PE (trinal exam)
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
drug
is any substance that causes a physical, emotional, or psychological change in a person.
change in physical, emotional psychological.
ex: methamohetamine
medicine
are chemicals or compounds used to cure, halt or prevent disease. It is also to substance/s used in treating disease or illness.
-cure
-halt/stop
-prevent
-treat
ex: Biogesic
herbal drugs
can be classified as drugs because they have an effect, through mild on the body. Because they are mild, it does are not controlled by law.
over the counter drugs
can be legally bought without the doctor's prescription.
analgesic
are used to relieve pain.
aspirin
acetaminophen
ibuprofen
analgesic (3) kinds
stimulants
are opposite of sedatives, they make you more alert.
prescription drugs
are drugs that require a doctor's prescription.
prescription
- is a doctor's written order to a pharmacist that a patient is allowed to purchase a drug.
- includes the drug's name, direction for use and amount of drugs to be used.
heart rate
refers to the speed of the heartbeat, specifically the number of heartbeats per unit of time.
60-100 bpm
normal human heart
- children, 10 years and older, and adults
resting heart rate
- is the heart pumping the lowest amount of blood you need because you're not exercising.
- is dependent on your living habits and a number of factors such as quality of sleep, stress level, exercise and eating habits.
40-60 beats per minute
well-trained athletes
body mass index (BMI)
- Is a number calculated from a person's weight and height.
- is a fairly reliable indicator of body fatness for most people.
posture
- position of the body when sitting or standing.
- It describes how your spine is aligned with your head, shoulders, and hips.
Postural Alignment
- starts its development from early period of life with development of the spine and its curvature.
Primary Curve
At first, at birth the spine has one "C"-shaped curve with one convexity and one concavity.
Cervical Curve
- Then, as the child is trying to raise his head from prone lying position, the ___________ starts to develop.
- is the curve of the neck and comprises the first seven spinal vertebrae.
- It starts at the base of the skull and extends downward to just above the thoracic portion of the spine. At best, it should look like a large, backward 'C' shape.
Lumbar Curve
In the early phase of education of walking, another curve will be developed, which is the lumbar curve.
Secondary Curves
These two curves (cervical and lumbar) are considered as ______.
good posture
- is the attitude which, is assumed by body parts to maintain stability and balance with minimum effort and least strain during supportive and non-supportive positions.
poor posture
is a position resulting from and deviation from ideally aligned erect posture
defects in joints
may suffer from stiffness or immobilization.
defects in bones
might experience shortening or deformity.
defects in muscles
could exhibit weakness, paralysis, or contractures. Problems with vision or hearing can also contribute.
Bad Habits
- Poor posture can be a consequence of habits developed from early childhood or stemming from occupational positions.
An example is continuous flexed positions of the trunk, common in certain jobs.
Good posture
- (standing tall, shoulders back, head up) can boost feelings of confidence and control.
- Studies show that people with upright posture tend to feel more self-assured and are perceived by others as more competent.
Slouched posture
can signal insecurity, fatigue, or low self-worth—even if that's not what you intend.
Mood and Emotions
For example, slumping may increase
feelings of sadness or low energy, while upright posture has been linked to more positive thoughts and better stress resilience.
First Impressions
Your posture contributes to nonverbal communication. People often judge traits like openness, assertiveness, or leadership potential based on posture—long before you speak.
Mind-Body Connection
Research in embodied cognition suggests that your physical stance can shape your thoughts and behaviors.
For example, "power posing"
(expansive postures) may help prepare you for leadership or challenging situations—even if only temporarily.
Long-Term Personality Effects
While posture itself doesn't change your core personality, habits shaped by posture over time (such as increased social engagement or decreased anxiety) can influence your traits and behavioral patterns.
