mendel to Mendeleev exam 2024
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
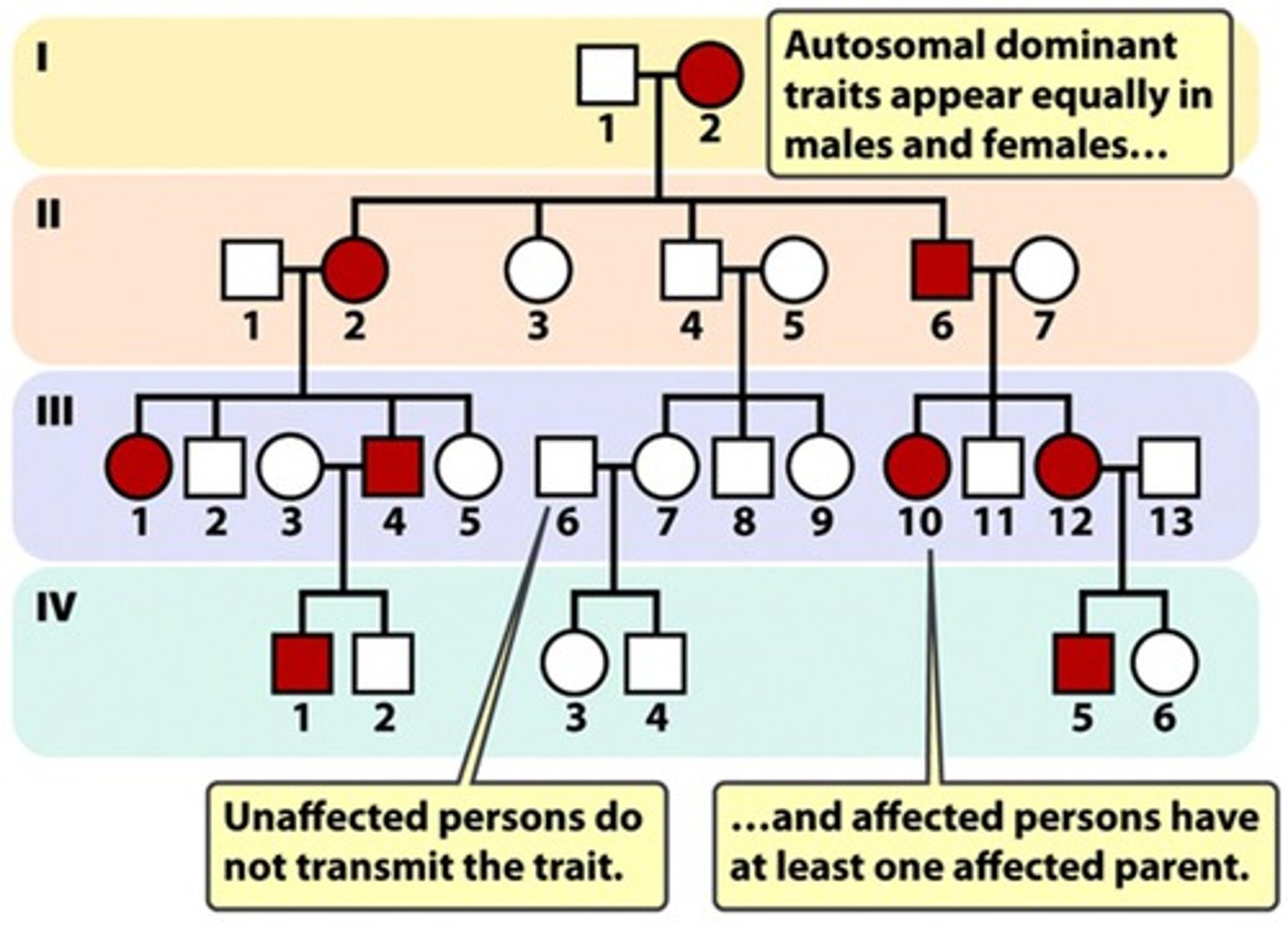
Traits of Autosomal dominant
- Traits appear equally in males and females.
- Unaffected parents do not pass on traits.
- Individuals affected must have at least one affected parent.
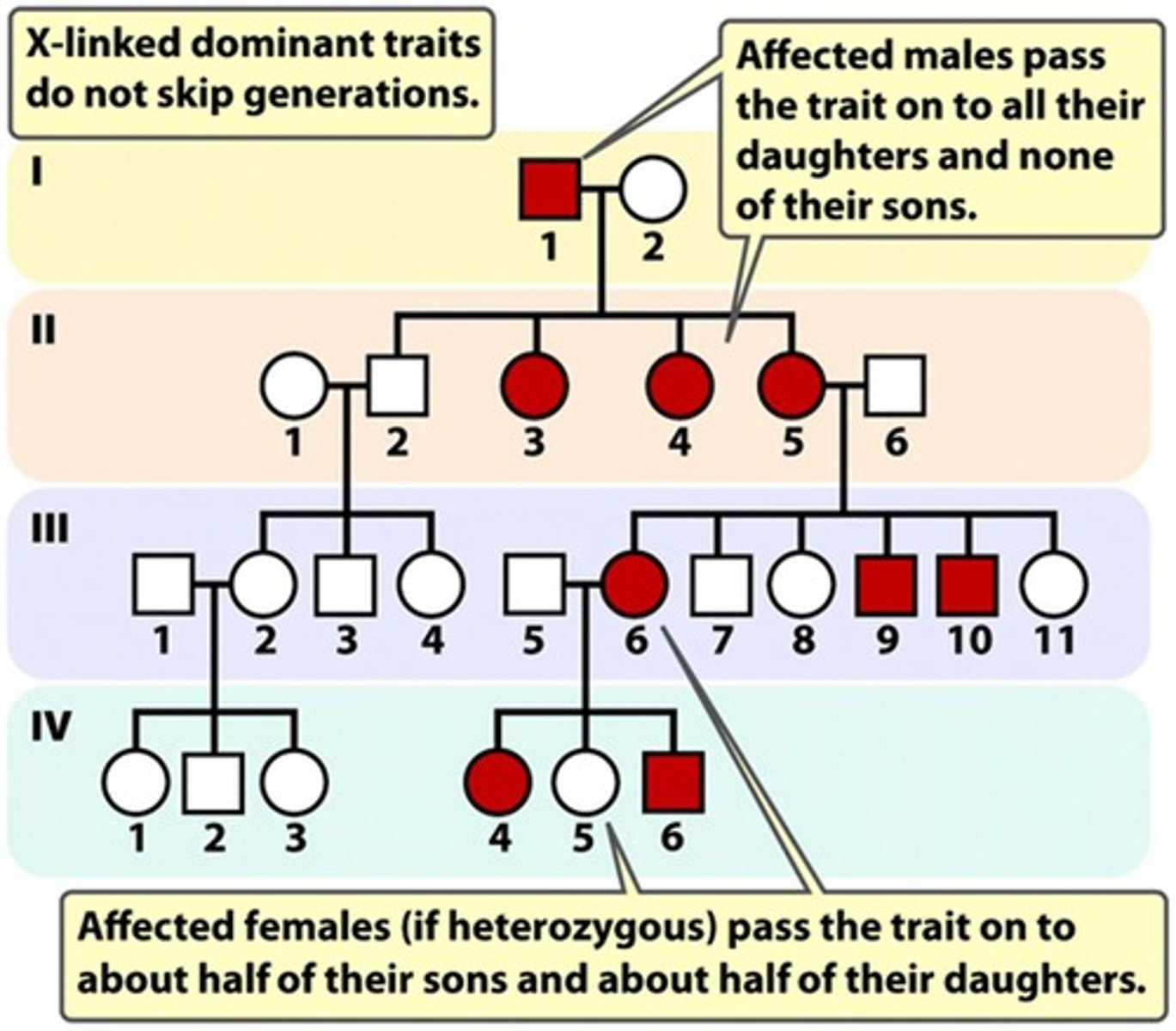
X - linked dominant traits
- X-linked dominant traits do not skip generations
- Affected males pass on the trait to all their daughters and none of their sons
Traits of X-linked recessive inheritance
- Trait is located on the X chromosome
- Females with trait must be homozygous recessive.
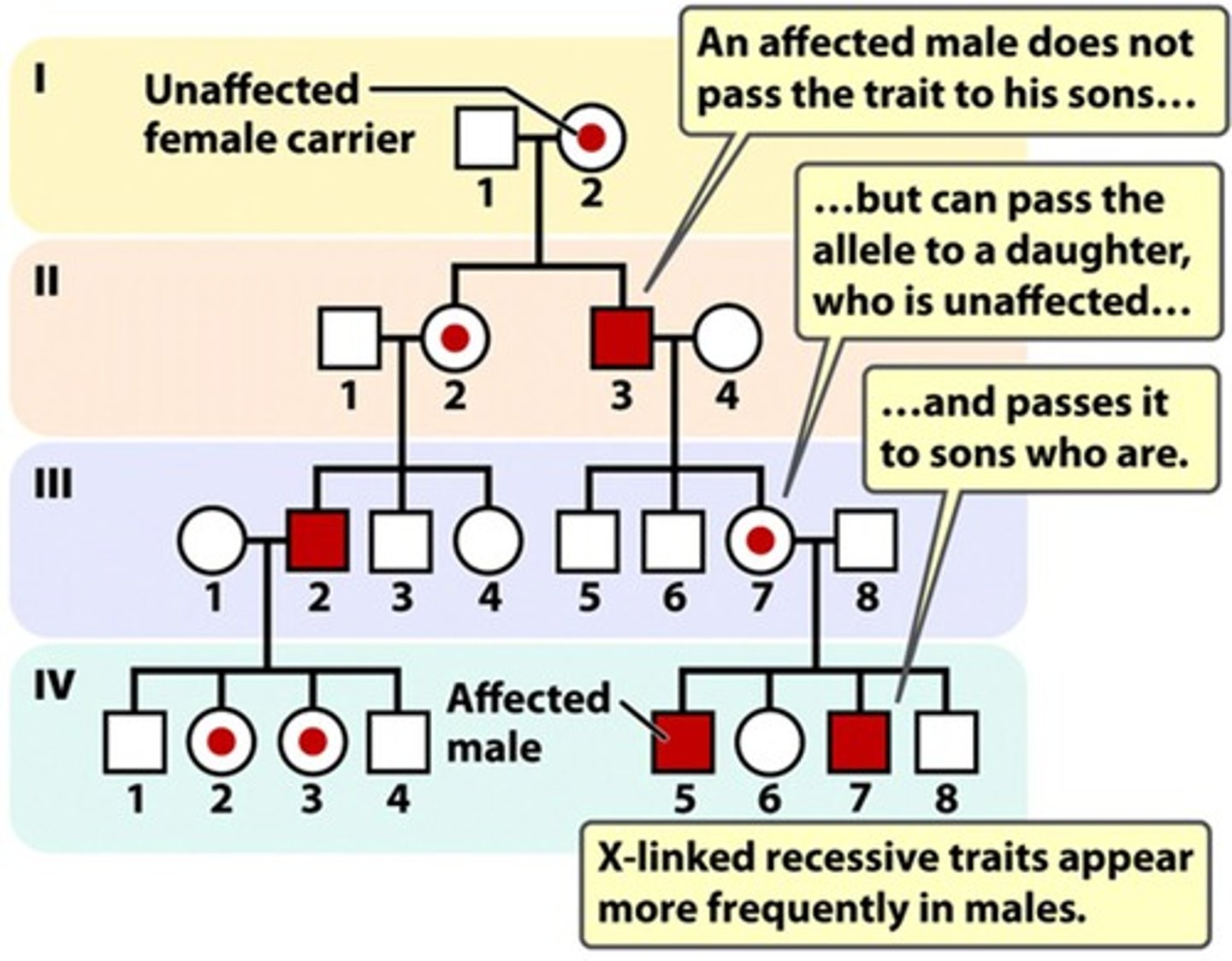
Define X-linked alleles
- Some genes are located on the X chromosome - they are described as X-linked traits.
