane
stigma or eyespot
a light-sensing organelle
flagella
locomotion
STRUCTURE OF A ALGAE
ALGAE SIZE
tiny, unicellular microorganisms
large, multicellular, plant-like seaweeds
ALGAE ARRANGEMENTS
colonies
strands
solitaries

ALGAE HABITAT
fresh water
salt water
wet soil
wet rocks
PHYLUM AND COMMON NAME
bacillariophyta
chlorophyta
chrysophyta
dinoflagellata
karenia brevis
zooxanthellae
euglenophyta
phaeophyta
rhodophyta

BACILLARIOPHYTA
diatoms

BACILLARIOPHYTA structural arrangement
unicellular

BACILLARIOPHYTA predominant color
olive brown

BACILLARIOPHYTA photosynthetic pigments
Chlorophyll c
Carotenoids
Xanthophylls

BACILLARIOPHYTA habitat
freshwater and seawater
CHLOROPHYTA
green algae
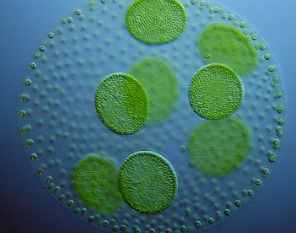
CHLOROPHYTA structural arrangement
unicellular/multicellular
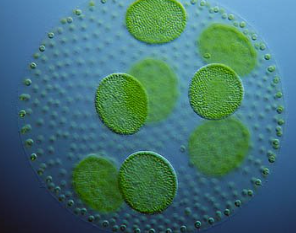
CHLOROPHYTA predominant color
green
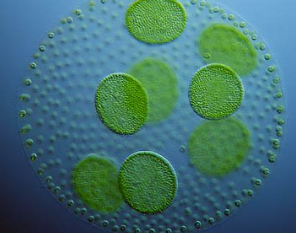
CHLOROPHYTA photosynthetic pigments
chlorophyll b
carotenoids
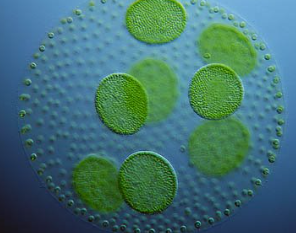
CHLOROPHYTA habitats
freshwater (predominant) and seawater
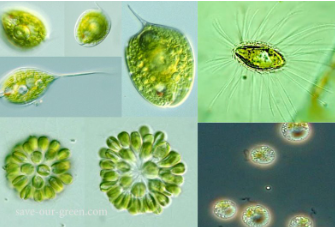
CHRYSOPHYTA
golden brown algae
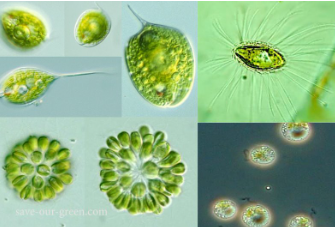
CHRYSOPHYTA structural arrangement
most unicellular flagellates
some are amoeboid