from frontal view
if the spine is viewed from the front or the back biew it seems to be straight and symmetrical
From sagittal view
If the spine is viewed from the lateral side, four normal curves will appear
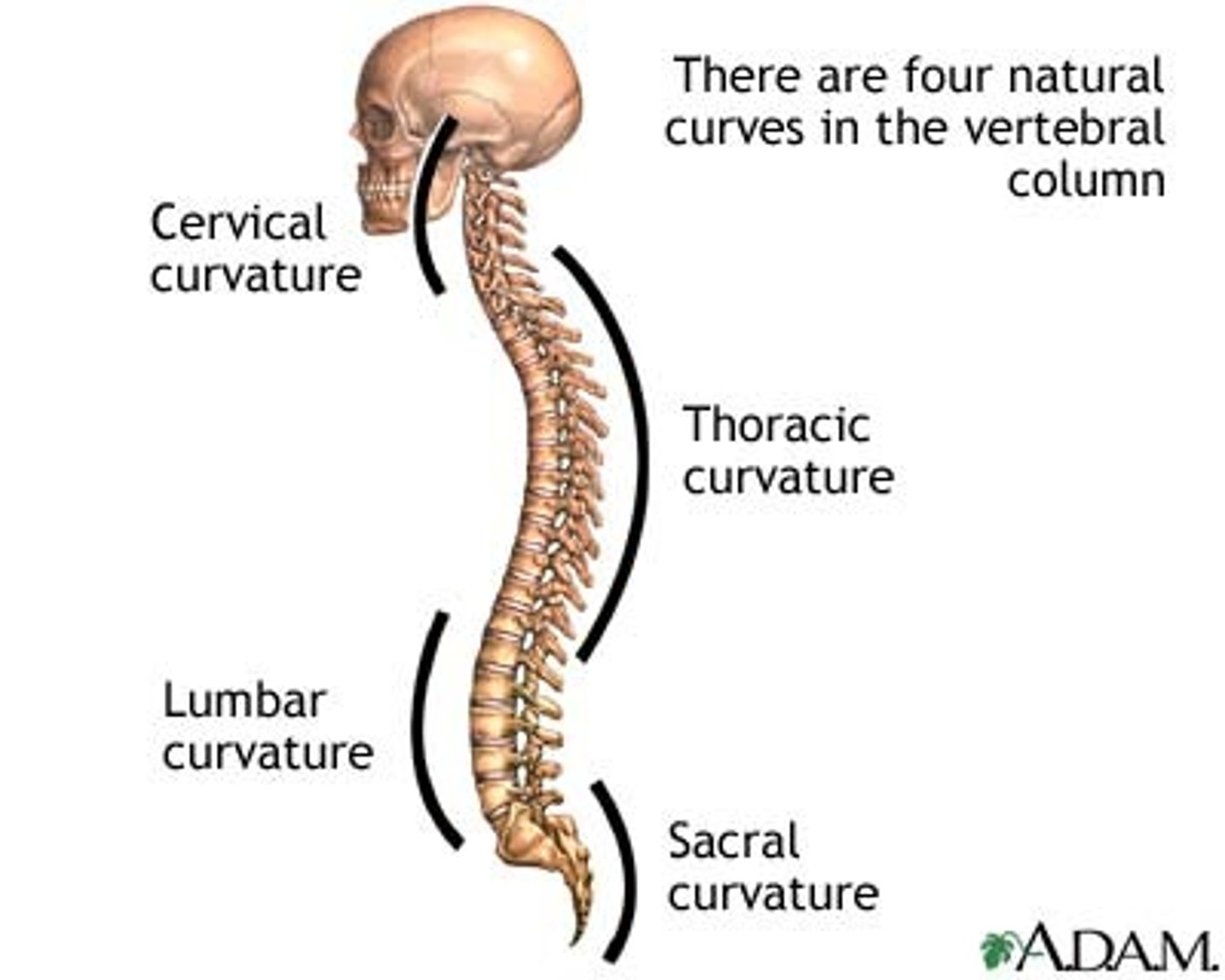
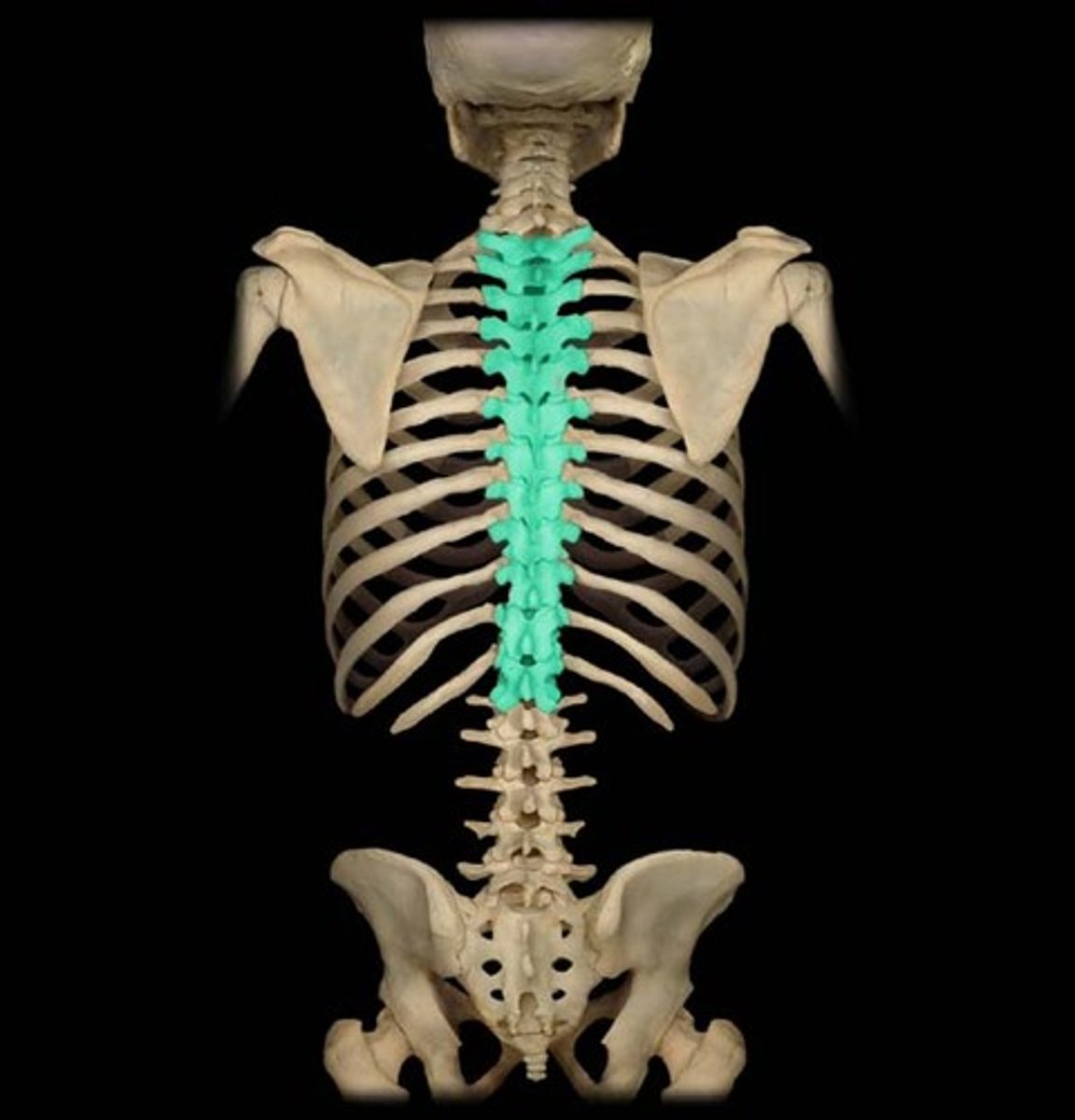
two Primary Curves
- These are the dorsal (thoracic) and sacral curves.
- They are characterized by being convex posteriorly (curving backward).
two secondary curves
These are the cervical and lumbar curves. They are convex anteriorly (curving forward).
neck of the human body
- is a bio-mechanical marvel.
- It possesses a wide range of mobility in nearly every direction.
- serves as a conduit for the major blood vessels to the brain and is the primary pathway of the central nervous system.
cervical (neck) region
is one of the most important areas of the body, and a growing body of research clearly shows that its structural integrity and function are absolutely critical to overall health and healing.
Central Nervous System
The brain and the spinal cord make up the _______________
spinal cord
- is often thought of as just a cable that transmits nerve messages, but it is actually a direct part of the brain.
- plays a crucial role in the health and homeostasis of the human body by sending and receiving billions of nerve messages every single second.
Cervical Lordosis
- It is a curvature of the cervical spine or the vertebrae in the neck region.
The lumbar curve
- is a uniquely human feature.
- If you think of dogs, cats, horses, or any four legged animal they don't have a curve.