- Like traits located on autosomes, those on the X chromosome may be dominant or recessive.
- Since females have two X chromosomes they can be either homozygous or heterozygous for an X-linked trait
Dominant traits
- Dominant traits only need one copy of the allele to be visible in the appearance of an individual
Recessive traits
- These traits can only be seen in the appearance of an individual if there are two copies of this allele present.
How many chromosomes does a human have? how many are received from each parent?
- Humans have 46 chromosomes - 23 from your mother and 23 from your father
Define Karotypes
A picture that shows the chromosomes in pairs arranged in order from biggest to smallest.
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Name the key structures of DNA
Deoxyribose sugar, phosphate molecule, the four bases: Guanine, cytosine, adenine, and thymine.
How do the DNA bases pair?
A-T
G-C
Order of mitosis
interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
order of meiosis
Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I, Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II
Purpose of mitosis and daughter cells produced
The purpose of mitosis is to create two identical daughter cells that have the same set of chromosomes as the parent cell. Mitosis is a type of cell division that plays a key role in growth, development, and tissue repair:
Purpose of meiosis and daughter cells produced
Meiosis produces daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. These daughter cells are called haploid cells, and in humans, they become sperm and egg cells. four haploid daughter cells are produced.
What are some similaritys of mitosis and meiosis
Both mitosis and meiosis involve:
- Diploid parent cell.
- Stages of interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
- In metaphase individual chromosomes (pairs of chromatids) line up along the equator.
- During anaphase the sister chromatids are separated to opposite poles.
- Ends with cytokinesis.
What are some differences of mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis and meiosis are both types of cell division, but they have several key differences:
Purpose: Mitosis creates new body cells, while meiosis creates egg and sperm cells.
Number of cell divisions: Mitosis involves one cell division, while meiosis involves two.
Number of daughter cells: Mitosis produces two daughter cells, while meiosis produces four.
Chromosome number: Mitosis results in diploid daughter cells, while meiosis results in haploid daughter cells.
Genetic identity: Mitosis produces genetically identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces genetically different daughter cells.
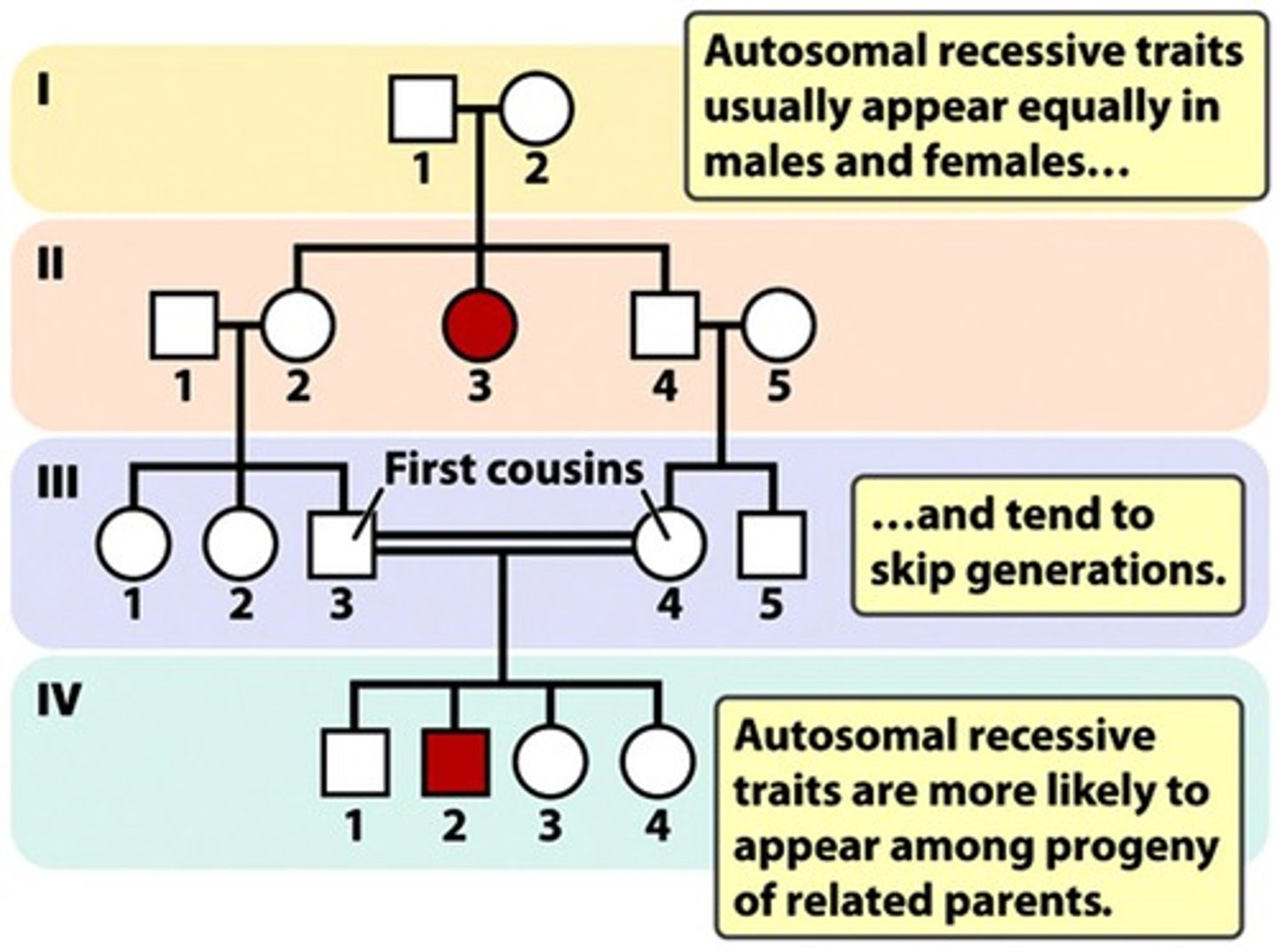
Traits of Autosomal recessive inheritance
- Trait is recessive and located on the autosome.
- Individuals with the trait must be homozygous recessive.
Define Allele
Different forms of a gene
Define homozygous alleles
When the alleles have the same information for a trait.
- If the alleles for a characteristic in a homologous pair are the same, the organism is said to be homozygous for that characteristic.
Define Heterozygous alleles
When the alleles have different information for a trait.
- If the alleles for a characteristic in a homologous pair are different, the organism is said to be heterozygous for that characteristic.
Genotypes
- combination of alleles an organism has for a particular characteristic or trait
Phenotype
- the physical expression of the trait or characteristic
Define chromosones
Coiled up lengths of DNA molecules. They carry a large number of genes to determine charateristics.
Define genes
the units of heredity that help determine the characteristics of an organism
Difference between autosomes and sex chromosones
The main difference between autosomes and sex chromosomes is that autosomes determine an organism's general traits, while sex chromosomes determine its biological sex.
Autosomes
These are the 22 numbered pairs of chromosomes that determine most of an organism's characteristics, such as body weight, height, eye color, and susceptibility to illnesses. Autosomes are present in identical pairs, with one coming from each parent.
Sex chromosomes
These are the 23rd pair of chromosomes and determine an organism's biological sex. In humans, females typically have two X chromosomes (XX), while males typically have one X and one Y chromosome (XY).
Define Haploid cells
A cell that contains one set or pair of chromosones.
Define Diploid cells
A cell that has two complete sets or pairs of chromosones.
Trends in the periodic table: atomic radius
On the periodic table, atomic radius generally decreases as you move from left to right across a period (due to increasing nuclear charge) and increases as you move down a group (due to the increasing number of electron shells).
Trends in the periodic table: electronegativity
On the periodic table, electronegativity generally increases as you move from left to right across a period and decreases as you move down a group.
Properties of metals
Lustrous (shiny)
Hard.
High density (are heavy for their size)
High tensile strength (resist being stretched)
High melting and boiling points.
Good conductors of heat and electricity.
Properties of non metals
Not malleable or ductile, not shiny, poor conductors of heat and electricity, brittle, have low melting and boiling points
Ions
positively and negatively charged atoms
Ionic compounds
a compound composed of positive and negative ions
Anion
A negatively charged ion
Cation
A positively charged ion
Solubility
the ability of one substance to dissolve in another at a given temperature and pressure
Aqueous
dissolved in water
Polyatomic ions
ions that are made of more than one atom
Precipitate
A solid that forms from a solution during a chemical reaction.
