Exam Preparation and Cold War Overview
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Cold War
A period of geopolitical tension between the Soviet Union and the United States, characterized by political, military, and ideological rivalry from the end of World War II until the early 1990s.
George Kennan
An American diplomat and historian who is best known for his role in formulating the U.S. policy of containment towards the Soviet Union.
Containment
A foreign policy strategy aimed at preventing the expansion of an adversary's influence, particularly used by the U.S. during the Cold War to stop the spread of communism.

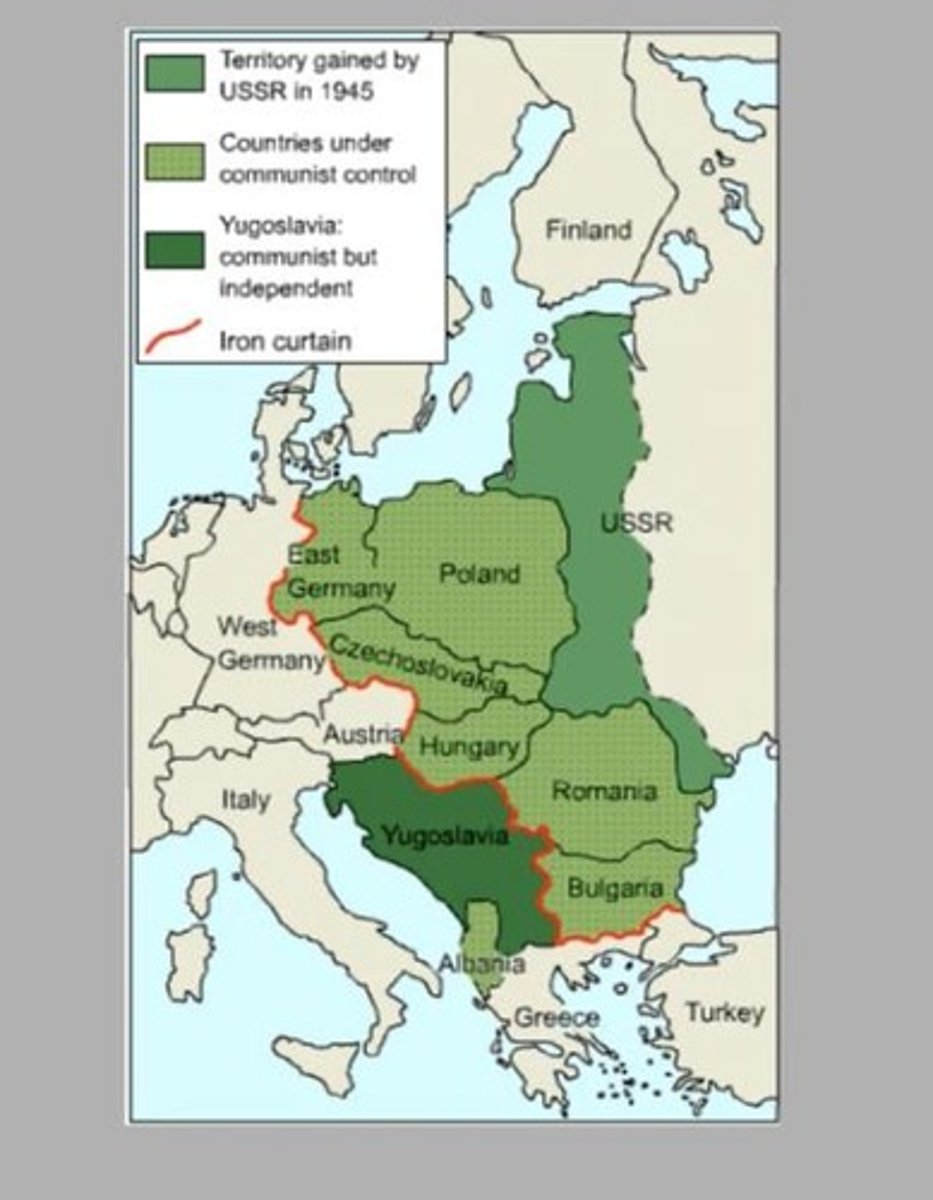
Iron Curtain
A term used to describe the division between the Soviet-controlled Eastern Europe and the Western democracies during the Cold War.
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, a military alliance formed in 1949 among Western nations to provide collective security against the Soviet Union.
Warsaw Pact
A military alliance of communist nations in Eastern Europe, established in 1955 in response to NATO.
McCarthyism
A campaign against alleged communists in the U.S. government and other institutions, characterized by heightened fears of communist influence in the 1950s.
Truman Doctrine
A U.S. policy established in 1947 to provide political, military, and economic assistance to countries threatened by communism.

Marshall Plan
An American initiative launched in 1948 to aid Western Europe's economic recovery after World War II, aimed at preventing the spread of communism.
Cuban Missile Crisis
A 13-day confrontation in 1962 between the United States and the Soviet Union over the presence of missile sites in Cuba, considered the closest the Cold War came to escalating into a nuclear conflict.
