HSC Business Finance
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Financial Management
the planning and monitoring of a business's financial resources to enable the business to achieve its financial objectives.
Profitability
maximise profits to satisfy shareholders in the short term and provide long term sustainability for the firm
Growth
increase the size of the business in the long term. Depends on the ability of the business to develop and use its asset structure to increase sales, profits and market share
Efficiency
minimise costs and manage assets so that maximum profit is achieved with the lowest possible level of assets.
Liquidity
ability to meet financial commitments in the short term - sufficient cash flow is required to meet financial obligations, or the business must be able to convert current assets to cash quickly
Solvency
ability to meet financial commitments in the long term - indicates risk of investment for shareholders and creditors. Measured using gearing (measures the percentage of the assets of the business that are funded by external sources).
Short Term Objectives
- Tactical and Operation plans
- Reviewed regularly to see if targets are being met or if changes need to be implemented
- Cash Flow and Liquidity
Long Term Objectives
- Strategic
- Broad goals which require a series of short term goals to assist in achievement
- Reviewed annually
- Solvency and Growth
Conflicts with Short Term and Long term objectives
- Long term goals can incur increased costs = lower overall profits in the short term
Eg: To achieve long term profitability, the business needs to invest in RnD, human resources or capital = high short term costs
Interdependence
The mutual reliance of the key business functions on one another to be committed to the same business goals and each working in a coordinated and collaborative way to achieve these goals
Interdependence of Finance
Operations - finance department relies on operations to produce the products
Marketing - to promote the products
Human Resources - manage staff
Each of these functions helps the business generate sales and therefore provide income to the finance departmen
Sources of Finance - Internal + External
Internal finance - funds generated from inside the business.
External finance - funds provided by sources outside the business, including banks, other financial institutions, government, suppliers or financial intermediaries.
Retained Profits
the amount of a business's net income that is kept within its accounts, rather than paid out to shareholders.
Capital
funds contributed by owners to establish and build the business.
Overdraft
the bank allows the business to overdraw their account up to an agreed limit for a specific time. Costs are minimal but interest is paid daily
Commercial Bills
Short term(1 - 6mths) loans(>$100k) issued by financial institutions. Borrower receives sum immediately and has to pay full amount plus interest at the end of the term. Secured against business assets
Factoring
Business can raise funds immediately by selling accounts receivable at a discount to another firm, the business will receive 90% of the amount receivable within 48hrs. Is very expensive as the business loses 10% of profit
Mortgage
loan secured by the property of the borrower (business). Used to finance property purchases and repaid with interest through regular repayments over an agreed period of time.
Debentures
Company issues a debenture to an investor who lends money to the company. This debenture is tied to business assets and the company promises to make regular interest payments at a fixed rate for a defined term to repay the loan to the investor.
Unsecured Notes
a loan from investors for a set period of time that is not secured against the business's assets. Higher rate of interest since it is unsecured and therefore more risky for investors.
Leasing
payment of money for the use of equipment that is owned by another party, enabling the business to use equipment without the large capital outlay.
Equity
funds raised by a business in exchange for ownership shares of the business. Unlike debt, it does not require repayments but investors gain a claim on future profits and decision making rights.
Ordinary shares
individuals purchase shares and become part-owners of a publicly listed company, entitling them to voting rights according to the number of shares owned as well as dividends.
New issue shares
security issued and sold for the first time on a public market through an Initial Public Offering (IPO) which generally requires a prospectus.
Rights issue Shares
privilege granted to shareholders to buy new shares in the same company.
Placements
allotment of shares made directly from the company to investors (additional shares are offered at a discount to their current trading price to special institutions or investors).
Share Purchase Plan
offer to existing shareholders in a listed company to purchase more shares in that company without brokerage fees and often with a discount and without issuing a prospectus (can only be a maximum of $15,000 in new shares to each shareholder).
Private equity
money invested in a private company not listed on the ASX to raise capital to finance future expansion/investment.