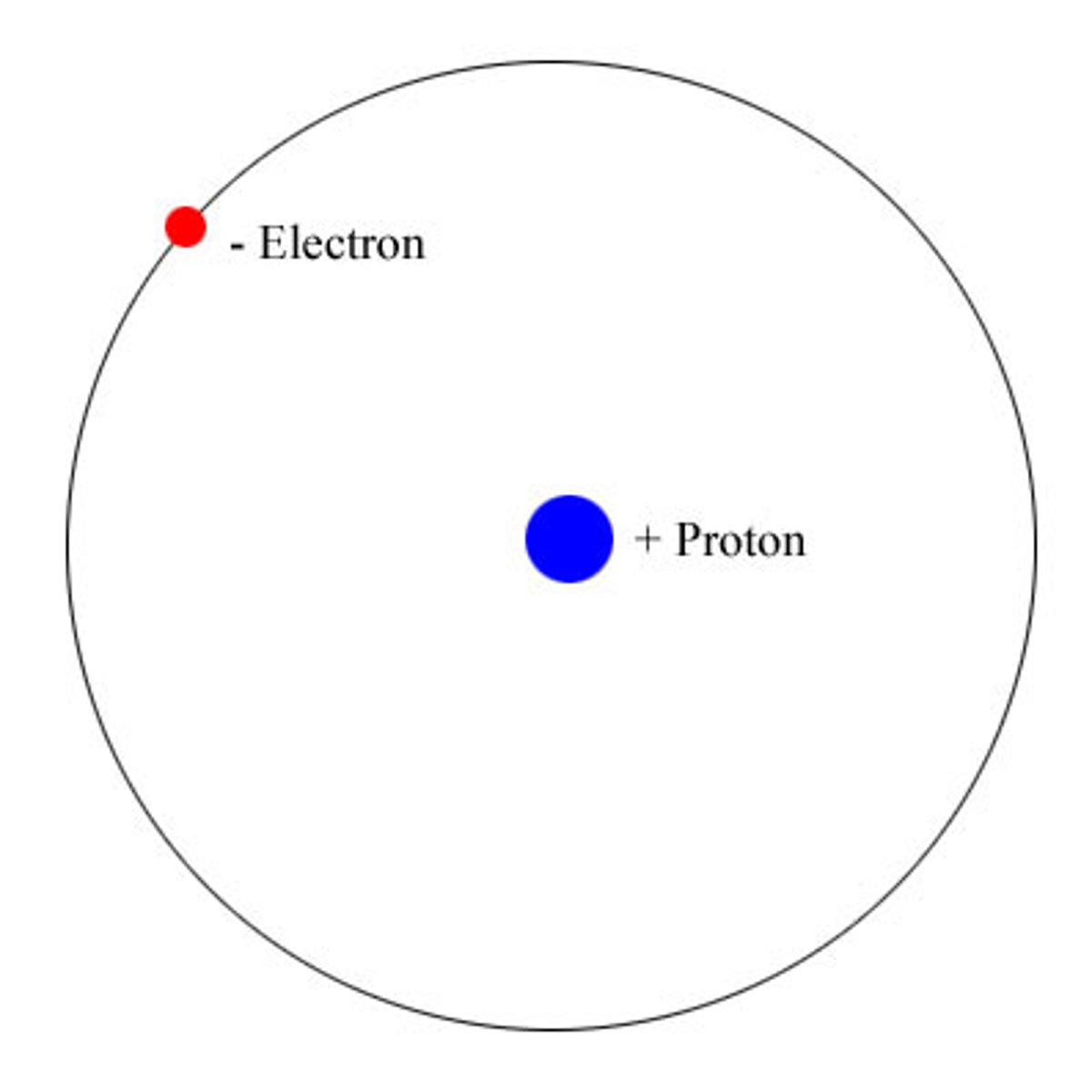
Bohr model for hydrogen
Atomic number: 1
Atomic configuration: 1
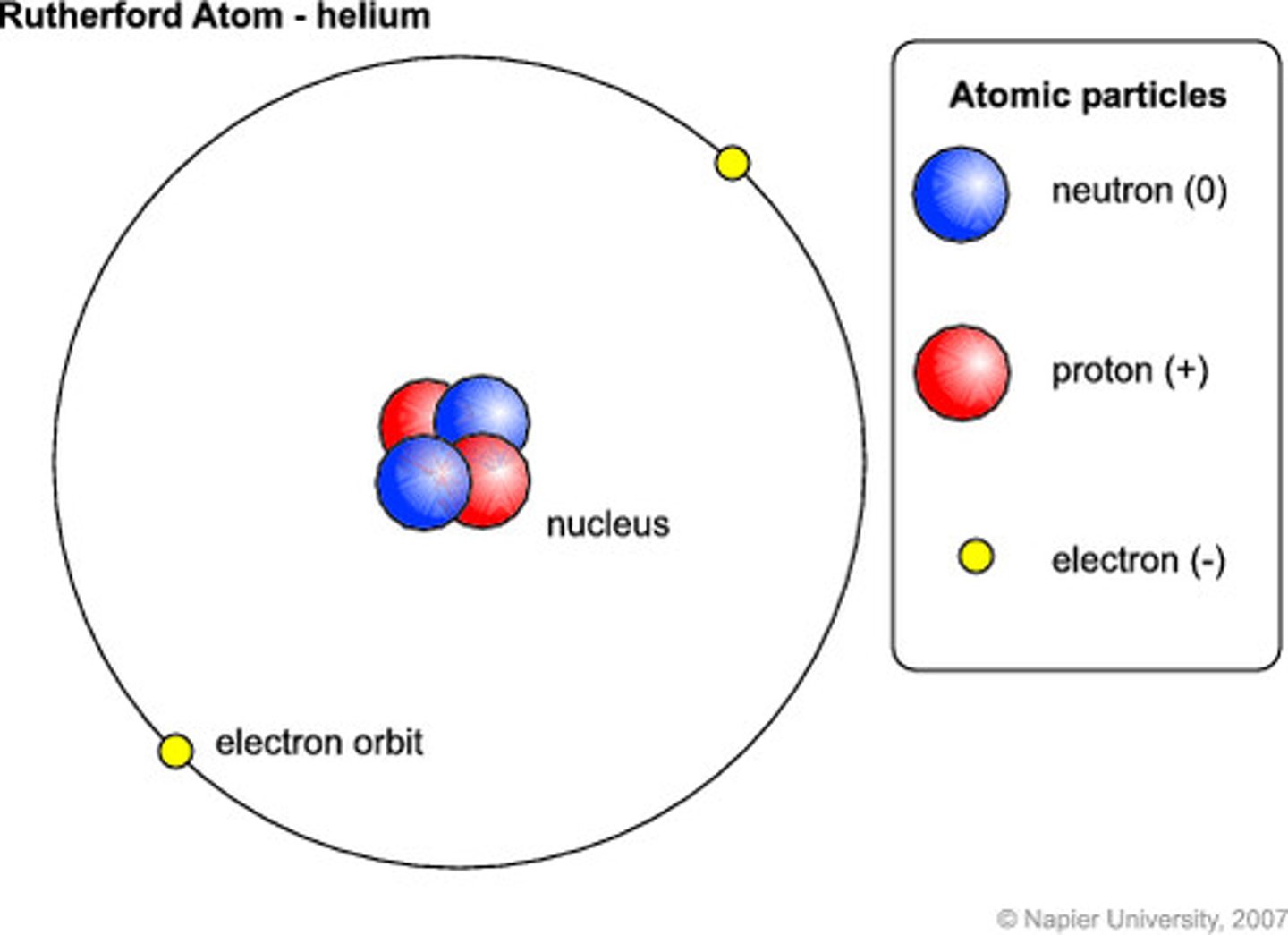
Bohr model for helium
Atomic number: 2
Atomic configuration: 2
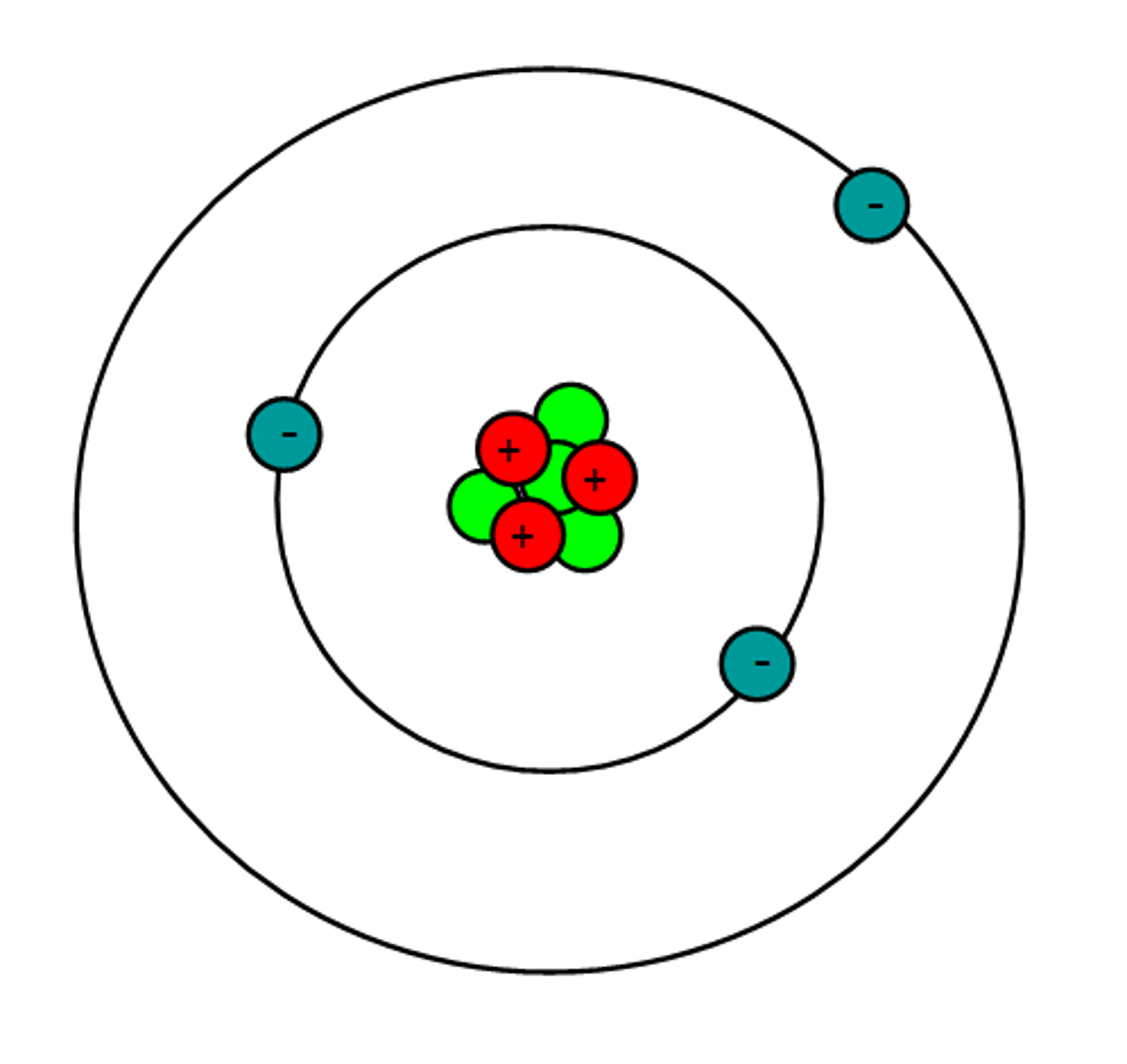
Bohr model for lithium
Atomic number: 3
Atomic configuration: 2, 1
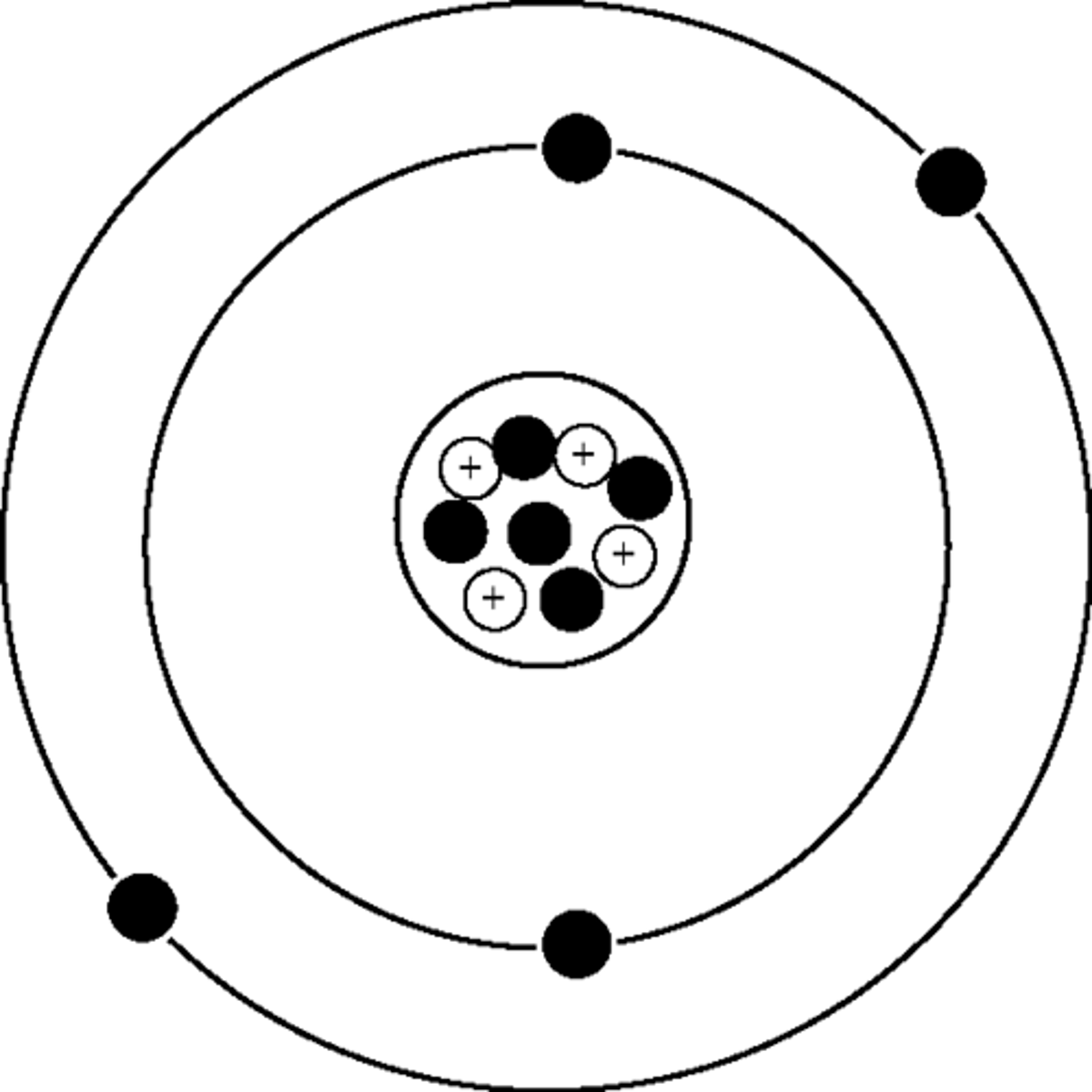
Bohr model for beryllium
