DOMAIN 1. Anatomy and Physiology
1/165
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
166 Terms
vasoconstriction in gastrointestinal tract?
arterial blood pressure increases, blood capillary pressure and blood supply decreases
vasodilation in the gastrointestinal tract?
Arterial blood pressure decreases; capillary blood supply and blood capillary pressure increase
Why do we want to think about forces that crease increased relaxation and decreased tone in the pre-capillary arterioles?
The pre-capillary arterioles regulate blood pressure and flow in the capillary networks. Increased relaxation of the sphincter muscles and decreased tone causes vasodilation, which increases the flow of blood and lymphatic fluid to tissues
relaxation in the pre-capillary arteriole bed?
More blood is reaching the capillary bed, increasing blood capillary pressure above 35 mm Hg
hot weather affect blood capillary pressure?
Heat causes vasodilation of the precapillary arterioles via the arterial limb, which raises blood capillary pressure, causing active hyperemia
injury from a fall affect blood capillary pressure?
trauma causes vasodilation of the precapillary arterioles via the arterial limb, which raises blood capillary pressure, causing active hyperemia
cellulitis affect blood capillary pressure
Infection causes vasodilation of the precapillary arterioles via the arterial limb, which raises blood capillary pressure, causing active hyperemia
DVT affect blood capillary pressure
Deep vein thrombus causes vasodilation of the precapillary arterioles via the venous limb, which raises blood capillary pressure, causing passive hyperemia
CHF affect blood capillary pressure
Congestive Heart Failure causes vasodilation of the precapillary arterioles via the venous limb raises blood capillary pressure causing passive hyperemia
CVI affect blood capillary pressure
Chronic venous insufficiency causes vasodilation of the precapillary arterioles via the venous limb, which raises blood capillary pressure, causing passive hyperemia.
malignant tumor affect blood capillary pressure
An obstructive tumor can cause vasodilation of the precapillary arterioles via the venous limb, which raises blood capillary pressure, causing passive hyperemia
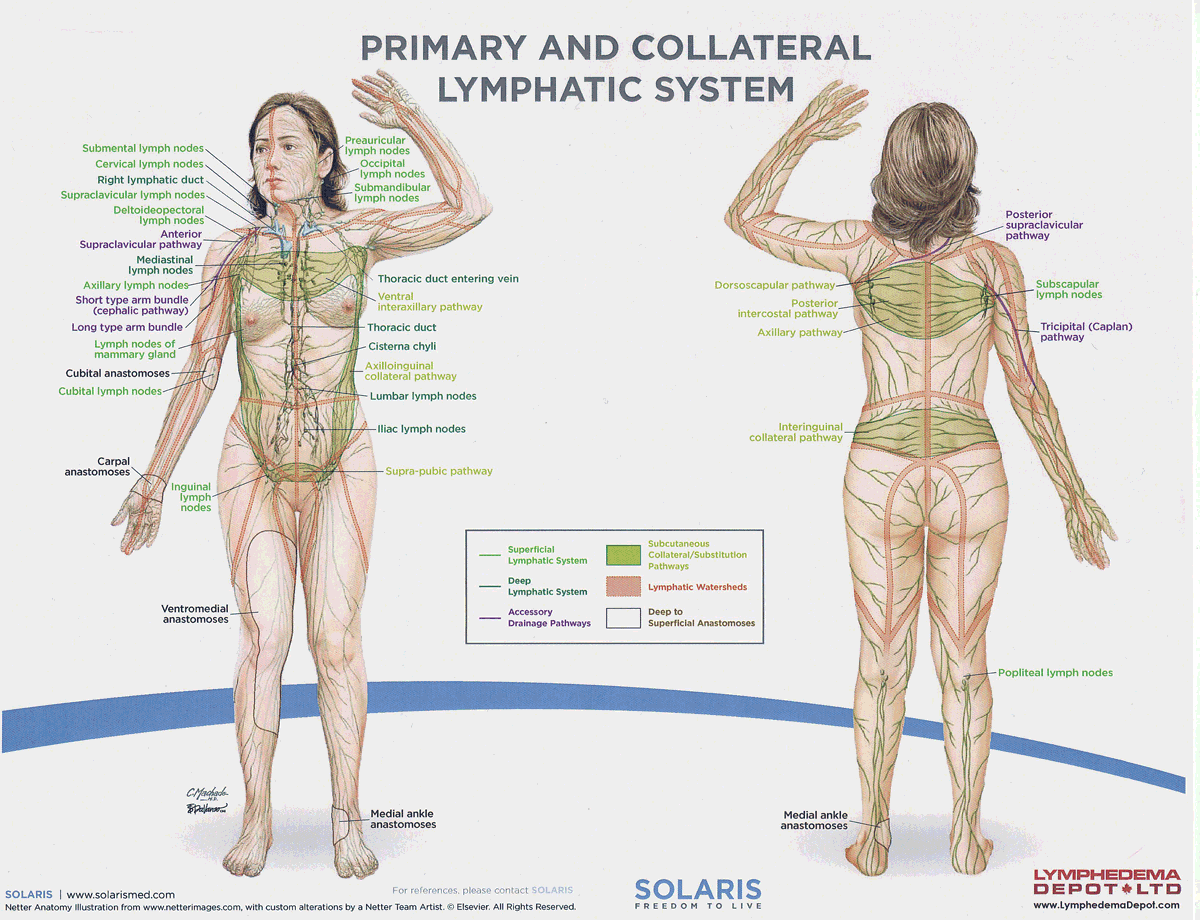
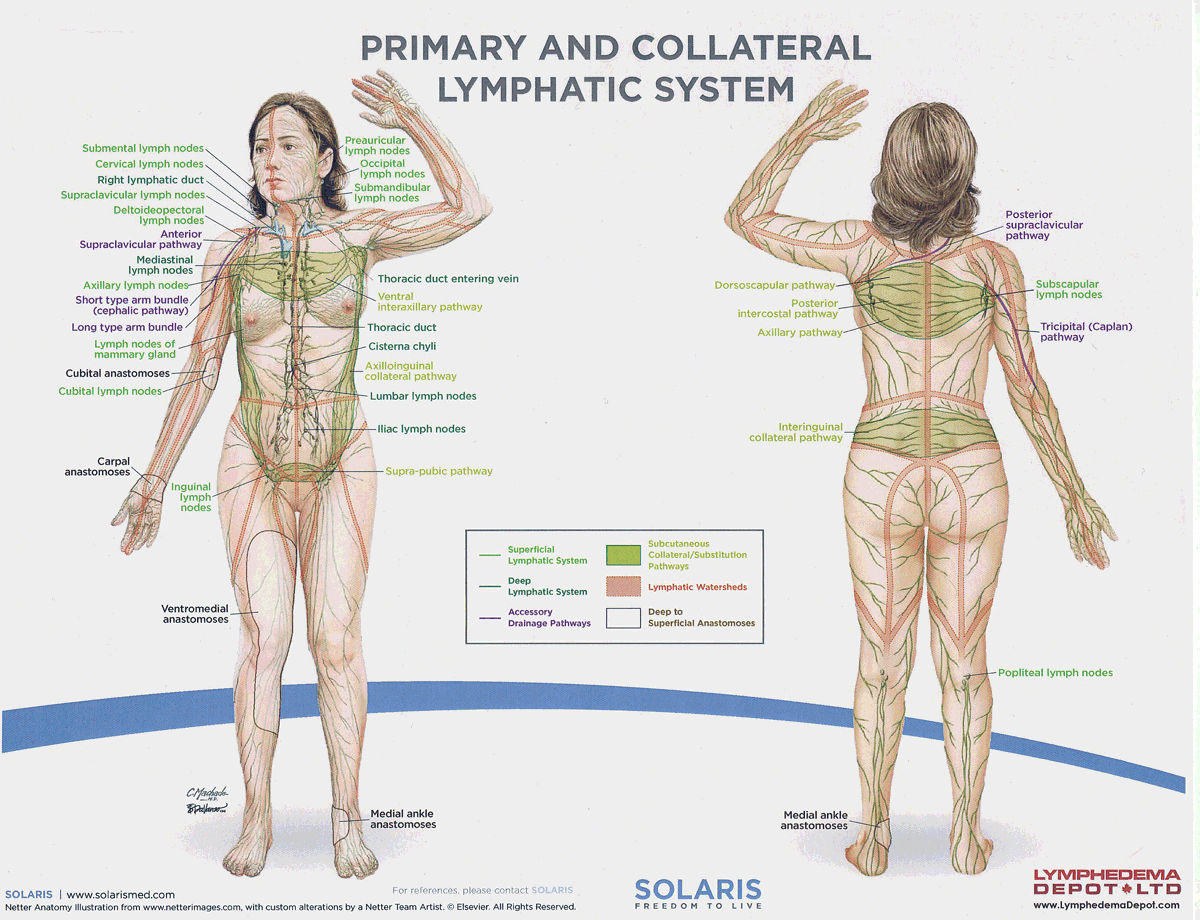
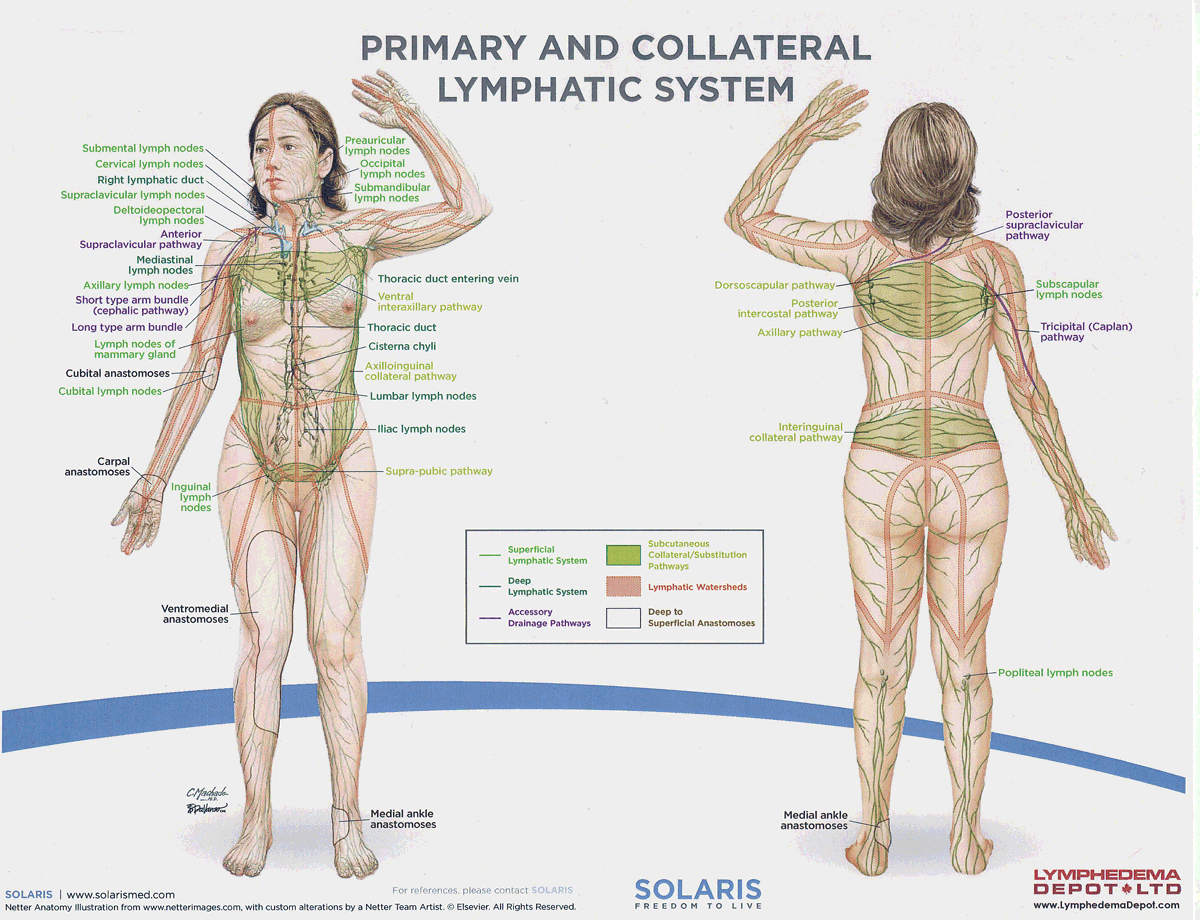
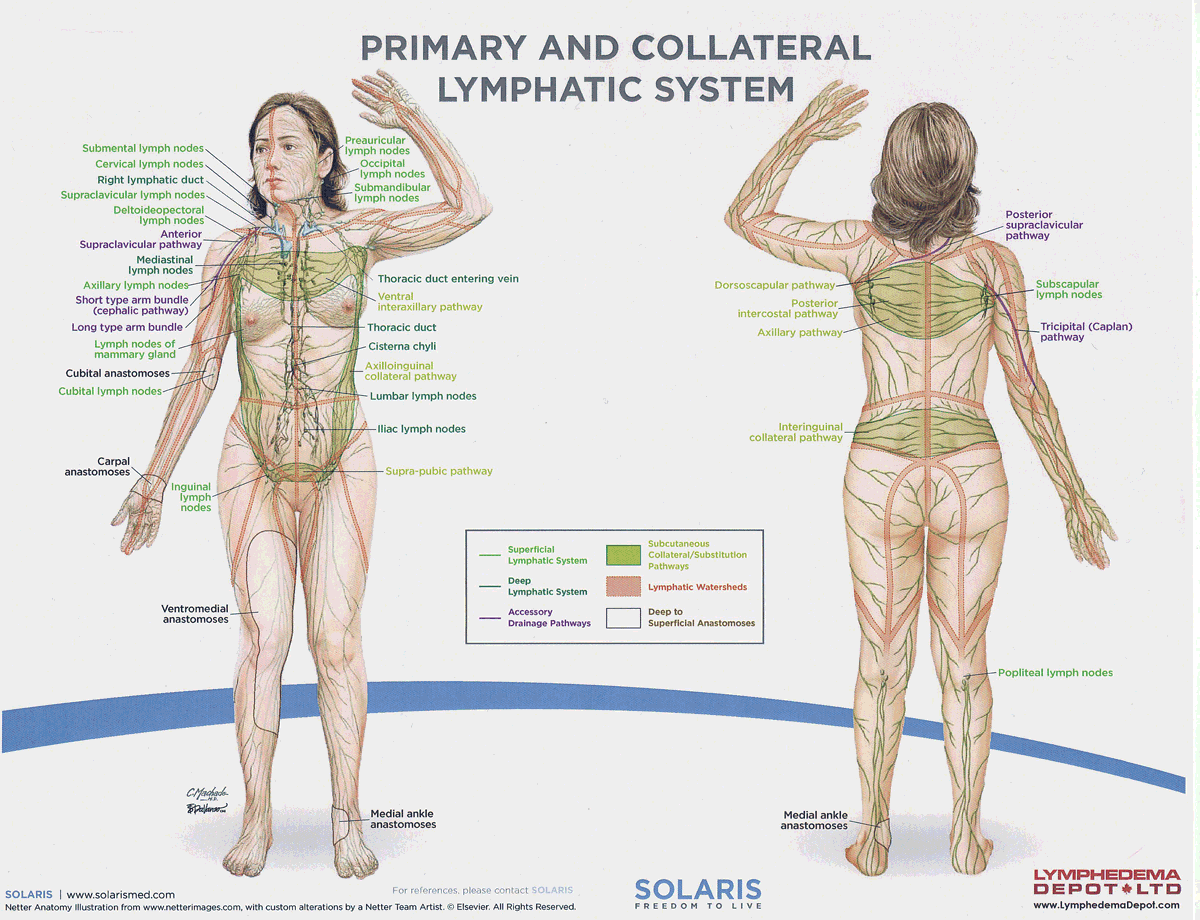
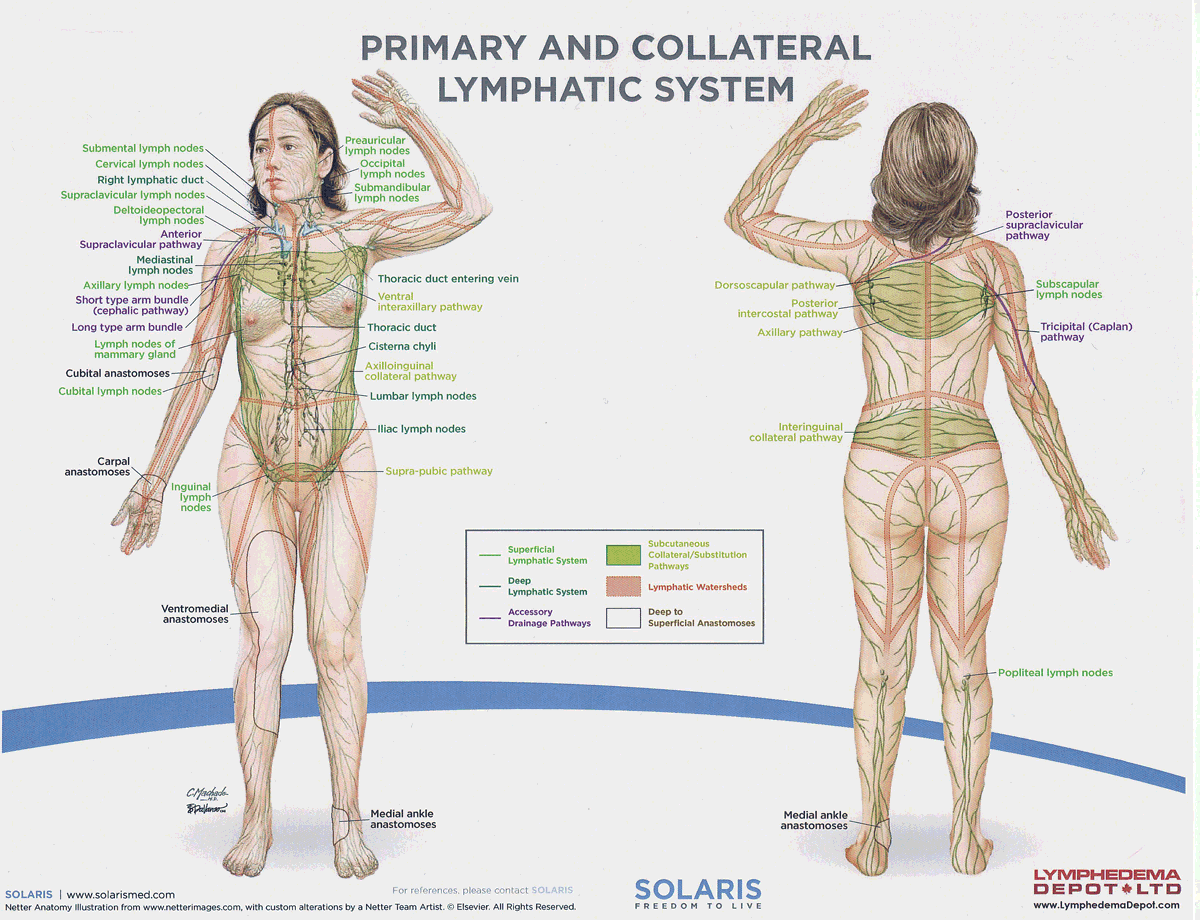
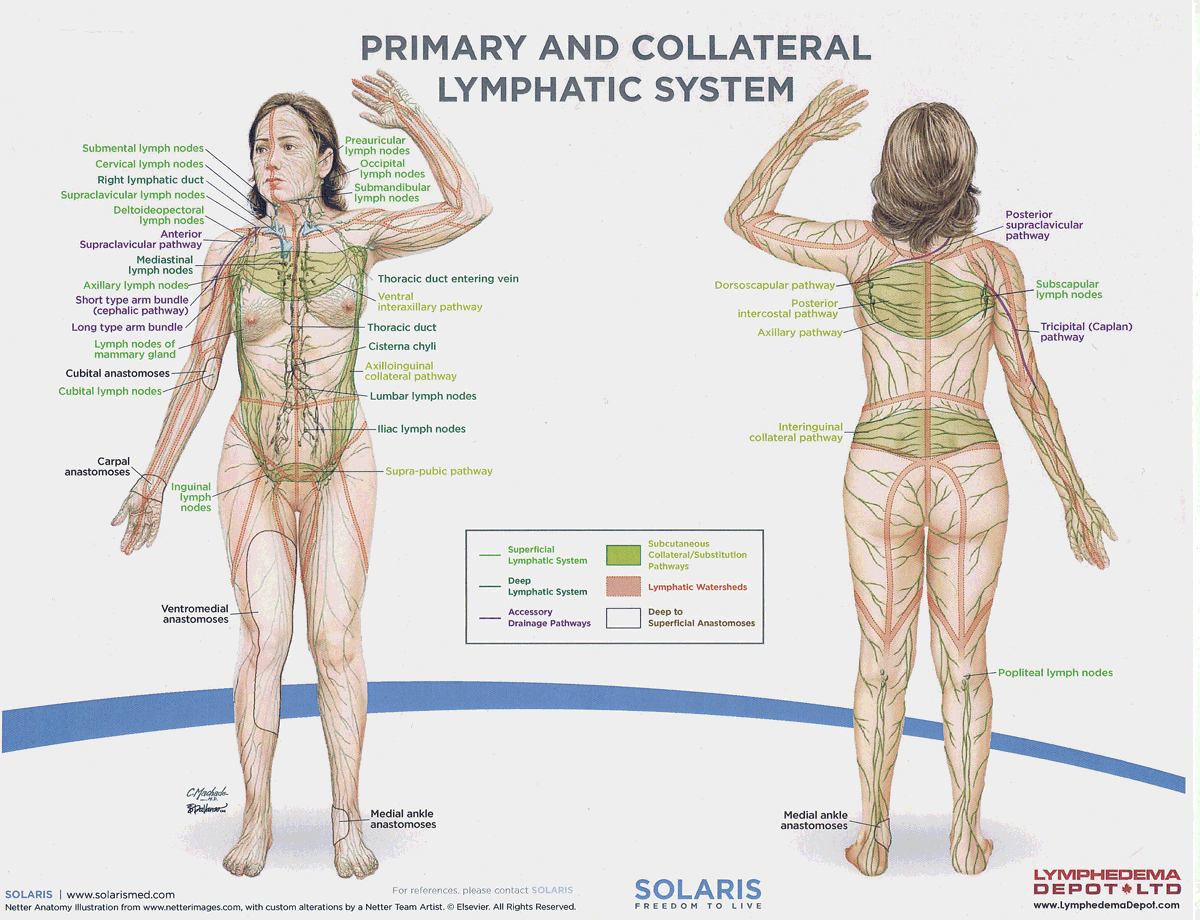
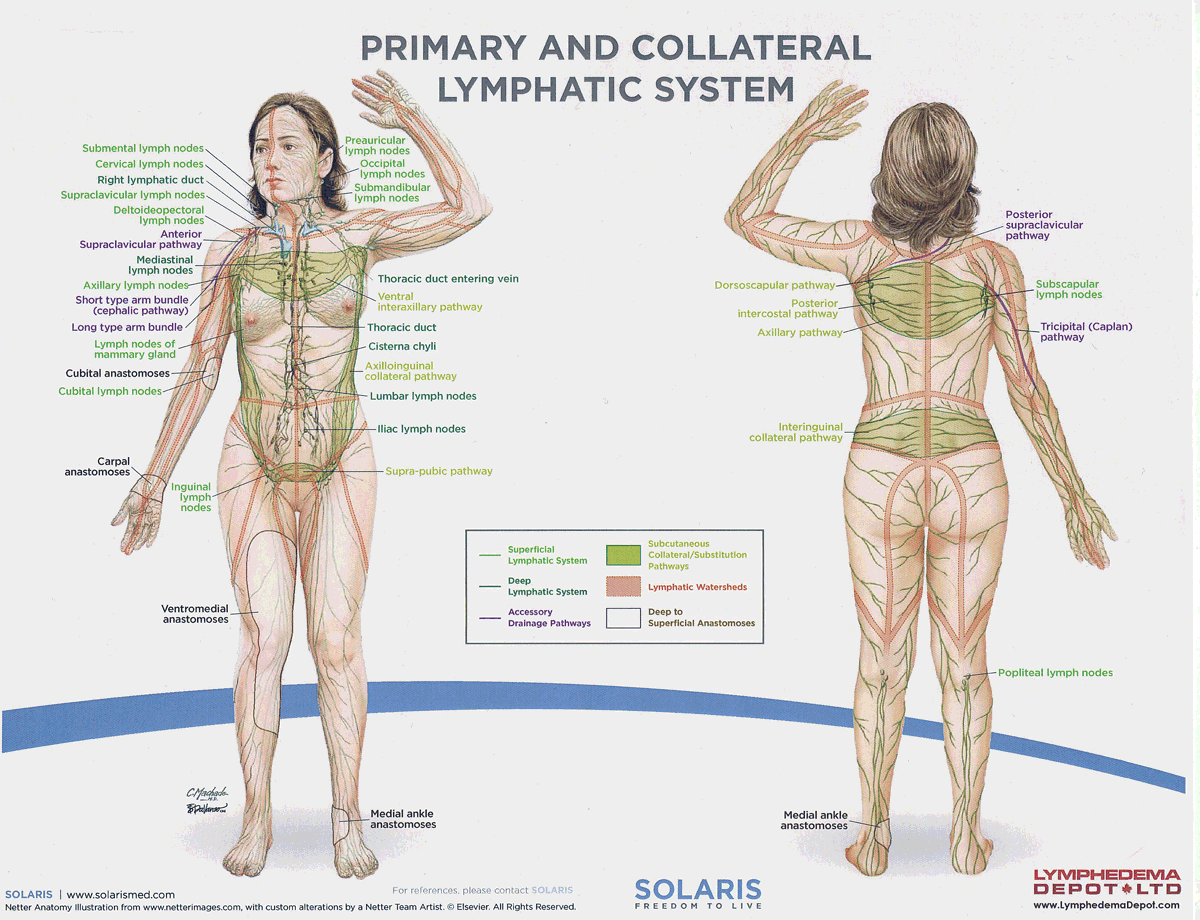
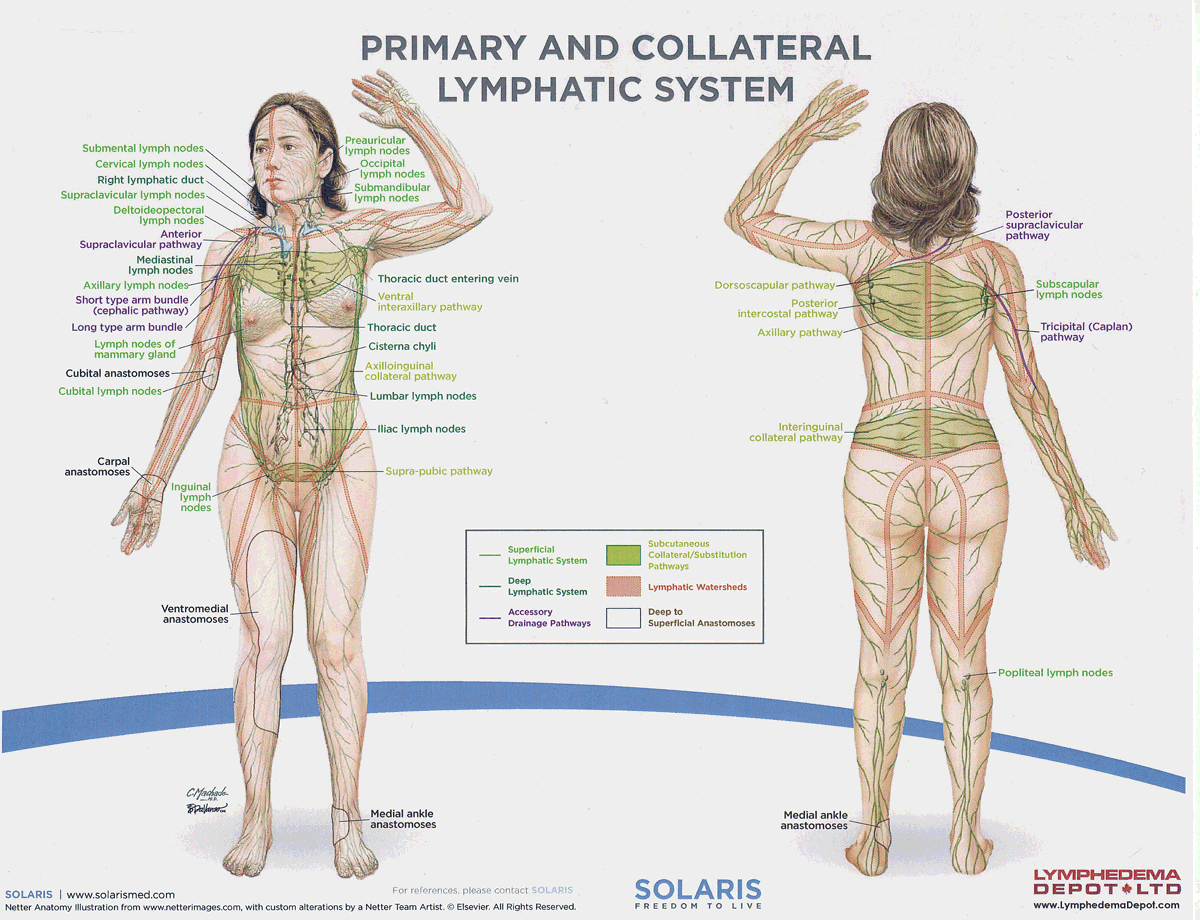
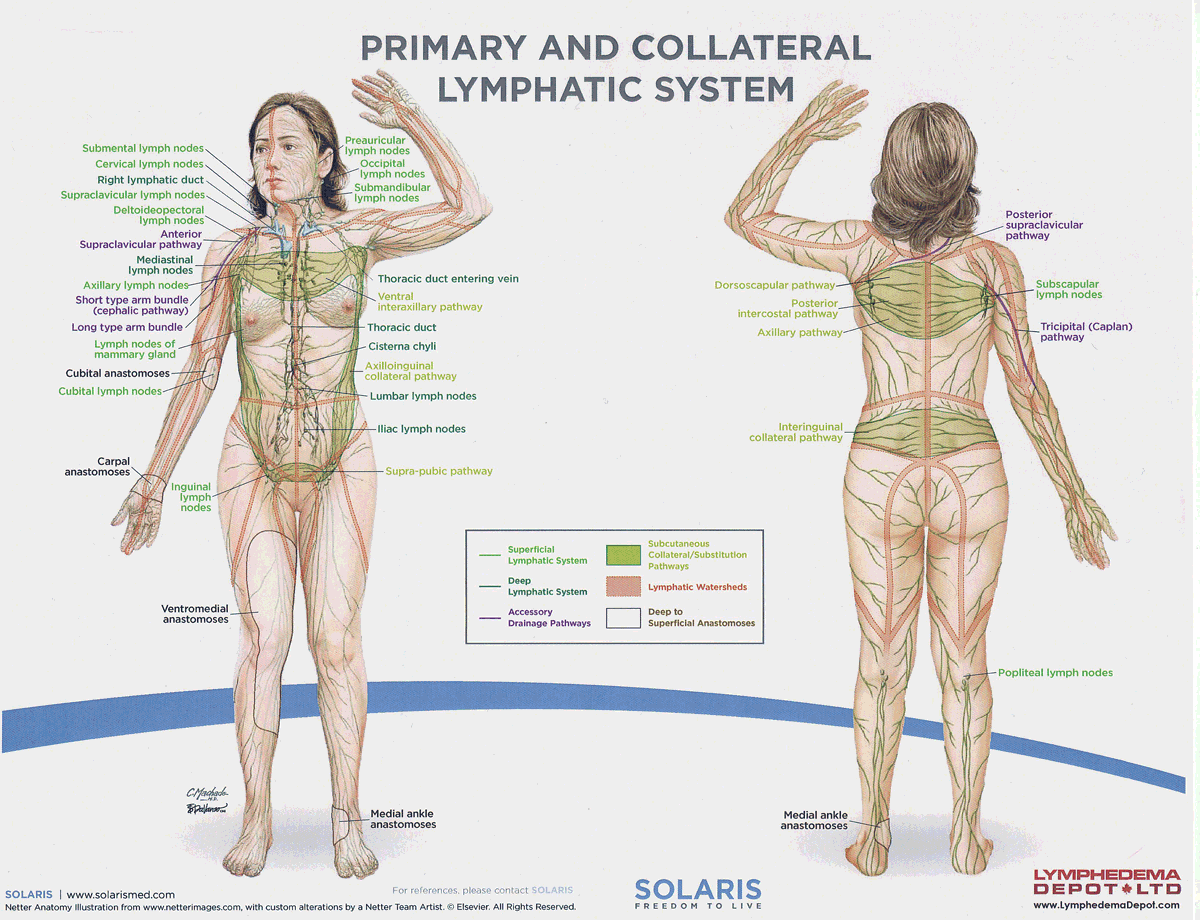
