Osteology of pectoral girdle
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is the angle of inclination at the humerus?
angle of inclination = the angle between the humeral head and the shaft.
head of humerus faces medially and superiorly, forming 135 degree angle of inclination with long axis of humeral shaft (frontal plane)
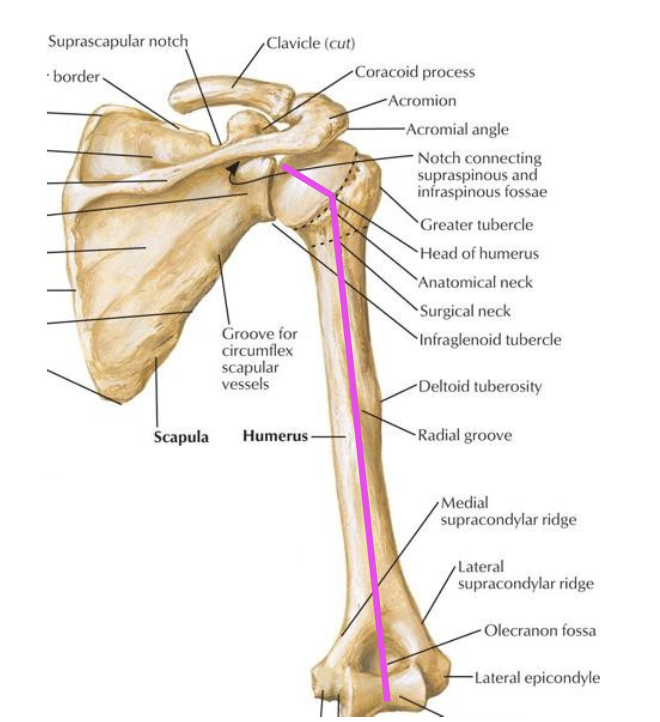
What is retroversion of the head of humerus?
The head is rotated 30 degrees posteriorly to medial-lateral axis thru the elbow (horizontal plane)
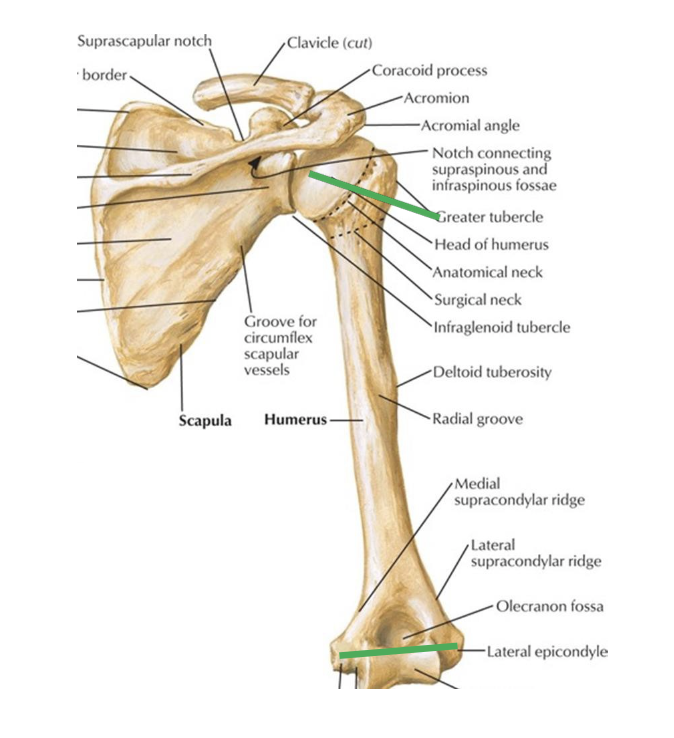
What are the joints of the pectoral girdle?
