Week 4 Corynebacterium, Listeria, Rhodococcus
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Small, short, pleomorphic Gram-positive rods
“Chinese letter patterns
Cell wall contains meso-diamino-pimelic acid (DAP) arabinogalactan, mycolic acid (also for myobacteria and nocardia)
Non-sporulating
Non-motile
Aerobic or facultatively anaerobic
Aerobic or facultatively anaerobic o Fermentative metabolism under certain conditions
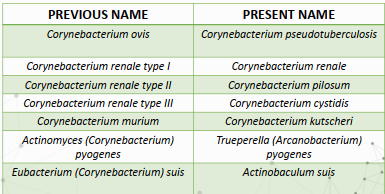
changes in nomenclature

Previously classified as Corynebacterium

Corynebacterium species
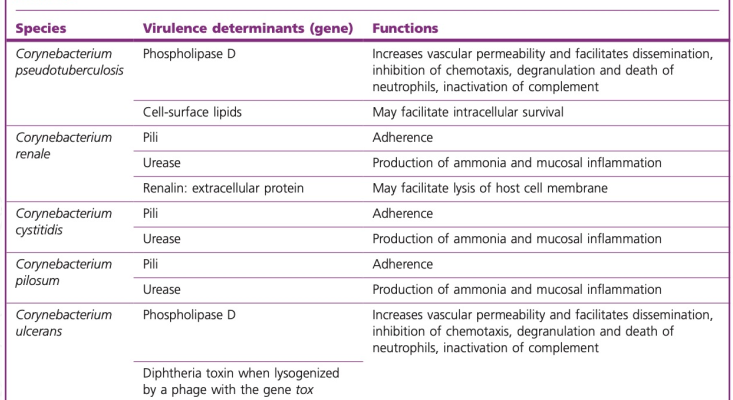
main virulence factors of pathogenic Corynebacterium spp and rhodococcus equi in vet med
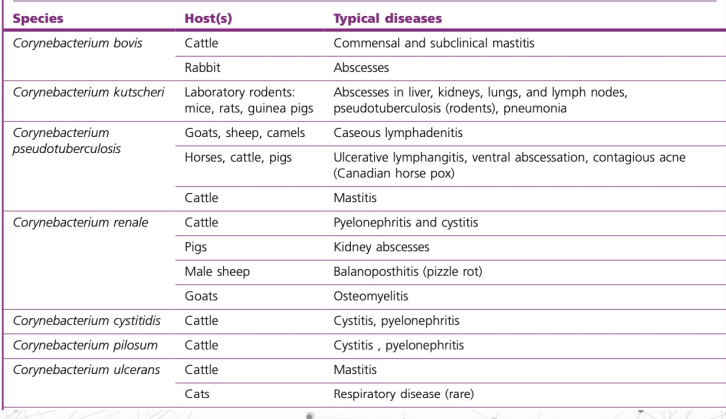
Main dx caused by major pathogenic Corynebacterium spp and rhodococcus equi to vet med
C. pseudotuberculosis
caseous lymphadenitis
ulcerative lymphadenitis
mastitis
C. Bovis
pyelonephritis
mastitis
C. Diptheria
respiratory diptheria & cutaneous diptheria
Prototype A-B toxin
Diptheria toxin
selective media
C. jeikeium
opportunistic infection to immunocompromised
multiple ATB resistance
Carriage on skin
C. urealyticum
UTI
urease hydrolyze urea
mitis- black with gray periphery
gravis- large gray
intermedius- small dull gray to black
3 morphologic type of diptheriae on tellurite containing media
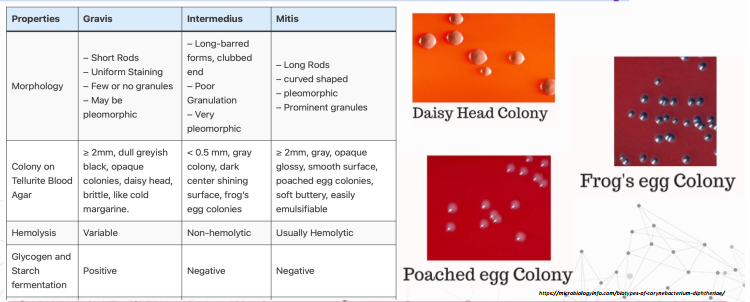
properties of the morphology
cystinase
Produce ____ on tinsdale medium
C renale
shows casein digestion on milk agar
R. equi, C. renale
Cell wall containstwo bacteria give an enhancement of the effect of the staphylococcal beta-hemolysin.
C. pseudotuberculosis
inhibition of the effect of the staphylococcal hemolysins
subcutaneous test
intracutaneous test
In vivo test
elek’s gel precipitation test
tissue culture test
in vitro test
remain viable for 2-3 weeks at 25-30
destroyed by heat
resistant to light, desiccation/freezing
easily destroyed by antiseptics
Corynebacterium prevention and control
penicillin, erythromycin
supportive therapy
antitoxin
corynebacterium treatment and immunization
Listeria
medium, non branching, short gram positive rods, non spore forming and non acid fast
singly in a short chain, no capsule
catalase +
oxidase -
motile
L monocytogenes