Atomic number: 4
Atomic configuration: 2, 2
Bohr model for boron
Atomic number: 5
Atomic configuration: 2, 3
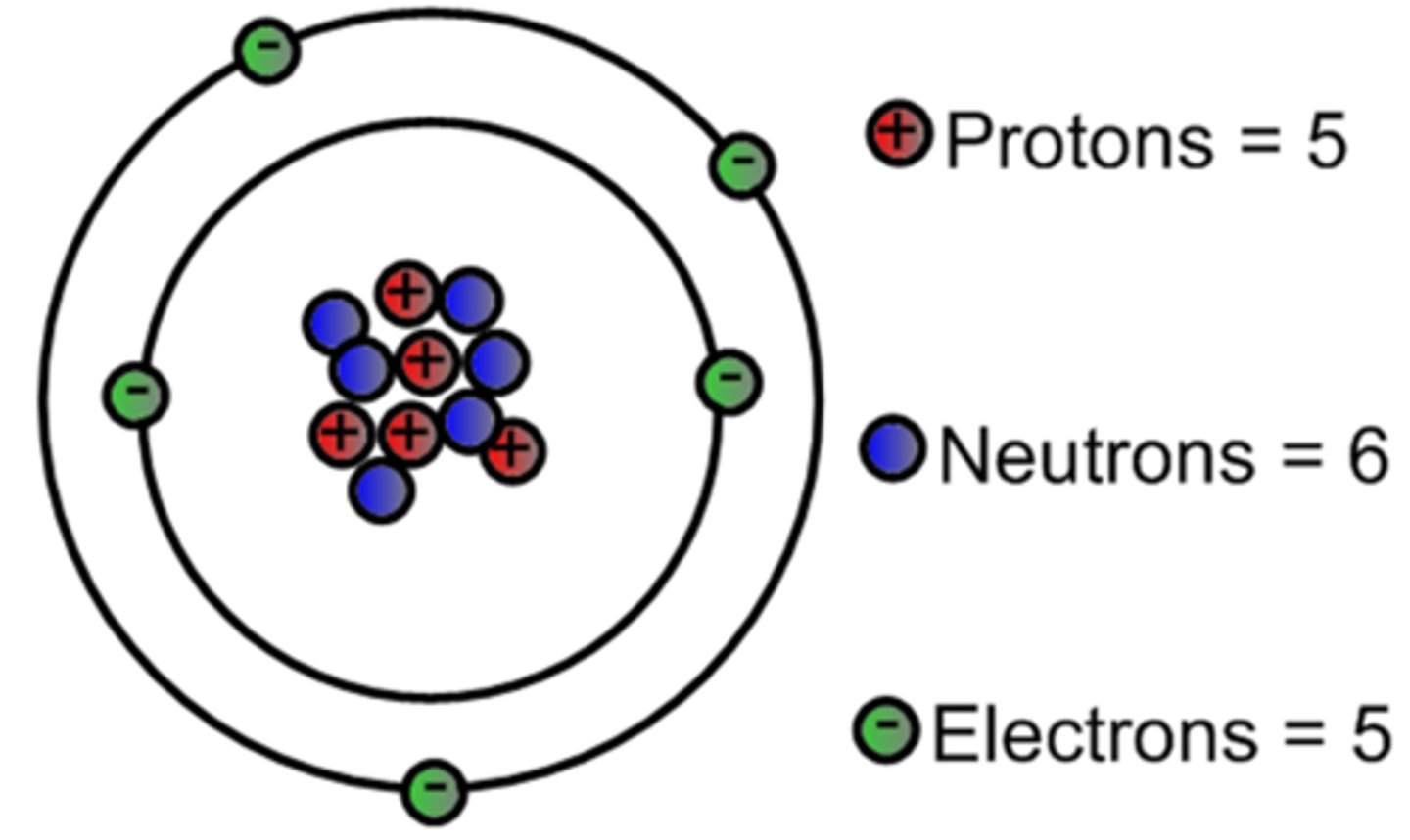
Bohr model for Carbon
Atomic number: 6
Atomic configuration: 2, 4

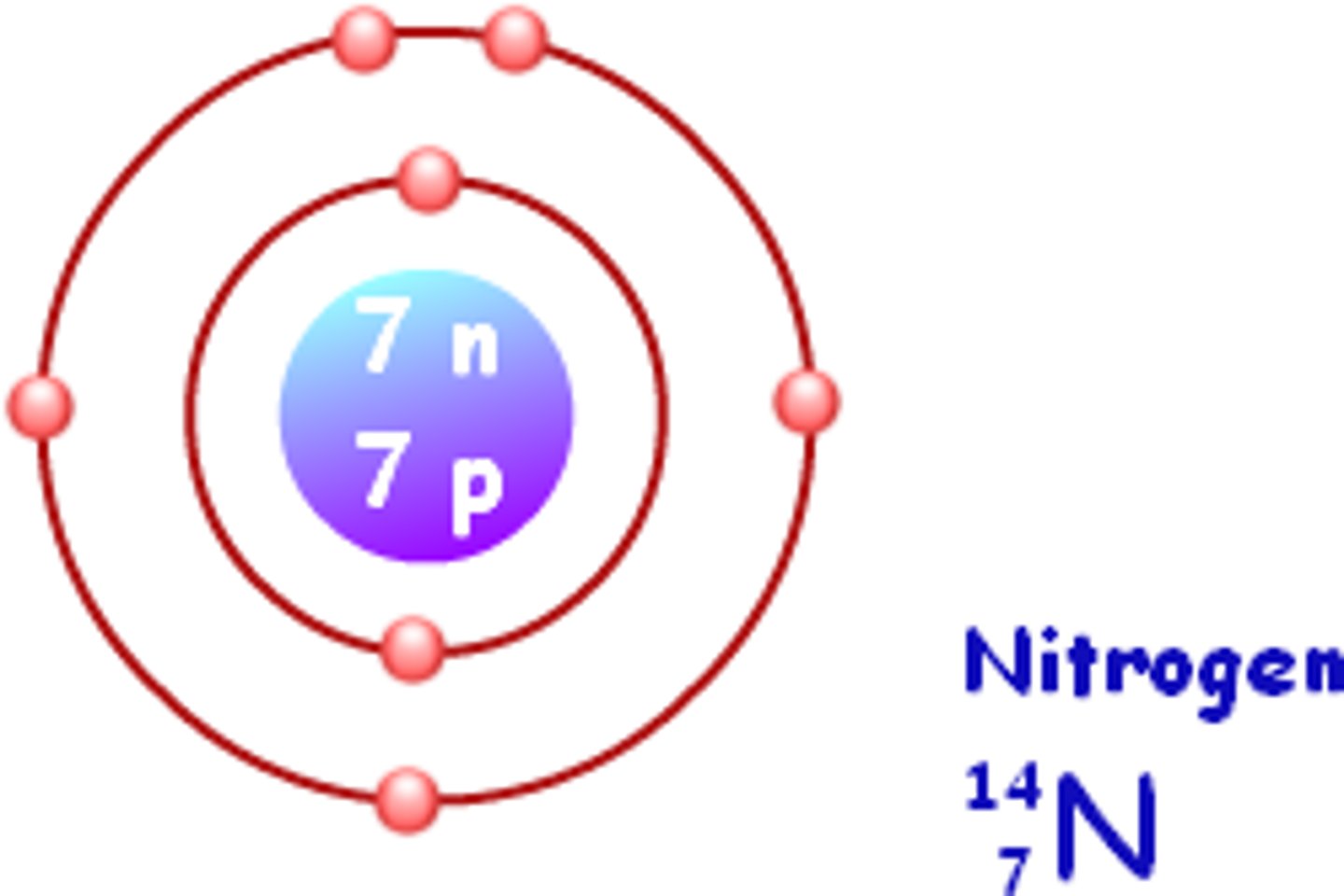
Bohr model for Nitrogen
Atomic number: 7
Atomic configuration: 2, 5
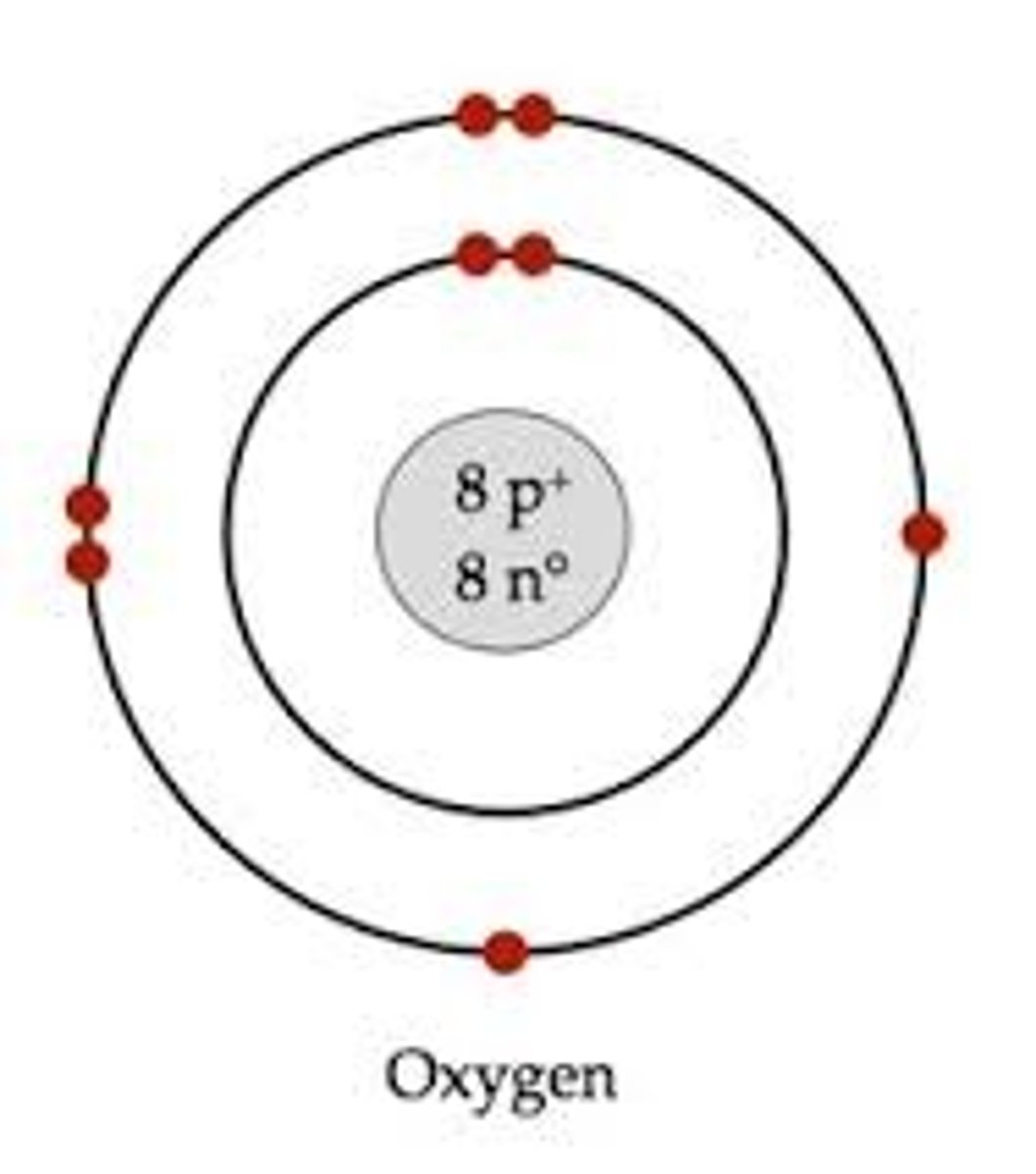
