Economic Foundations
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What is economics?
Economics is the study of how to allocate resources to maximise the welfare for all society. It studies the economic behaviour of individuals and groups and the economic relationships between them.
What is the central purpose of economic activity?
The production of goods and services to satisfy needs and wants.
What are the 3 main economic agents?
Consumers
Producers
Government
What are consumers?
People or organisations that use economic good or services
What are producers?
People or organisations that create and supply goods or services
What is the government?
A group of people who have the authority to govern a country
What is the economic problem?
How to best use limited resources to satisfy the unlimited wants of people
What is an economic choice?
Decisions made by individuals/firms/governments about which needs and wants to satisfy, and what goods and services should be produced and bought. They involve an opportunity cost.
What is opportunity cost?
The benefit of the next best alternative forgone when making a choice.
What is a budget deficit?
when government spending exceeds taxation receipts (also known as a fiscal deficit)
What is a budget surplus?
When government spending is less than taxation receipts (also known as a fiscal surplus).
What is capital?
Man made goods used to produce more goods including factories (plant), machines and roads in the production process
What is enterprise?
An entrepreneur risks financial capital and organises land labour & capital to produce output in the hope of profit
What is labour?
The physical and mental work of people whether by hand, by brain, skilled or unskilled, in the production process
What is land?
All natural resources (gifts of nature) including fields, mineral wealth, and fishing stocks
Whats the reward for the FoP?
Capital - interest
Enterprise - profit
Land - rent
Labour - wages
What is specialisation?
Where a country, firm or worker focuses on a particular task within the production process in order to gain greater efficiency.
What is the division of labour?
Dividing a job into many specialised parts, with a single worker or a few workers assigned to a particular task in the production process
What is exchange?
Where buyers and sellers come together in a market place to negotiate prices.
What are the benefits of specialisation to a worker?
More skills developed
Focus on specific tasks
Specialist training
What are the costs of specialisation to a worker?
Job can become boring
Less flexibility to switch jobs - need retraining
What are the benefits of specialisation to a firm?
Greater output
Lower cost due to increased efficiency
Ability to be more competitive
Fewer mistakes
What are the costs of specialisation to a firm?
Morale may fall
Worker and production are interdependent
Absences need to be covered
What are the benefits of specialisation to a region?
Efficient use of resources
Creates jobs for residents
Specific infrastructure development
What are the costs of specialisation to a region?
Risk of low demand
Rising costs if materials/labour are taken from other regions
What are the benefits of specialisation to a country?
Economies of scale and efficiency
Job creation
Revenue to the government
Improves living standards
What are the costs of specialisation to a country?
Danger of unemployment
Over-exploitation of resources
Negative externalities
What is the primary sector of the economy?
Involves extraction of natural resources/raw materials for industry e.g. agriculture
What is the secondary sector of the economy?
involves the production of goods in the economy, i.e. transforming materials produced into finished goods. Consumer and capital goods are made.
What is the tertiary sector of the economy?
Provides services such as banking, finance, insurance, retail, education
What is the quaternary sector of the economy?
Involves information processing e.g. R&D
What is the chain of production?
The stages that a product goes through from the raw materials to consumer receiving the finished product.
What are the 3 factors of deindustrialisation?
Globalisation
Education and training
Technology
What is economic growth?
Measures the increase in economic activity of an economy over a period of time.
What is GDP?
The value of all goods and services produced within an economy over a given period of time.
What is employment?
Refers to the employment of labour in the economy. It's important as people rely on wages for most of their income.
What is unemployment?
When workers who are able and willing to work are unable to find employment at current wages.
What is price stability?
The general level of prices is kept constant or grows at an acceptably low rate without volatility
What is inflation?
The sustained rise in the general price level over time
What are the Bank of England's two main objectives?
Manage inflation to stay on target at 2%
Support the Governments aims for economic growth and development
What is an interest rate?
The cost of borrowing and the reward for saving (percentage change)
What is the balance of payments?
It records the money flows into and out of a country over time. A record of the financial transactions of one country with the rest of the world.
What is the current account?
Measures the inflow and outflow of goods, services, investment incomes and transfer payments (imports and exports)
What is the balance of trade?
The difference in value between a country's imports and exports
What is the circular flow of income?
An economic model that depicts how money flows around the economy.