Financial Institutions: BUF SAIL
Banks, Investment Banks, Finance Companies, Life Insurance Companies, Superannuation funds, Unit Trusts, ASX
Banks
receive savings as deposits from individuals, businesses and governments, and make investments and loans to borrowers. Supervised by the RBA.
Investment banks
provide specialised services in borrowing and lending to businesses and offer a wide variety of loans that can be customised to suit the business's specific needs. They trade money and securities, arrange long-term finance for company expansion, provide working capital and give advice on forex, mergers and takeovers.
Finance companies
non-bank financial intermediaries regulated by APRA and specialise in smaller commercial finance. Provide short to medium term loans to businesses and individuals through personal and secured loans. Major providers of lease finance, some do factoring and cash-flow financing, raise capital through debentures.
Life insurance companies
provide cover and a lump sum payment in the event of death. Provide both equity and loans to the corporate sector through receipts of insurance premiums, which provide funds for investment.
Superannuation funds
all employers must make a financial contribution to a fund that will provide benefits to an employee when they retire. Superannuation funds invest the money received from superannuation contributions in company shares, property and managed funds.
Unit trusts
take funds from a large number of small investors and invest them in specific types of financial assets. Usually connected to a management firm that offers a diversified management portfolio for investors.
ASX
market where shares are bought and sold. Functions as a market operator, clearing house and payments facilitator and oversees compliance with operating rules.
ASIC
- An independent statutory commission that enforces and administers the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth) and protects consumers in areas of investment, life and general insurance, superannuation and banking (except lending).
- Assists in reducing fraud and unfair practices in financial markets and financial products.
- Ensures that companies adhere to the law, collect information about companies and disclose financial information in annual reports.
- If a business breaches the law, ASIC investigates and determines an appropriate remedy (imprisonment and/or monetary penalties) which generates negative publicity for the business.
Company Taxation
- All Australian businesses that have been incorporated (i.e. public and private companies) are required to pay company tax on profits at a flat rate of 30% of net profit (or 25% for small businesses).
- Tax reforms to progressively reduce the company tax rate are aimed at improving Australia's international competitiveness and making Australia a more attractive place to invest.
Economic Conditions
Positive Economic conditions = increased consumer spending creating increased consumer demand and lower interest rates, thus businesses are more likely to borrow money and invest money(increased production, hiring staff..)
Negative Economic conditions = low consumer spending and higher interest rates, therefore lower demand and reduced cash flow and less likely to borrow.
Availability of Funds
Refers to the ease with which a business can access funds (for borrowing) on the international financial markets.
Various conditions and rates apply and these will be based primarily on risk, demand and supply and domestic economic conditions.
The Global Financial Crisis caused a sharp increase in interest rates that reflected the high level of risk in lending.
Interest Rates
Interest rates represent the cost of borrowing money.
The higher the level of risk involved in lending to a business, the higher the interest rates.
Processes: PIMFLE
P - Planning
I - Implementing
M - Monitoring and Controlling
F - Financial Ratios
L - Limitations of financial reports - DNA CNT
E - Ethical Issues
Financial Needs:
A business must know its needs to know where its headed and how it will get there.
- this can be dependent on their size, growth, economic conditions, future plans, capacity to source finance
- Important financial info like revenue statements, balance sheets, income statements..etc are necessary before future plans can be made
Budget
provide information in quantitative terms about requirements to achieve a particular purpose.
- Reflect strategic planning decisions about how resources are to be used.
- Show cash required for planned outlays, cost of capital expenditure against earning capacity, estimated use and cost of raw materials and inventory and number and cost of labour hours required for production.
Influenced by past figures and trends, potential market or market share, proposed expansion or discontinuation of projects, proposals to alter price or quality, current orders and plant capacity, external environment, etc.
Operating Budgets
relate to the main activities of a business and may include budgets relating to sales, production, raw materials, direct labour, expenses and COGS.
Project Budgets
relate to capital expenditure and R&D, includes information about the purpose of the asset purchase, lifespan of the asset and revenue to be generated from the purchase.
