fetal environment pt 1 (jo copy)
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
What size should the CRL be when a heartbeat can be seen?
Greater than 5 mm
When should GSD or MSD be measured?
Early as 5 weeks
How accurate is GSD or MSD?
± 10 days
What is the most accurate way to determine the fetal growth rate (FGR)?
Abdominal circumference
What is the normal measurement for the lateral ventricle?
Less than 10 mm
What is included in the fetal environment?
Amniotic fluid
Umbilical cord
Placenta
Uterus
what should we look for in the cervix?
cervical incompetence
What is the normal measurement for cervical length in the third trimester?
how do we measure?
always want it to be over 2.5 cm
transvaginal from internal to external os
too short of a measurement in the 3rd trimester?
less than 2.5 cm
the myometrium should be __________ to the placenta?
hypoechoic
What are focal uterine contractions?
Muscular contractions that move from cervix towards fundus and can be seen on US
what are Braxton Hicks contractions?
false labor
move from fundus towards cervix
how to differentiate a fibroid vs focal uterine contraction?
Focal Uterine Contractions- change size and location during the exam
sit in anterior portion of placenta-likely a contraction
Fibroids remain same size and location throughout the exam
how to differentiate between a fibroid and a subchorionic hematoma?
color Doppler!!!
fibroid will have some internal flow
Rescan in a few days: Subchorionic hematoma will become more cystic in appearance.
What are the roles of the placenta?
Protection
Nutrition
Respiration
Excretion of waste
Storage
Hormone secretion
placental functions? (in depth- don’t study)
Protection: filtering harmful substances out of mother’s blood
Nutrition: nutrient exchange (mother’s blood—> fetus’ blood)
Respiration: O2 and CO2 exchange (mother’s and fetus’ blood)
Excretion: metabolic waste transfer (fetus’ blood —> mother’s blood) for processing & excretion by mother’s body.
Storage: stores carbs, proteins, Ca2+, & iron; released to fetal blood as needed.
Hormone Secretion: produced by syncytiotrophoblast; helps maintain pregnancy.
HCG, Estrogens, Progesterone
where does fetal blood enter the placenta?
through umbilical cord
when can placental position and configuration be seen sonographically?
by end of 1st trimester
what is the chorionic villus?
functional unit of placenta
made up of arteries and veins from embryo and intervillous spaces
what are intervillous spaces?
spaces which fill up with maternal blood
What composes the fetal portion of the placenta?
Chorion frondosum (chorionic plate)
What composes the maternal portion of the placenta?
Decidua basalis of endometrium
When maternal environment is poor, the placenta becomes…
More efficient at nutrient, oxygen, and waste product transfer to protect fetus
(T/F) The placenta has an unlimited ability to compensate for a poor maternal environment.
False; There are limits to placentas ability to compensate
What occurs when stresses exceed the ability of the placenta to compensate?
Placenta is damaged and fetus is at risk of IUGR and fetal demise
During the first trimester, the fetus is designed to develop at a…
Low oxygen state
(T/F) More oxygen is required by embryo as development becomes more complex.
True; By this time, placenta will have developed enough to provide for fetus
What is the normal insertion point of an umbilical cord on the placenta?
Near center
What is a battledore placenta?
umbilical cord inserts near edge of placenta
a= normal insertion; b= battledore insertion
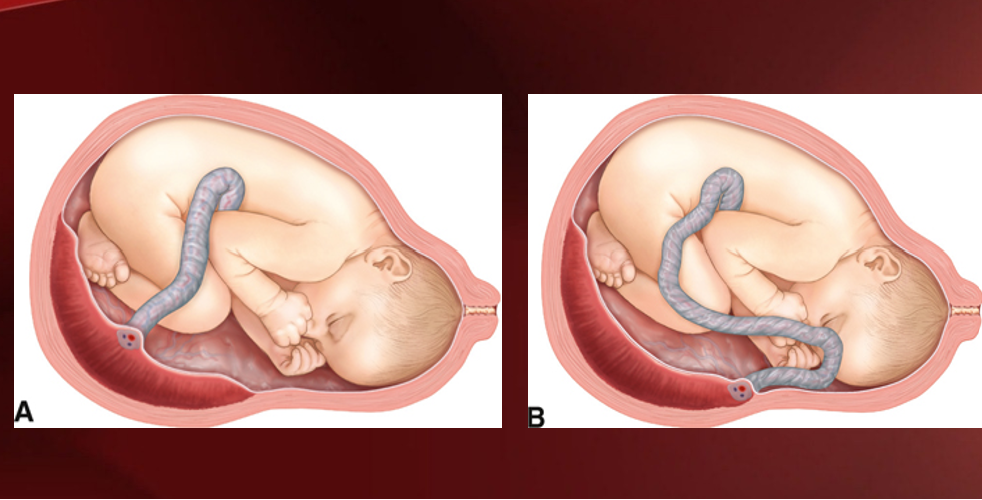
What is another term for battledore placenta?