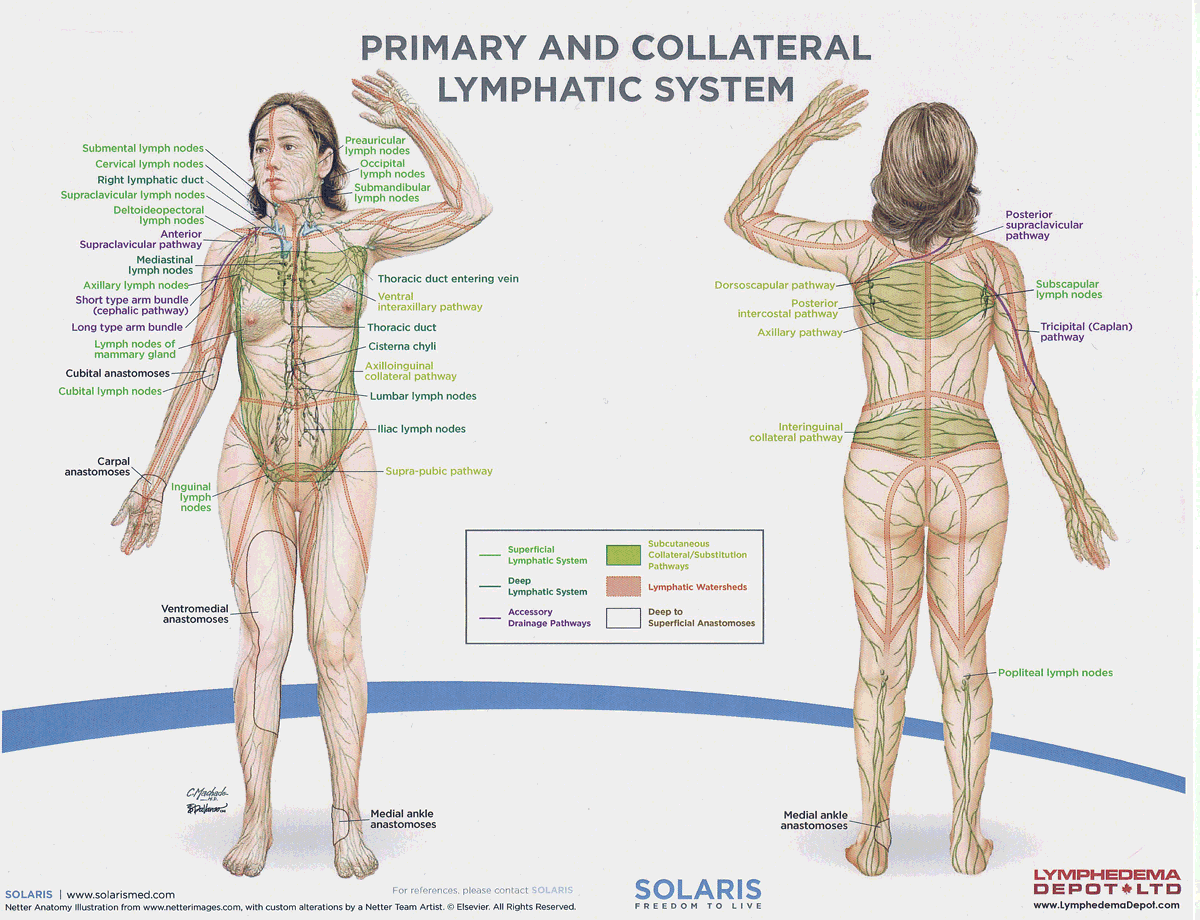
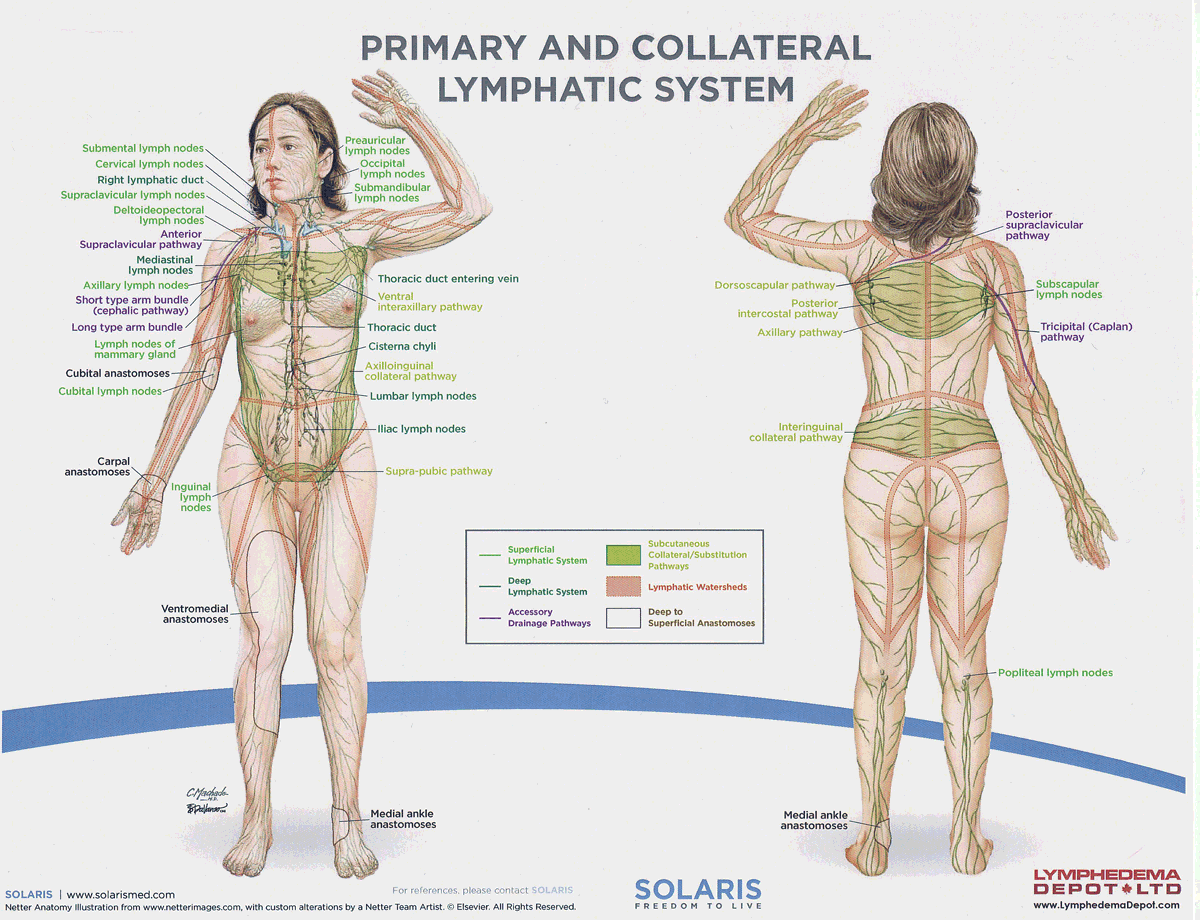
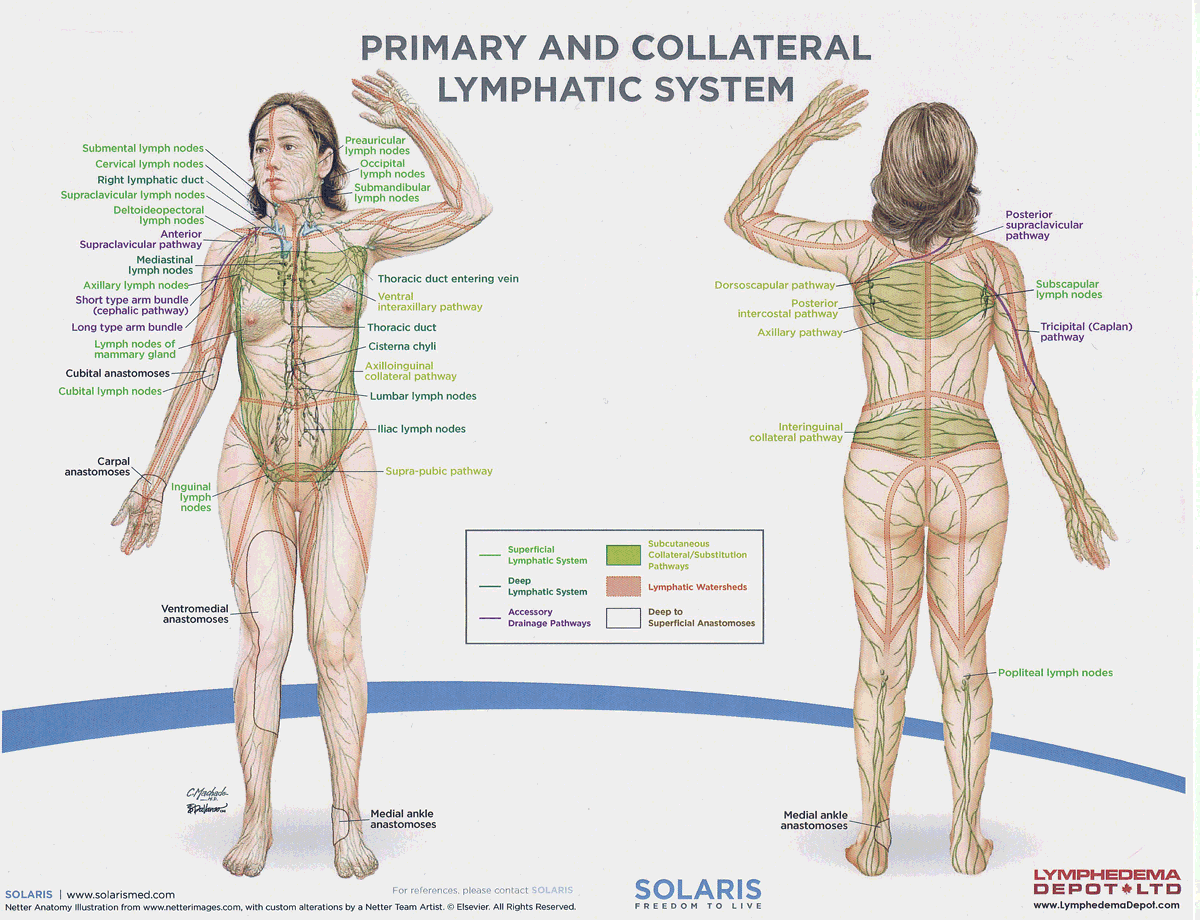
watersheds
4: Median-Sagittal, Transverse, Clavicular, Spine of the scapula, Chaps
Anastomoses
8 anastomoses. anterior and posterior inter-axillary; anterior and posterior inter-inguinal; L and R axillo-inguinal; L and R inguino-axillary watershed
duct drains 25% daily amount of lymph from right upper body
Right lymphatic duct
Which duct drains 75% of the daily lymph
Thoracic duct
lymph vessels absorb lymph
capillaries, some pre-collectors
lymph vessels transport lymph
some pre-collectors, collectors, trunks, ducts
lymph vessels have valves
some pre-collectors, collectors, trunks, ducts
lymph vessels have swinging flaps
lymph capillaries, allow lymph to enter when the flaps are open and swing shut when the lymph is inside to facilitate absorption
lymph
When interstitial fluid is absorbed from extracellular spaces (interstitium) into lymph capillaries
lymph node
filter bacteria, toxins, and dead cells; produce white blood cells (lymphocytes); regulate protein concentration in lymph
dynamic insufficiency
What happens to transport capacity and functional reserve during a mechanic insufficiency
axillo-inguinal vs the inguino-axillary anastomoses?