Sternoclavicular joint
Acromioclavicular joint
Glenohumeral joint
Scapulothoracic joint (not true anatomical joint)
What is scapulohumeral rhythm?
how humeral abduction is achieved
scapula and humerus move in 1:2 ratio as arm is raised (ABD) overhead
When arm is abducted 180 degrees, 60˚ occurs by upward rotation of scapula and 120˚ is by rotation (abduction) of the humerus at the GH joint
the initial 30 degrees only involves glenohumeral motion
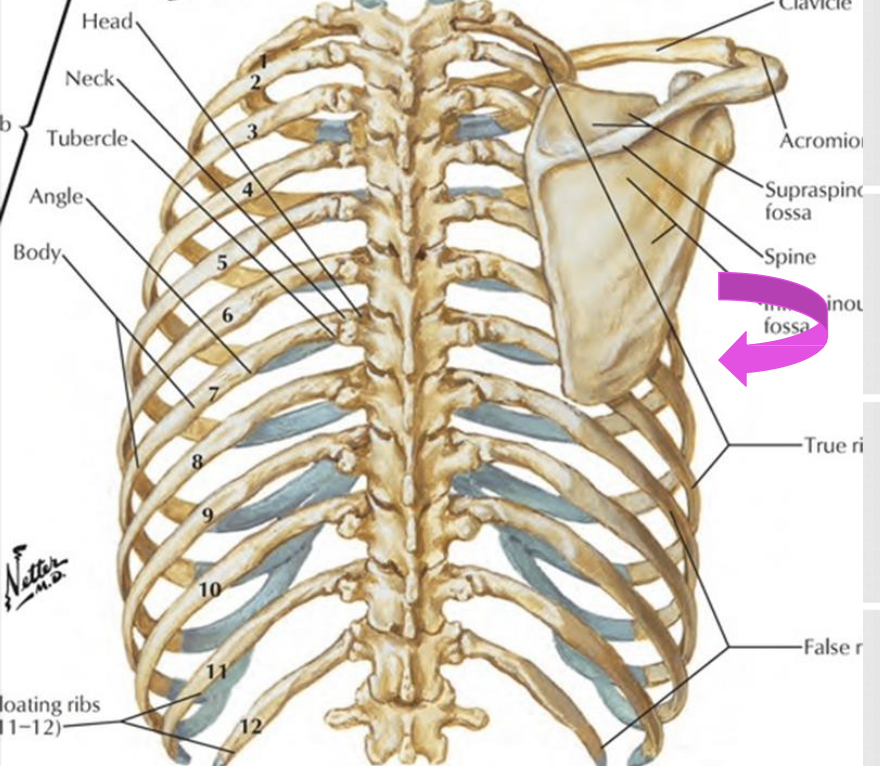
What passes through the spinoglenoid notch?
suprascapular nerve
spinoglenoid notch = passageway in posterior scapular region for the suprascapular nerve
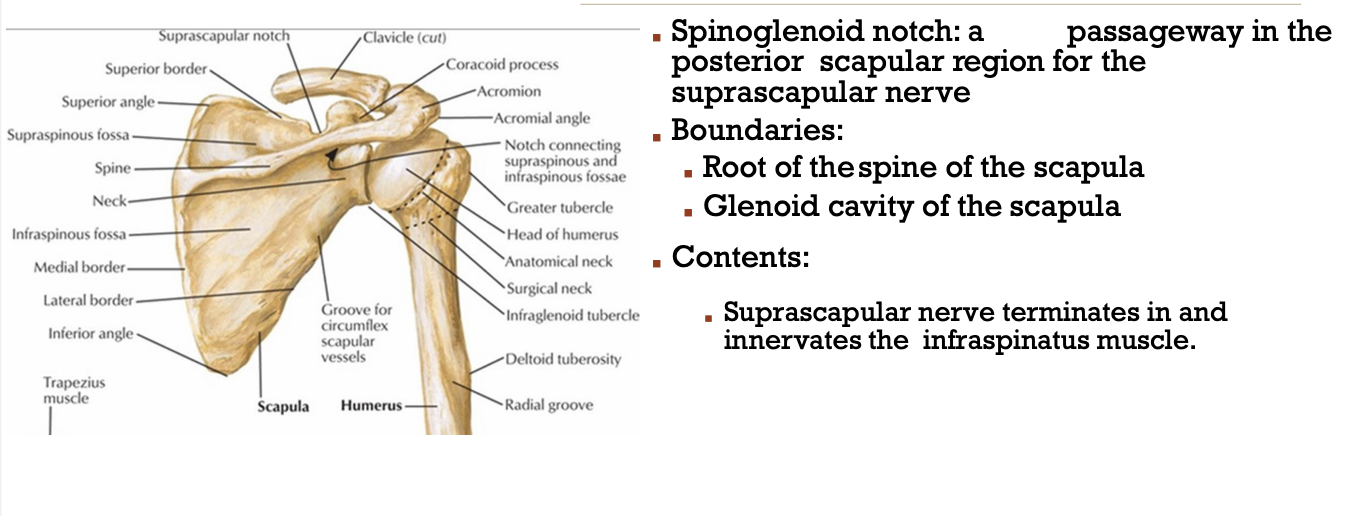
What does the suprascapular nerve innervate?