Detente
A period of relaxed tensions and improved relations between the U.S. and the Soviet Union during the 1970s, marked by arms control agreements.
Proxy War
A conflict where two opposing countries or parties support combatants that serve their interests instead of waging war directly, common during the Cold War.
Berlin Wall
A barrier that divided East and West Berlin from 1961 to 1989, symbolizing the ideological divide between communism and democracy.
Space Race
A competition between the United States and the Soviet Union for supremacy in space exploration, which became a significant aspect of the Cold War.
Fall of the Berlin Wall
The event in 1989 that marked the end of the Cold War, symbolizing the collapse of communist control in Eastern Europe.
Communism
A political and economic ideology advocating for a classless system in which the means of production are owned communally.
Stalinism
A political system characterized by totalitarianism, state control of the economy, and the suppression of dissent, associated with Joseph Stalin.
Self-determination
The principle that nations have the right to determine their own political status and pursue their own economic, social, and cultural development.
Eastern Bloc
The group of socialist states in Central and Eastern Europe under the influence of the Soviet Union during the Cold War.
Western Allies
The countries that opposed the Axis powers during World War II, primarily the United States, the United Kingdom, and France.
Post-war order
The political and economic arrangements established after World War II to promote stability and prevent future conflicts.
Free elections
Elections that are conducted fairly and openly, allowing citizens to choose their representatives without coercion.
Ideological conflict
A struggle between different belief systems, particularly between capitalism and communism during the Cold War.
Capitalism
An economic system characterized by private ownership of the means of production and the operation of the economy for profit.
Détente
A period of relaxed tensions and improved relations between the United States and the Soviet Union during the Cold War, particularly in the 1970s.
Domino Theory
The belief that the spread of communism in one country could lead to a chain reaction of similar events in neighboring countries.
Nuclear Arms Race
The competition between the United States and the Soviet Union to develop and accumulate more nuclear weapons during the Cold War.
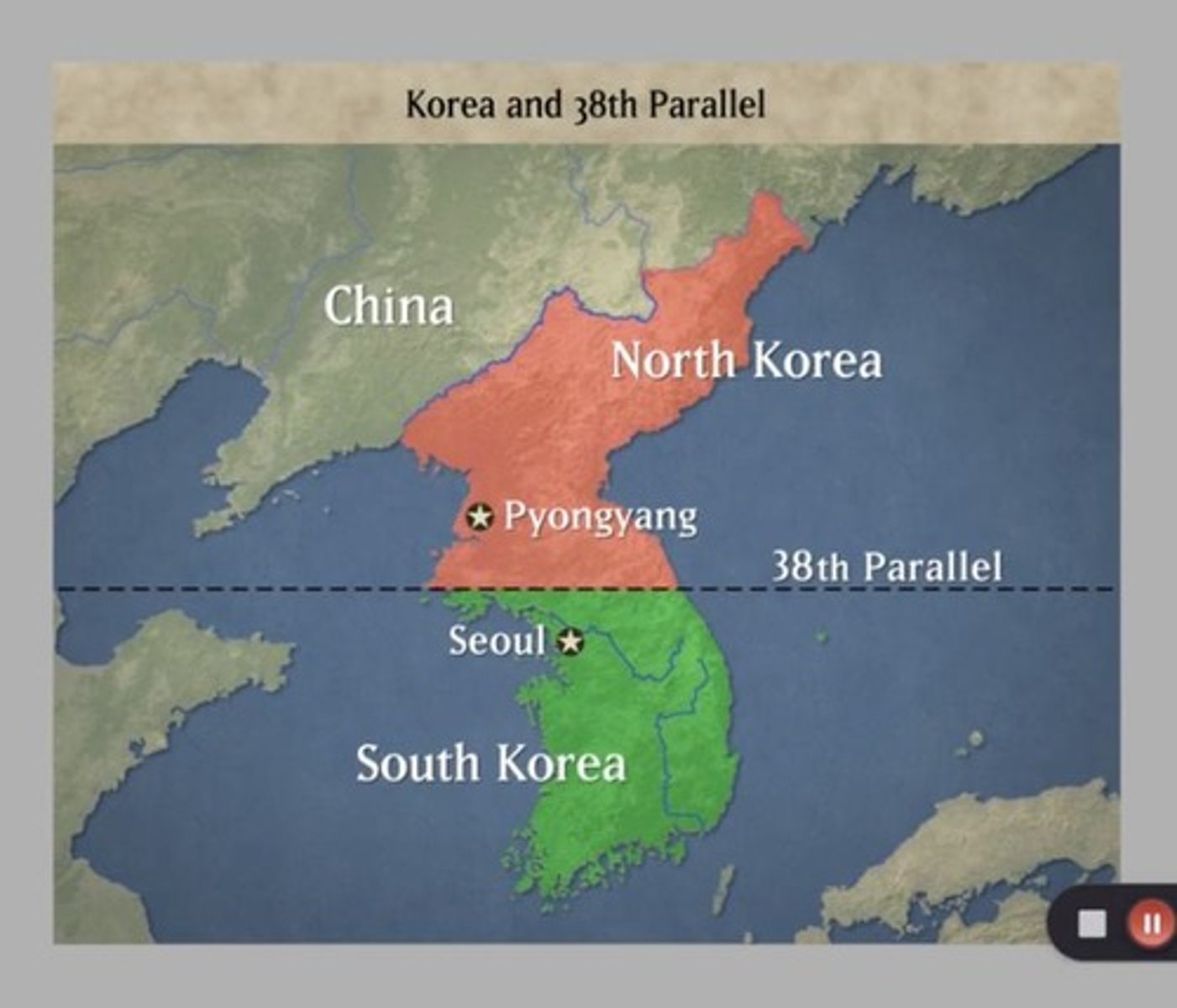
Korean War
A conflict from 1950 to 1953 between North Korea, supported by China and the Soviet Union, and South Korea, supported by the United States and other Western nations.