Financial Budgets
relate to the financial data of a business - budgeted income statement, balance sheet and cash flow.
Record Systems
Mechanisms employed by a business to ensure that data are recorded and the information provided by record systems is accurate, reliable, efficient and accessible.
- Important as management bases decisions on this information so it must be accurate/reliable.
Financial Risks
The risk to a business of being unable to cover its financial obligations, such as the debts that a business incurs through borrowings. If a business is unable to meet its financial obligations, bankruptcy will result.
- Increased borrowing = increased risk due to greater debt + costs
Finance Controls
the policies and procedures that ensure that the plans of a business will be achieved in the most efficient way.
- Theft, fraud, damage/loss of assets and errors in record systems all prevent the business from achieving its goals.
Debt Financing(ADV)
- Funds are usually readily available and can acquired at short notice
- Increased funds should lead to increased earnings and profits
- Interest payements are tax deductible
- Flexible payment periods and types of debt are available
Debt Financing(DISADV)
- Increased risk if debt comes from financial institutions because interest, bank charges and government charges may increase
- Security is required by the business
- Regular repayments have to be made
- lenders have first claim on any money if the business ends in bankruptcy
- Debt can be expensive EG: interest must be paid
Equity Financing(ADV)
- Does not have to be repaid unless the owner leaves the business
- Cheaper than other sources of finance as there are no interest payments
- The owners who have contributed the equity retain control over how that finance is used
- Low gearing(use resources of the owner and not external sources of finance)
- less risk
Equity Financing(DISADV)
- Lower profits and lower returns for the owner
- The expectation that the owner will have about the return on investment(ROI)
- Long, expensive process to obtain funds
- ownership is diluted
Matching terms to sources of finance
Short term financing methods must be used for short term goals, long term financing methods must be used for long term goals
Cash Flow Statement:
Indicates the movement of cash receipts and cash payments resulting from transactions over a period of time.
- Can identify trends and be a useful predictor of change.
- Only cash transactions are included.
- Used by creditors, owners and shareholders to see the cash position of the business.
Activities are categorised as:
- Operating activities - cash flows relating to the provision of G&S
- Investing activities - cash flows relating to the purchase and sale of non-current assets and investments
- Financing activities - cash flows relating to the borrowing activities of the business

Income Statement:
Shows operating efficiency - income earned and expenses incurred with resultant profit or loss.
Shows operating and non-operating income earned, COGS and other expenses incurred.
Analysis enables managers to make comparisons and analyse trends before making financial decisions

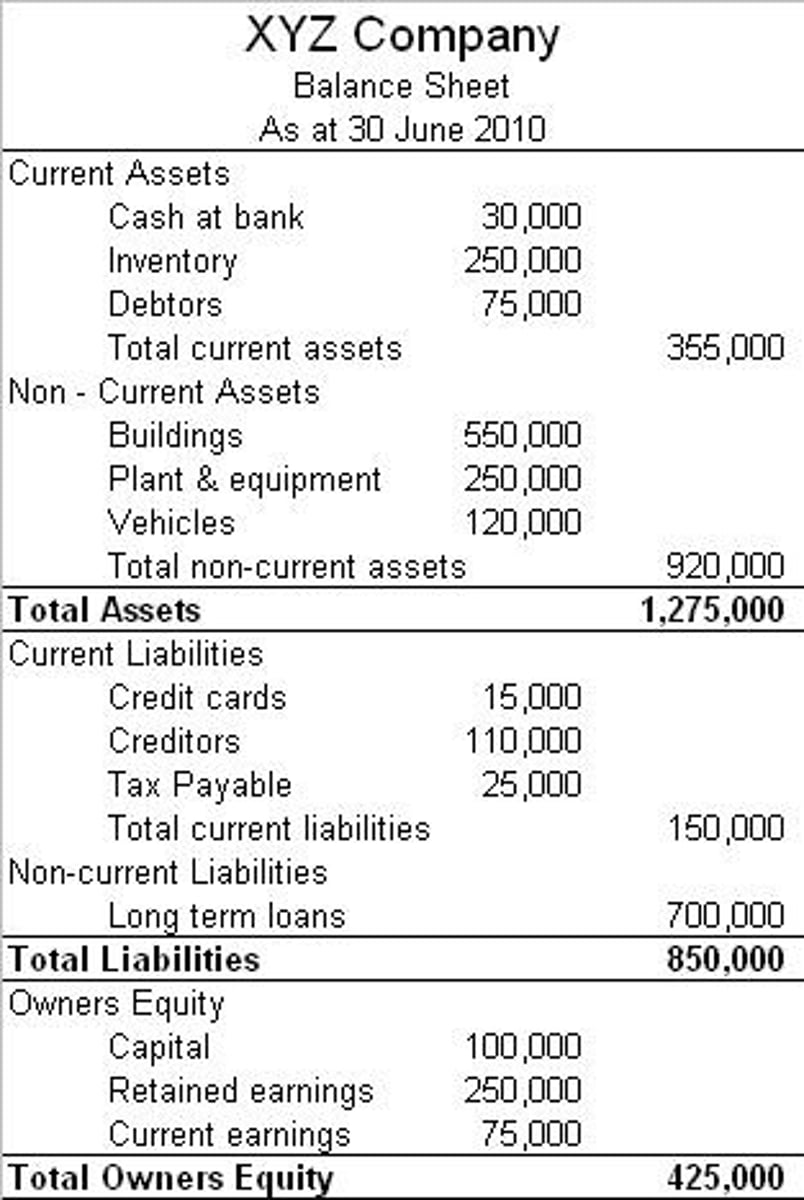
Balance Sheet:
Balance Sheet - represents a business's assets and liabilities at a particular point in time and represents the net worth (equity) of the business.
Prepared at the end of the accounting period and shows the financial stability of the business.
Assets = Liabilities + Owners' equity
Assets - items of value owned by the business.
Liabilities - what is owed by the business.
Owners' equity - funds contributed by the owners.
Shows whether the business has enough assets to cover its debts, the interest and money borrowed can be repaid, assets are being used to maximise profits and owners are making a good return on their investment.
Financial Ratios
The a financial ratio utilises financial information to provide numerical value to learn about a business. Interpretation of these ratios involves making judgements and decisions using data gathered.
Users will compare figures, percentages or ratios for departments, different products, different branches or against the industry and monitor trends over a number of years to make comparisons between items within a financial statement, selling expenses and sales.
Types of Financial Ratios:
Vertical - within one financial year
Horizontal - different financial years
Trend - periods of 3-5 years
Liquidity
the extent to which the business can meet its financial commitments in the short term(<12 months)
- The business must have sufficient resources to pay its debts and enough funds for unexpected expenses.
- The firm must ensure that it has enough current assets that could be used to generate cash quickly, but not so much that the resources are not being used for producing revenue.
Current Ratio
measures a business's ability to pay back their current liabilities with their current assets.
- A current ratio of 2:1 generally indicates a sound financial position but it depends on the type of firm, how other firms in the industry are operating and factors in the external environment.
- The higher the current ratio, the more capable the business is of meeting their short-term obligations.