Axillo-inguinal is oriented from upper to lower extremity; inguino-axillary is oriented from lower to upper extremity.
Starling’s Law
Average BCP 25 mm Hg = Colloid Osmotic Pressure of plasma 25 mm Hg because ultrafiltration = 10 mm Hg and Reabsorption = -10 mm Hg
Starling’s Equilibrium matter?
It describes how ultrafiltration and reabsorption forces are equivalent (10 mm Hg + -10 mm Hg = 0) since all fluid entering the interstitium returns to the blood capillaries
Where within the blood capillaries is the average capillary blood pressure higher?
Arterial branch
Where is protein concentration greater
Plasma
How much gross ultrafiltrate is reabsorbed into the venous capillary tract?
90% of the gross ultrafiltrate is reabsorbed
What happens to the 10% of fluid that is ultrafiltered and not reabsorbed? What is it called?
Net ultrafiltrate is transported by the lymph vessels and forms the lymphatic load
How much is blood capillary pressure in the arterial limb?
35 mm Hg
How much is blood capillary pressure in the venous limb
15 mm Hg
What is the average blood capillary pressure
25 mm Hg
How does ultrafiltration cause a gradient effect in the blood capillaries? What is the effect of this gradient?
BCP in the arterial limb is higher than the colloid osmotic pressure of the plasma, which creates a gross filtration force of 10 mm Hg, which promotes fluid movement out of the capillaries into the interstitial space, leading to tissue perfusion.
How does reabsorption cause a gradient effect in the blood capillaries? What is the effect of the gradient
BCP in the venous limb is less than colloid osmotic pressure of the plasma, which creates a net reabsorption force of -10 mm Hg, promoting fluid movement back into the capillaries from the interstitial space, aiding in maintaining blood volume and pressure.
What is a pre-lymphatic channel
A vessel that collects excess interstitial fluid and transports it to the lymphatic system beginning with the capillaries
lymph
interstitial fluid in lymphatic system that is made up of fatty acids, water, cellular particles, lymphocytes
lymphatic system
network of vessels that absorb, collect, and transport lymph from interstitial spaces to the venous system
interstitial fluid
fills gaps between tissue and organ cells, brings oxygen and nutrients to cells and removes waste from cells
lymphatic loads
Amount of lymph circulating in the lymphatic system at a given time
lymph capillaries
vessel made up of overlapping endothelial cells that open/close to absorb lymph fluid due to swinging flaps that have anchoring filaments attached to allow for the uptake of interstitial fluid and proteins. They do not contain valves, and can absorb fluid in all directions.
lymph precollectors
small lymphatic vessels that collect lymph from lymph capillaries and transport it to larger lymphatic vessels. They help in the drainage and filtration of lymph fluid. Some contain valves.
lymph collectors
larger lymphatic vessels that receive lymph from precollectors and transport it to the lymph nodes. They play a crucial role in the lymphatic drainage system. Contain valves to prevent backflow. They also help maintain lymph flow toward the thoracic duct and right lymphatic duct.
lymph trunks
large lymph vessels with valves
that collect lymph fluid from lymph collectors throughout the body and transport lymph to drain into the thoracic duct or right lymphatic duct.
lymph ducts
the final channels in the lymphatic system that transport lymph from the lymph trunks to the venous system where it re-enters the bloodstream. They have valves.
lymph nodes
small, bean-shaped structures that filter lymph fluid, produce lymphocytes, regulate protein concentration in lymph, trap harmful substances and contain immune cells that help fight infection. 600-700 lymph nodes are in the human body. They are distributed throughout the body, majority in the abdominal region, neck, and axillary, and inguinal regions.
thoracic lymph duct
the largest lymphatic vessel in the body, responsible for draining 75% of the daily lymphatic load, from the left side of the head, neck, chest, abdomen, and both lower limbs into the venous system.
right lymphatic duct
the lymphatic vessel that drains 25% of the daily lymphatic load from the right side of the head, neck, right arm, and the right side of the chest into the venous system.
right jugular trunk
a lymphatic vessel that drains lymph from the cervical lymph nodes on the right side of the head and neck into the right lymphatic duct.
left jugular trunk
a lymphatic vessel that drains lymph from the cervical lymph nodes on the left side of the head and neck into the thoracic lymph duct.
right subclavian trunk
a lymphatic vessel that drains lymph from the right axillary lymph nodes on the right upper limb and the right side of the thorax into the right lymphatic duct.
left subclavian trunk
a lymphatic vessel that drains lymph from the left axillary lymph nodes on the left upper limb and the left side of the thorax into the thoracic lymph duct.
right broncho-mediastinal trunk
a lymphatic vessel that drains lymph from the right bronchi, lungs and mediastinum into the right lymphatic duct.
left broncho-mediastinal trunk
a lymphatic vessel that drains lymph from the left bronchi, lungs, and mediastinum into the thoracic lymph duct.
right lumbar trunk
a lymphatic vessel that drains lymph from the right
inguinal lymph nodes to the cisterna chyli
left lumbar trunk
a lymphatic vessel that drains lymph from the left inguinal node into the cisterna chyli
intestinal trunk
a lymphatic vessel that drains lymph from the small intestines to the cisterna chyli
median-sagittal lymphatic watershed
An anatomical boundary that separates lymphatic drainage between the right and left sides of the body, influencing lymph flow and drainage patterns.
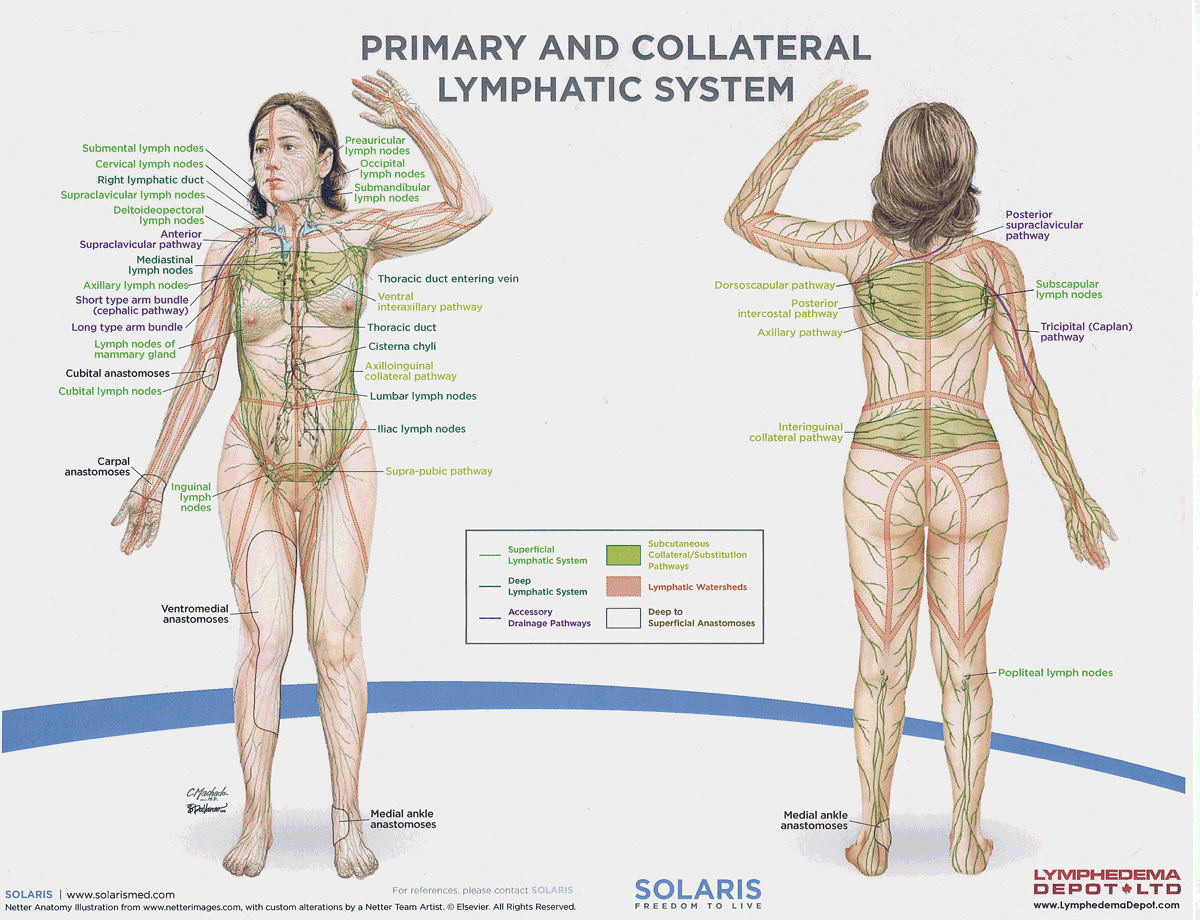
transverse watershed
An anatomical boundary that separates lymphatic drainage in the transverse plane, influencing lymph flow between the upper and lower body regions.
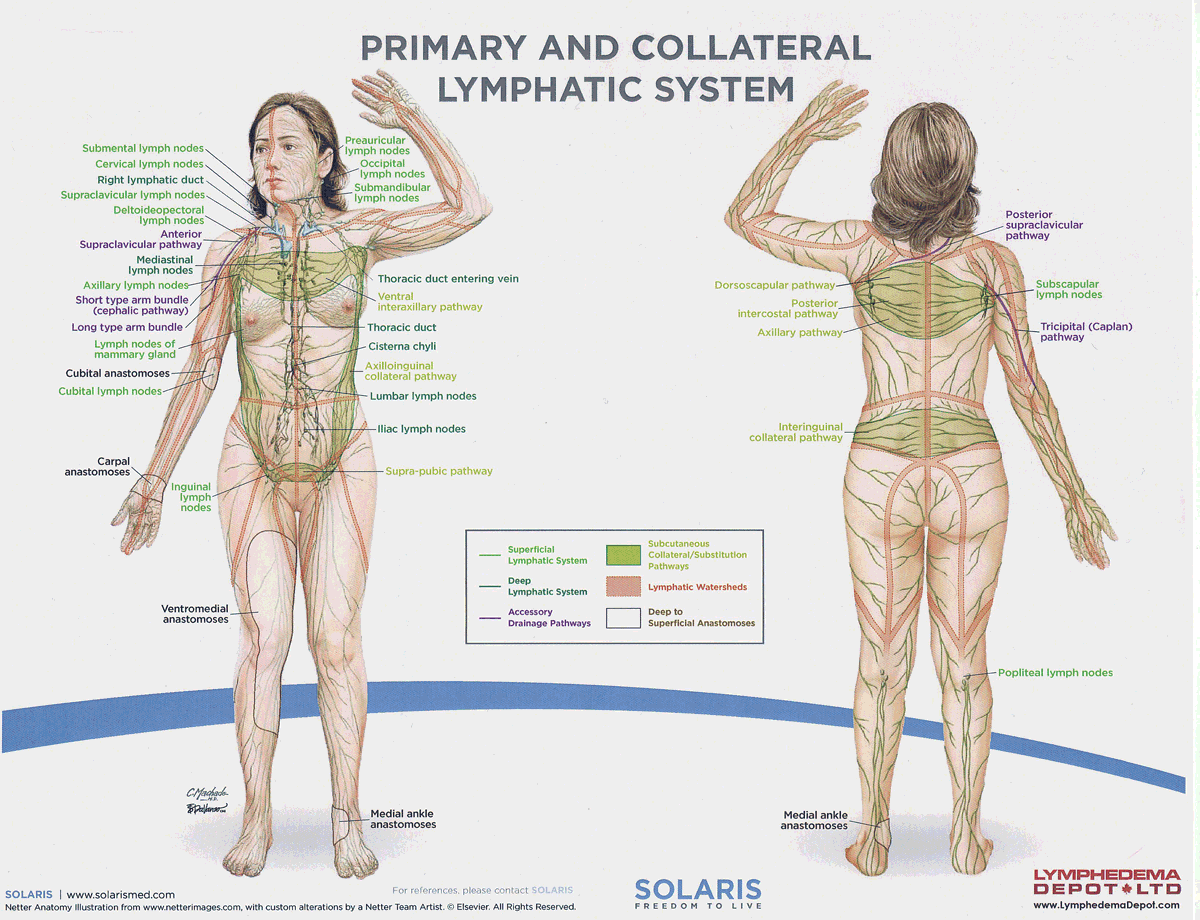
clavicular watershed
An anatomical boundary that separates lymphatic drainage between the upper limbs and the head, neck, and thorax, affecting lymph flow and drainage patterns.
