Cellular Reproduction
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Chromosomes
Structures that contain genetic info in the form of DNA
Homologous chromosomes
The two chromosomes in a diploid pair present in a genome; one from the mother and one from the father for their traits to be inherited
Genome
All of the DNA possesssed by an individual organism
Haploid
Only one pair of DNA in the cell
Gametes
Type of cell only involved in sexual reproduction
Genes
Sequences of DNA that code for proteins
Locus
The location of genes on a chromosome
Chromatin
Unpackaged DNA, not prepared for cell division; the entire complex of DNA and associated proteins
Mitosis
The stage of the cell cycle where the cell divides; somatic cell division for growth, maintenance, and development
Meiosis
Cell division specific to the production of gametes (sex cells)
Interphase
The majority of time a cell spends during the cell cycle (90%)
Cell normally performing its function
Undergoes preparation for mitosis
G1 Phase
First gap: little change while the cell is preparing to replicate chromosomes
S Phase
Synthesis: DNA replication stage; diffuse chromatin condenses into sister chromatids and centrosomes begin creating mitosis spindle
G2 Phase
Second gap: final preparations for mitosis stage; organelles duplicate and cytoskeleton dismantles
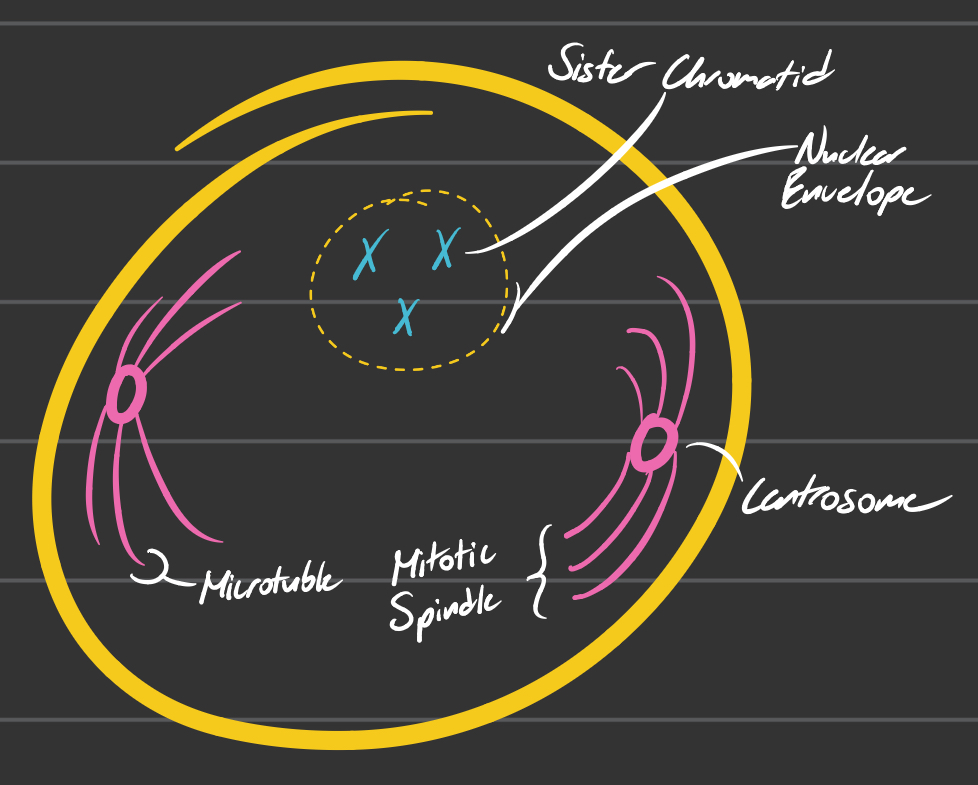
Prophase
Chromosomes condense and become visible
Mitotic spindle made of fibers called microtubules emerge from centrosomes
Nuclear envelope breaks down
Centrosomes move toward opposite poles
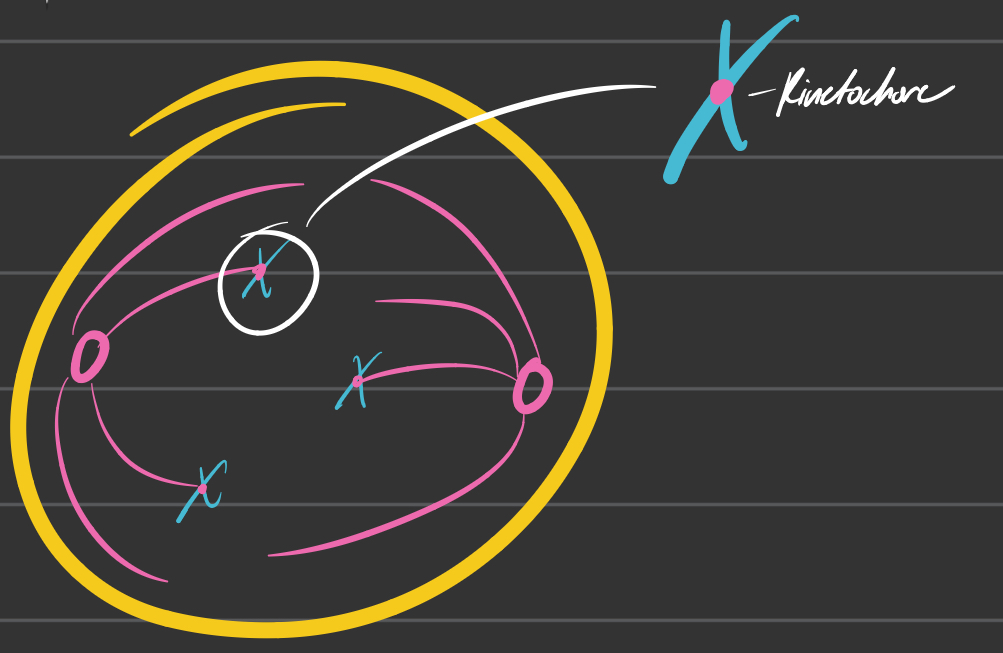
Prometaphase
Chromosomes continue to condense
