Nursery Managment Test 3
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
1. Describe the two components of a pot-in-pot nursery.
Combination of container and field production • Socket pots – set in ground, 3-6” above grade• • Insert pot – contains growing media and theplant
Advantages of pot and pot
• Advantages (like contatiner:
• Year-round harvest
• Shipping easier
• Less root loss
• INSULATION OF ROOTS
• Advantages: Like field production• Irrigation
• Plant in ground → stability
pot in pot advatages over both container and field
Greater growth and less production time
ground covering managment
Pot in pot disadvantages
cost
drainage
root growth escape
socket and insert stick together
pot sags
spacing flexibility
advantages of inground fabric containers
ADVANTAGES• Lower cost & less time than B&B• No skill or machinery
• 80% roots retained → harvest year-round• Trees can be held then above ground• Root-pruning
Disadvantages of in-ground fabric containers
DISADVANTAGES• Initial bag cost high
• Care when planting (tears → roots growout of bag
•Cultivating/fertilizing difficult
• Bag integrity
• Hard to remove bag when planting
• Species specificity (some struggle)
• Dug with shovels or backhoe
• Remove fabric before planting
Describe the two different types of liners and the two propagation methods of how they are generated.
Liners = small propagules
-Field liners
-container liners
-sexual- seeds
asexual-grafting,division and cutting
Know what a nursery owner must consider for propagation of plants via sexual or asexual methods.
Cost - seed is cheaper
• Ease - seed is easier
• Speed/time required - species specific
• Reliability / degree of success (speciesspecific)
• Time of the year (species specific)
• Skill required (cuttings and grafting more)• Best fit for business???
-quality
Know the three aspects of the propagation environment that must be modified for liner cultivation.
1. Moisture
2. Air and root zone temperature3. Air circulation
Describe how we prevent moisture loss and any pertinent aspects of those systems.
humidity tents, intermittent mist systems and fog systems
Mist system components
timer-frequency and application
-water control leaf
-mist nozzles (location)
Things to consider with intermittent mist systems
cost, disease (more moisture = more diseases) and leaching
Things to consider with intermittent Fog systems
• Like mist... Consider money
• Disease: inc. moisture → inc. disease
• Leaching
• Clean water → clog nozzles
• Working environment → foggy
Describe how we modify the air and root zone temperature of the liner propagation environment.
• Air: 70-80F days and 60F nights
• Root zone: 70-75F
• Shading
• Bottom heat (winter)
Explain the importance of air circulation in liner production.
mixes air and reduces disease
Explain how we maintain sanitation in the liner propagation environment
clean stock plants and seed, clean substrate, clean propagation tools and remove infected plants
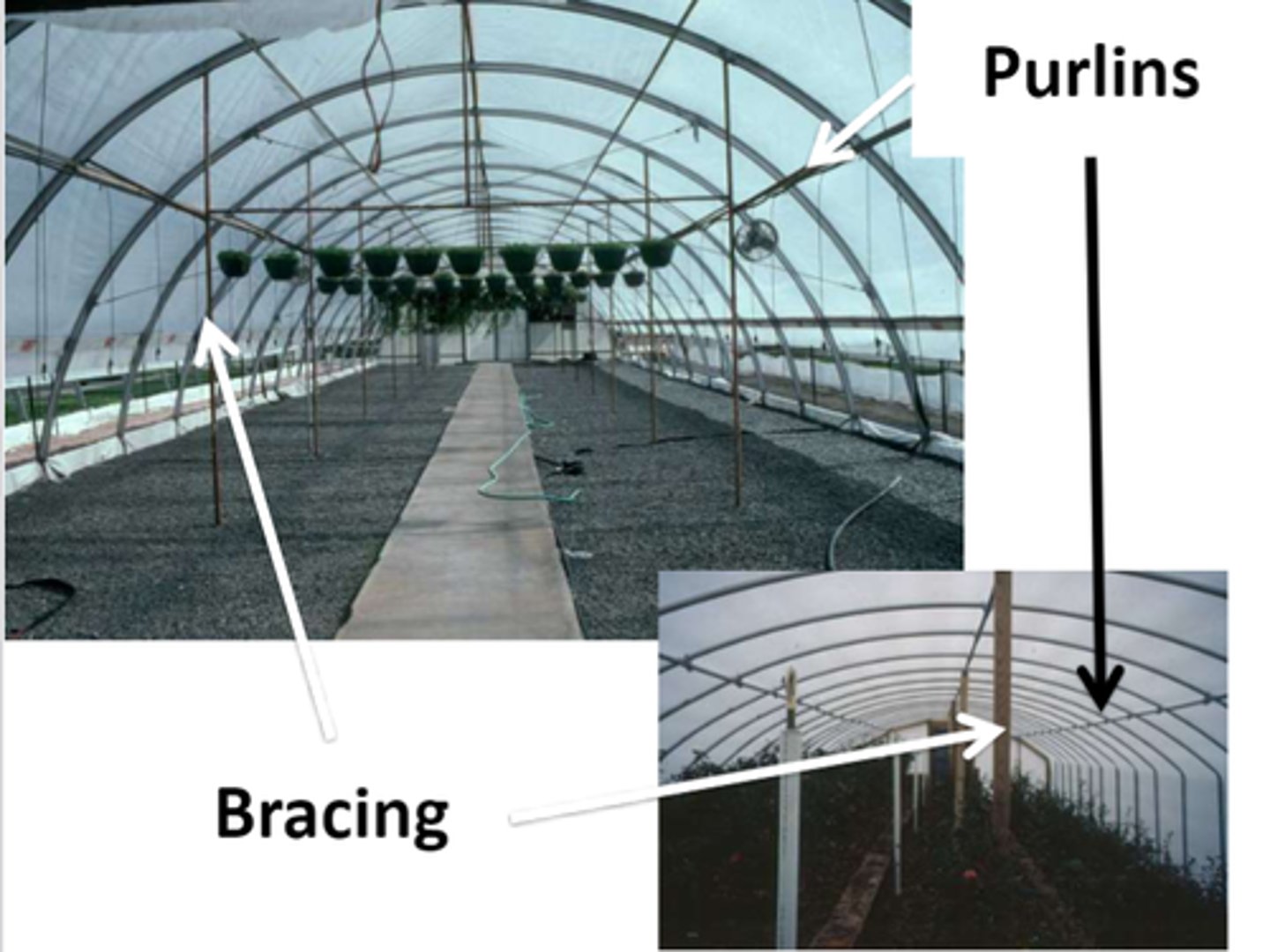
Describe a quonset hut constuction and it's correct orientation
-Bows
-bracing
-endwalls
-drainage
• End walls orient N-S
• Further N orient E-W
Explain how we acclimatize plants from propagation.
expose to ambient growing conditions, reduce mist exposing to more drought and fertilize