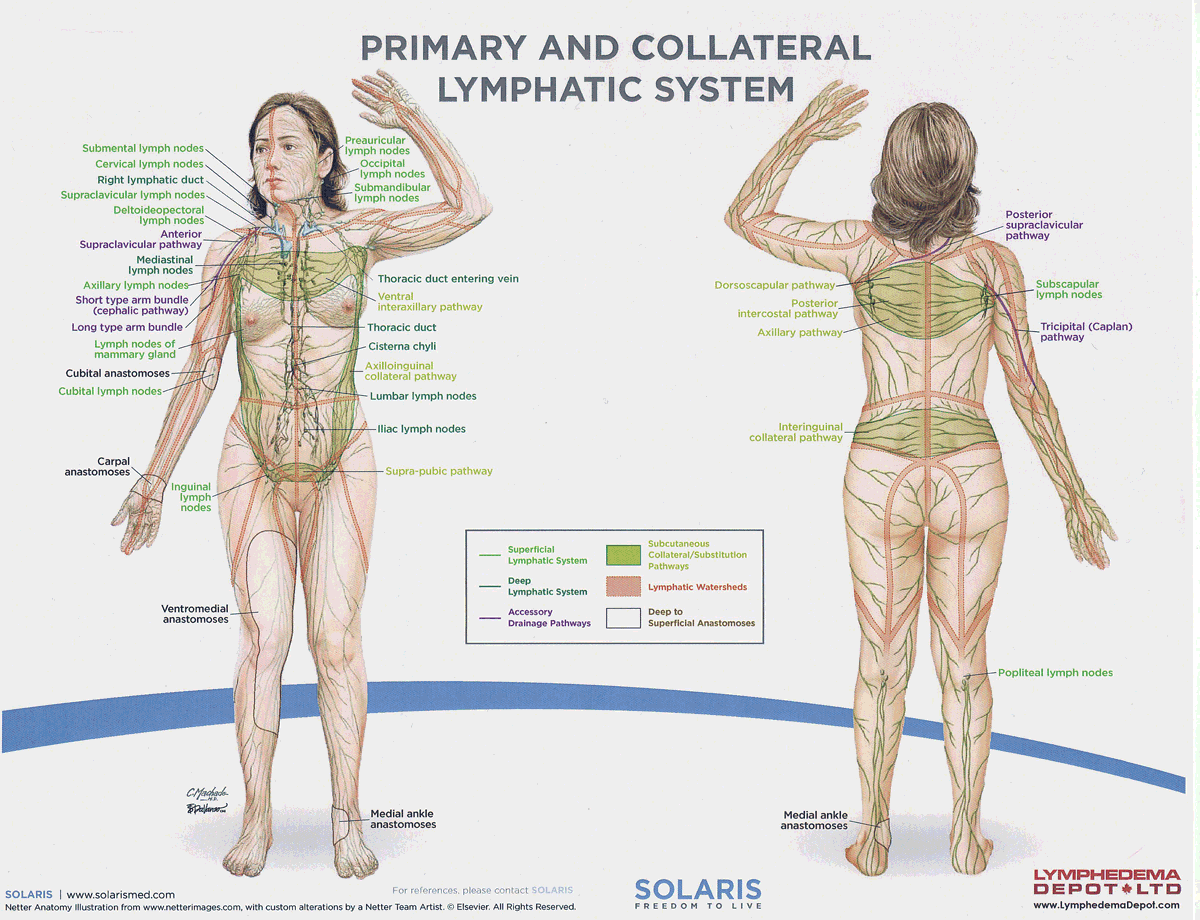
spine of the scapula watershed
An anatomical boundary that separates lymphatic drainage between the upper limbs and the back, influencing lymph flow and drainage patterns in the region.
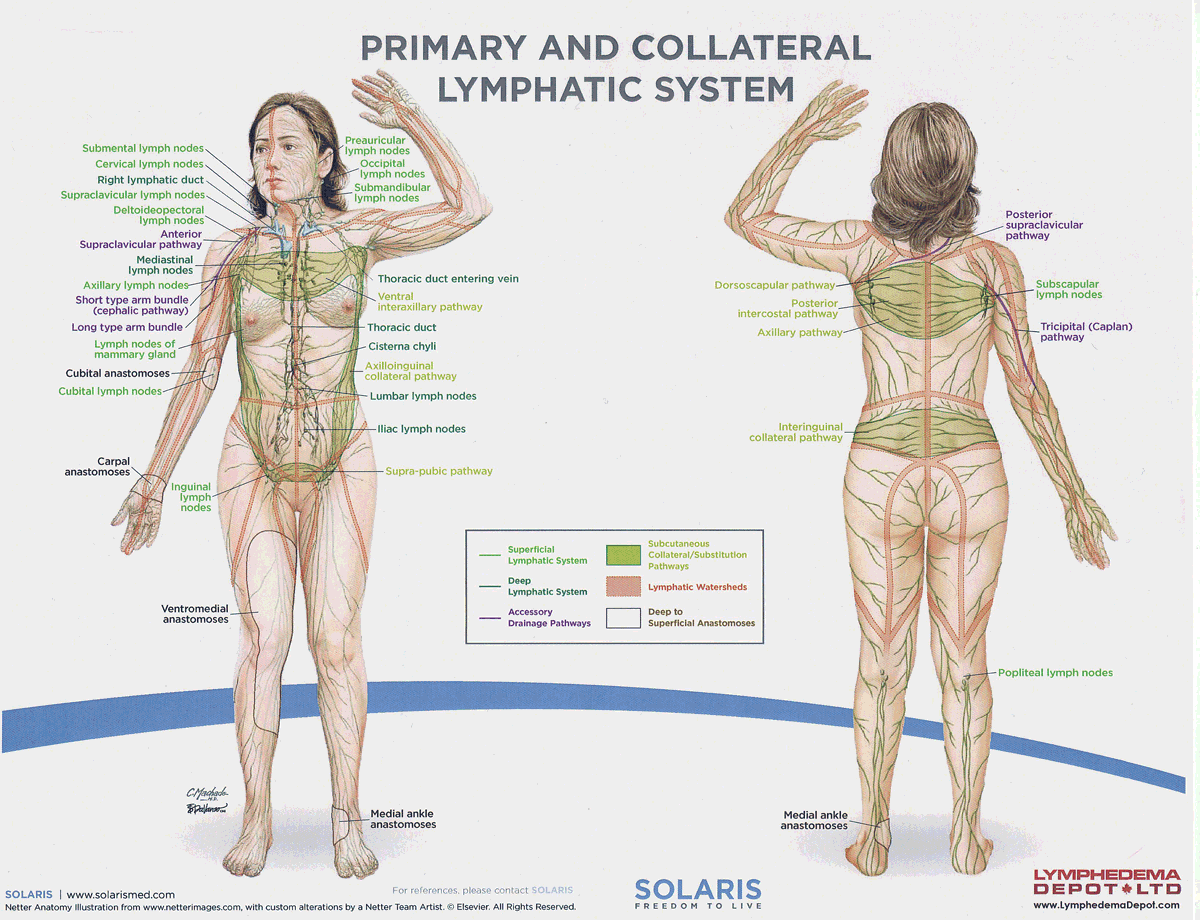
chaps watershed
An anatomical boundary that separates lymphatic drainage between the lower limbs and the pelvis, affecting lymph flow and drainage patterns in this area.
lympho-lymphatic anastomosis
A connection between lymphatic vessels that allows for the exchange of lymph, facilitating drainage and immune function across regions of the body.
regional lymph nodes
Clusters of lymph nodes located in specific areas of the body that filter and drain lymph from that respective area.
axillary lymph nodes
Lymph nodes located in the armpit region that filter lymph from the upper limbs, breasts, and upper torso, playing a crucial role in immune response.
inguinal lymph nodes
Lymph nodes located in the groin area that filter lymph from the lower limbs, external genitalia, and lower abdominal wall, contributing to the body's immune defense. These nodes are vital for filtering lymph from the lower body and responding to infections.
femoral triangle
An anatomical region in the upper thigh that contains important structures, including the femoral nerve, artery, and vein, and serves as a passageway for blood vessels and nerves to the lower limb.
intercostal lymph nodes
Lymph nodes located between the ribs that filter lymph from the thoracic wall and parts of the breast, playing a role in the body's immune response.
occipital lymph nodes
Lymph nodes located at the back of the head that filter lymph from the scalp and neck, contributing to immune defense.
mastoid (retroauricular) lymph nodes
Lymph nodes located near the mastoid process of the skull that filter lymph from the ear and surrounding areas, playing a role in the immune response.
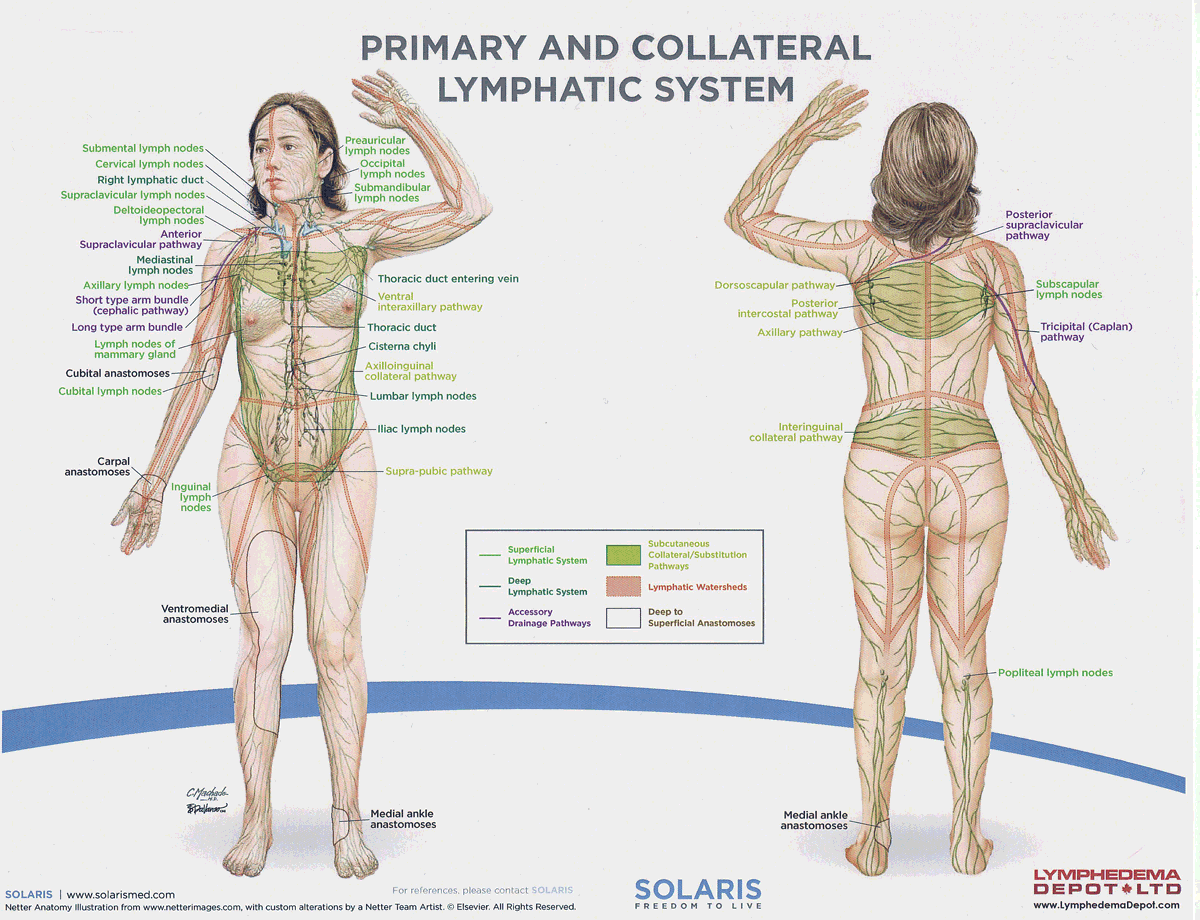
parotid (preauricular, infraauricular) lymph nodes
Lymph nodes located near the parotid gland that filter lymph from the face, scalp, and ear, aiding in immune function.
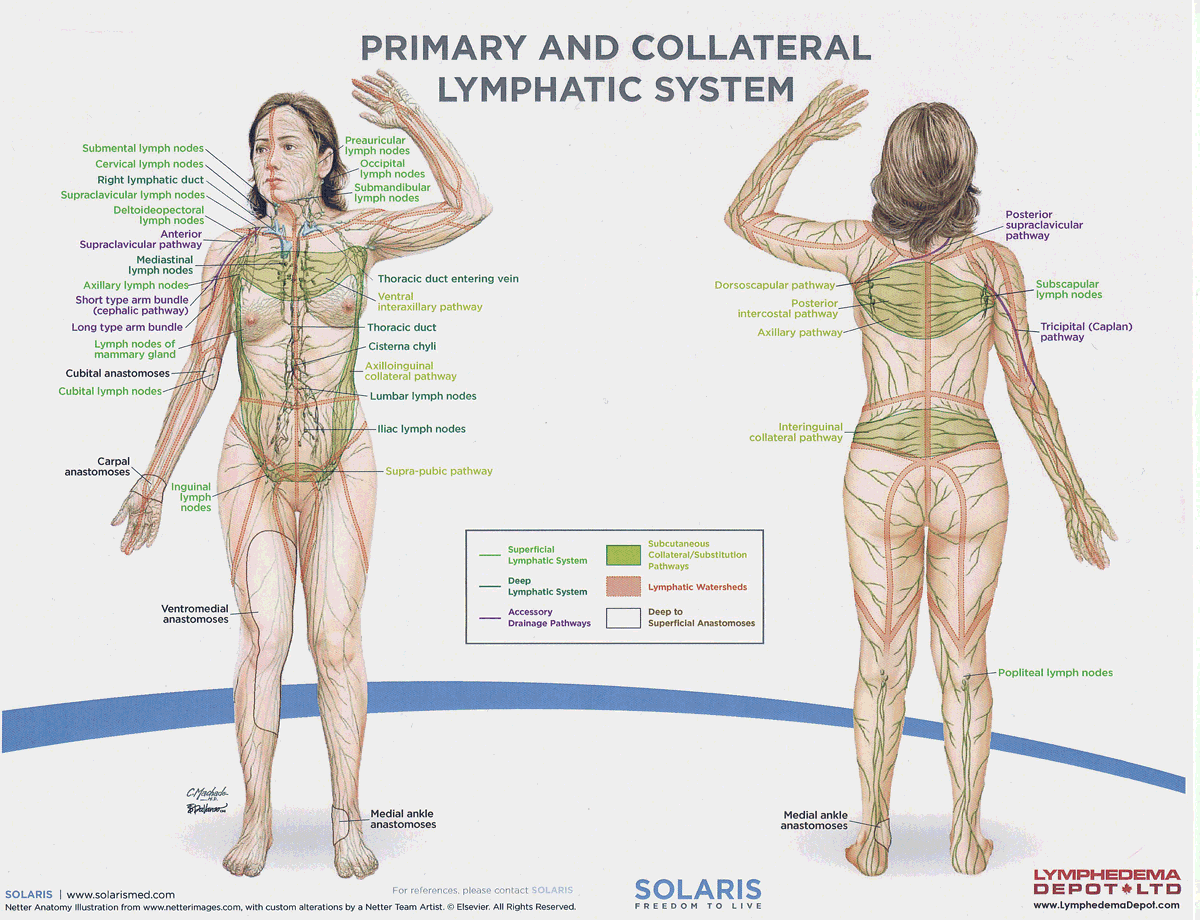
submandibular lymph nodes
Lymph nodes located beneath the jaw that filter lymph from the floor of the mouth, tongue, and parts of the face, contributing to the immune system.