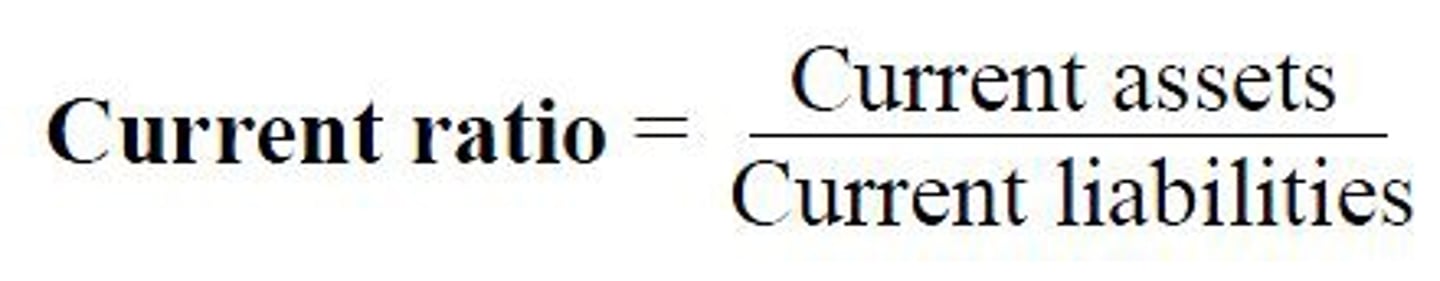
Solvency
the ability of a business to meet its financial commitments in the longer term (>12 months).
Gearing
the proportion of debt (external finance) and the proportion of equity (internal finance) that is used to finance the activities of a business.
- The more highly geared the business (i.e. higher proportion of debt to equity), the greater the risk for the business but the greater potential for profit.
- There is no optimum level of gearing - it depends on return on investment, cost of debt, size and stability of the business's earning capacity, interest rates, business confidence and economic indicators.
Debt to Equity Ratio
total liabilities/total equity
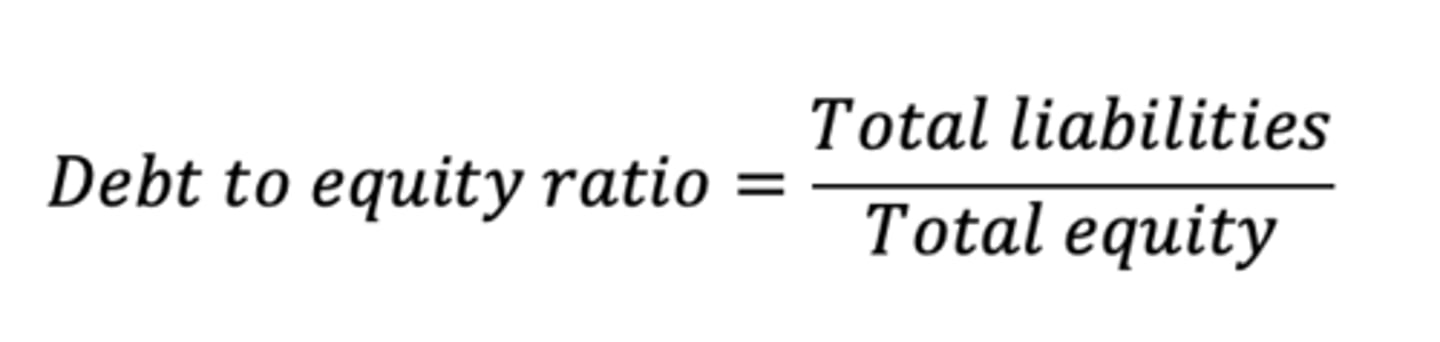
Profitability ratios
Indicates the business's capacity to use resources to earn profits
- owners and shareholders want to know whether the firm is earning an acceptable return on their investment
Gross Profit Ratio
gives the percentage of sales revenue that results in gross profit and indicates the effectiveness of planning policies concerning pricing, discounts, valuation of stock, etc.

Net Profit Ratio
shows the amount of sales revenue that results in net profit and illustrates the amount of sales revenue that results in net profit

Return on Equity Ratio
shows how effective the funds contributed by the owners have been in generating profit, and hence a return on their investment.
- The return to the owners has to be greater than any return that could be gained from alternative investments. Higher ratio is better.
RoE = Net profit/Total Equity
Owners are not only interested in the return for the current year but also in comparing the current year's return with previous years and against industry averages.
Efficiency
the ability of a business to use its resources effectively in ensuring financial stability and profitability of the business.