Soviet Expansionism
The policy of the Soviet Union to expand its influence and control over other nations, particularly in Eastern Europe and Asia, during the Cold War.
U.S. Information Agency (USIA)
A U.S. government agency created to disseminate information and counteract communist propaganda during the Cold War.
Mao Zedong
The leader of the Communist Party of China who established the People's Republic of China in 1949 after winning the Chinese Civil War.
38th Parallel
The latitude line that served as the pre-war boundary between North and South Korea, which became the dividing line after the Korean War.
Ideological Debate
A discussion or argument that focuses on differing beliefs and values, particularly regarding governance and economic systems.
Kitchen Debates
A series of informal discussions in 1959 between U.S. Vice President Richard Nixon and Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev, highlighting the differences between American consumerism and Soviet ideology.
Consumer Demand
The desire of consumers to purchase goods and services, which drives the production and supply in a capitalist economy.
Military-Industrial Complex
The relationship between a country's military and the defense industry that supplies it, often influencing public policy and economic decisions.
Duck and Cover
A civil defense strategy used during the Cold War, teaching children how to protect themselves in the event of a nuclear attack.
Federal Investment
Government spending aimed at stimulating economic growth, often directed towards specific sectors such as defense or infrastructure.
Nuclear Family
A family unit consisting of two parents and their children, often idealized in 1950s American culture as a symbol of stability and safety.
American Dream
The national ethos of the United States, suggesting that prosperity and success are achievable through hard work and determination, often represented by home ownership and family life.
Consumer Culture
A social and economic order that encourages the acquisition of goods and services in ever-increasing amounts, often linked to identity and lifestyle.
Propaganda
Information, especially biased or misleading, used to promote a political cause or point of view, often seen in advertising during the Cold War.
Espionage
The practice of spying or using spies to obtain political or military information, particularly relevant in the context of the Cold War.
Baby Boomers
The generation born during the post-World War II baby boom, characterized by a significant increase in birth rates.
Advertising
The activity of producing advertisements to promote products or services, which played a significant role in shaping societal norms during the Cold War.
Julius Rosenberg
An American engineer who, along with his wife, was convicted of espionage for allegedly passing atomic secrets to the Soviet Union.
Soviet Union
A socialist state that existed from 1922 to 1991, known for its opposition to the United States during the Cold War and its promotion of communism.
Ethel Rosenberg
The wife of Julius Rosenberg, accused of assisting in her husband's espionage activities and convicted alongside him.
Atomic weapon
A bomb that derives its destructive power from nuclear reactions, specifically fission or fusion.
Perjury
The act of lying or making false statements under oath, often in a court of law.
Lavender Scare
A term used to describe the persecution of gay men and women in the U.S. government during the Cold War, based on fears of their potential disloyalty.
Alger Hiss
A former U.S. State Department official accused of being a Soviet spy, later convicted of perjury.
Sing Sing Prison
A maximum-security prison located in New York, where the Rosenbergs were executed.
Nuclear annihilation
The complete destruction of human life and civilization due to nuclear warfare.
Espionage Act of 1917
A U.S. law that made it a crime to interfere with military operations or support U.S. enemies during wartime.
Red Scare
A period of intense fear of communism and its potential influence on American society, particularly during the early and late 20th century.
Nuclear proliferation
The spread of nuclear weapons and technology to nations not recognized as Nuclear Weapon States.
Joseph McCarthy
A U.S. Senator from Wisconsin known for his role in the anti-communist movement, particularly for making unsubstantiated claims about communist infiltration in the federal government.
Censure
An official reprimand or condemnation of a member of Congress for inappropriate behavior or misconduct.
Rosenberg Case
The trial and execution of Julius and Ethel Rosenberg, who were accused of espionage for allegedly passing atomic secrets to the Soviet Union, which heightened fears of communist infiltration.
Loyalty Oaths
Declarations required from government employees affirming their allegiance to the United States, often used during the McCarthy era to screen for potential communist sympathizers.
Blacklisting
The practice of denying employment to individuals based on their suspected political beliefs or affiliations, particularly during the McCarthy era.
Nuclear War
A potential conflict in which nuclear weapons are used, which was a significant concern during the Cold War era.