Biochemistry - Module15B 2026 Ratio
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
A. Marked reduction in the synaptic concentration of acetylcholine leading to weakness and loss of muscle tone
Match the following conditions or diseases to the correct underlying mechanism and/or consequence.
Botulism
A. Marked reduction in the synaptic concentration of acetylcholine leading to weakness and loss of muscle tone
B. Progressive weakness throughout the day due to reduced acetylcholine receptor count
C. Loss of Renshaw cell function leading to spastic paralysis and overdrive of the sympathetic nervous system
D. Immune-mediated destruction of calcium channels at the presynaptic terminal
B. Progressive weakness throughout the day due to reduced acetylcholine receptor count
Match the following conditions or diseases to the correct underlying mechanism and/or consequence.
Myasthenia Gravis
A. Marked reduction in the synaptic concentration of acetylcholine leading to weakness and loss of muscle tone
B. Progressive weakness throughout the day due to reduced acetylcholine receptor count
C. Loss of Renshaw cell function leading to spastic paralysis and overdrive of the sympathetic nervous system
D. Immune-mediated destruction of calcium channels at the presynaptic terminal
C. Loss of Renshaw cell function leading to spastic paralysis and overdrive of the sympathetic nervous system
Match the following conditions or diseases to the correct underlying mechanism and/or consequence.
Poisoning from Tetanus toxin
A. Marked reduction in the synaptic concentration of acetylcholine leading to weakness and loss of muscle tone
B. Progressive weakness throughout the day due to reduced acetylcholine receptor count
C. Loss of Renshaw cell function leading to spastic paralysis and overdrive of the sympathetic nervous system
D. Immune-mediated destruction of calcium channels at the presynaptic terminal
D. Immune-mediated destruction of calcium channels at the presynaptic terminal
Match the following conditions or diseases to the correct underlying mechanism and/or consequence.
Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome
A. Marked reduction in the synaptic concentration of acetylcholine leading to weakness and loss of muscle tone
B. Progressive weakness throughout the day due to reduced acetylcholine receptor count
C. Loss of Renshaw cell function leading to spastic paralysis and overdrive of the sympathetic nervous system
D. Immune-mediated destruction of calcium channels at the presynaptic terminal
B. Acetylcholine
Match the following structures/nuclei with the neurotransmitters they produce or respond to.
Nucleus basalis of Meynert
A. Endorphins / endogenous opioids
B. Acetylcholine
C. Dopamine
D. Serotonin
D. Serotonin
Match the following structures/nuclei with the neurotransmitters they produce or respond to.
Raphe nuclei in the brainstem
A. Endorphins / endogenous opioids
B. Acetylcholine
C. Dopamine
D. Serotonin
C. Dopamine
Match the following structures/nuclei with the neurotransmitters they produce or respond to.
Ventral tegmental area in the midbrain
A. Endorphins / endogenous opioids
B. Acetylcholine
C. Dopamine
D. Serotonin
A. Endorphins / endogenous opioids
Match the following structures/nuclei with the neurotransmitters they produce or respond to.
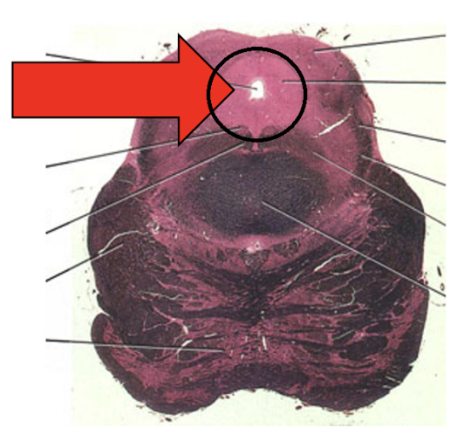
The group of neuronal cell bodies pointed by the arrow (area in the black circle)
A. Endorphins / endogenous opioids
B. Acetylcholine
C. Dopamine
D. Serotonin
A. Cobalamin (C. Pyridoxine)
Which of the following IS required in the process of converting serotonin to melatonin?
A. Cobalamin
B. Thiamine
C. Pyridoxine
D. Ascorbate
C. Synthesis of Acetylcholine from Acetyl-CoA and Choline
Which of the following processes will be impaired LEAST when there is Vitamin B6 deficiency?
A. Synthesis of Serotonin from Tryptophan
B. Synthesis of Histamine from Histidine
C. Synthesis of Acetylcholine from Acetyl-CoA and Choline
D. Synthesis of GABA from Glutamate
B. Fusion of Acetyl-CoA and Choline to form Acetylcholine
Which of the following processes relies on adequate levels of glucose despite it NOT being a rate-limiting step in the metabolism of the neurotransmitter involved?
A. Hydroxylation of Tryptophan to form Serotonin’s precursor
B. Fusion of Acetyl-CoA and Choline to form Acetylcholine
C. Hydroxylation of Tyrosine to form Dopamine’s precursor
D. Hydroxylation of Histidine to form Histamine’s precursor
A. Increase
A drug that inhibits GABA transaminase will ___________ synaptic levels of GABA.
A. Increase
B. Decrease
A. Increase
A drug that inhibits monoamine oxidase in serotonergic neurons will ____________ availability of serotonin.