Infraspinatus muscle
What movements occur in sternoclavicular joint?
gliding in vertical plane
gliding in ant-post plane
rotation around longitudinal axis
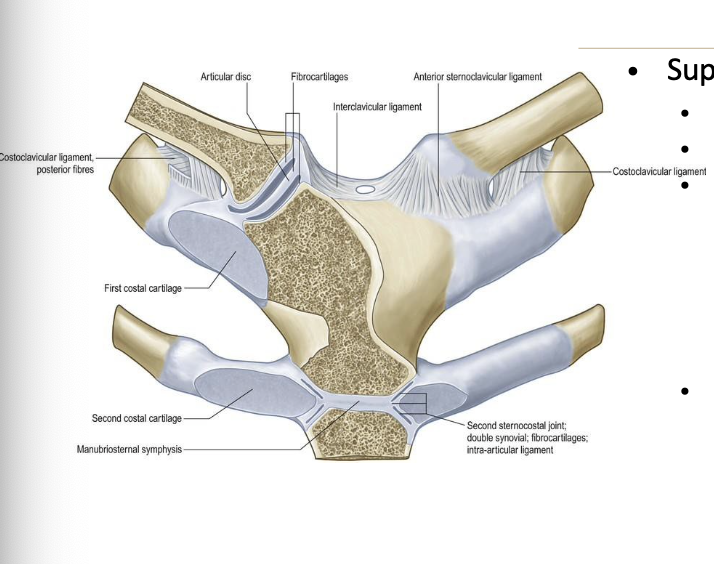
What structures support the SC joint?
Joint capsule
Articular disc
Intrinsic ligaments
anterior sternoclavicular ligament
posterior sternoclavicular ligament
Extrinsic ligaments
interclavicular ligament
costoclavicular ligament
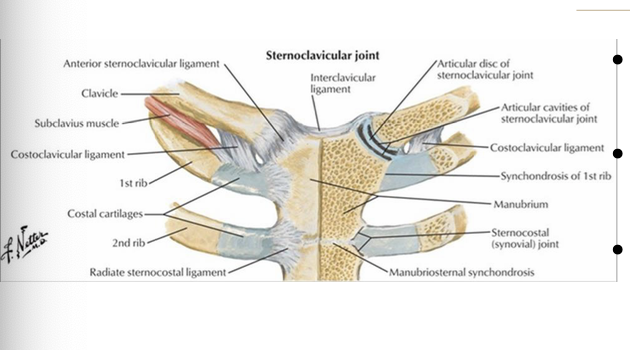
What arteries supply the SC joint?
internal thoracic and suprascapular arteries
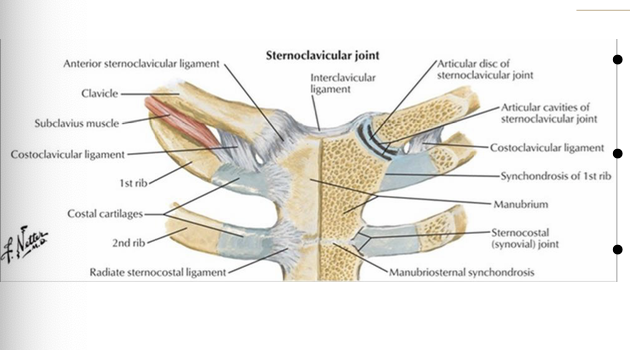
What nerves supply the SC joint?
medial supraclavicular nerve and the nerve to subclavius
What are the supporting structures of the acromioclavicular (AC) joint?
