Pathophysiology Pulmonary Infections
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Upper respiratory tract infection
• Viral- Rhinovirus; adenovirus; coronaviruses; parainfluenza; respiratory syncytial virus; typically symptomatic
Upper respiratory tract infection S/S
nasal drainage, stuffiness, sore throat, PND, headache, malaise
Upper respiratory tract infection transmission
Contaminated surface, hand to mouth/eyes/nose
Rhinitis
inflammation of nasal passages
Sinusitis
inflammation of the sinuses
Rhinosinusitis
inflammation of the nasal and paranasal sinus mucosa; Pathogen: H. influenza, S. pneumoniae, rhinovirus
Rhinosinusitis S/S
face pain, purulent drainage, fever, HA
Rx: antibiotics, decongestants
Rhinosinusitis Bacterial
duration about 4 weeks; severe onset (fever, purulent drainage), worsening symptoms, or >10 days with symptoms
Rhinosinusitis Viral
duration is 5-7 days
allergic rhinitis
Type I hypersensitivity, an allergic reaction to airborne allergens that causes an increased flow of mucus
Allergic Rhinitis S/S
Nasal drainage (clear, watery), itching/burning eyes, nose, throat, nasal congestion
Rx: antihistamines, decongestants, nasalcorticosteroids, desensitization(immunotherapy)Allergic Rhinitis
Influenza
Viral infection of upper/lower respiratory tract- Often epidemic, can cause death- Children: highest rate of infection- Elderly/immunocompromised: higher severity•
Influenza
• Transmission: droplet infection• Incubation: 1-4 days• Contagious: 1 day before sx. to5 days after illness, longer for children, immunosuppressed
Influenza A
most common- highly contagious-- also affects birds, pigs, horses
Subtypes of Influenza A
Based on surface glycoproteins- Change antigens on cell membranes → newsubtypes
Hemaglutinin (HA)
part of the influenza A virus that allows for attachment to the cell and subsequent endocytosis; attachment proteins
Neuroaminidase (NA)
aids viral replication and release from host cell
Drift
minimal/small changes antigens
Shift
Both H and N antigens change
URI, viral pneumonia, complicating bacterial infection
3 syndromes of seasonal influenza
Influenza Pathophysiology
Upper airway infection- Damage ciliated/epithelial cells• Lower respiratory tract- Shedding, bronchial/alveolar cells• Secondary bacterial infection- ↓ natural defenses- ↑ bacterial adhesion
Influenza symptoms
Abrupt onset• Fever, malaise, chills, muscle aches, HA, watery nasal discharge, sore throat, dry cough• Peak: 3-5 days
viral pneumonia symptoms
Fever, tachypnea, cyanosis, tachycardia- Rapid progression of symptoms (within 1 day of influenza onset)- Survivors often develop acute pulmonary fibrosis
H1N1 S/S
similar to seasonal flu, some diarrhea/vomiting, extremely high fevers
Differences- Timing- Population more serious in adults < 25years old
Influenza prevention
Vaccine: everyone aged 6 months and older;
Especially high risk:- 6-59 months old; 50 years and older- Asthma, diabetes, chronic lung disease, HF, Pregnant women, Immunocompromised- Nursing facility & long-term care residents
Pneumonia
inflammation and infection of bronchioles and alveoli in lung parenchyma
Risk factors:
immunocompromised, elderly, lung disease
Pneumonia defense mechanisms
- Nasopharyngeal IgA- Cough reflex- Mucocilliary system- Alveolar macrophagesPneumonia
community acquired pneumonia