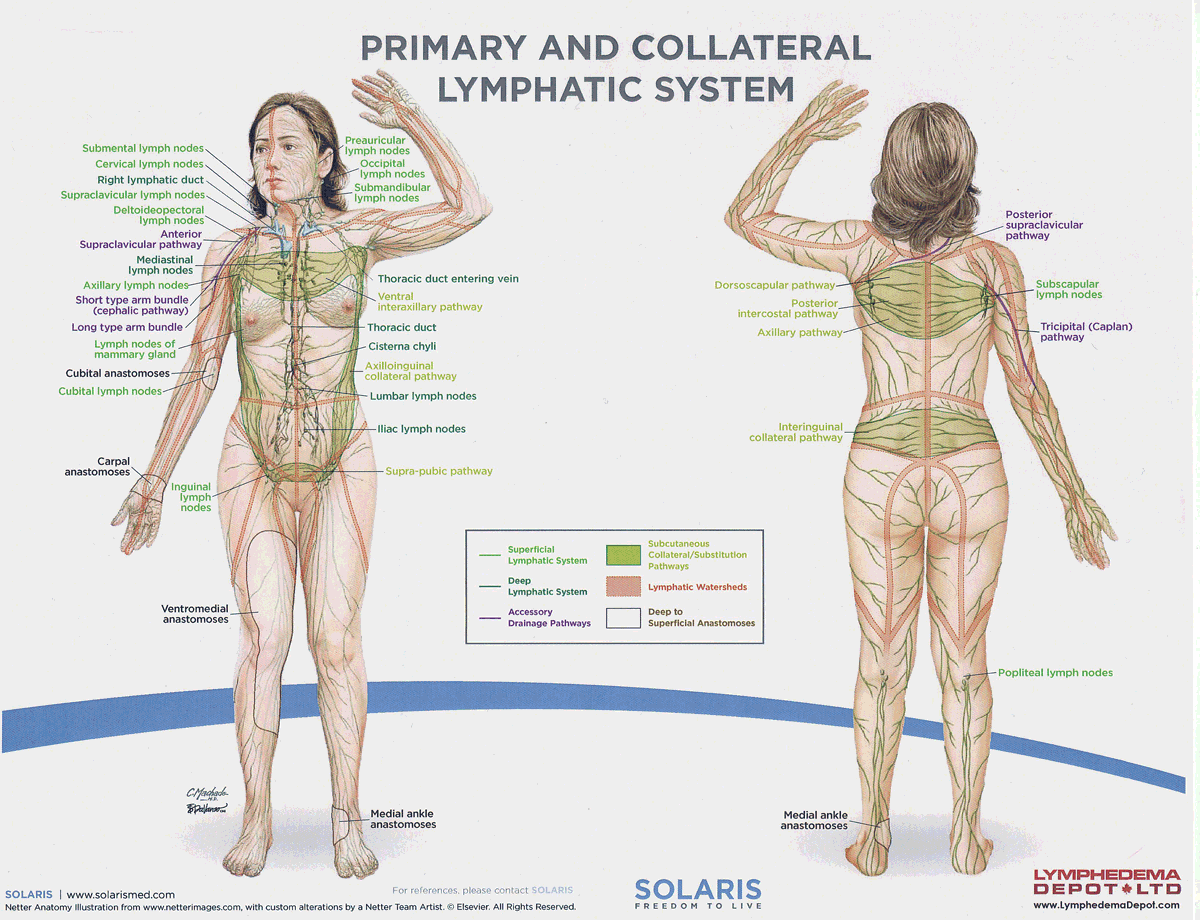
submental lymph nodes
A lymph node located beneath the chin that filters lymph from the lower lip, anterior floor of the mouth, and tip of the tongue, playing a role in the immune response.
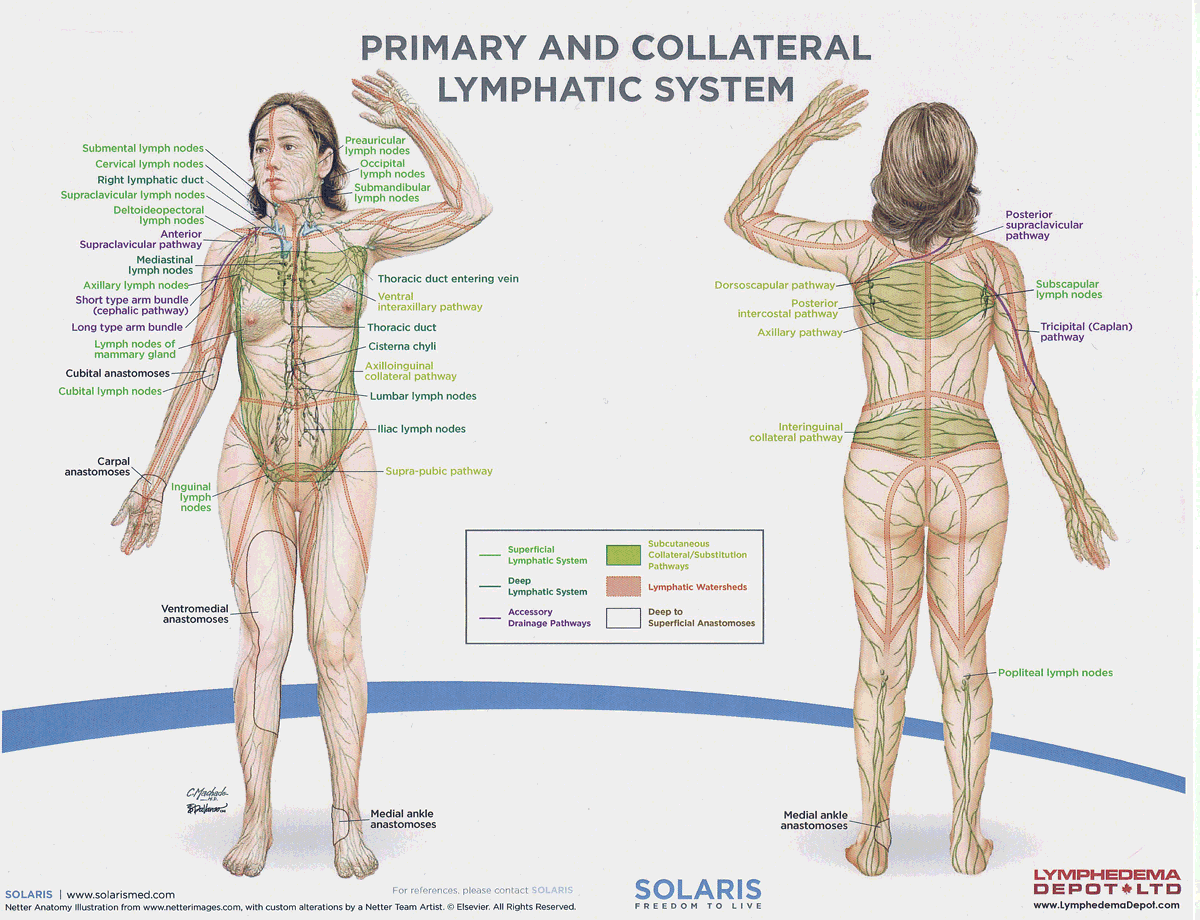
pericervical lymphatic circle
A group of lymph nodes located around the neck that filter lymph from the head and neck regions, playing a significant role in the immune response.
facial lymph nodes
A collection of lymph nodes located in the face that filter lymph from the facial structures, helping to facilitate the immune response.
lingual lymph nodes
A group of lymph nodes located in the tongue that filter lymph from the tongue and surrounding areas, contributing to the immune response.
retropharyngeal lymph nodes
A group of lymph nodes located behind the pharynx that filter lymph from the throat and surrounding regions, playing a role in the immune response.
superficial external jugular lymph nodes
Lymph nodes located along the external jugular vein that filter lymph from the scalp, face, and neck, aiding in the immune response.
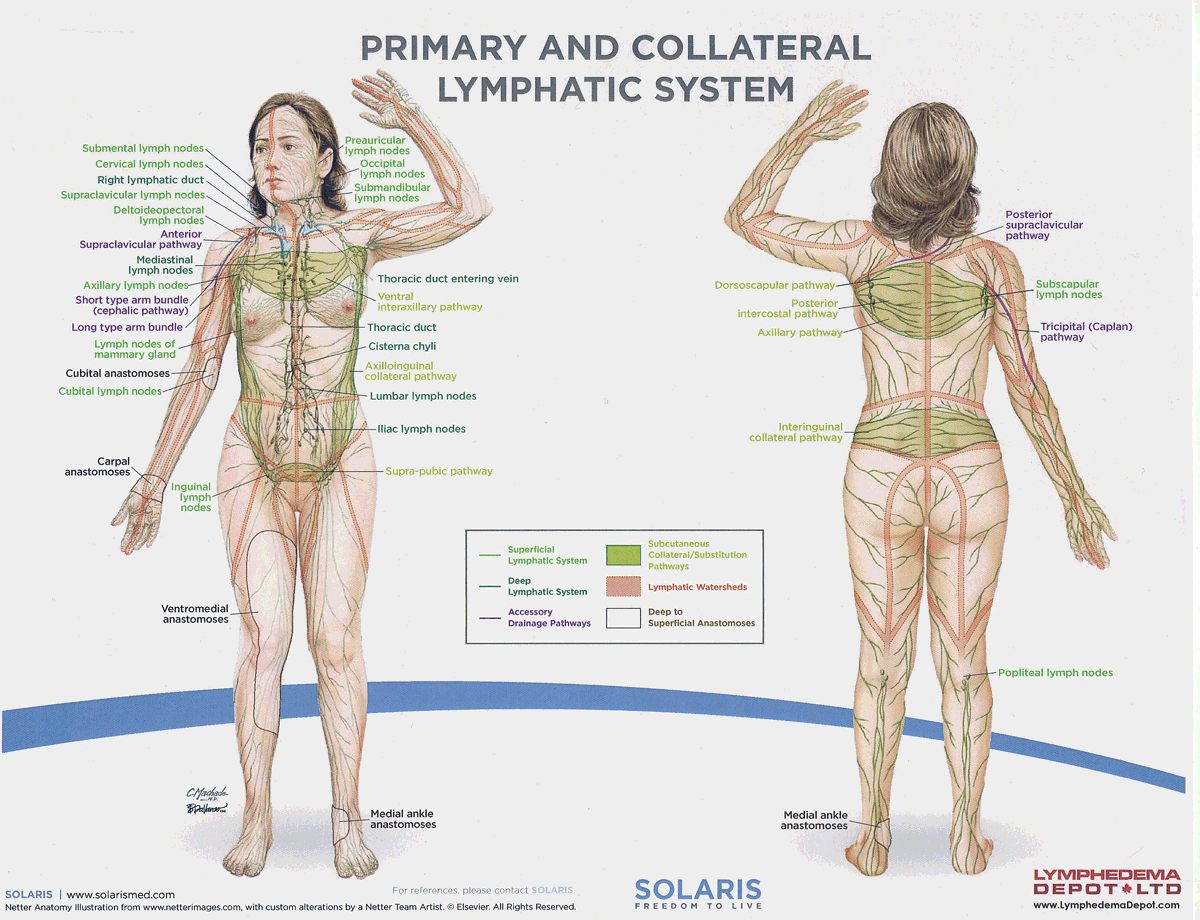
deep lateral cervical nodes
A group of lymph nodes located deep in the lateral cervical region that filter lymph from the neck and surrounding areas, supporting the immune system.