Joint capsule
articular disc (fibrocartilage - gliding)
acromioclavicular ligament
coracoacromial ligament
coracoclavicular ligament (2 ligaments)
- conoid ligament
- trapezoid ligament
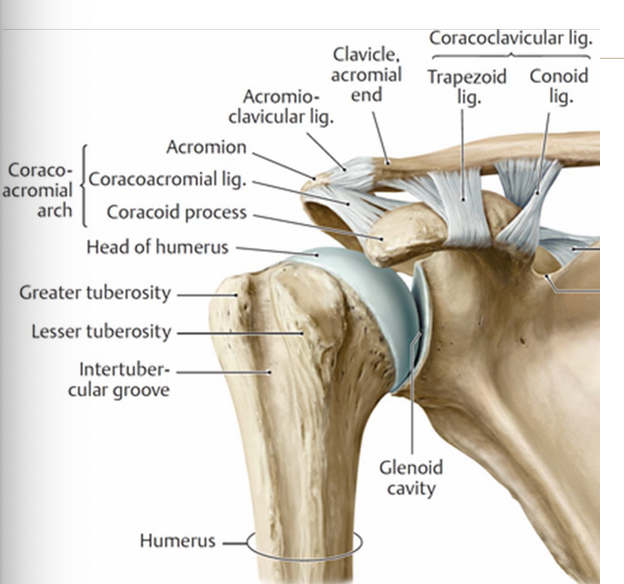
AC joint blood supply
suprascapular arteries
thoracoacromial arteries
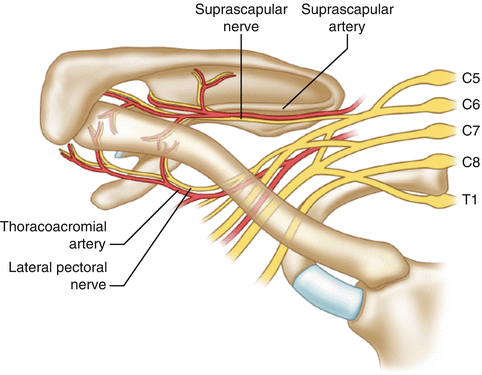
AC joint nerve supply
lateral pectoral nerve
axillary nerve
lateral supraclavicular nerve
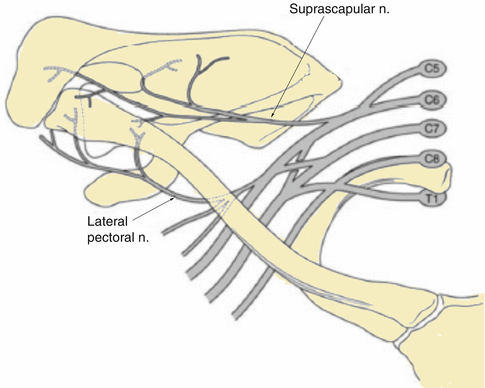
What type of joint is the scapulothoracic joint?
a physiological joint
no direct contact between scapula and thorax
scapula glides on thorax instead
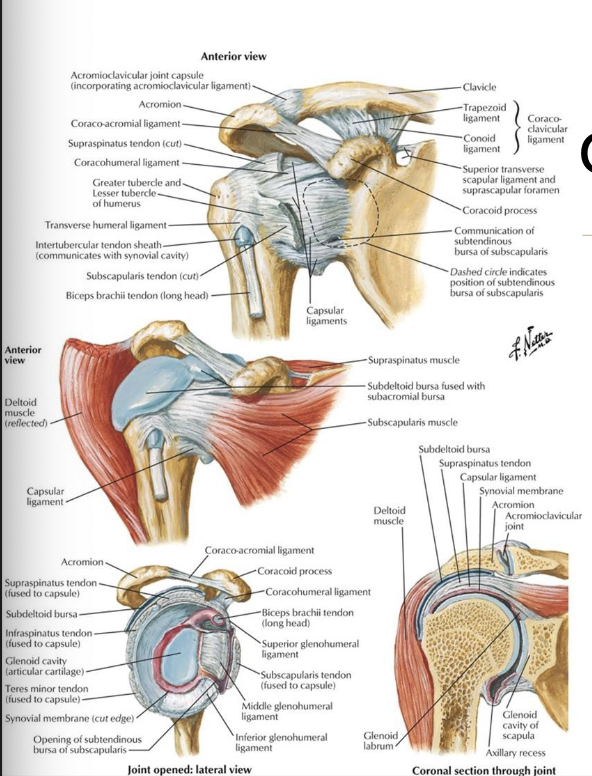
What covers the articulation of the glenohumeral joint?