a type of pneumonia that results from contagious infection outside of a hospital or clinic; streptococcus pneumoniae most common
Hospital acquired pneumonia
pneumonia occurring 48 hours or longer after hospital admission and not incubating at the time of hospitalization. Not present on admission, nosocomial, usually bacterial, associated with antibiotic resistance, ventilator associated pneumonia
Typical pneumonia
Inhalation or aspiration of virulent organism• Inflammatory/immune response- Complement activation, antibody production- Opsonization of bacteria- Release inflammatory mediators andtoxins from organism → capillarypermeability & edema- Damage to bronchial/alveoli mucous membranes- Bronchioles/alveoli fill with fluid/debris (exudate)• Consolidation of lung tissue- Problems with ventilation and oxygenation- Recovery: macrophages digest fibrin & bacteria
Pneumonia S/S
Fever, chills, ↑RR- Cough, purulent sputum- Can progress to bacteremia and sepsis
Dx: CXR
Prevention - pneumococcal vaccines
Legionella pneumophilia
From water: Aerosolized water• Pneumonia with diarrhea, confusion, hyponatremia
Atypical pneumonias
Damage epithelium; invade alveolar septum/wall and interstitial lung tissue
Viral pneumonias
Frequently "interstitial", NOT alveolar; respiratory syncytial, influenza; atypical
Fungal Pulmonary Infections
Rare and self limiting in healthy individuals• Opportunistic infection• Pneumocystis Jiroveci (PJP)• Histoplasmosis, blastomycosis, coccidiomycosis- Found in soil, rotting wood/vegetation, river valleys- Regional distribution- Granuloma formation
Fungal pulmonary infections S/S
mild, flulike sx, productive cough, fever, night sweats, weight loss
Tuberculosis
• Risk factors: foreign born, HIV positive, congregatesettings (prisons, shelters)• Organism mycobacterium tuberculosis- Rod shaped, acid-fast, waxy capsule- Spread by droplet nuclei- Atypical infections• m. avium intracellulare, m. avium complex
Primary Tuberculosis
• Inhaled droplets activate inflammatory/ immune system• Macrophages and T lymphocytes seal off colony → Gohn Focus(aka: granuloma or tubercule)• Caseous necrosis: center ofgranuloma• Enter lymph → granuloma formation in lymph nodes• Gohn Complex = lung lesion and lymph node granuloma
Latent TB
one of two things that happens after a TB infection; organism contained, no active disease, lesions calcify
Primary progressive TB
(5%) one of two things that happens after a TB infection; organism continues to spread in lungs
Secondary TB
Reactivation of primary lesion or reinfection• More likely if chronic disease or immunocompromised: HIV, DM, malnutrition, elderly• Reactivation: necrotic tissue liquefies and drains into bronchus secondary activeTB
Latent TB
No symptoms of TB disease.• TB screen positive• CXR normal• Respiratory specimens are smear and culture negative.• Cannot spread TB bacteria to others.• Should consider treatment to prevent active TB disease
Active TB
Symptomatic• TB screen positive• CXR abnormal (usually)• Respiratory specimens are usually smear or culture positive• May spread TB bacteria to others• Needs treatment for TB disease
Tuberculosis S/S
Primary infection maybe asymptomatic• Low grade fever, sweats• Anorexia, weight loss• Cough - purulent, hemoptysis• Dyspnea• Other organ involvement- Death in 5 years if untreated
TB difficult to treat
- Due to resistance- Waxy capsule- Bacteria can live/divide within old lesionsTB - cont.