others non-motile
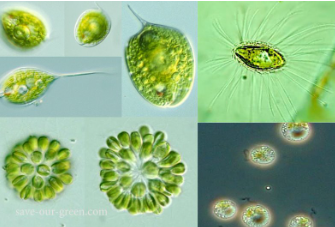
CHRYSOPHYTA predominant color
golden olive
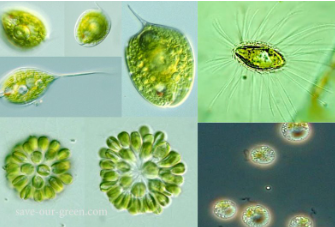
CHRYSOPHYTA photosynthetic pigments
chlorophyll c
carotenoids
xanthophylls
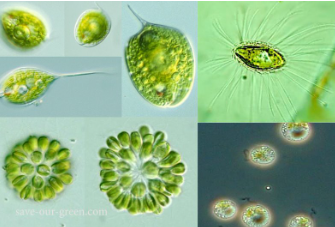
CHRYSOPHYTA habitat
freshwater
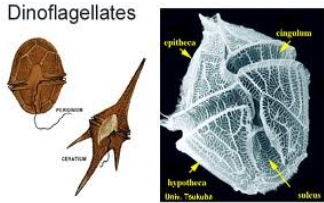
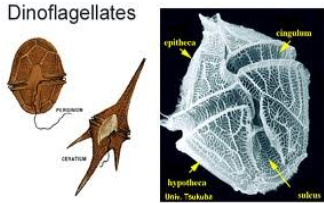
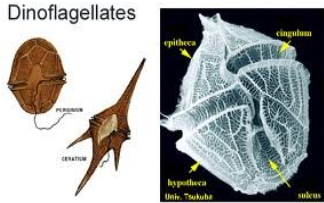
DINOFLAGELLATA
dinoflagellates
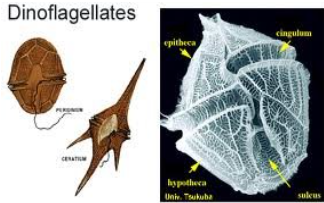
DINOFLAGELLATA structural arrangement
unicellular
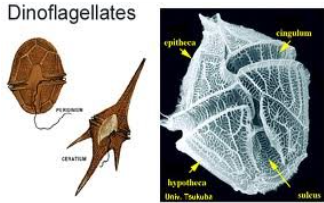
DINOFLAGELLATA predominant color
brown
DINOFLAGELLATA photosynthetic pigments
chlorophyll c
carotenoids
xanthophylls
DINOFLAGELLATA habitat
freshwater/ seawater
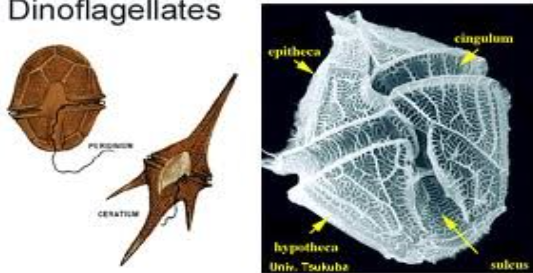
DINOFLAGELLATA
possess two flagella
one wrap around a groove along the middle of the cell
one trailing free
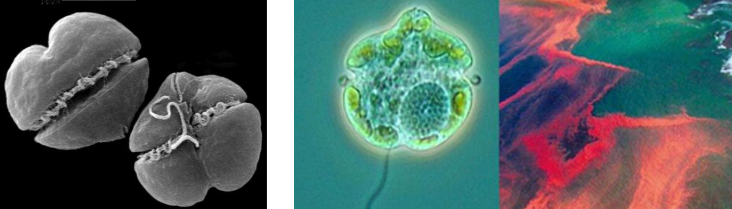
KARENIA BREVIS
(scanning electron micrograph)
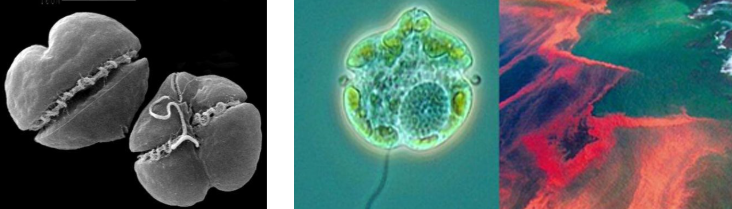
KARENIA BREVIS
they form blooms that color the water red, reddish-brown, yellow
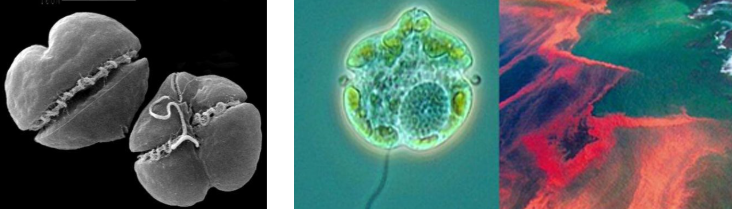
KARENIA BREVIS
common cause of red tide in Florida
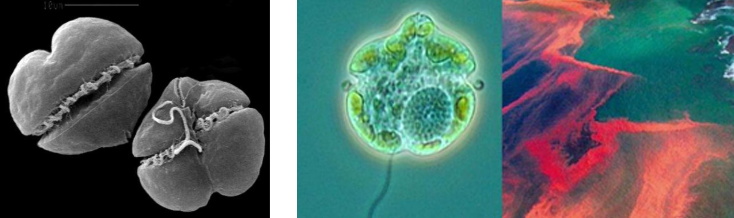
KARENIA BREVIS
behavioral changes