- it’s bones are the largest in the spine because of their role in bearing weight. To facilitate this function there is very little twist available in the lower spine especially compared with its ability to flex and extend.
Kyphosis
- is an abnormally excessive convex curvature of the spine as it occurs in the thoracic and sacral regions.
lordosis
- Abnormal inward concave lordotic curving of the cervical and lumbar regions of the spine.
- It can result from degenerative disc disease; developmental abnormalities, most commonly Scheuermann's disease; osteoporosis with compression fractures of the vertebra; multiple myeloma; or trauma.
kyphosis or "hyperkyphosis"
When the "roundness" of the upper spine increases past 45°
Scheuermann's Kyphosis
is the most classic form of hyperkyphosis and is the result of wedged vertebrae that develop during adolescence. The cause is not currently known and the condition appears to be multifactorial and is seen more frequently in males than females.
kyphotic
lordotic posture
Abnormal posturing
- refers to rigid body movements and chronic abnormal positions of the body.
- This symptom is not the same as showing poor posture or slumping over. Rather, it's a tendency to hold a particular body position or to move one or more parts of the body in an abnormal way.
- When a muscle contracts, the muscles on the other side of the joint normally offer some resistance to the contraction. In abnormal posturing, however, the muscle groups fail to offer resistance when a muscle contracts. This results in atypical movement of the head or back, or stiff or arched feet
Opisthotonos
is a posture in which the neck is tilted back and the back is stiff and arched.
