Class 11: Chapter 6 - Organizing
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is an organization?
A group of individuals who work together toward a common goal.
What are the different types of legal organizations?
Sole proprietorship
Partnership
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
Corporation
Cooperatives
What is a sole proprietorship?
A business that is owned and operated by one person.
What are the pros of a sole proprietorship?
It’s is simple to organize and shut down
Has few legal restrictions
The owner is free to make all decisions
Profit is only taxed once
What are the cons to a sole proprietorship?
The owner faced unlimited liability for the debts of the business
May be difficult to raise capital to fund growth
Duration of the business is limited to the life of the proprietor
What is a partnership?
An association of two or more partners to carry on as co-workers of a business for profit.
What are the pros of partnerships?
Relatively easy to organize
Has few legal restrictions
Managerial skills, decision making abilities, and financial resources are combined
Does not pay taxes - the partners do on their individual tax forms
What are cons of partnerships?
Divided decision-making authority
Potential damage to the business when partners disagree
Unlimited liability for debt
What is a limited liability company (LLC)?
A business structure that protects it owners from personal liability for business debts.
What are the characteristics of LLC?
Limited personal liability for the debts and actions
No maximum number of members
Provide management flexibility
Pass-through taxation
Income is taxed once
What are corporations?
Legal entities owned by shareholders, who have no liability beyond loss of the value of their stock.
What are the pros of corporations?
Owned by founder and/or partners
Civil liability limited to stock in corporation
Have perpetual life
What are the cons of corporations?
Difficult and expensive to organize
Income is taxed twice: once as corporate income tax the year is made, and again as personal income tax when the after-tax profit is distributed as dividends
Subject to many state and federal controls
What are cooperatives (co-ops)?
A special type of organization owed by users and customers, to whom earnings are usually distributed tax-free in proportion to patronage.
In order to purchase things, a membership is required
What are examples of co-ops?
REI is the most well known co-ops
Most commonly used in rural areas to handle distribution of farm products and electricity
How do cooperatives work?
Each member buys a share initially for a few dollars, and they can cast one vote to elect the board members who can manage it.
What must effective organizing consider?
The basic mission and long-range objectives established for the organization and the strategy conceived to accomplish them.
What are Peter Drucker’s three questions to help identify the key activities?
In what area is excellence required to achieve the company’s objectives?
In what areas would lack of performance endanger the results, if not the survival, of the enterprise?
What are the values that are truly important to us in this company?
What is a limited partnership?
At least one general partner with unlimited liability. The others have limited liability. (One partner is responsible for liabilities)
Ex) Your business has a corporate credit card and your buddy creates debt… you are now also in debt
In strategic planning, what are the keys to organization?
Mission/Vision
Long range objectives
What assets are needed
What knowledge is requred
To exist, an organization must incorporate what?
Verifiable objects - planning
Clear idea of duties and responsibilities
Understand the direction of authority
Supply quality information - communication
What is organizing?
Identification/classification of the required activities
Proper grouping of those activities
Assignment of a manger to each activity
With authority to do or delegate (delegation = big duty)
Horizontal and vertical integration (structure that interacts both ways)
Describe Hierarchical Organizations.
Every entity (except 1) subject to a single other entity
Most dominant type among large corporations
What is a pro to Hierarchical Design?
The shallow design allows communication to flow efficiently.
What are the patterns of Departmentation?
Basic
Functional
Product
Geographic
Describe basic organizational structure.
Everyone does everything
What is an example of basic organization?
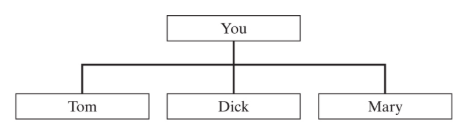
What is functional departmentation?
Everyone has their own role and reports to one boss at the top/
What is an example of functional departmentation?
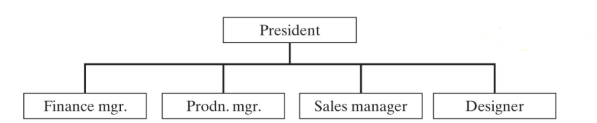
What is product departmentation?
A structure based on the product being produced.
What is an example of product departmentation?
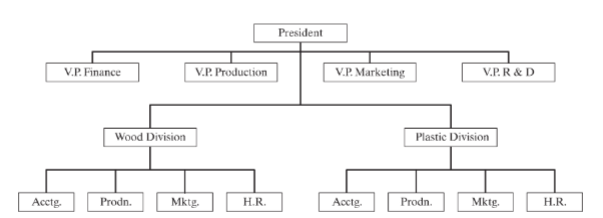
What is geographic departmentation?
A structure based on geography of the company.
What is a example of geographic departmentation?
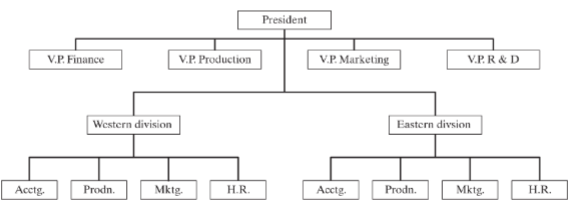
What is mixed departmentation?
A structure with a combination of product and geographical structures.
What is an example of mixed departmentation?
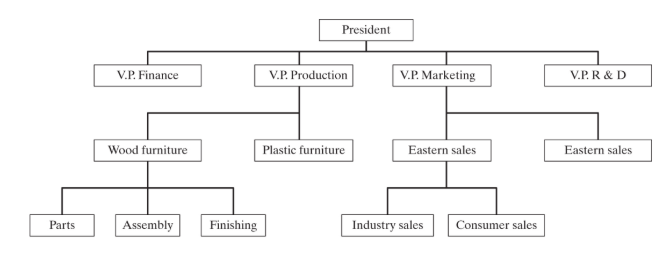
What is the “span of 4”?
One top manager or CEO
4 high-level managers below the CEO
4 mid or low-level managers below the high-level manager
Each mid or low-level manager will have 4 workers
What is the “span of 8”?
One CEO has 8 managers reporting to him/her
It could be the 8 managers have 8 more managers under them!
At the bottom, 8 workers report to some supervisor
What are factors that determine effective span?
How well people are trained
How well are people qualified to perform the job (need to look over shoulder)
Perform routine activities or balance multiple projects
Require staff assistance
What is the difference between something that has a small span vs. a large span?
A routine activity has less span whereas balancing multiple projects has more span.
What are current trends regarding span of control?
Information Revolution facilitates increasing span
20 or more subordinates at any level
No more than 5 levels at most
What are line staff?
Superior/Subordinate relationships typically represented vertically in organizational charts
What are administrative staff?
Advisory in nature, degree of influence may vary
– Provide advice on request
– Recommendations when appropriate
– Consulted by line but have no direct
authority over line
– May have concurring authority - veto
authority over line
What are service staff?
Centralized support functions
– Custodial/physical plant
– Security/Safety
– Medical
– IT/computers. Etc
How can an organization be structured?
Can be deep top to bottom
Wide across with many functions
Layered as such
Shallow top to bottom and
Wide or narrow
Too deep = slow communications and slow to act
Too wide = too many functions to be coordinated
What are the 3 basic types of production organizations?
Production
Mass production
Process production
Describe production organizations.
“job shop,” custom small batches, order-driven.
ex) local machine shop
Describe mass production organizations.
Auto assembly, furniture, air conditioners
Most common type
Ex) Apple, Tesla, Ford
Describe process production.
Continuous processing
Ex) refineries, cement plants, beer brewing
What is the definition of a team?
Small number of people who are committed to a common goal, objectives, and approach to the goal