hyaline (articular) cartilage
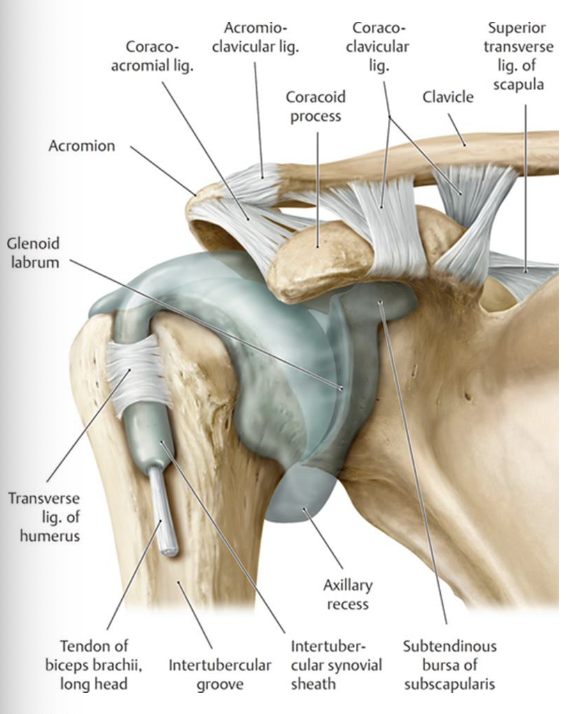
What classification is the GH joint?
synovial, triaxial, ball and socket joint
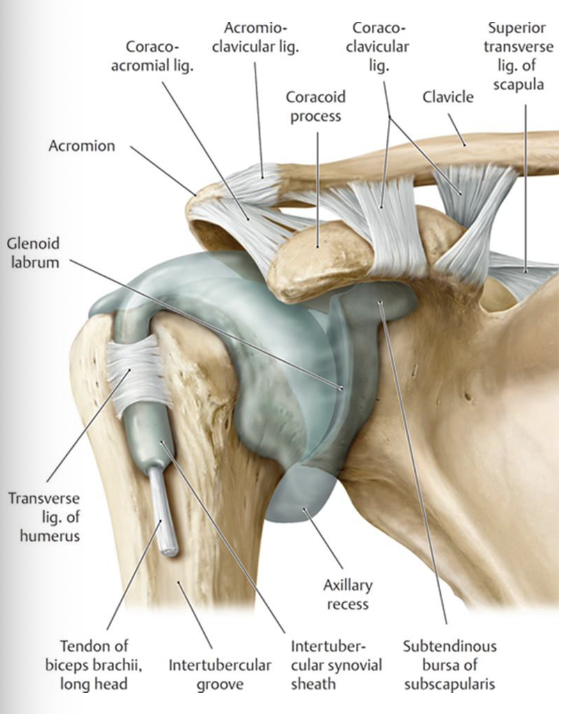
What are the supporting structures of the GH joint?
Glenoid labrum
- joint capsule
-glenohumeral capsular ligaments (3 of them)
-coracohumeral ligament
-transverse humeral ligament
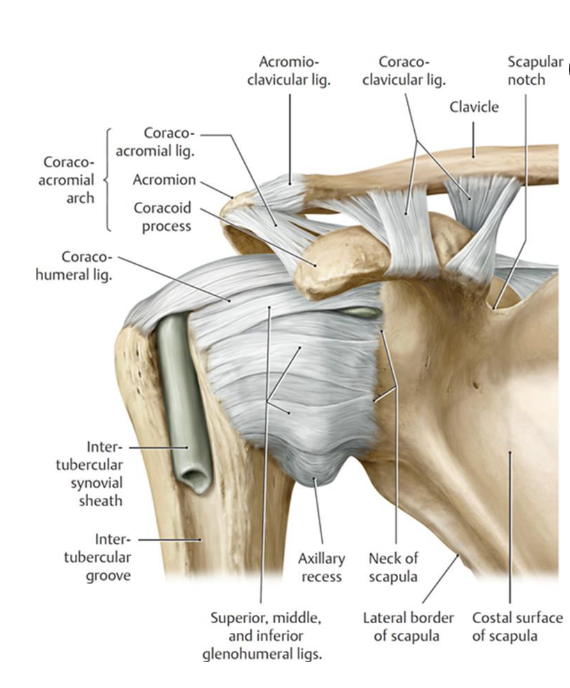
What are the glenohumeral capsular ligaments and when are they taut?