Bohr model for Oxygen
Atomic number: 8
Atomic configuration: 2, 6
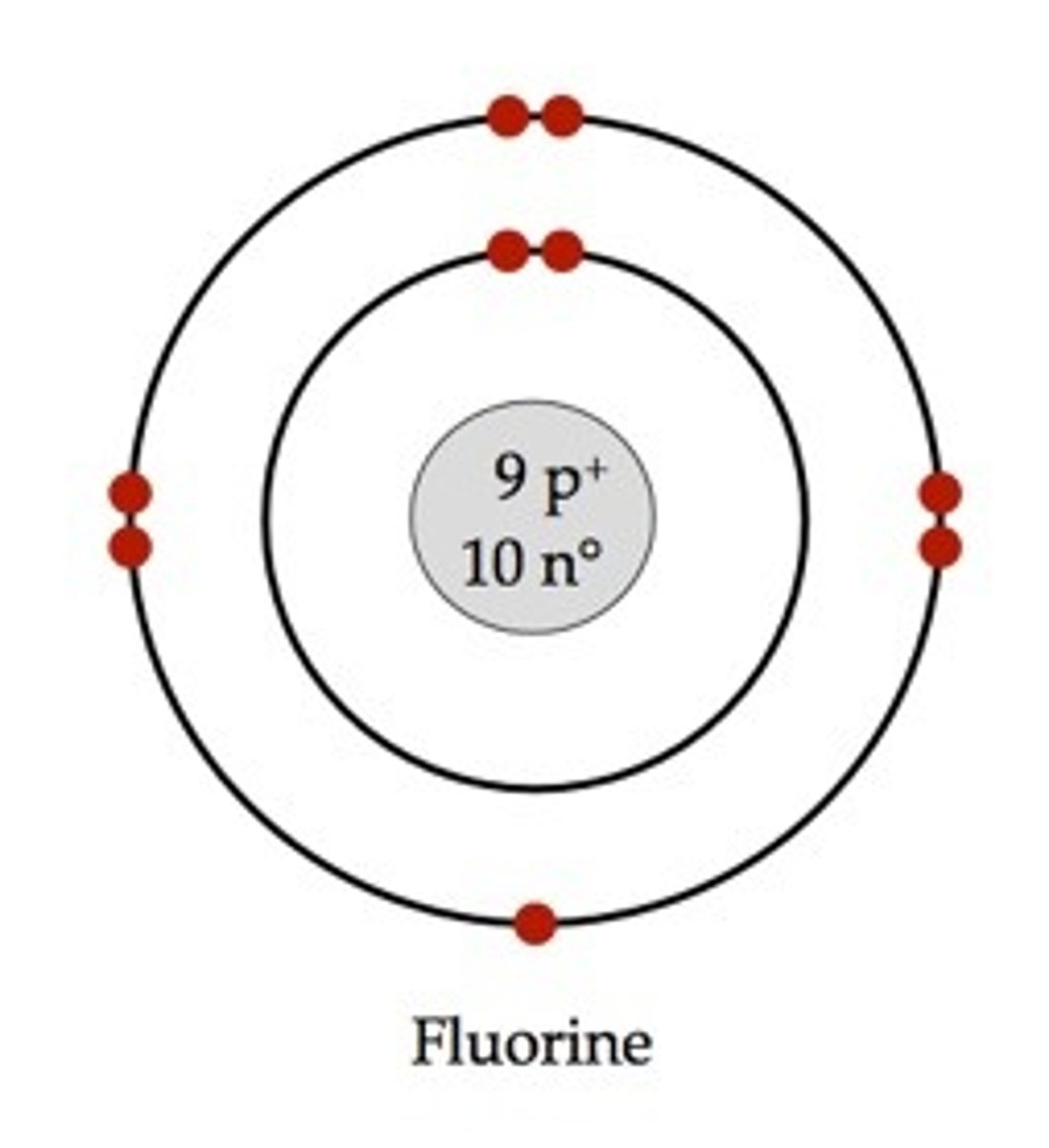
Bohr model for Fluorine
Atomic number: 9
Atomic configuration: 2, 7
Bohr model for neon
Atomic number: 10
Atomic configuration: 2, 8
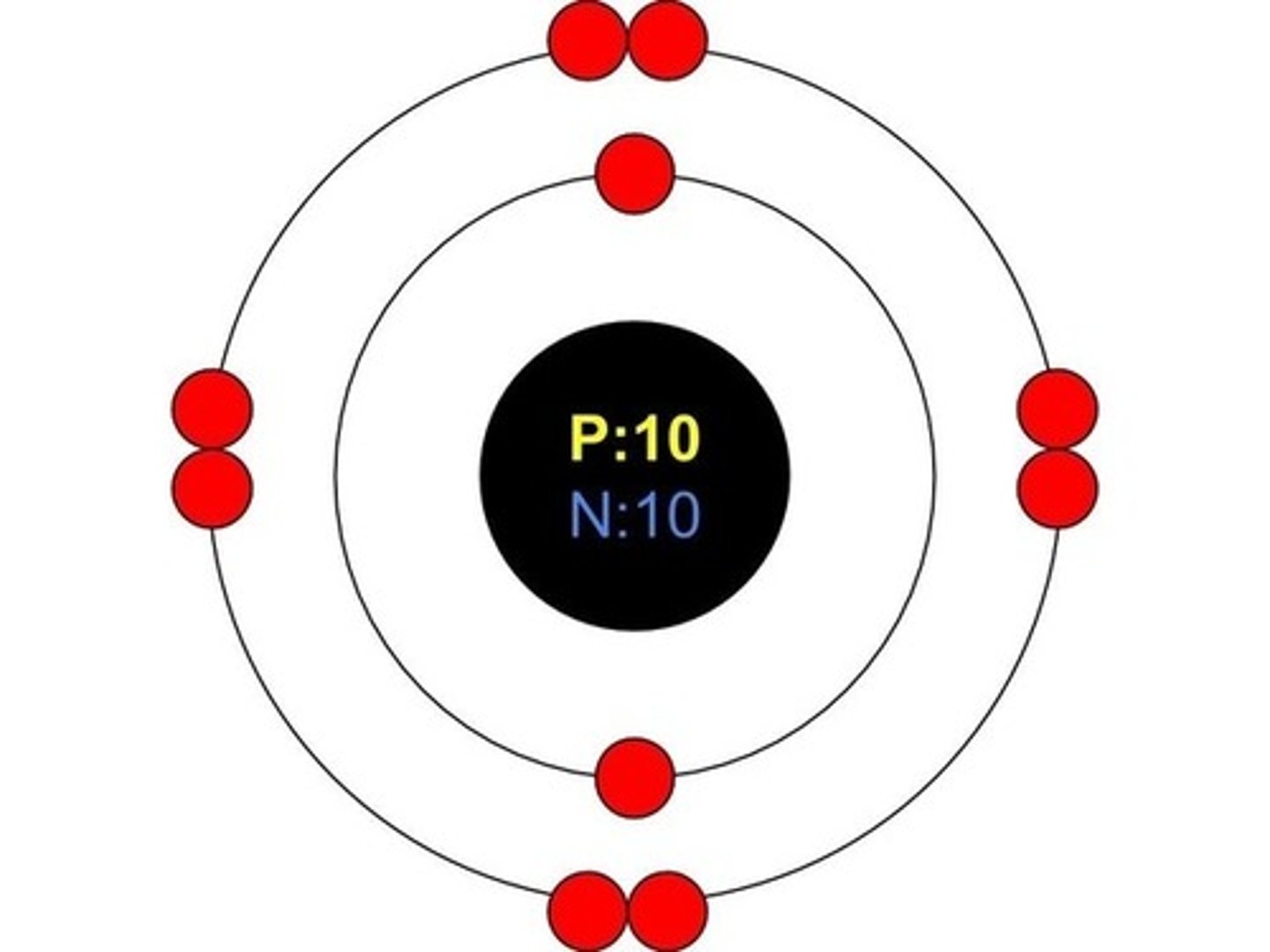
Bohr model for sodium
Atomic number: 11
Atomic configuration: 2, 8, 1
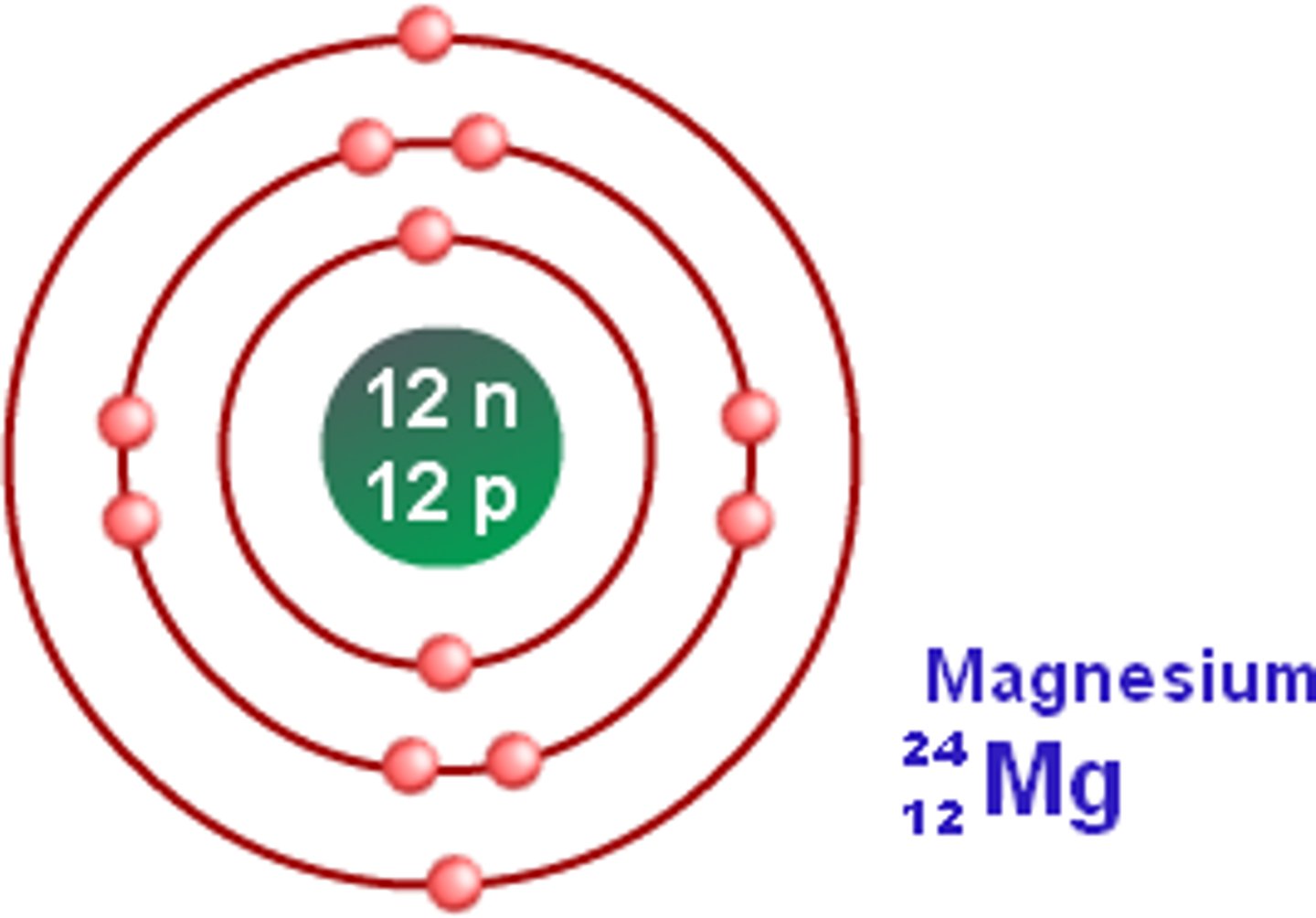