- Relates to the effectiveness of management in directing and maintaining the goals and objectives of the firm - the more efficient the firm, the greater its profits and financial stability.
Expense Ratio
compares total expenses with sales and indicates the amount of sales that are allocated to individual expenses, such as selling, administration, COGS and financial expenses. Indicates day-to-day efficiency of the business.
Expense Ratio = Total Expenses/Sales
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
measures the effectiveness of a firm's credit policy and how efficiently it collects its debts (how quickly debtors pay their accounts). To determine the length of time it takes to convert the balance
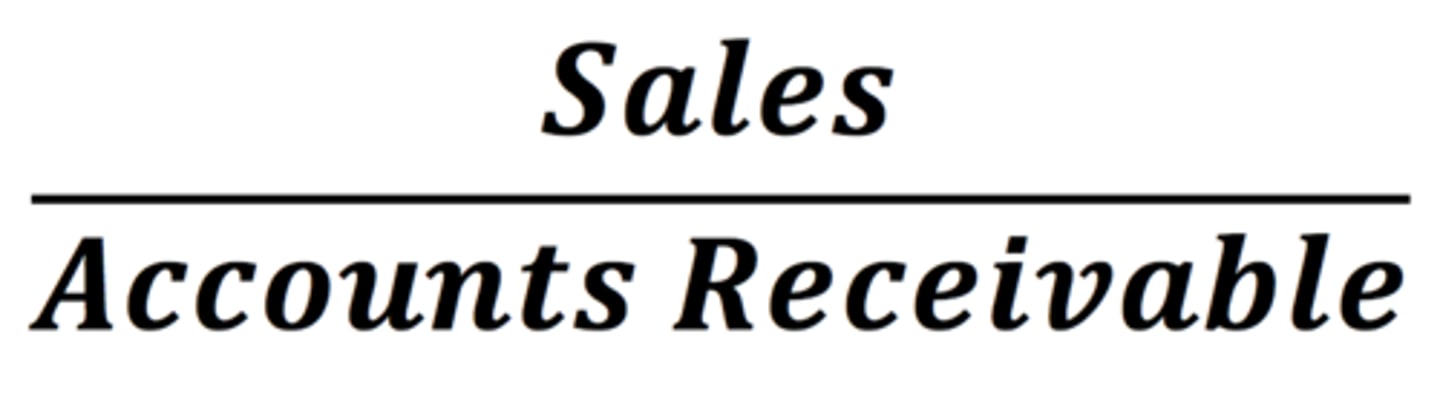
Comparative Ratio Analysis
Over different time periods - look at figures and ratios over several years to indicate directions and trends.
Against standards - comparing results against industry benchmarks.
With similar businesses - firms may access relevant business statistics from a number of sources, including the ABS.
Limitations of Financial Reports: NCVTDN
- Normalised earnings
- Capitalised expenses
- Valuing assets
- Timing issues
- Debt repayments
- Notes to the financial statements
Normalised earnings
Earnings djusted to take into account changes in the economic cycle or remove one-off items that will affect profitability to show true earnings and enable easier comparison to figures later.
Eg: large crash in earnings due to covid therefore normalised earnings would be utilised to generate a more accurate showing of earning over periods of time)
Capitalising Expenses
a business records an expense as an asset on the balance sheet rather than as an expense on the income statement (common example is R&D)
- understates expenses and overstates profits = makes the business look better than it is for investments or buying.
Valuing Assets
historical cost (value at time of purchase but distorts true value as it does not show appreciation/depreciation), intangibles (e.g. goodwill(reputation)) are hard to estimate and if they are included in the balance sheet they are often overvalued to make the business appear more financially stable, methods of calculating depreciation of assets can vary.
Timing Issues: Accrual and Cash Accounting
Accrual accounting - record expenses and sales as they take place,
Cash accounting - track money coming in and going out of the business
The matching principle states that expenses incurred by a business must be recorded on the income statement for the same accounting period when revenue relating to those expenses was earned.
