chirality
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
constitutional/structural isomers e.g. C2H6O
compounds with the same molecular formula but different bond pattern
conformational isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula and bond pattern (stereoisomers) with rotations about single bonds only
configurational isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula and bond pattern (stereoisomers) that cannot rotate around single bonds only
chiral
molecules that cannot be superimposed upon their mirror images e.g. hand
has no plane of symmetry
optically active - can rotate the plane of polarised light
achiral
molecules that can be superimposed upon their images e.g. mirror images
any molecule with a plane of symmetry is achiral
enantiomers
a pair of molecules that are related as non-superimposable mirror images e.g. chiral molecules
each pair of enantiomers rotates the plane of polarized light in an opposite direction
enantiomers rotate light in opposite directions but by the same number of degrees
stereogenic center
a carbon with four different groups attached to it. Gives rise to two stereoisomers
chiral carbon
tetrahedral carbon attached to four different atoms or groups of atoms
its mirror image will become a different compound (enantiomer)
plane-polarized light
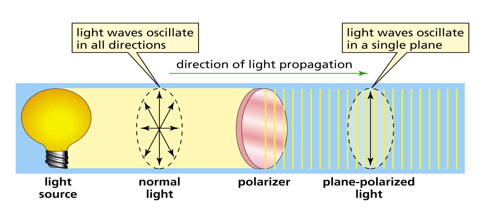
difference between two enantiomers
if one enantiomer rotates plane polarized by light by x degrees in a clockwise directions, then the other enantiomer will rotate plane polarized light by x degrees in the counterclockwise direction
d - dextrorotatory - (+) enantiomer → rotate clockwise
l - levorotatory - (-) enantiomer → rotate counterclockwise
racemic mixture
50-50 mixture of two enantiomers e.g. the (d, l) or (+, -) mixture will give no optical rotation as they will cancel each other out
specific rotation
observed rotation depends on the length of the cell and concentration, as well as the strength of optical activity, temperature, and wavelength of light
T is the temperature and λ is the wavelength of light