-superior GH lig: taut w/ ADD
-middle GH lig: taut w/ ER when 90 degrees ABD
-inferior GH lig: taut w/ ABD
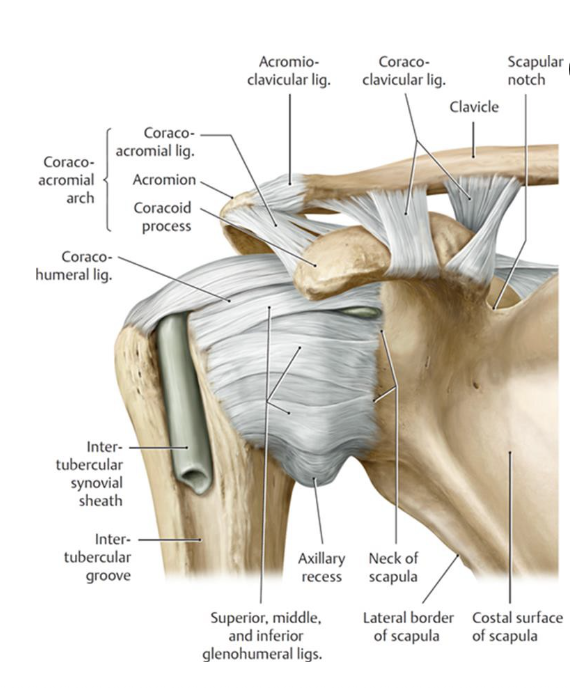
What motion is the coracohumeral ligament taut with?
taut with ER
(location: base of coracoid process to greater tubercle)
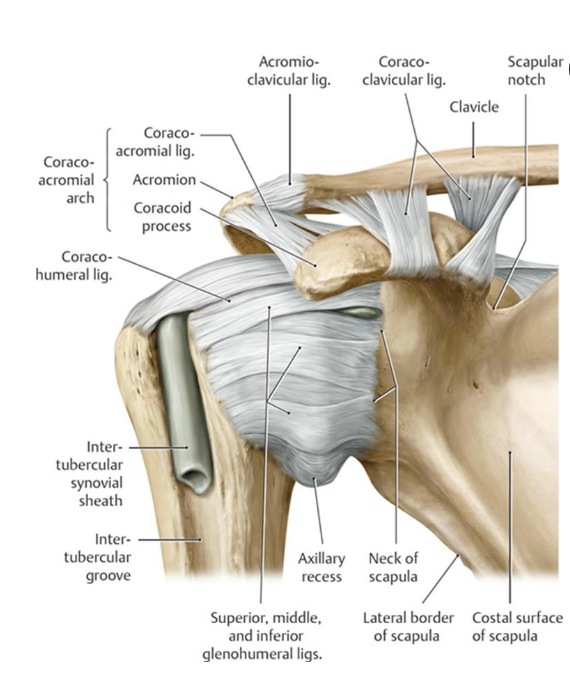
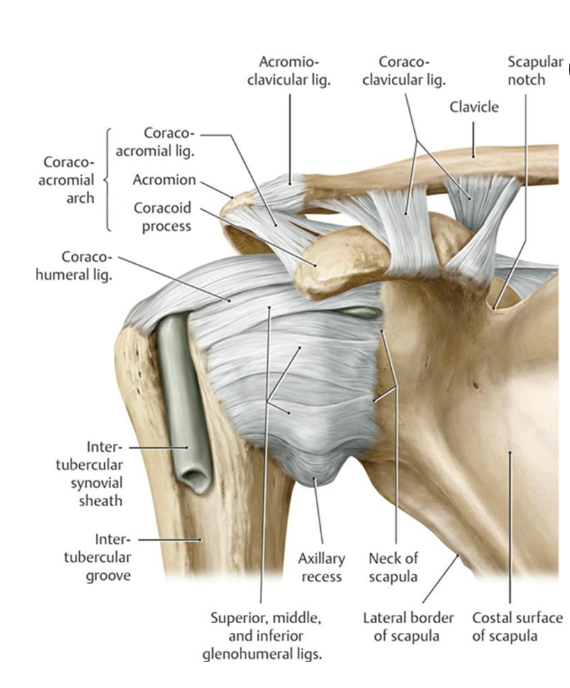
What motion is the transverse humeral ligament taut with?