Bohr model for magnesium
Atomic number: 12
Atomic configuration: 2, 8, 2
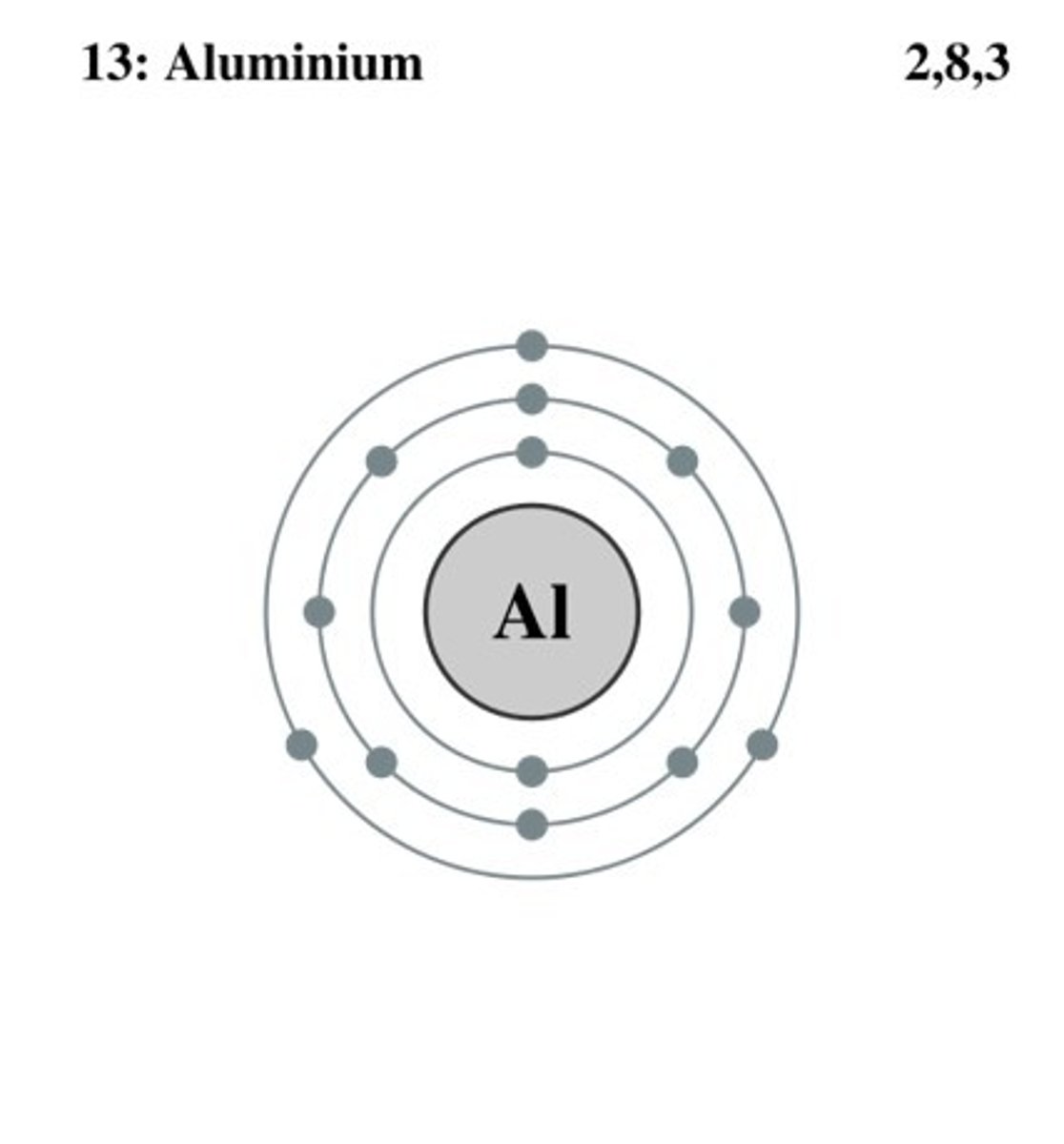
Bohr model for aluminium
Atomic number: 13
Atomic configuration: 2, 8, 3
Bohr model for silicon
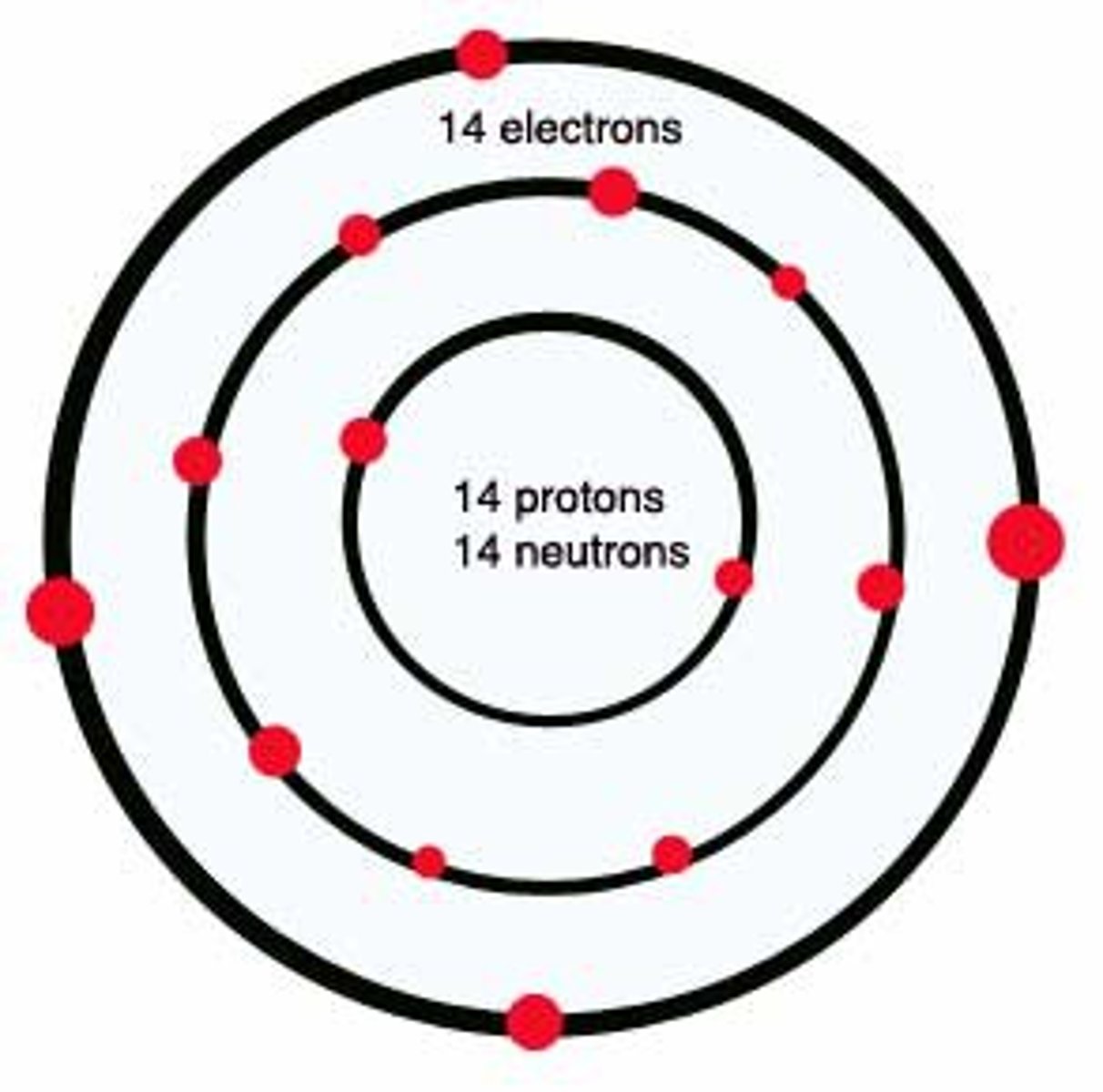
Atomic number: 14
Atomic configuration: 2, 8, 4
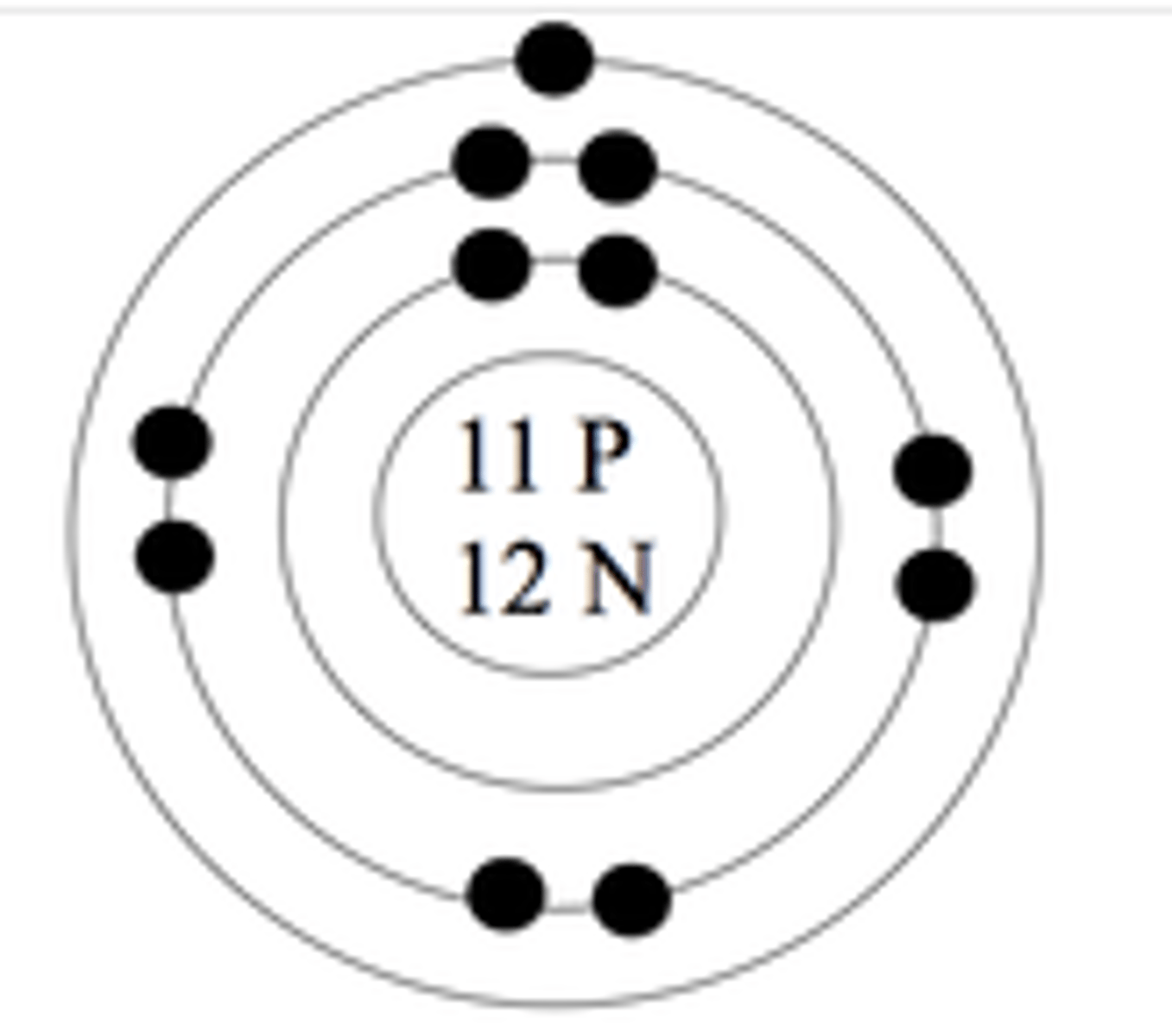
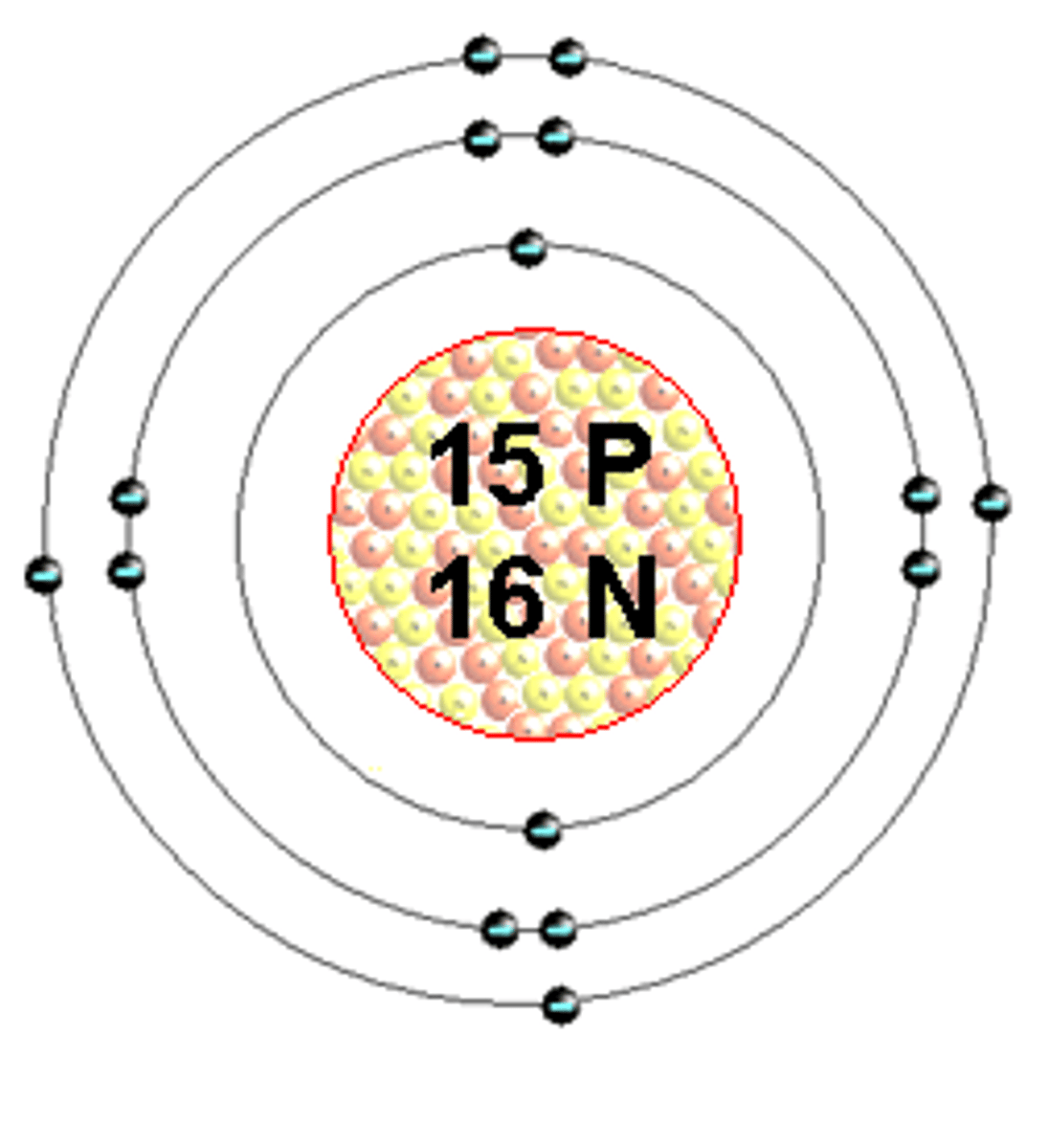