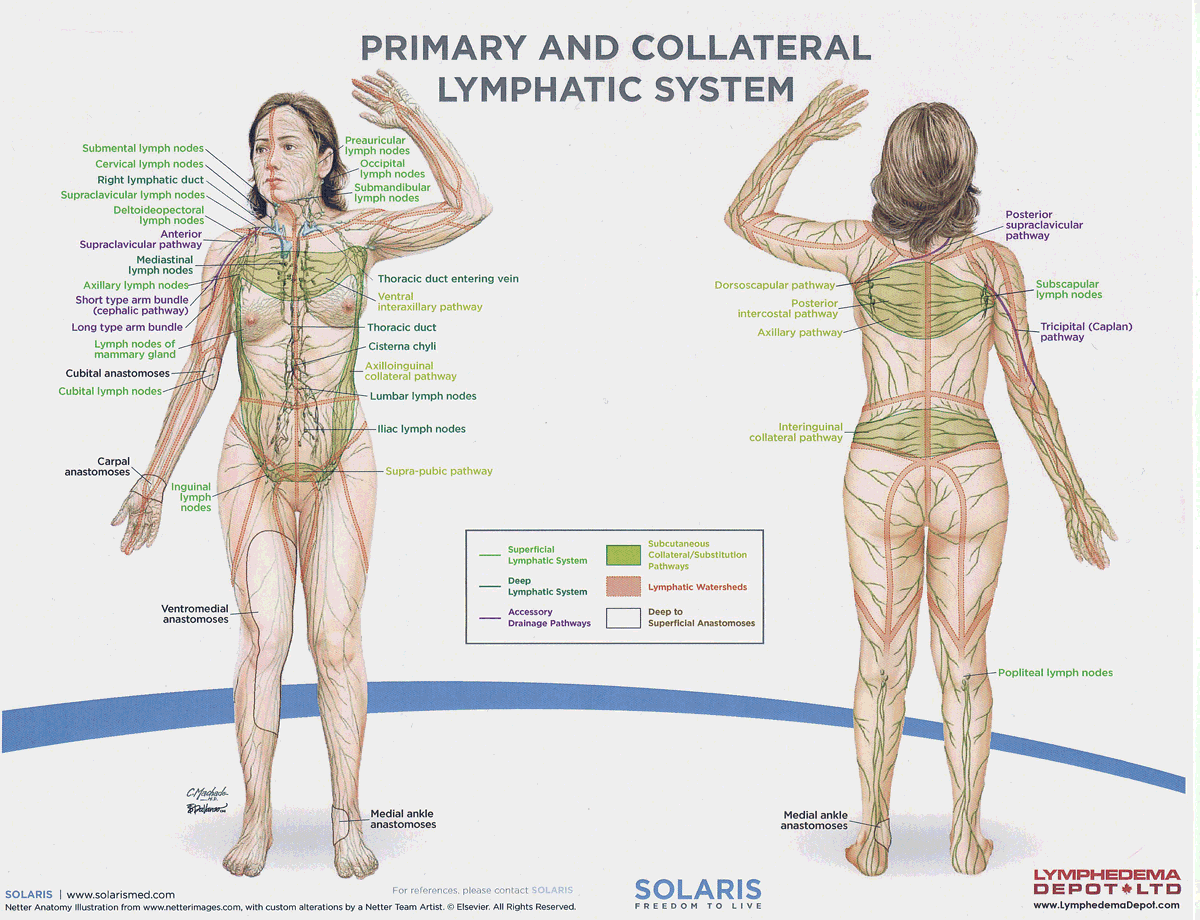
accessory lymph nodes
Lymph nodes located near the accessory spinal nerve that drain lymph from the shoulder and neck regions, contributing to the immune response.
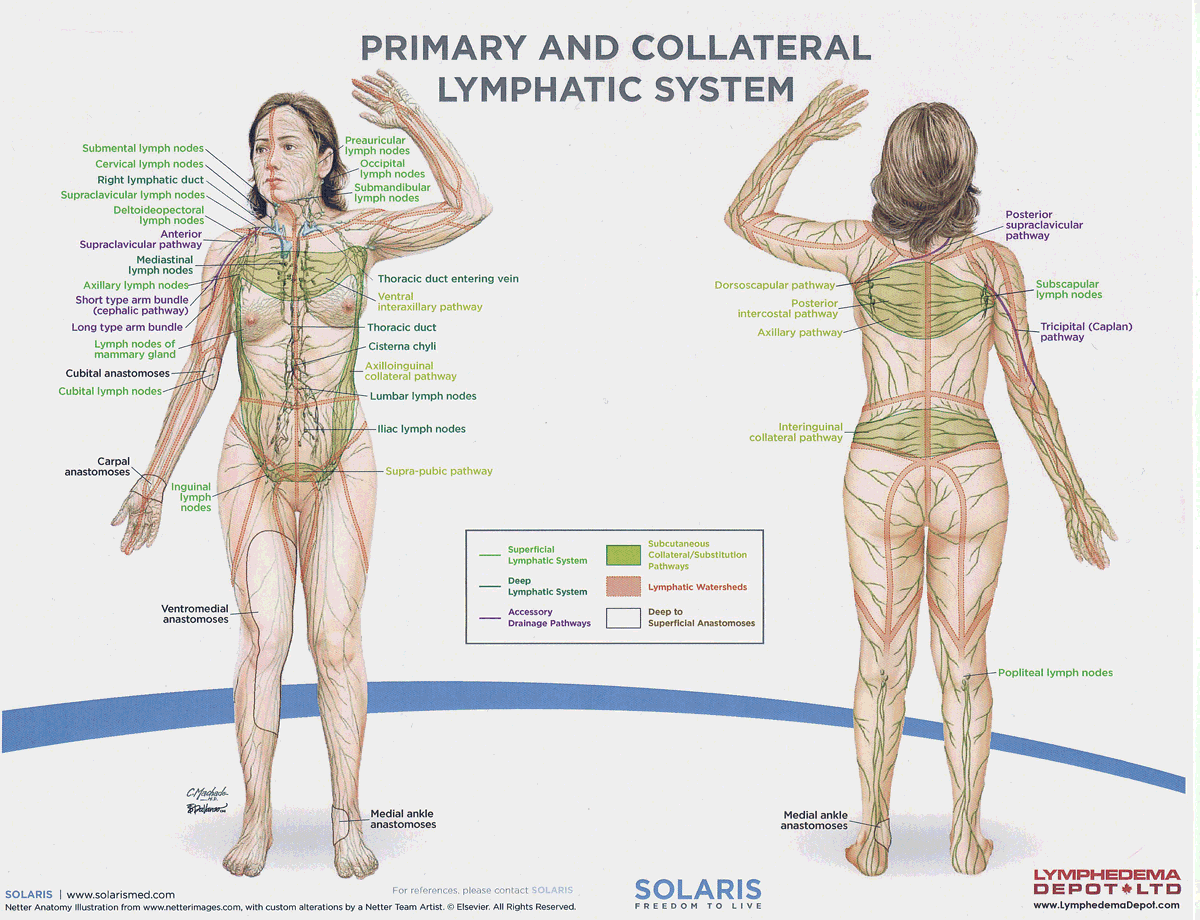
internal jugular lymph nodes
Lymph nodes situated along the internal jugular vein that filter lymph from the head and neck, playing a crucial role in the body's immune defense.
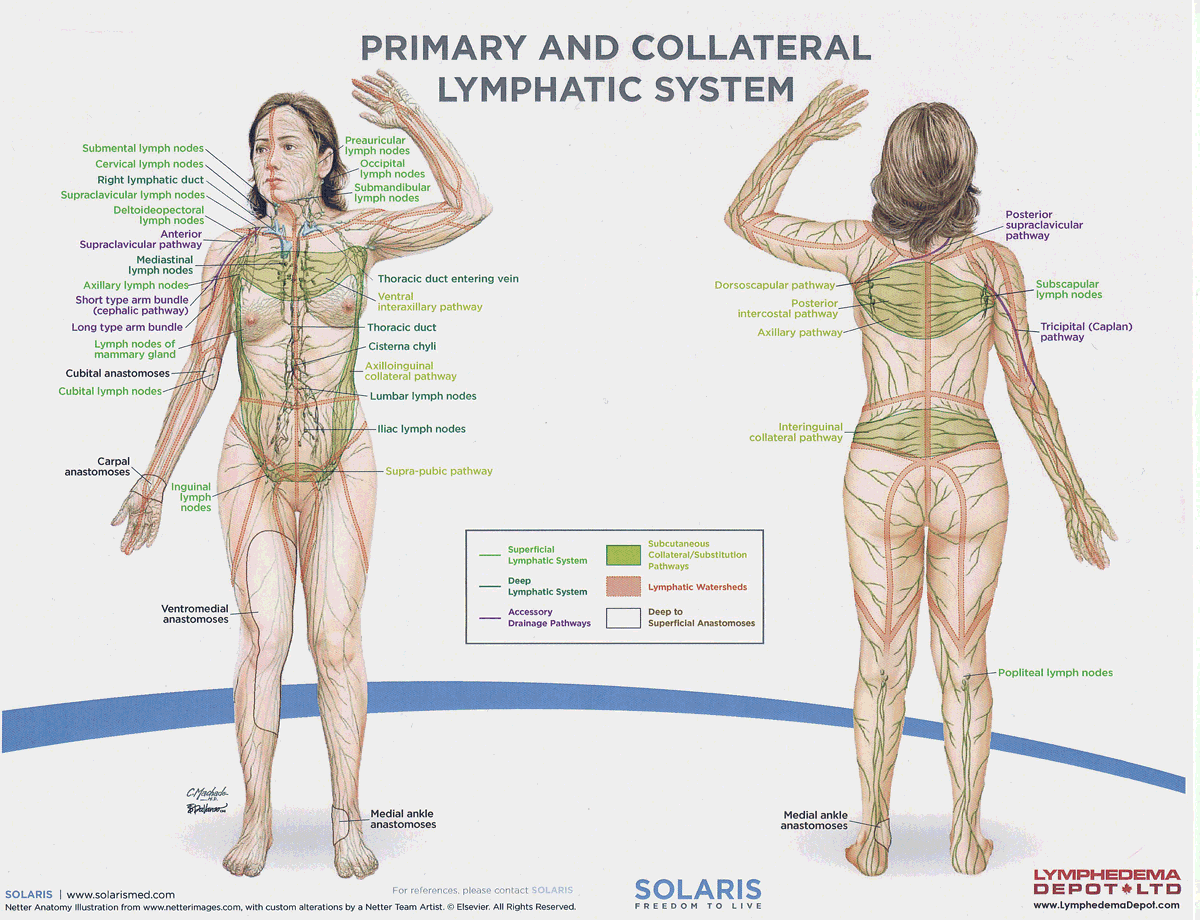
supraclavicular lymph nodes
Lymph nodes located above the clavicle that filter lymph from the upper extremities, neck, and thoracic cavity, playing a significant role in immune function.
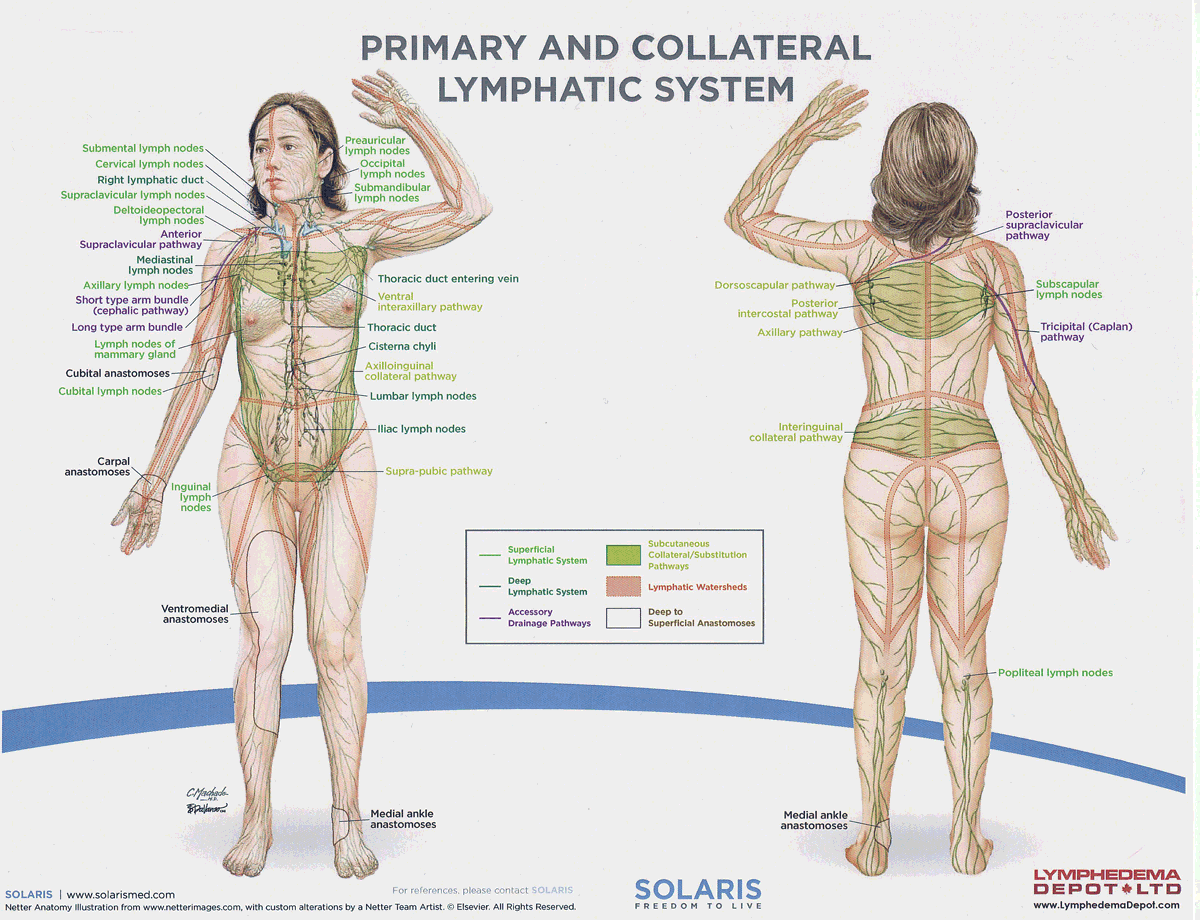
frontal lymph nodes
Lymph nodes located in the forehead region that drain lymph from the frontal scalp and forehead, contributing to the immune response.