trick question - always taut lol
(location: greater tubercle to lesser tubercle of humerus)
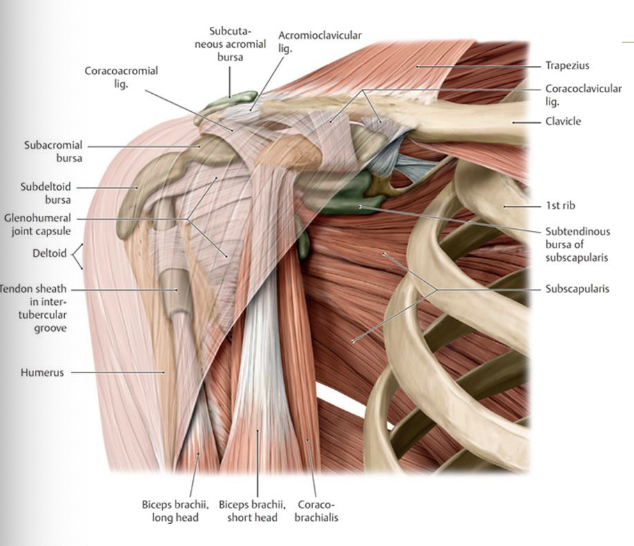
What are three main bursae in the shoulder region?
-subacromial bursa
-subdeltoid bursa
-subscapular bursa
thumb down ABDuction of shoulder -- why is it more limited than thumb up?
greater tuberosity of humerus bumps into acromion; whereas when thumb up, greater tuberosity is posteriorly rotated so it is posterior to acromion.
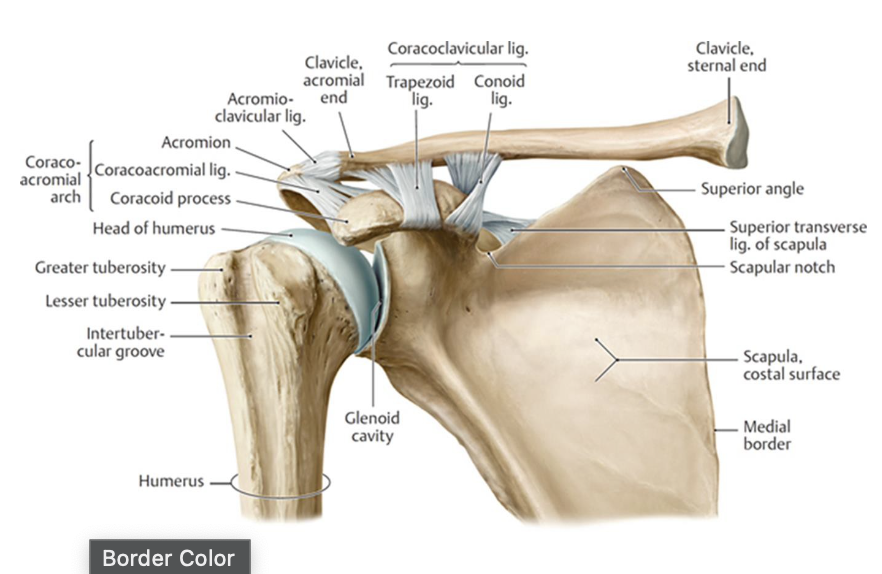
What is considered the "roof" of the glenohumeral joint?