Marginal insertion
What is the significance of a battledore placenta?
Not clinically significant unless cord is delivered before baby causing cord prolapse (leads to hypoxia and fetal demise)
What is a velamentous placenta?
When umbilical cord branches out into separate vessels before actually entering placenta
a= normal; c= velamentous
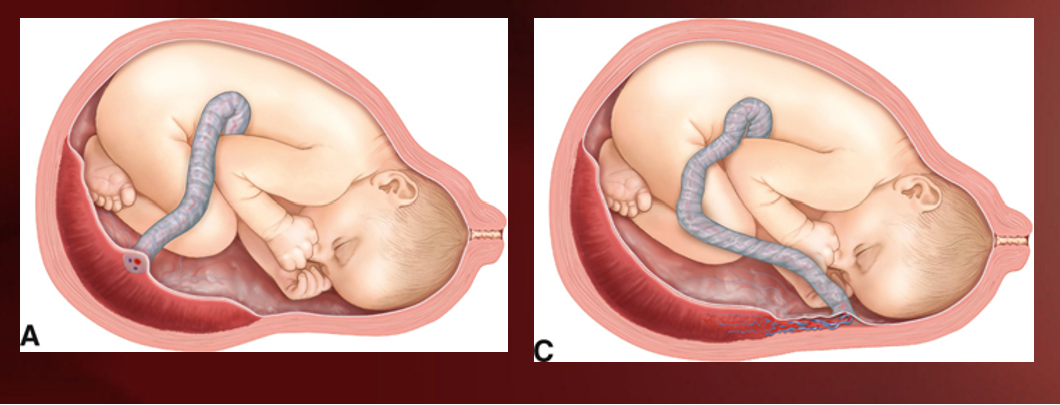
What is the significance of a velamentous placenta?
Increased risk of fetal hemorrhage in cases of vasa previa
placentomegaly (thick placenta) causes?
placental hydrops (edema of placental tissue/ ground glass appearance)
gestational trophoblastic disease
Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome
confined placental mosaicism (abnormal karyotype of placenta, but not of fetus)
thin placenta causes?
maternal HTN/ pre-eclampsia
placental infarction
maternal diabetes (type 1)
abnormal placental development
The placenta is an…
Endocrine gland
What is the function of the hCG secreted by the placenta?
Secreted during first trimester to keep corpus luteum from degenerating so progesterone levels remain high to maintain pregnancy
What is the function of the estrogen secreted by the placenta?
Secreted during second trimester to help maintain pregnancy and prepare breasts for lactation
What is the function of the progesterone secreted by the placenta?
Secreted during second trimester to help maintain pregnancy and prepare breasts for lactation
When would a translabial scan be performed?
When evaluating for bulging membranes
(T/F) As the pregnancy progresses, the texture of the placenta changes as it matures/ages.
True; It ages, but it DOES NOT age at same rate in every pregnancy
Which maternal conditions or habits are known to accelerate the maturation process of the placenta?
Diabetes (Type 1)
Pre-eclampsia
Hypertension
Smoking
Which maternal conditions or habits are known to decelerate the maturation process of the placenta?
Gestational diabetes
Rh isoimmunization
How is the maturity of the placenta evaluated?
Grade 0: Homogenous
Grade 1: Small cystic spaces
Grade 2: Small cystic spaces with calcifications
Grade 3: “Cumulous cloud” and heterogenous appearance with calcifications
What does IUGR mean?
Fetal growth restriction
What is the normal thickness of the placenta at it’s midpoint?
2-4 cm
What is placentomegaly?
When placenta exceeds 5 cm in thickness and is called placenta hydrops
How can the age of the placenta be determined just by looking at the thickness?
2 cm thick = 20 weeks gestation, 3 cm thick = 30 weeks gestation, etc.
What is a thin placenta?
When placenta measures less than 1.5 cm in thickness
(T/F) IUGR causes placental thinning.
False; IUGR is a RESULT of placental insufficiency which can also cause placental thinning
What is an accessory or succenturiate placenta?
Smaller lobe of placental tissue connected to main placenta by blood vessels but NOT placental tissue
What are the risk factors associated with an accessory or succenturiate placenta?
Increased risk of fetal hemorrhage due to vasa previa
Increased risk of retained fetal tissue
Increased risk of placental infarctions
What is vasa previa?
Prescence of umbilical cord vessels across internal os and cause increased risk of vessel rupture or hemorrhage during delivery due to vessels in membrane not protected by placental tissue (ruptured membranes)
What is considered a normal placental location?