A. Increase
B. Decrease
A. Disturbances in bowel motility, diarrhea or sometimes constipation
A drug that inhibits reuptake of serotonin may produce these effects due to activity outside the CNS:
A. Disturbances in bowel motility, diarrhea or sometimes constipation
B. Palpitations, increase in heart rate and contractility, bronchodilation
B. Disturbance of sensorium and cognitive impairment
A drug that inactivates acetylcholine receptors in the CNS may produce these unwanted effects:
A. Delusions, anxiety and difficulty sleeping
B. Disturbance of sensorium and cognitive impairment
A. Decreased heart rate with increased production of mucosal secretions
A drug that inhibits acetylcholinesterase in synapses found in the autonomic nervous system may produce these side effects:
A. Decreased heart rate with increased production of mucosal secretions
B. Increased heart rate with dry mouth and flushing
A. Increase in motivation alongside a sense of anticipation of something good i.e. fulfillment and satisfaction
A drug that directly activates dopaminergic receptors in the prefrontal cortex will most closely produce which of the following effects:
Choose the best answer.
A. Increase in motivation alongside a sense of anticipation of something good i.e. fulfillment and satisfaction
B. A peaceful, relaxing feeling free of worries and stressing thoughts
C. A rewarding feeling of intense pleasure, euphoria and visceral satisfaction
D. Heightened senses with enhanced attention and concentration
C. Blocks reuptake of dopamine promoting loss of impulse control, increased aggression and an all-powerful feeling leading to risky behavior
Cocaine, a powerful stimulant
A. Binds to opioid receptors while also promoting release of dopamine from the VTA, 5HT from the raphe nuclei, and NE from the locus ceruleus
B. Blocks NMDA-receptors causing distortion of how reality is perceived
C. Blocks reuptake of dopamine promoting loss of impulse control, increased aggression and an all-powerful feeling leading to risky behavior
B. Blocks NMDA-receptors causing distortion of how reality is perceived
Phencyclidine (angel dust), an illegal hallucinogen
A. Binds to opioid receptors while also promoting release of dopamine from the VTA, 5HT from the raphe nuclei, and NE from the locus ceruleus
B. Blocks NMDA-receptors causing distortion of how reality is perceived
C. Blocks reuptake of dopamine promoting loss of impulse control, increased aggression and an all-powerful feeling leading to risky behavior
A. Binds to opioid receptors while also promoting release of dopamine from the VTA, 5HT from the raphe nuclei, and NE from the locus ceruleus
Heroin (a more potent, addictive variant of morphine)
A. Binds to opioid receptors while also promoting release of dopamine from the VTA, 5HT from the raphe nuclei, and NE from the locus ceruleus
B. Blocks NMDA-receptors causing distortion of how reality is perceived
C. Blocks reuptake of dopamine promoting loss of impulse control, increased aggression and an all-powerful feeling leading to risky behavior
D. Excessive glutamatergic activity in both cerebral hemispheres
A 57-year-old male suffered from myocardial infarction (heart attack) which led to cardiac arrest. He was revived after 5 minutes of CPR. However, despite being able to breathe without a mechanical ventilator, he is unresponsive to sound or even painful stimuli. Which of the following abnormal neurotransmitter activity most likely CAUSED the patient’s current condition?
A. Impaired release of GABA secondary to cleavage of synaptobrevin
B. Diminished cholinergic projections to the hippocampus
C. Marked drop in the dopamine and serotonin levels in the prefrontal cortex
D. Excessive glutamatergic activity in both cerebral hemispheres
C. Decreased dopaminergic inputs from the midbrain to the basal nuclei/ganglia
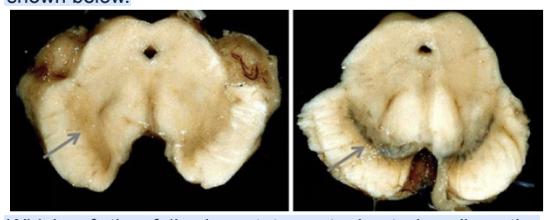
A 70-year-old male has been suffering from frequent falls. His muscles are rigid and his fingers exhibit tremors at rest. After his demise, an autopsy was performed. His brain (LEFT) along with a normal brain (RIGHT) are shown below. Which of the following statements best describes the patient's condition and the symptoms mentioned?
A. Loss of dopaminergic neurons projecting to the prefrontal cortex
B. Decreased activity of the tuberoinfundibular tract
C. Decreased dopaminergic inputs from the midbrain to the basal nuclei/ganglia
D. Loss of connections from the ventral tegmental area to the limbic cortex
A. Difficulty in sustaining focus while performing tasks with frequent procrastination in a patient with ADHD – abnormal levels of norepinephrine and dopamine in the prefrontal cortex (D. Hallucinations and bizarre out-of-this-world delusions during a psychotic episode – excessive dopamine reaching the prefrontal cortex)
Which of the following clinical manifestations is most accurately paired with the correct underlying neurotransmitter derangement? e.g. Intractable seizures - excessive glutamatergic activity (or impaired glutamate reuptake)
A. Difficulty in sustaining focus while performing tasks with frequent procrastination in a patient with ADHD – abnormal levels of norepinephrine and dopamine in the prefrontal cortex
B. Progressive cognitive deterioration with eventual inability to perform activities of daily living – decreased production and release of glutamate from neurons in the frontal lobe
C. Anhedonia and thoughts of suicide in a patient with depression – excessive serotonergic activity in the amygdala and hippocampus
D. Hallucinations and bizarre out-of-this-world delusions during a psychotic episode – excessive dopamine reaching the prefrontal cortex