EG: A business could delay a purchase until after the financial year to make the business look better on paper(better profit, less expenses)
Debt Repayments
financial statements do not disclose how long the business has had or has been recovering the debt, the capacity to repay the debt, adequacy of provisions for recovering debt, provision for doubtful debts, etc.
- Makes businesses look better for investment or purchase
Notes to the financial statements
contain information left out of the main documents such as the accounting methodologies used, how figures were calculated and procedures used to develop them.
Ethical Issues related to Financial Reports
Any attempt to engage in creative accounting to portray a more favourable but inaccurate financial picture should always be avoided.
Directors must act in good faith, avoid conflicts of interest and exercise power for proper purpose.
Audits
independent checks of the accuracy of financial records and accounting procedures
- assist in safeguarding against unnecessary waste, inefficient use of resources, misuse of funds, fraud and theft - internal, management and external audits are essential.
Record Keeping
source documents must be created for every transaction (cash transactions that are not recorded can understate profits and reduce tax burdens).
Reporting Practices
provide stakeholders with access to financial information.
Financial Strategies: GWCP
- Cash flow management
- Working Capital management
- Profitability management
- Global Financial management
Cash flow
the money that flows in and out of your business throughout a given period
Cash flow statements
indicate the movement of cash receipts and cash payments resulting from transactions over a period of time, which enables a manager to identify trends and predict changes.
Distribution of payments
distributing payments throughout the month, year or other period so that large expenses do not occur at the same time and cash shortfalls do not occur. Enables a more equal cash outflow each month rather than large outflows in particular months.
Discounts to debtors for early payment
most effective when targeted at those debtors who the largest amounts over the financial year
Factoring
selling accounts receivable for a discounted price to a finance company so the business saves on the costs involved in following up on unpaid accounts and debt collection
Working Capital
refers to the funds available for the short term financial commitments of a business
Net working capital = current assets - current liabilities
Working Capital management:
involves determining the best mix of current assets and current liabilities to achieve the objectives of the business
Control of current assets: Cash
Cash allows a business to pay its debts, repay loans and pay accounts in the short term to ensure that it survives in the long term.
- planning for the timing of cash receipts, cash payments and asset purchases avoids the situation of cash shortages and excess cash
- businesses try keep cash balance at a minimum - however if they don't have the cash to pay they might use an overdraft
Control of current assets: Accounts receivable
A business must monitor its accounts receivable and ensure that their timings allow the business to maintain adequate cash resources - the faster debtors pay the better the firm's cash position
- Must loan to good credited customers, send monthly reminders, follow up on overdue accounts and organise/negotiate on acceptable payback periods(ie, every 30 days etc), have policies for collection of bad debts
Control of current assets: Inventories
Too much inventory or slow moving inventory leads to cash shortages while insufficient inventory of quick selling items may lead to loss sales
- Inventory turnover must be sufficient to generate cash to pay for purchases and pay suppliers on time - maintain credit
- business needs to balance holding stock and selling enough stock to balance cash
Control of current liabilities: Accounts payable
A business must monitor its payable and ensure that their timing allows the business to maintain adequate cash resources
- could take advantage of creditors discounts to reduce costs and improve cash flow
- accounts must be paid on time to avoid extra charges - not paying on time leads to bad credit which affects future borrowing
Floor stock finance
borrowing against inventor and repaying the debt as they sell inventory
Consignment finance
suppliers provide stock but the business only needs to pay for it when the stock is sold
Control of current liabilities: Loans
Short term loans are expensive so they should be used less
other costs incurred by obtaining a loan need to be monitored to minimise overall costs
must weigh up options and investigate alternative sources of finance incase it is cheaper
Build positive relationships with lenders - good credit
Control of current liabilities: Overdrafts
Banks require that regular payments be made on overdrafts and may charge account keeping fees, establishment fees and interest on the money borrowed
- These charges need to be carefully monitored as charges vary depending on the type of overdraft established
- must have a policy for using and managing overdrafts to limit overspending and increased debts