Anywhere as long as it is more than 2 cm away from internal os of cervix
When should the cervix and placental relationship be evaluated for placental previa?
20 weeks
What is placenta previa?
When placenta will come out first in a vaginal delivery due to it’s close proximity to internal os
What is a low-lying placenta?
When inferior margin of placenta is less than 2 cm from internal os
What is a marginal previa?
When inferior margin of placenta comes up to edge of internal os but does not cover any part of it
What is partial previa?
When inferior margin of placenta partially covers internal os
What is complete previa?
When placenta completely covers internal os
What is abnormal placental attachment (MAP)?
When placental tissue has invaded uterine wall beyond decidua basalis to some degree
What are the risk factors associated with abnormal placental attachment (MAP)?
History of C-section
Placenta previa
What is placenta accreta?
When placental tissue attaches to myometrium, extending just beyond basal endometrium
What is placenta increta?
When placental tissue invades deeply into myometrium but does not perforate uterine wall
What is placenta percreta?
When placental tissue perforates uterine wall and can invade neighboring tissues
What occurs in 90% of cases of placenta percreta?
Hysterectomy required immediately after C-section
What is the sonographic appearance associated with MAP in the second and third trimester?
Anterior placental implantation
Loss of myometrial clear zone
Swiss cheese appearance or multiple vascular lakes
What is the clear zone measurement that indicates accreta?
Less than 1 mm
What is a subchorionic bleed or hematoma?
Collection of blood between chorion and uterine wall that is seen during first trimester and resolves on its own
What is a subamniotic bleed or hematoma?
Collection of blood between amnion and chorion
what is an intraplacental bleed? what is it caused by?
bleeding within placental tissue
caused by:
intervillous thrombosis
Kline’s hemorrhage/ intraplacental cavernae
What is a retroplacental bleed or hematoma?
Collection of blood between placenta and uterine wall that causes placental abruption
What is placental abruption?
Separation of basal plate of placenta (maternal) from uterine wall
uterus hemorrhages into retroplacental space
How is placental abruption classified?
Location
Presence or absence of vaginal bleeding
ex: retroplacental/ central and marginal
or classified by degree of separation:
ex: partial or complete
What is a retroplacental/ central placental abruption?
Separation behind central portion of placenta, away from placenta edge or margin
often concealed with no vaginal bleeding
What is a marginal placental abruption?
Separation at edge or margin of placenta
often apparent with vaginal bleeding
What are the risk factors associated with placental abruption/ hemorrhage?
Maternal hypertension (HTN)
prior placental abruption
short umbilical cord
uterine anomalies
retroplacental fibroid
abdominal trauma
placenta previa
smoking
cocaine/ meth use
What is intervillous thrombosis?
Common and not significant hemorrhage that occurs from tears in chorionic villi vessels and results in mixing of maternal and fetal blood
What is placental infarct?
Focal lesion caused by ischemic necrosis due to occlusion of spinal arteries
What is the sonographic appearance associated with acute placental infarct?
Hypoechoic
What is the sonographic appearance associated with chronic placental infarct?
Hypoechoic or cystic
Calcifications
What are venous lakes or lacunae?
Irregular anechoic spaces located beneath chorionic plate
What is the presence of numerous prominent lakes associated with?
Placenta accreta
What is the most common non-trophoblastic tumor of the placenta?
Chorioangioma
What is chorioangioma?
Benign, vascular tumor similar to hemangioma
What is the significance of the size of a chorioangioma?
Small and solitary: Not significant
Large and multiple: May cause severe complications including death
What is the sonographic appearance associated with chorioangioma?
Well-defined mass
Increased vascularity
When is the umbilical cord formed?
Week 7 gestation
What is the original appearance of the umbilical cord?
Two umbilical veins
Two umbilical arteries
What is the final umbilical cord configuration?
One umbilical vein
Two umbilical arteries
What is the function of the umbilical vein?
Carries oxygenated blood from placenta to fetus
Where does the umbilical vein enter the fetus?
Umbilicus and runs lateral to left portal vein
What does the umbilical vein connect to?
Enters portal sinus and connects to ductus venosus, bypassing hepatic circulation
After birth, the umbilical vein forms the…
Ligamentum Teres (Round ligament)
After birth, the ductus venosus forms the…
Ligamentum Venosum
What is the function of the umbilical arteries?
Carry partially deoxygenated blood from fetus to placenta
Where do the umbilical arteries arise from?
Internal iliac arteries and run along sides of fetal bladder to umbilicus where they enter umbilical cord
After birth the umbilical arteries form the…
Superior vesicle arteries
Median umbilical ligaments
What do the superior vesicle arteries supply blood to?
Bladder
What structures do the median umbilical ligaments connect?
Bladder to anterior abdominal wall