Coracoacromial arch: formed by coracoacromial ligament (attaching between coracoid process and acromion process)
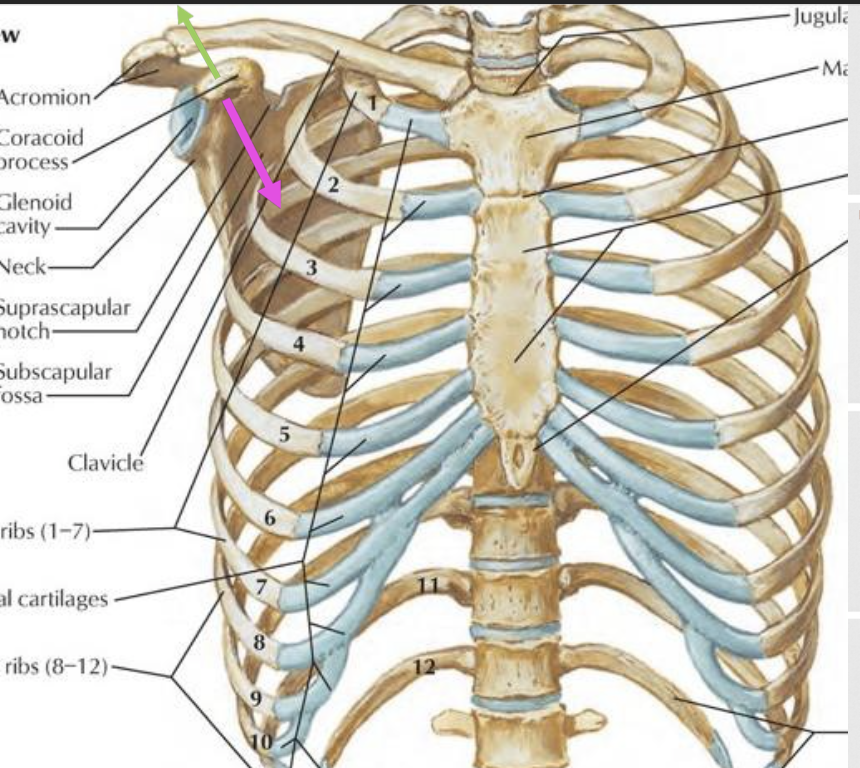
movements of scapula on thorax - sagittal plane
anterior tilt
movement about coronal (frontal) axis
coracoid process moves in anterior and caudal direction
inferior angle moves in posterior and cranial direction
this movement associated with elevation
posterior tilt
movement about coronal (frontal) axis
coracoid process moves posterior and cranial
inferior angle moves posterior and caudal
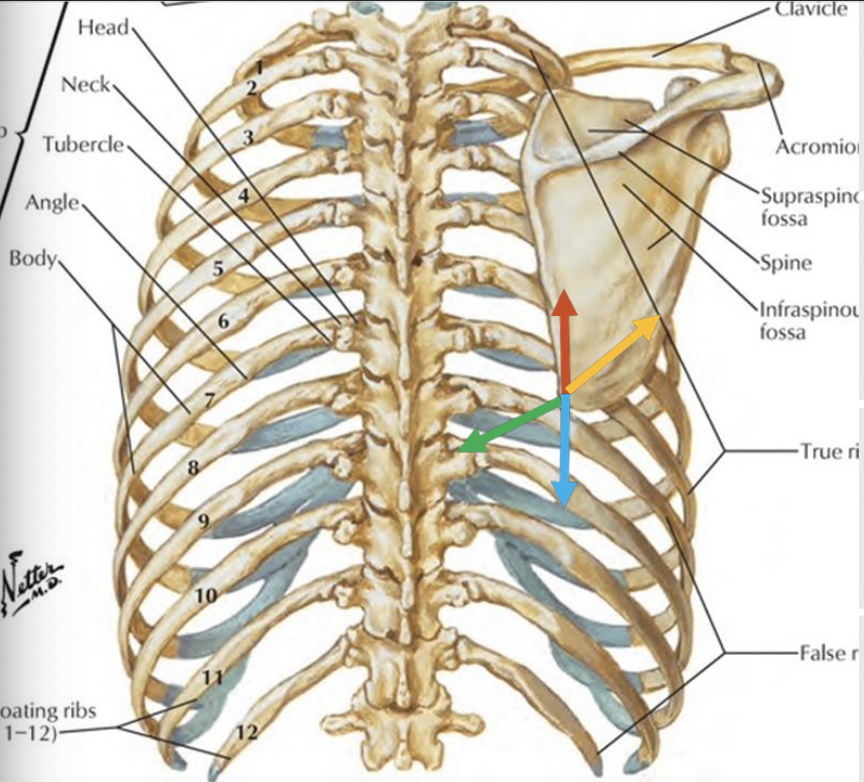
movements of scapula on thorax - frontal plane
elevation
gliding movement which scapula moves cranially
“shrugging” motion
depression
gliding movement in which scapula moves caudally
involves some posterior tilt
upward rotation
movement about sagittal axis in which inferior angle moves laterally and glenoid cavity moves cranially
downward rotation
movement about sagittal axis in which inferior angle moves medially and glenoid cavity moves caudally
movements of scapula on thorax - transverse plane
protraction (abduction)
gliding movement in which scapula moves away from vertebral column
retraction (adduction)
gliding movement in which scapula moves toward the vertebral column