L. ivanovii
L innocua
3 pathogenic species
L. monocytogenes
most important pathogenic
soil, silage, sewage effluent and stream water
asymptomatic fecal carriers
habitat of listeria
soil contamination and ingestion of contaminated feed
silage dx = listeriosis
listeria transmission
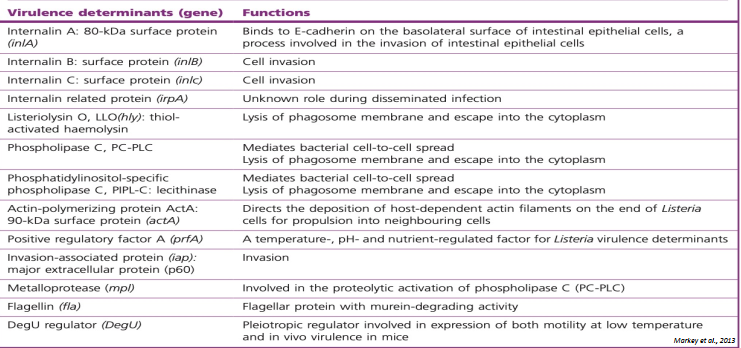
virulence factor of listeria
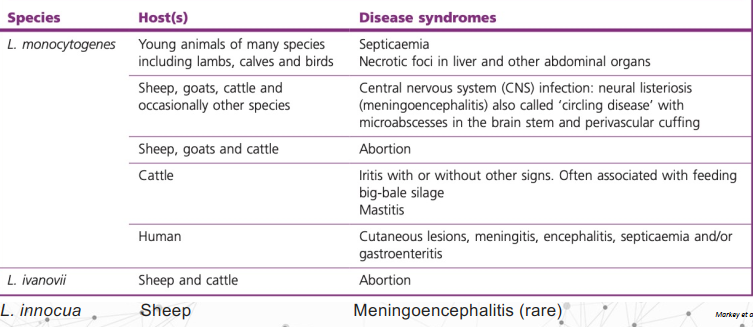
main host and dx syndromes of pathogenic listeria species
Septicemic form
Listeria dx that attacks monogastrics and neonates
listerial septicemia
Listeria dx that attacks chinchillas
septicemia in neonates
Listeria dx that attacks horses
encephalitis form- circling disease, most common form in cattle (subacute to chronic)
abortion- 7months cattle 12 weeks in sheep
conjunctivitis- contaminated silage
Listeria dx that attacks Ruminants
L. monocytogenes
CAMP test with S. aureus enhancement of the effect of the staphylococcal beta-haemolysin by ____ but not by L. Ivanovii
L. ivanovii
Cam test with R. equi no rxn with L monocytogenes and enhancement of haemolysis by
poor quality silage should not be fed to pregnant woman
silage feeding should be discontinued if outbreak of listeriosis is confirmed
feeding method with min direct ocular contact
at pasture, reduced the risk by feeding through than the frround
vaccination
prevention and control of listeria
ATB oxytetracycline/penicillin
b lactams, macrolides, tetracyclines, sulfonamides, chloramphenicol
submission for culture and ATB sensitivity testing
NSAID
cephalosporins and fluroquinolones are not active
Tx of listeria
Rhodococcus
gram +, aerobic, coccus/rods
capsulated
soil —> contaminated with horse and farm animal
Rhodococcus equi
Previous name: Corynebacterium equi
human opportunistic pathogen in immunocompromised humans.
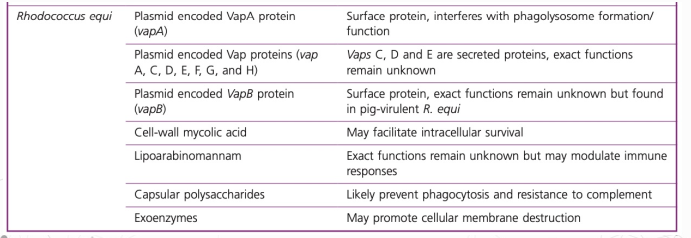
R. equi virulence determinants

R.. equi dx
susceptible to erythromycin and extended spectrum macrolides, rifampin, fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides, glycopeptides, amp-sulbatumol and imipenem
•2/3rd are susceptible to clindamycin, chloramphenicol, tetracyclines, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
resistant in vitro penicillin and cephalosporins
avoid B-lactam
R. equi treatment