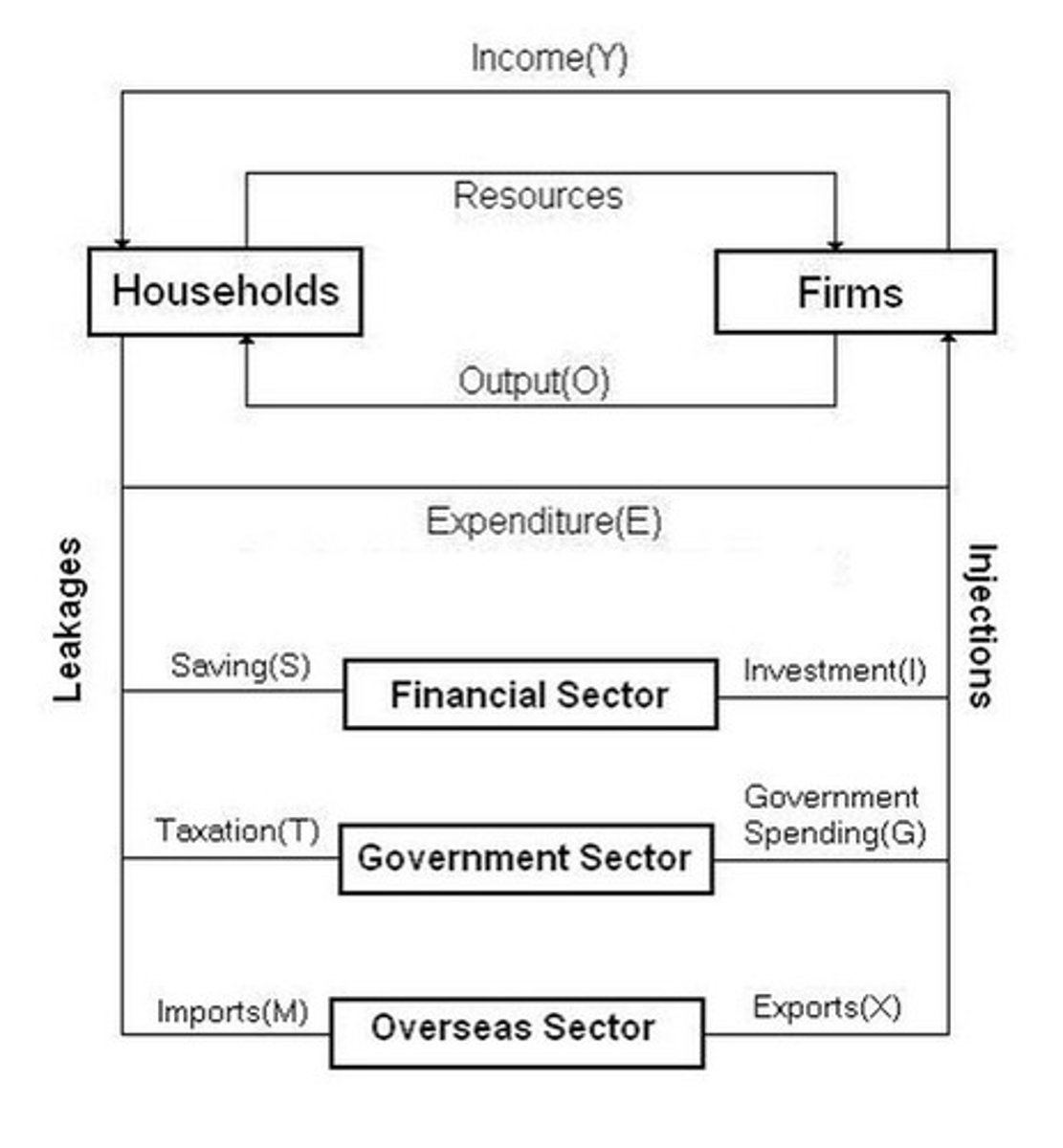
What is an injection/leakage?
Income and expenditure entering/exiting the circular flow of the economy
What is aggregate demand?
The total spending on domestic goods and services produced in the economy. AD = C + I + G + X - M
What is national income?
The total value of the economy as measured by the incomes received in that economy
What is a multiplier?
Any increase in spending in the economy will give a bigger overall eventual increase in income