muscular impairments
disorientation
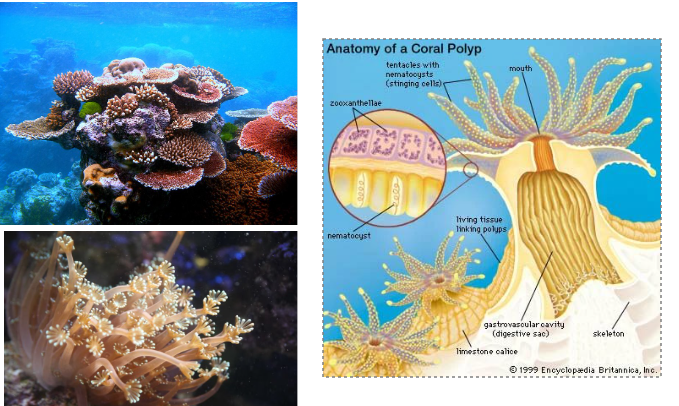
ZOOXANTHELLAE
important in reef-building coral
they fix carbon dioxide by photosynthesis, release organic matter used by coral, and help in the formation of coral skeleton
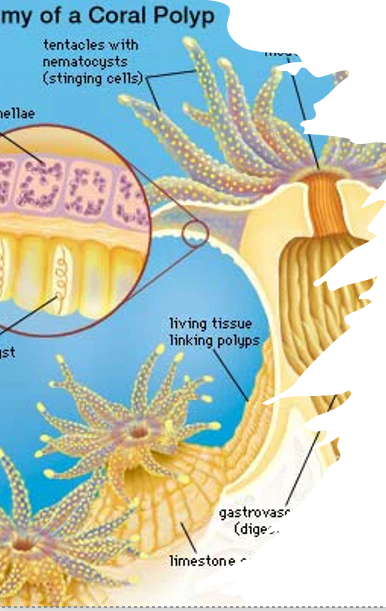
CORAL ANATOMY
Corals provide the zooxanthellae with a protected environment, and the coral polyp cells produce carbon dioxide and water that the zooxanthellae need for photosynthesis.
The zooxanthellae use energy from the sun to turn the carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and help the coral to remove wastes.
Most importantly, zooxanthellae supply the coral with the building blocks of sugars and proteins, which are the products of photosynthesis.
The coral uses these products to make proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, and produce calcium carbonate. This leads to coral growth and reproduction.
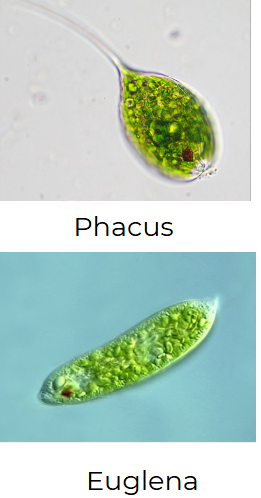
EUGLENOPHYTA
euglena
EUGLENOPHYTA structural arrangement
unicellular
EUGLENOPHYTA predominant color
green
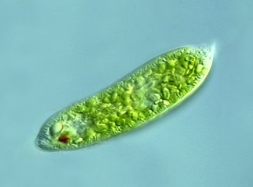
EUGLENOPHYTA photosynthetic pigments
chlorophyll b
carotenoids
xanthophylls
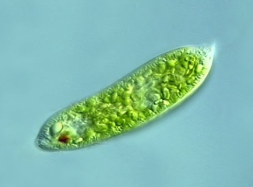
EUGLENOPHYTA habitat
freshwater