Bohr model for phosphorus
Atomic number: 15
Atomic configuration: 2, 8, 5
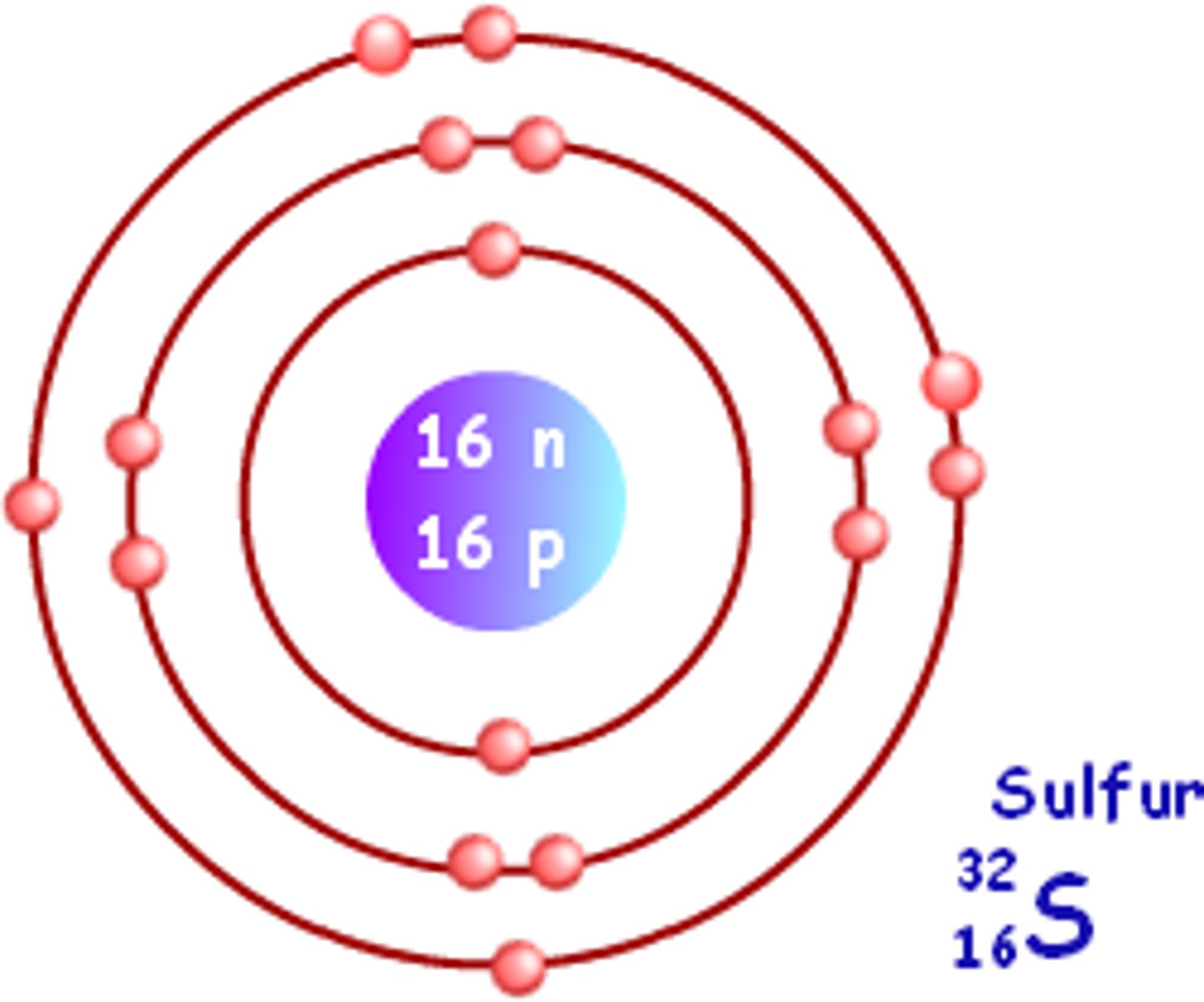
Bohr model for sulfur
Atomic number: 16
Atomic configuration: 2, 8, 6
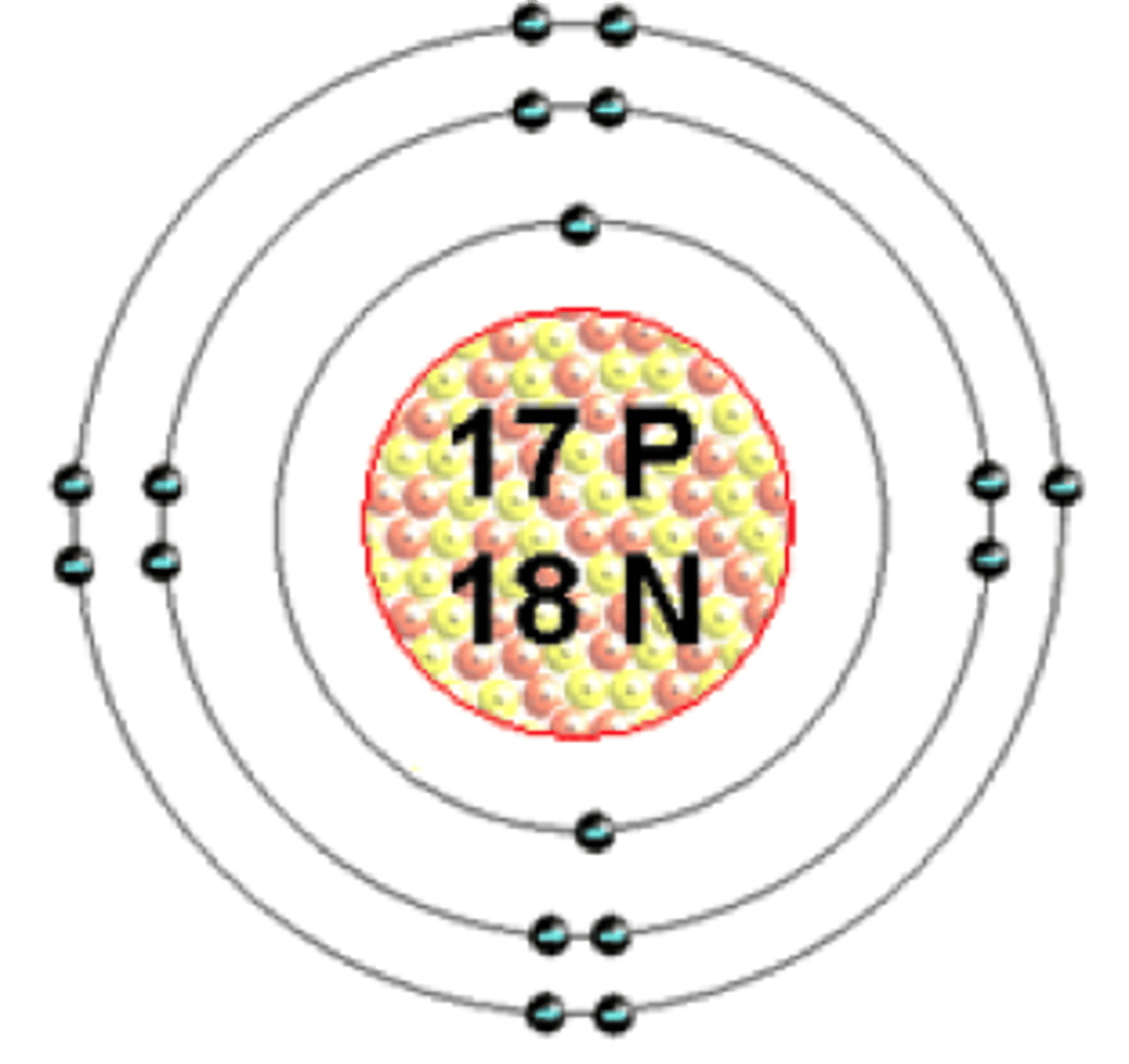
Bohr model for chlorine
Atomic number: 17
Atomic configuration: 2, 8, 7
Bohr model for potassium
Atomic number: 19
Atomic configuration: 2, 8, 8, 1