Kinetochores appear at the centromeres
Mitotic spindle microtubules attach to the kinetochores
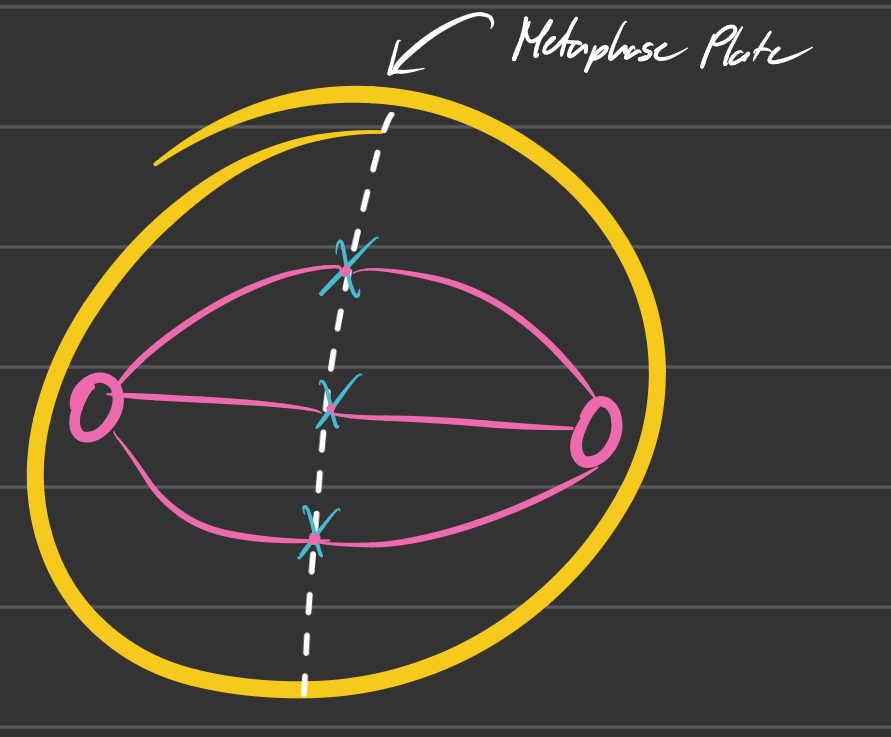
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up at an imaginary line called the metaphase plate
Each sister chromatid is attached to a spindle fiber originating from opposite poles
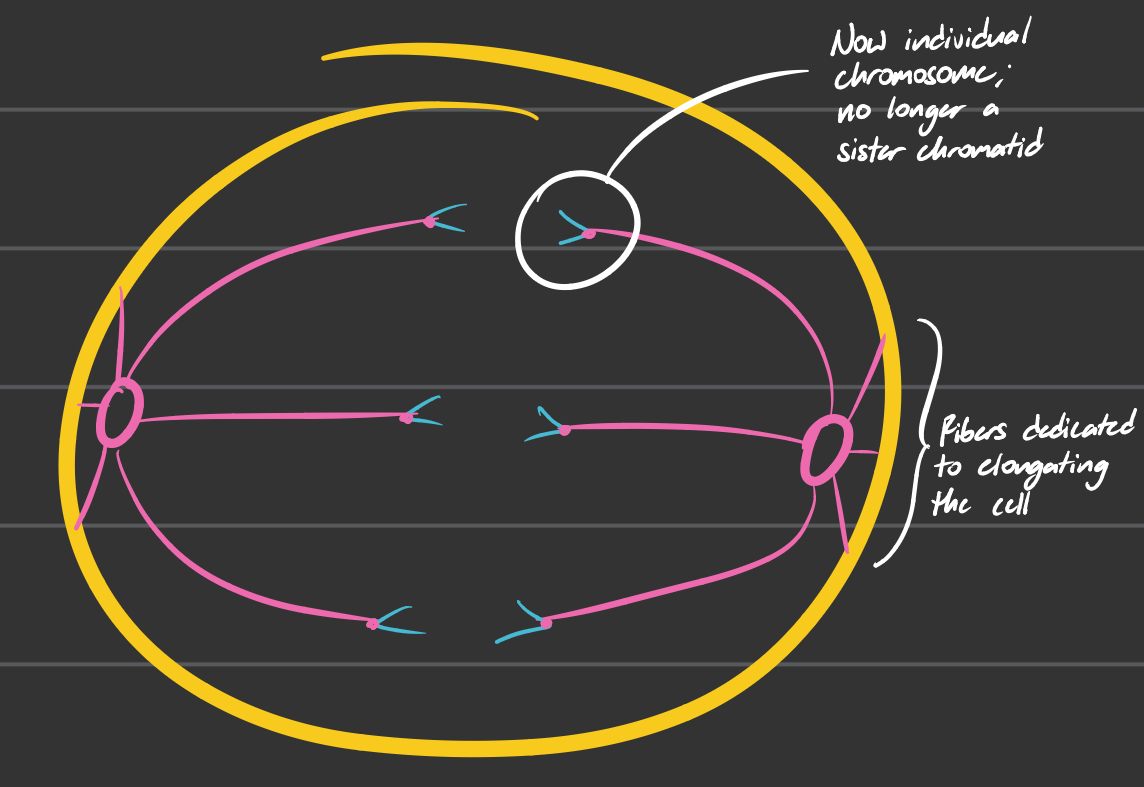
Anaphase
Centromeres split in two
Sister chromatids pulled apart are now chromosomes
Certain microtubules/spindle fibers begin to elongate the cell
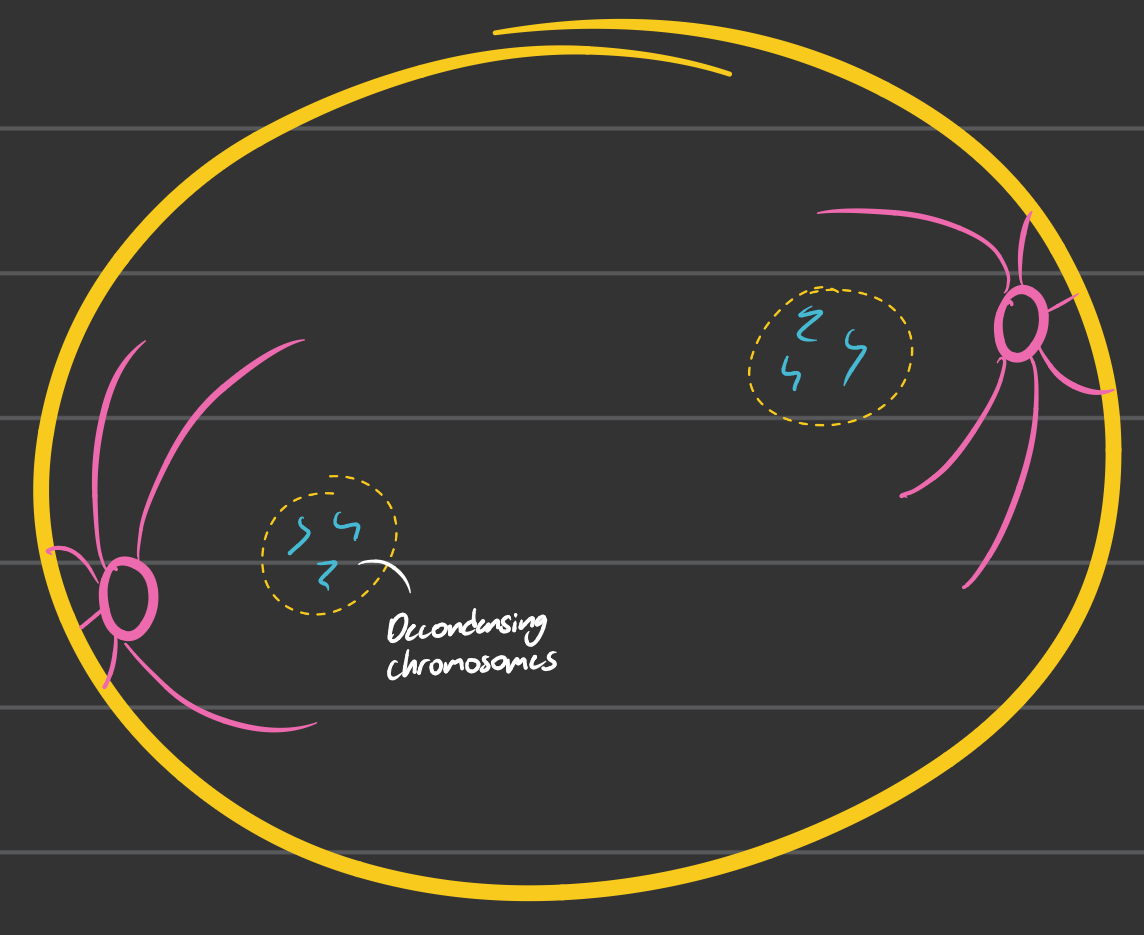
Telophase
Chromosomes arrive at opposite poles and begin to de-condense
Nuclear envelope material surrounds each set of chromosomes
Mitotic spindle breaks down
Spindle fibers continue to push the poles apart
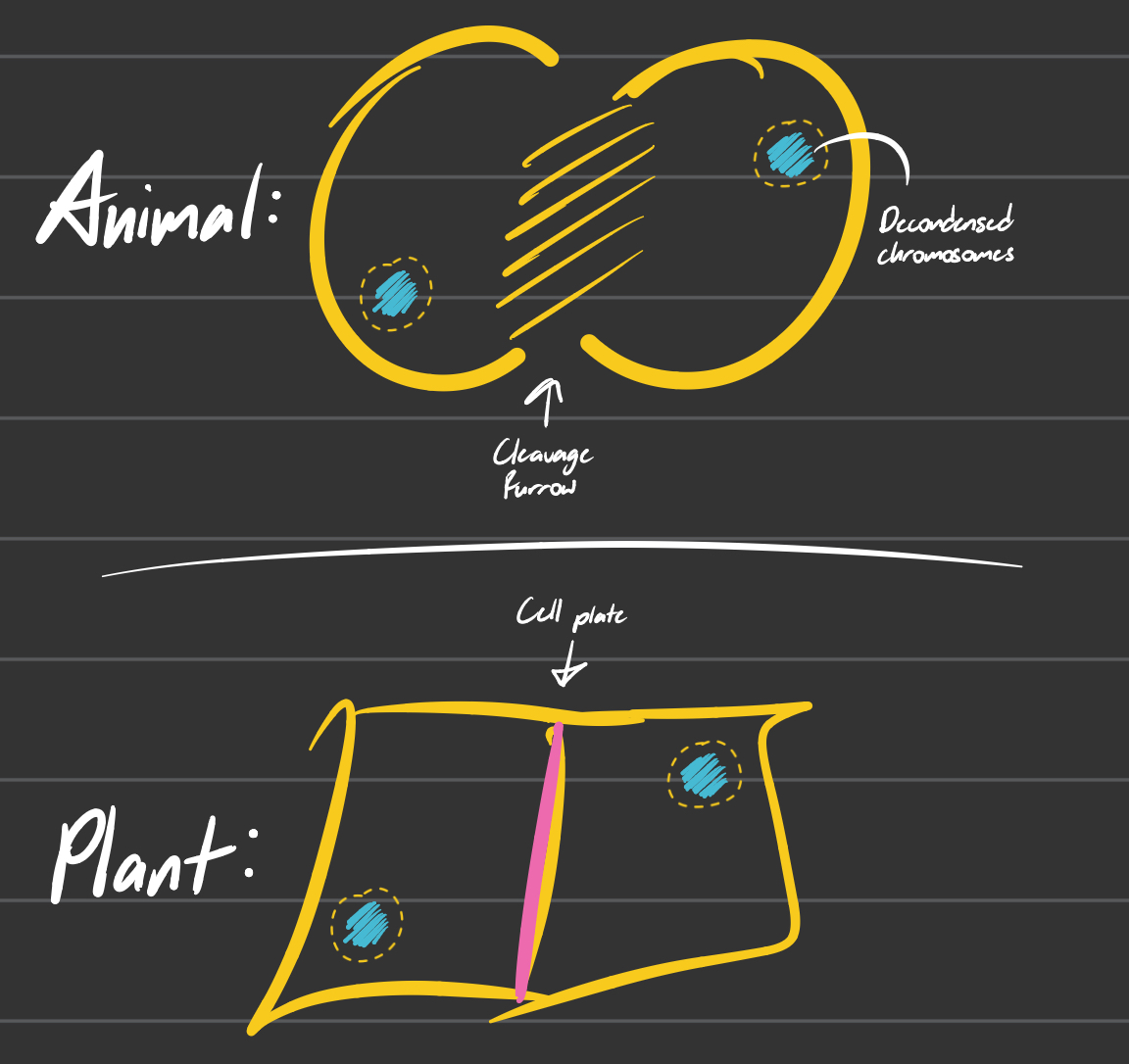