PHAEOPHYTA
brown algae

PHAEOPHYTA structural arrangement
multicellular seaweeds

PHAEOPHYTA predominant color
olive brown

PHAEOPHYTA photosynthetic pigments
chlorophyll c
carotenoids
xanthophylls

PHAEOPHYTA habitat
seawater: most commonly cold environments

RHODOPHYTA
red algae

RHODOPHYTA structural arrangement
multicellular seaweeds

RHODOPHYTA predominant color
red to black

RHODOPHYTA photosynthetic pigments
chlorophyll d
carotenoids
phycobilins

RHODOPHYTA habitat
seawater/freshwater; most commonly tropical environments
ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE
FOOD SOURCE
SOURCE OF PHYCOCOLLOIDSALGIN
CARRAGEENAN
AGAR
FERTILIZER
FOOD ADDITIVES
CORALINE ALGAE
EUROPE
NUTRITION SUPPLEMENT
SOURCE OF BIOFUELS
FOOD SOURCE
people discovered that many seaweeds are edible
some of red and brown algae
seaweed is a big business in China, Japan, Korea and other nations
SOURCE OF PHYCOCOLLOIDS
gelatinous chemicals that are used in food processing and manufacturing of other products
ALGIN
major source is giant kelp (Macrocystis)
Laminaria
ALGIN
stabilizer and emulsifier
baking industry
thickener and emulsifier
manufacture
textile industry
ALGIN stabilizer and emulsifier
ice cream, cheese, and toppings
ALGIN baking industry
prevent frosting and pies from becoming dry
ALGIN thickener and emulsifier
pharmaceutical and chemical industries
ALGIN manufacture
shampoo, shaving creams, plastics, pesticides
rubber products, paper, paints, and cosmetics
ALGAE textile industry
thickens the printing paste to provide sharper prints
CARRAGEENAN
obtained from red algae
Irish moss (Chondrus) in the North Atlantic
Eucheuma in the tropics
used as an emulsifier
AGAR
has the ability to form jellies
used to protect ham, fish, and meats during canning, in low-calorie foods, and as a emulsifier
used in laxatives and other pharmaceuticals and cosmetics
used as a medium in which to grow bacteria
used in research involving the analysis of proteins and DNA
obtained from red algae
Geledium, Gelidiella, and Pterocladiella
coralline algae
used in Europe to reduce the acidity of soils
sources of biofuels
form of ethanol and oil
Medical Significance
very rare cause of human infections
Prototheca
protothecosis
lives in soil and can enter the wounds
produces subcutaneous lesion to a crusty, warty-looking lesion
can cause debilitating and fatal infection as it enters the lymphatic system especially of immunosuppressed individuals
Eukaryotic Microbes: PROTOZOA
eukaryotic organism under the kingdom PROTISTA
animal-like organisms
most are unicellular, ranging from 3 µm to 2,000 µm
most are free-living found in soil and water
pellicles, cytostomes, contractile vacoules, pseudopodia, cilia, and flagella
they do not have chlorophyll to make their own food
some ingest whole algae, yeast, bacteria, and smaller protozoans as their source of nutrients
others live in dead and decaying organic matter
eukaryotic organism kingdom
kingdom PROTISTA
eukaryotic organism unicellular range
3 µm to 2,000 µm
Eukaryotic Microbes _______ to make their own food
do not have chlorophyll
some ingest whole algae, yeast, bacteria, and smaller protozoans as their __________
source of nutrients
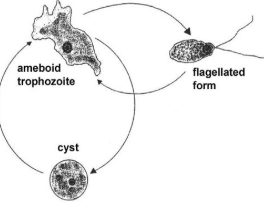
Stages of the Life Cycle of Protozoans
Trophozoite stage
Cyst stage
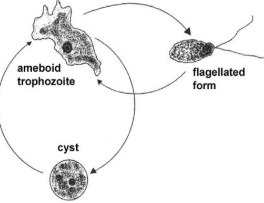
Trophozoite stage
motile, feeding, dividing stage in a protozoan’s life cycle
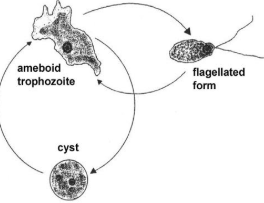
Cyst stage
non-motile, dormant, survival stage
it is like in some ways, bacterial spores
some protozoans are parasites
they break down and absorb nutrients from the body of the host in which they live
many protozoans are pathogens
Malaria
Giardiasis
African sleeping sickness
Amebic dysentery
protozoans form symbiotic relationship with the ___
host animals
e.g intestinal protozoa in termites digest the wood eaten by termites to absorb nutrients necessary for life
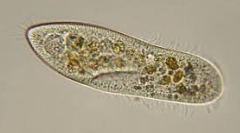
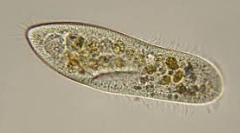
CILIATES
the most complex of all protozoans
Means of movement
cilia
Method of asexual reproduction
transverse fission
Method of sexual reproduction
conjugation
Representatives
Balantidium coli, Paramecium, Stentor, Tetrahymena, Vorticella
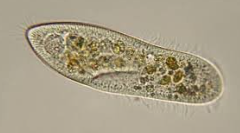
CILIATES Means of movement
cilia
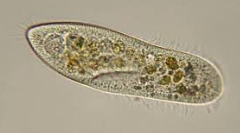
CILIATES Method of asexual reproduction
transverse fission
CILIATES Method of sexual reproduction
conjugation
CILIATES representatives
Balantidium coli, Paramecium, Stentor, Tetrahymena, Vorticella
Cilia
hairlike structures that are on the surfaces of the organisms