Describe characteristics of outdoor propagation areas
Seed beds
Cold frames
Liner beds
Width: 36, 42, and 48"for equipment
factors that affect spacing in outdoor propagation areas
species, growth rate and size of propagule
What is a mother stock area and the ways that it can be used.
• Large, separate area
• Display gardens
For propagation containers, what must be considered?
Flats with cell inserts- consider root growth
Beds & community flats
Explain the reasoning of keeping records for propagation and what should be recorded.
Successes and failures
Method of propagation
Time of the year
Treatment
Numbers (shrinkage)
Label and track stock/supply
Final Word on Cash Flow
Liners - turn over 3-4 crops per season
Many nurseries don't grow their own liners
High cost/ft2
Describe characteristics you look for quality plants.
-no sign of pruning
-uniformity of shape
-full or well-shape canopy
-healthy roots
-good propagation
-planted correctly
-maintain proper spacing -minimal pruning
what happens if you miss pruning?
can create holes in the canopy
When should you stake plants?
-stake only when necessary
-prevent blowing over
-developing straight trunks
-anchoring when newly planted.
-protection during shipping
-stake taller than the plant
good staking is
-non-abrasive
-short term
What are the different pruning techniques
• Heading cuts - cutting back to a healthy node
• Thinning cuts - reducing the number ofbranches
• Rejuvenation cut - cutting back to the base toallow new growth
Know what should be pruned the first year.
FIRST YEAR AFTER PLANTING
• Focus on root growth
• Leave lower branches
• Taper and caliper
• Minor corrective pruning
• 4 D's: Dead, dying, diseased, and damaged
• Crossing branches
what are the two different growth habits
decidous and evergreen
Describe how to prune single stems, deciduous trees.
Single trunk (Acer)
Proper canopy height
Full canopy
Scaffold limb development
Describe how to prune modified leaders deciduous trees
• 3-5 modified leaders (Cercis)• Low, widescaffold limbs• Manage lateralbranch length
Describe how to prune Multiple Stemmed deciduous trees
• 3-5 main stems (Betula)
• Remove lowestbranches thatoriginate fromthese main stems
• Foliage of the canopyup top
Be able to detail practices you need to perform to maintain growth in 2+ years for deciduous trees.
• Over next two years, manage rapid growth
1. Remove Competing Limbs
2. Maintain the Central Leader
3. Crooked or missing central leader
4. Scaffold Limb Management
5. Canopy Height Measurement
Describe what to do when you lose a main leader.
staking and taping
what are the different evergreens trees and shrubs?
broadleaf and conifers
how to prune broadleaf evergreen
• Sheared 3-6x / season
• Remove all tips
• Soft growth
• Head back to promote branching density.
Maintain 8-10" of height above canopy
how to prune Needle evergreen
Minimal pruning
Some can be sheared
Watch dead zone
Pruning of pines, Spruces, Firs
Not much
Reduce growth
Cut back candles
Watch dead zone
If lose leader Stake top-most branch up
describe how to prune Deciduous Shrubs
Remove all tips (soft growth)
Watch shape
Be true to species
What are some specialty trees adn requirements for them?
• Espalier• Needs aframe• Topiary
• Labor and work to maintain
• Consider the species