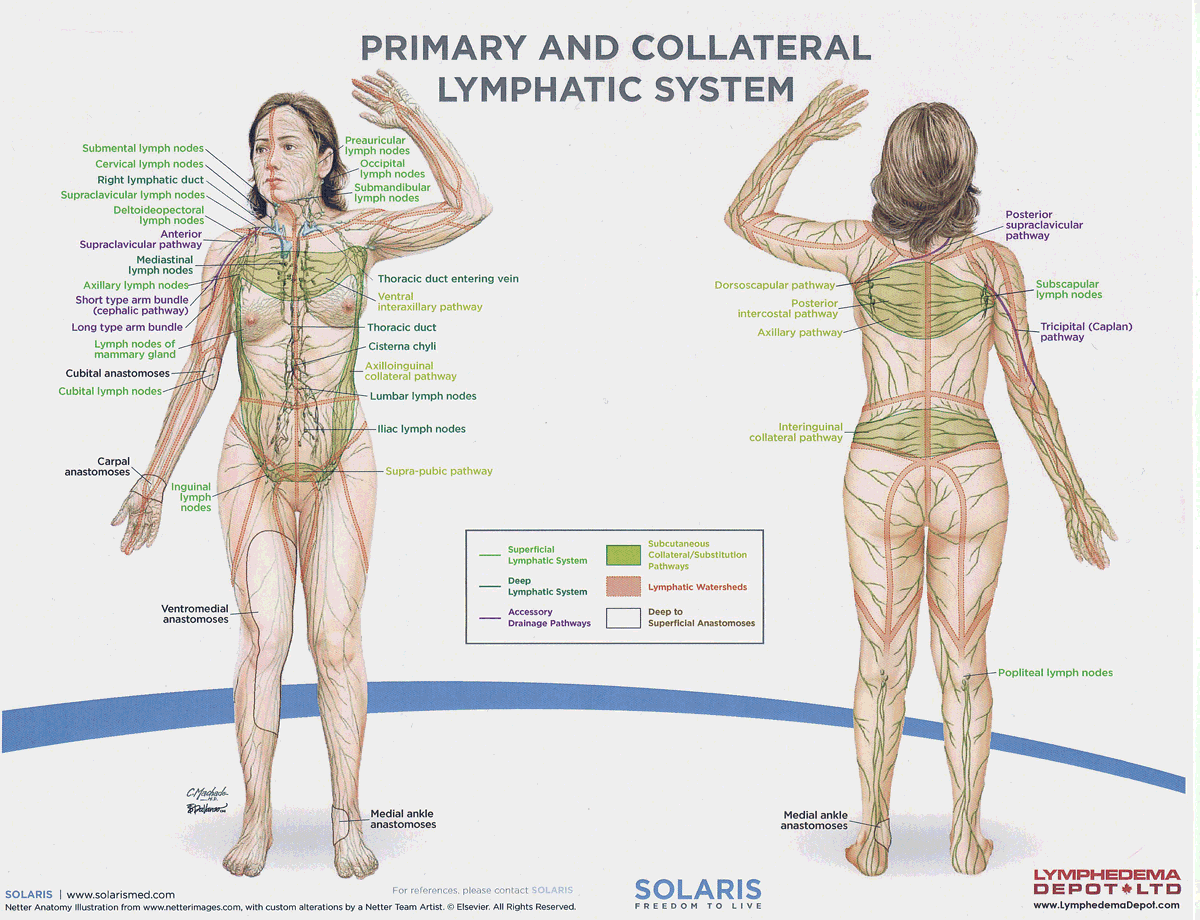
parietal lymph nodes
Lymph nodes located near the parietal bone of the skull that drain lymph from the lateral aspects of the head, aiding in the immune response.
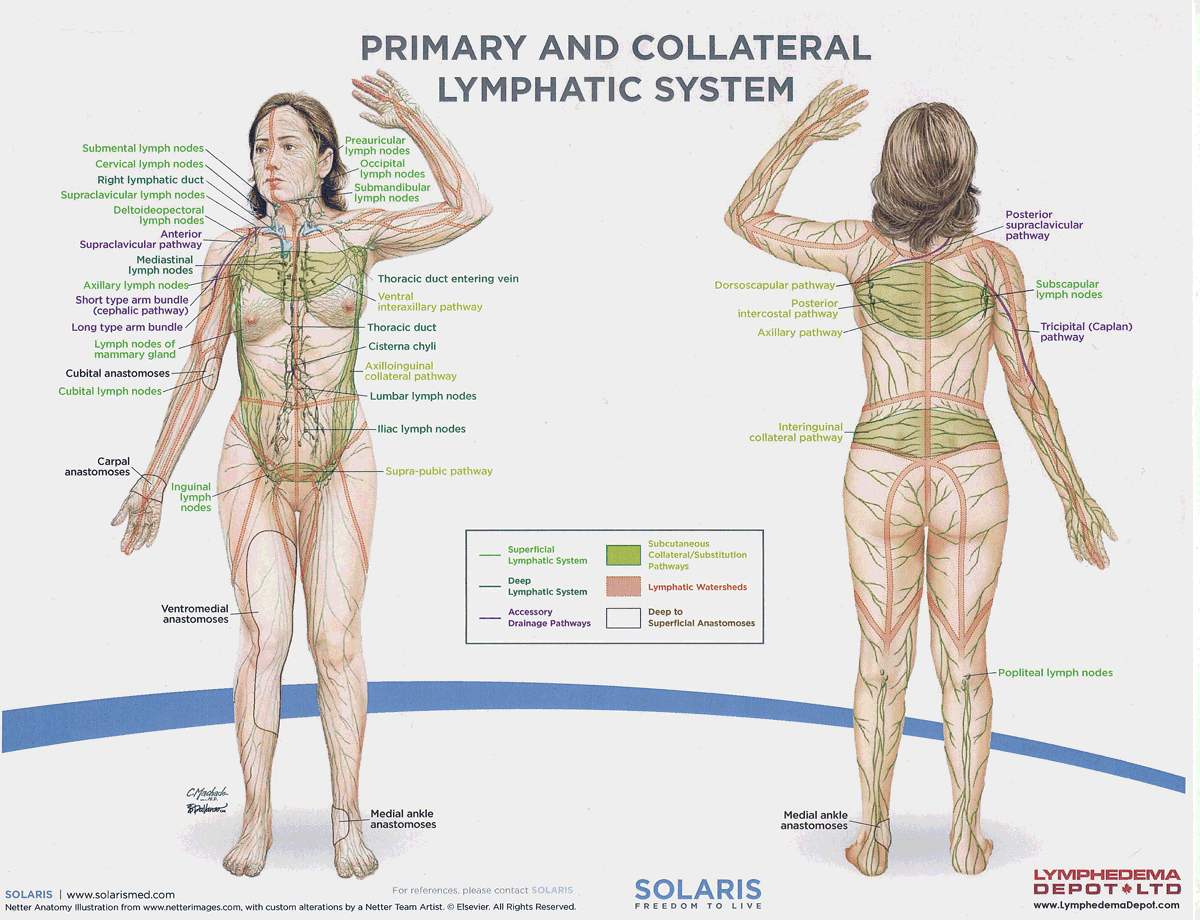
lumbar lymph nodes
Lymph nodes located in the lower back region that drain lymph from the pelvis and lower limbs, playing a crucial role in immune surveillance.
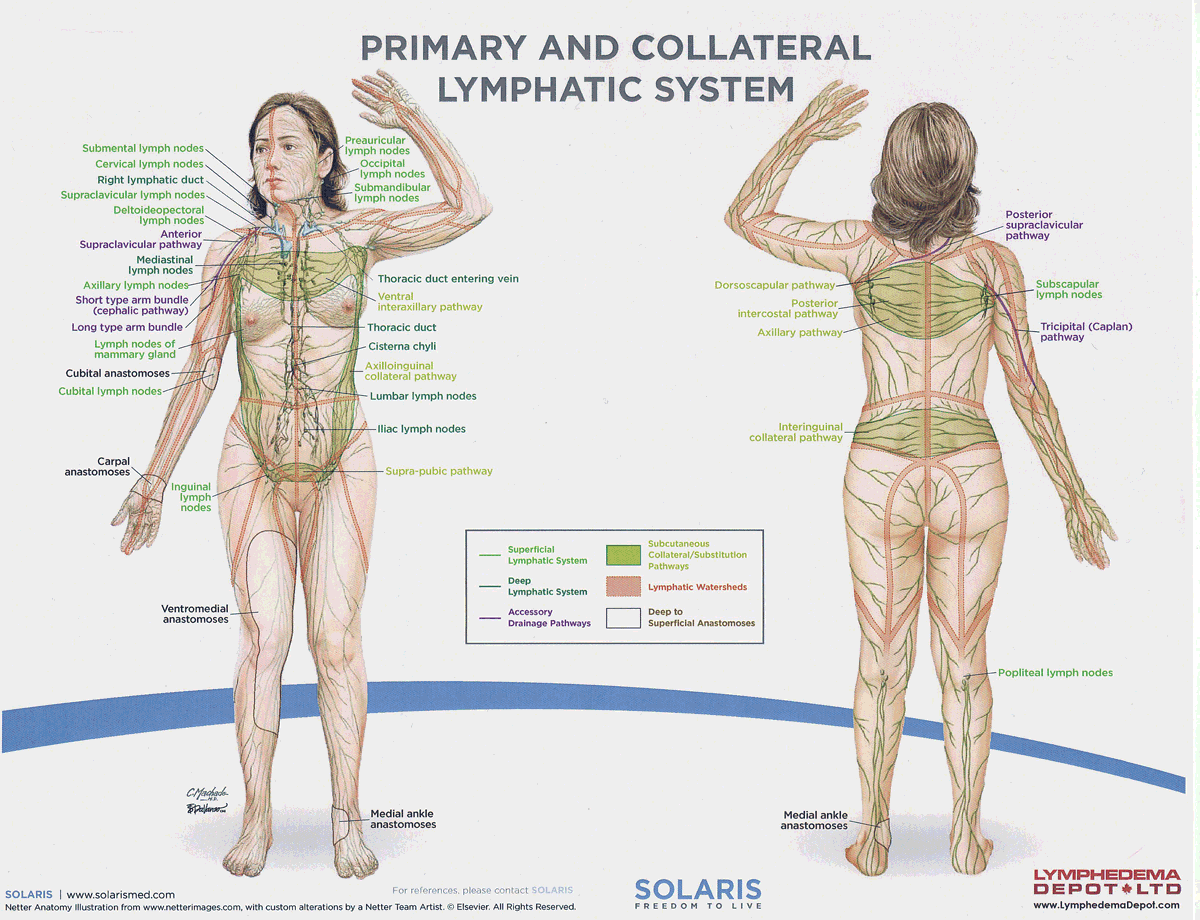
iliac lymph nodes
Lymph nodes located in the pelvic region that drain lymph from the lower abdomen, pelvis, and lower limbs, important for immune function.
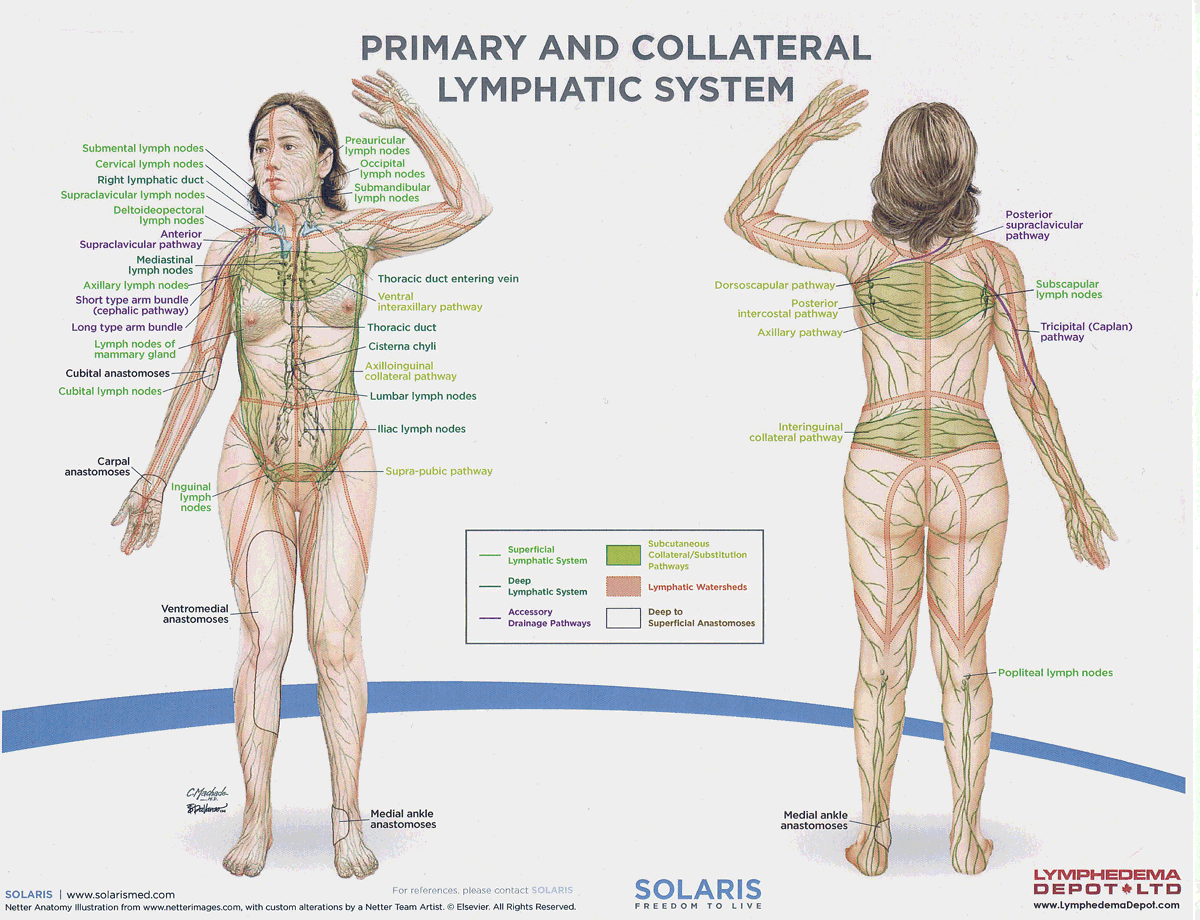
Name four lympho-lymphatic watersheds
median sagittal, chaps, transverse, clavicular
The regional lymph nodes for the chin and lower lips are
submental lymph nodes
The lymph ultimately enters the blood stream at
at the area of the left and right subclavian and internal jugular veins
Perforating vessels
exist in the precollectors network
The greatest accumulation of lymph nodes
is found in the head, neck, and abdomen
The superficial lymphatic vessels can be found
atop the muscles fascia within the subcutaneous fat
Which statement best describes the “lymphangion”?
the functional unit between distal and proximal valve
In which vessels do we find valves
veins, lymph collectors, lymph trunks
The upper extremities drain via
axillary lymph nodes, subclavian trunk, venous angles
Which best describes lymphatic capillaries?
containing endothelial cells, basement membrane, anchoring filaments
Name three lymph trunks within the deep lymphatic system:
subclavian, lumbar, and intestinal
A territory can be described best as:
a specific region of skin drained by a group of lymph nodes
If a patient receives a pelvic lymphadenectomy, lymphedema can occur:
in the genitals, in 1 or both LEs