Balantidium coli
causes dysentery in underdeveloped countries
usually transmitted to humans from drinking water contaminated by swine feces
the only ciliates that causes disease to humans

causes dysentery in underdeveloped countries
Balantidium coli

usually transmitted to humans from drinking water contaminated by swine feces
Balantidium coli

the only ciliates that causes disease to humans
Balantidium coli

AMEBAE
Means of movement
pseudopodia (false feet)
Method of asexual reproduction
binary fission
Method of sexual reproduction
flagellated sex cells when present
Representatives
Amoeba, Naegleria, Entamoeba histolytica
ameboid movement
extends the pseudopodium in the direction it intends to move and then the rest of the cell slowly flows into it
phagocytosis
ingest food by surrounding a food particle with pseudopodia
pinocytosis
ingesting of fluids for nutrients
food vacoule
a membrane-bounded container for food

AMEBAE Means of movement
pseudopodia (false feet)

AMEBAE Method of asexual reproduction
binary fission

AMEBAE Method of sexual reproduction
flagellated sex cells when present

AMEBAE Representatives
Amoeba, Naegleria, Entamoeba histolytica
ameboid movement
extends the pseudopodium in the direction it intends to move and then the rest of the cell slowly flows into it
phagocytosis
ingest food by surrounding a food particle with pseudopodia
pinocytosis
ingesting of fluids for nutrients
food vacoule
a membrane-bounded container for food
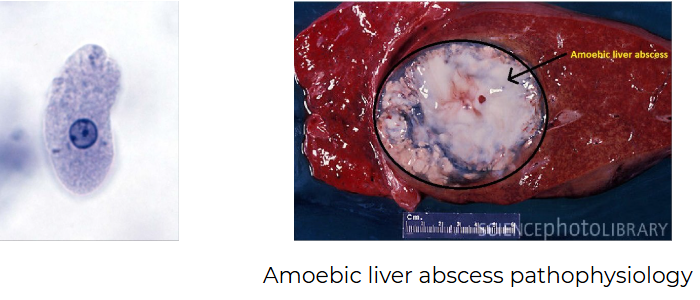
Entamoeba histolytica
causes amebic dysentery and extraintestinal abscesses
Dysentery
Dysentery
gastrointestinal disease caused by bacterial or parasitic infections. Symptoms include diarrhea, fever, nausea, vomiting, weight loss and stomach cramps.
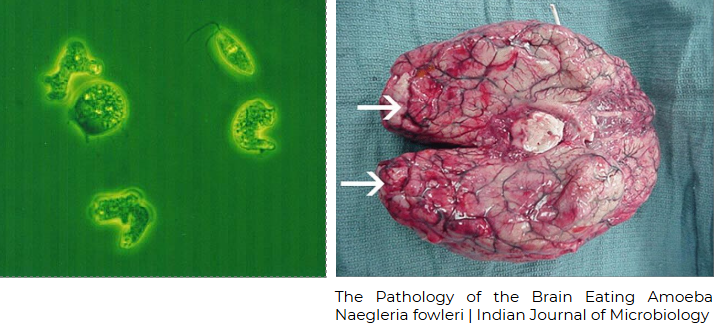
Naegleria fowleri
causes primary amebic meningoencephalitis
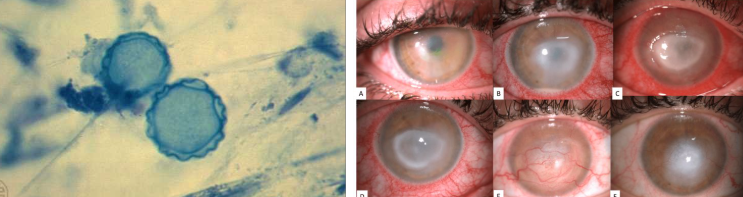
Acanthamoeba spp.
cause eye infections [keratitis]
a rare parasitic eye infection that affects the cornea