Cytokinesis
Animal cells: a cleavage furrow separates the daughter cells
Plant cells: a cell plate, the precursor to a new cell wall, separates the daughter cells
Purines
Adenine and Guanine; have 2 rings
Pyrimidines
Thymine and Cytosine; have 1 ring
Origin of replication
Where replication starts on a DNA strand
Specified by a particular nucleotide sequence
Where proteins attach to separate the double helix
Replication proceeds in both directions to create a replication bubble
Leading strand
Strand made continuously by DNA polymerase
Lagging strand
Strand made in fragments (Okazaki fragments) by DNA polymerase
Diploid dominant
Life cycle of animals; multicellular organisms with diploid somatic cells (2n) and only sperm and egg are gametes (n)
Haploid dominant
Life cycle of fungi; sexual reproduction results in zygospore (2n) formation and the rest of the cycle is haploid (n)
Alteration of generations
Life cycle of plants
Diploid sporophyte produces spores
Spores become a haploid gametophyte
Gametophyte produces sperm and egg
Sperm fertilizes the egg and together form a diploid zygote
Zygote grows grows into a sporophyte
Heredity
The transmission of traits from one generation to the next
Genetics
The study of heredity
Genotype
The genetic composition of an organism
Phenotype
An organism’s physical appearance based on genotype
Law of Segregation of Chromosomes
Pairs of alleles segregate during gamete formation
Monohybrid cross
AA x aa → Aa x Aa
Results in AA, Aa, Aa, aa
3:1
Law of Independent Assortment
“How one allele pair separates is independent of how other alleles separate”
Dihybrid cross
AABB x aabb
9:3:3:1