Decorticate posture
is characterized by a stiff body, straight legs, and clenched fists.
Decerebrate posture
is characterized by rigid limbs, pointed toes, and a backward tilt to the head and neck.
Visceroptosis
- is a prolapse or a sinking of the abdominal viscera (internal organs) below their natural position.
- is a condition in which the abdominal organs fall to a lower part of the abdomen.
Ptosis
- being the defining term, any or all of the organs may be displaced downward.
- When only the intestines are involved, the condition is known as enter____.
gastroptosis
When the stomach is found below its normal position.
Physical Fitness
- The ability to carry out daily task with vigor and alertness, without fatigue and with ample energy to enjoy leisure time pursuits and to meet unforeseen emergencies.
- The ability to last, to bear up, to withstand stress and to persevere under difficult circumstances where an unfit person would give up.
Cardiovascular Endurance
= the ability to continue or persist in strenuous tasks involving large muscle groups for extended period of time.
Muscular Endurance
= the ability of the muscle to apply a maximal force repeatedly or to sustain muscular contraction for a certain period of time.
Muscular Strength
= the maximal one-effort force that can be exerted against a resistance.
Speed
= the ability to perform a movement with a short period of time.
Power
= the rate at which one can perform work(strength over time)
Agility
= the ability to rapidly change the position of the entire body in space, with speed and accuracy.
Flexibility
= the ability to bend any part of the body without breaking.
Balance
= the ability to maintain equilibrium despite extraneous influences or force.
Coordination
= the ability to use the senses, such as sight and hearing together with the body parts in performing motor task, smoothly and accurately.
Reaction Time
= the time elapsed between stimulation and the beginning of the reaction to it.
Cardiovascular Disease
- refers to the disease of the heart and blood vessels.
Coronary Heart Disease ( CHD)
- is the result of a gradual buildup of cholesterol and other fatty substances in the inner of the walls of one or more of the coronary arteries of the heart.
- These fatty deposits is caused by thickening of the inner walls of the coronary arteries and narrowing of the vessels, resulting in a condition known as Atherosclerosis
ARTHEROSCLEROCIS
- hardening of your arteries from plaque building up gradually inside them. Plaque consists of fat, cholesterol and other substances.
- This plaque buildup limits blood flow
angina pectoris
- is a chest pain caused by a temporary lack of oxygen to the heart muscle. This condition usually occurs when one or more of the coronary arteries is partially closed.
- can also be caused by spasm of the heart blood vessel.
Myocardial Infarction
- results when an area of tissue in the heart dies because of prolonged of oxygen in the arteries due to an interrupted blood supply.
coronal
- Myocardial infarction is also known
Cardiovascular Respiratory
- decrease in oxygen consumption
- decrease in heart function
function:
- decrease in body water
- decrease in lung function
Blood
- decrease in blood cell mas
- decrease in clotting activity
- increase in total cholesterol
Metabolic Regulatory
- decrease in bowel functions
- decrease in immune system
Nervous System
- sleep pattern disorders function
- deterioration of sense organ function
- deterioration of intellectual capacity
Fat Cell Theory
= fat cell number can increase during early life because of nutritional and genetic influences.
= during adulthood, fat cell number increase when obesity is severe enough. These extra fat cells are near impossible to remove.
Set-Point Theory
= Body weight is powerfully regulated.
= When human are overfed or underfed, powerful adjustment in energy expenditure are made to defend body weight.
= This body weight " set point" can be raised through high fat diets and lowered through exercise.
Dietary Obesity
= When humans or animals are fed highly palatable diets ( fat, sugar) obesity is promoted.
= Low energy diets ( fruits, vegetable, whole grains, with low levels of visible fats, sugar and high-fat animal product) helps humans to eat less calories.
Physical Education
- is the instruction of physical exercise and games, especially in schools, designed to improve physical fitness, develop motor skills, and promote health and wellness.
- It is a process of teaching motor skills, knowledge and attitudes to enable individuals to participate pleasurable at the very least in exercise, games, dance, sports, and recreational activities.
Body
- functions optimally with regular and proper use and deteriorate with misuse and disuse.
Article XIV, Section 19, 1987 Constitution of the Republic of the Philippines
" The State shall promote Physical Education and encourage sports program, league competition, and amateur sports including training for international competition to foster self-discipline, teamwork, and excellence for the development of a healthy and alert citizenry."
head
forward
Cervical Spine
- Hyper-lordosis (hyper-extended)
Thoracic Vertebrate
increased flexion
Lumbar Vertebrate
Hyper-lordosis;(hyperextended).
Pelvis
- Anterior tilt (forward and down)
Knees
- hyperextended
Ankle joints
- plantar flexed, legs are behind midline.