Final Exam Possible SAQs
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Ch8: Find the effect size, describe the strength of the effect size, use the specific sentence outline, other possible explanations?
Find effect size: may be given to us, but the equation is… (mean1 - mean2)/standard deviation
Cohens criteria for strength: 2% (small effect), 5% (moderate effect), and 8% (strong/large effect)
“(effect size)% of the variability in (Y) can be explained by (X)”
Possible explanations: will vary (think about confounds)
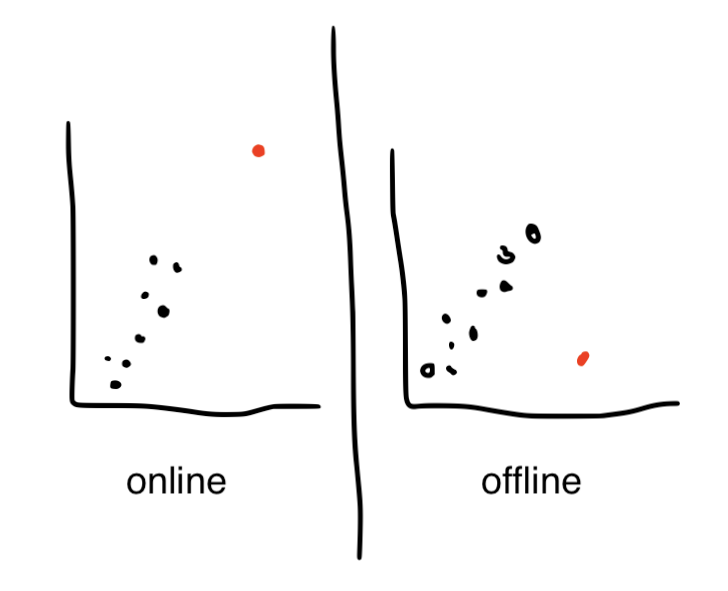
Ch8: Outliers - Know outliers, online outliers, and offline outliers
outliers - an extreme score; can be detected through standard deviation (more than 3 sd’s away from the mean) or visually from a scatterplot; greater impact on smaller sample sizes
online outlier - follows pattern of data and makes correlation coefficient appear stronger
offline outlier - doesn’t fall in line with data and makes correlation coefficient look weaker
Ch4: describe at risk vs at minimal risk
at risk - risk is above everyday risk; would have to be modified; ie run across a highway
at minimal risk - at or below everyday risk; ie run across a crosswalk
Ch10: Qualitative vs quantitative differences in independent variables
qualitative - differences in type or kind of IV
ex. exercise: G1 - run a mile/day; G2 - swim a mile/day
quantitative - differences in amount of IV
ex. exercise: G1 - run 30min/day; G2 - run 60min/day
Ch10: types of independent variables - be able to identify which one is being described on the exam
often used together:
environmental - manipulation of the subjects’ physical or social environment
instructional - differences in verbal instructions given to the subjects
invasive - creating physical changes in the subject’s body; ex. drug study (drug v. placebo)
Ch10: matched random assignment - what is it? give an example.
researchers try to increase the similarity among the experimental groups; pretests subjects on a measure known to be relevant to the outcome of a study
ex. Effects of caffeine on memory: give memory test → rank subjects based on scores → group subjects → split the pairs (ie one person from pair gets caffeine and the other one doesn’t)
Ch11: Be able to name the threat to internal/external validity and what is it a threat to (internal/external?)
pseudo-experiments - threat to internal validity
history - threat to internal validity
maturation - threat to internal validity
regression toward the mean - threat to internal validity
Hawthorne effect - threat to internal validity
testing effect - threat to internal validity
homogeneous attrition (experimental mortality) - threat to external validity
heterogeneous attrition (experimental mortality) - threat to internal validity
Ch11: What does OS = TS + ME mean? Give an example.
Observed Score = True Score + Measurement Error
explanation for regression toward the mean
ex. 80 = 90 + sick; 80 = 70 + good at guessing
ex. IQ test - if someone gets a 130:
Explanation 1) OS = TS → not likely because there is no measurement error
Explanation 2) TS > 130 → not likely bc that’s way above the mean
Explanation 3) TS < 130 → more likely bc that means that the TS is actually closer to the mean
Ch12: “Design an __ X __ … study”
2 × 3 study - “Effects of diet and exercise on stress levels”
1st IV - no diet and diet (2 levels)
2nd IV - no exercise, exercise 1hr/week, and exercise 2hrs/week (3 levels)
2 main effects; 6 interactions/groups
2 × 3 × 4 study - “Effects of diet, exercise, and grade level on stress levels”
1st IV - no diet and diet (2 levels)
2nd IV - no exercise, exercise 1hr/week, and exercise 2hrs/week (3 levels)
3rd IV - freshman, sophomore, junior, and senior (4 levels)
3 main effects; 24 interactions/groups