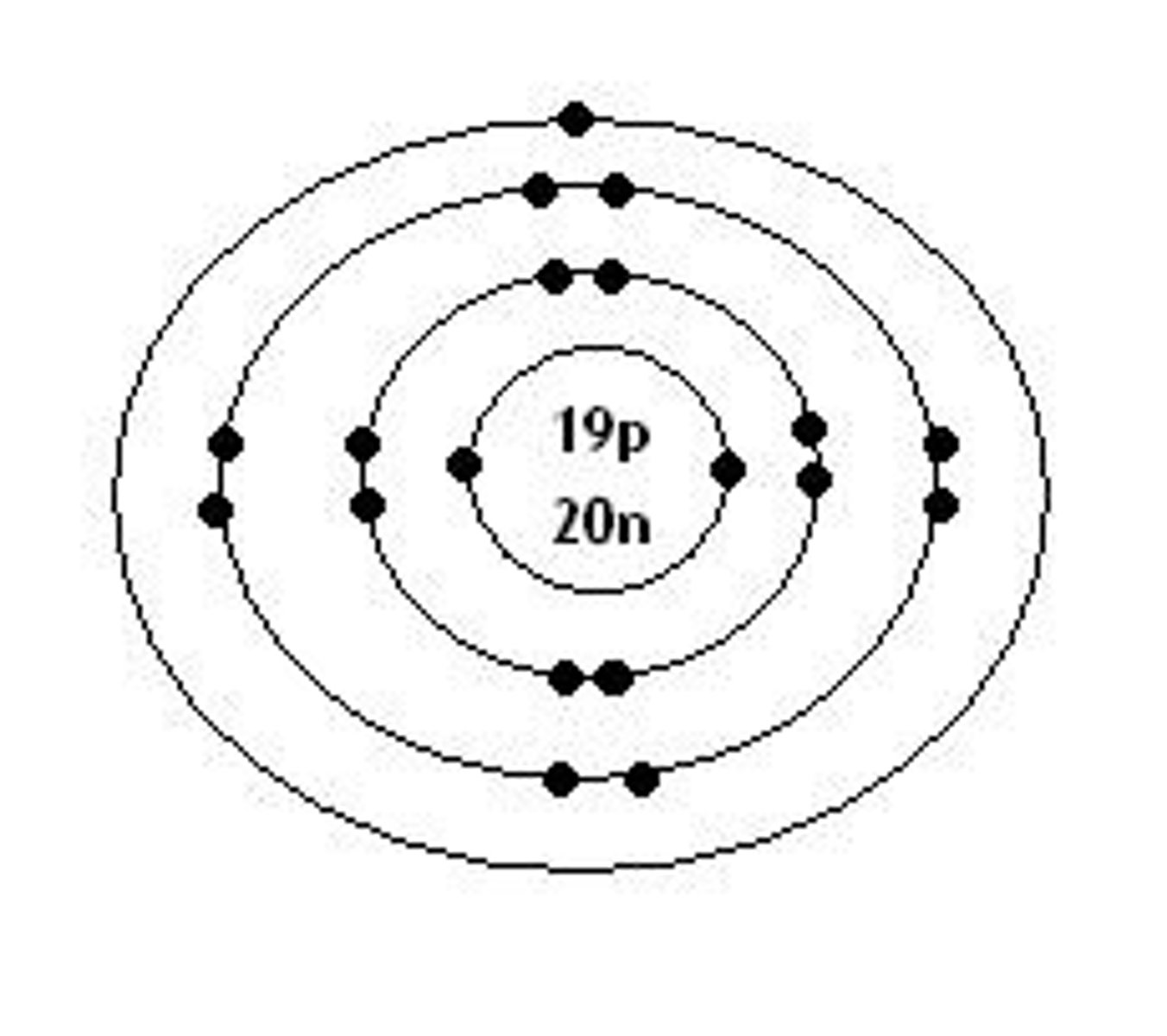
Bohr model for calcium
Atomic number: 20
Atomic configuration: 2, 8, 8, 2
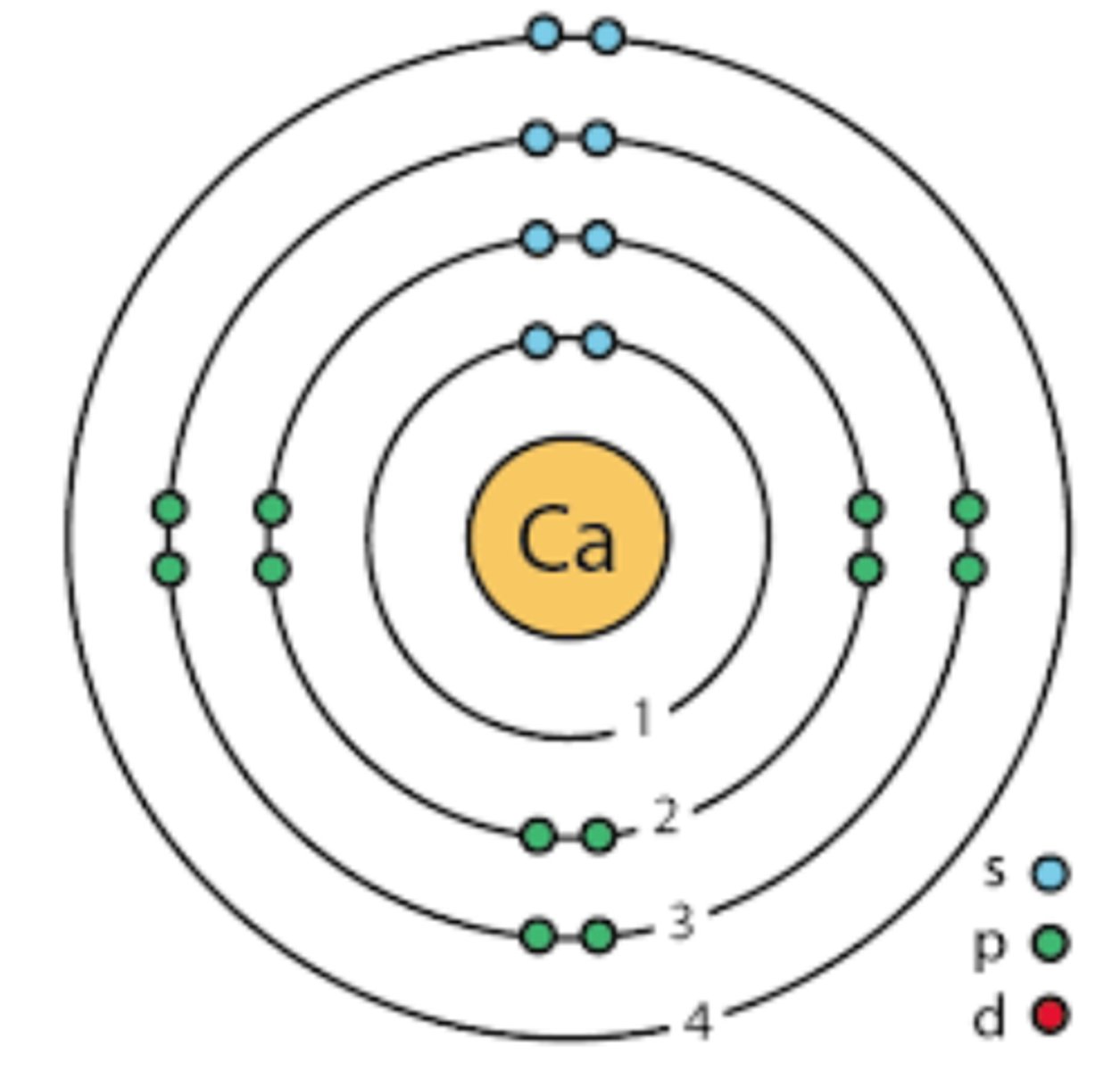
Homolygous
term used to refer to chromosomes in which one set comes from the male parent and one set comes from the female parent
homologous chromosomes
Pair of chromosomes that are the same size, same appearance and same genes.