acute respiratory disease
-most common in infants/children
-small diameter airways
-lung maturity
infant respiratory distress syndrome
caused by immature lungs --> too little surfactant in the alveoli; lungs collapse with each breath (atelectasis), increased work of breathing and hypoxia, hyaline membrane forms
infant respiratory distress syndrome S/S
cyanosis, retractions, ↑ RR
Tx: O2, CPAP, surfactant,mechanical ventilation,steroids to motherduring preterm labor
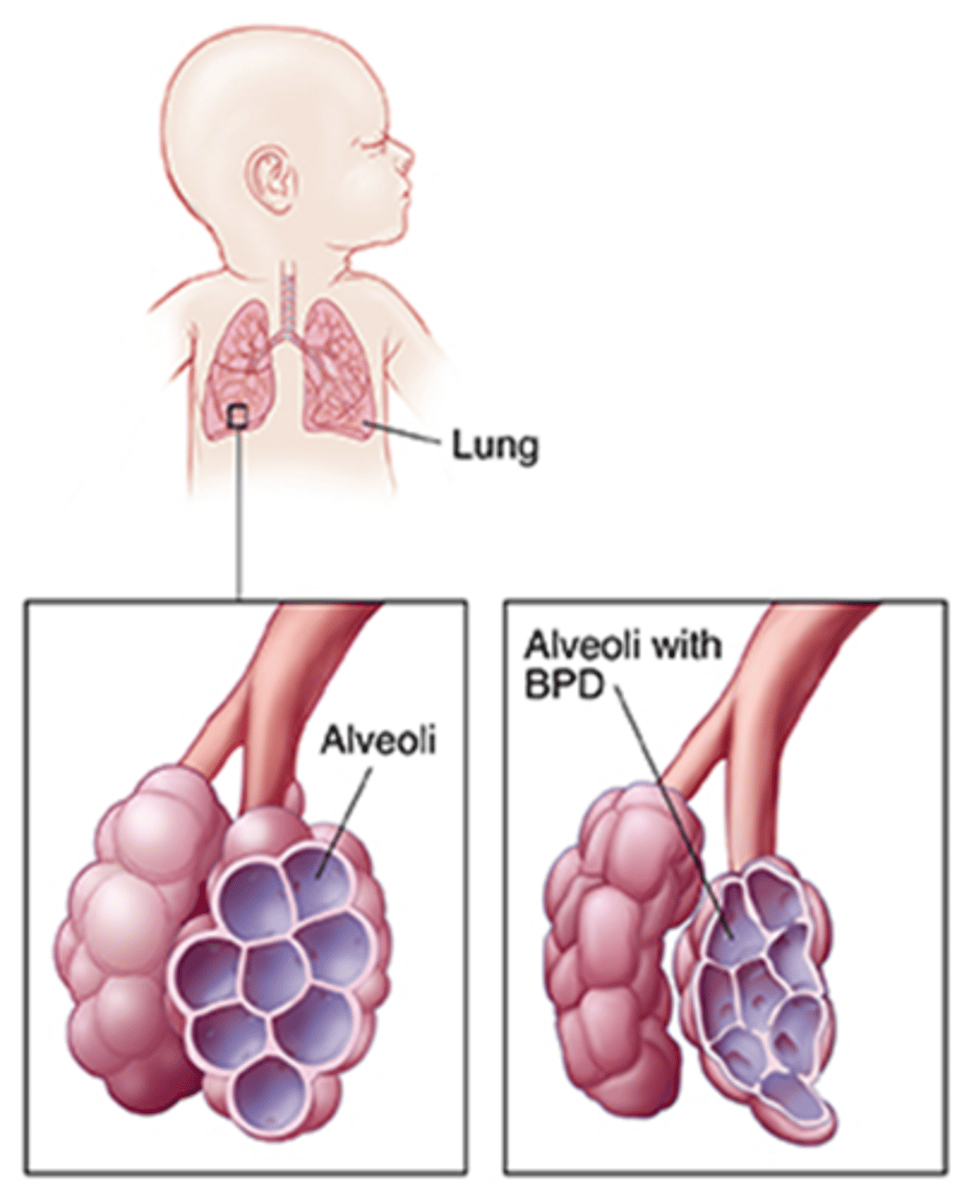
bronchopulmonary dysplasia
chronic lung disease in infants due to mechanical ventilation or prolonged O2; alveolar hypoplasia, alveolar fibrosis
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia S/S
Persisten hypoxia, chronic respiratory distress, retractions, tachycardia, rapid RR;
Tx: mechanical ventilation
Viral Croup
viral infection, acute laryngotracheobronchitis, obstructive subglottic region (below vocal cords)
Viral croup S/S
barking cough, hoarseness, inspiratory stridor
May subside with humidity, cold air
Worsen at night
Croup cough sound, can progress to airway obstruction
Tx: epinephrine, humidified O2,trach or endotracheal tube (if severe)
Epiglottitis
Inflammation/edema epiglottis/pharynx• Common causes: H.Influenza, strep, staph• Acute onset• Edema epiglottis can cause airway obstruction
Epiglottitis S/S
Sore throat, stridor, fever, mouth open/chin thrust forward, drooling
Tx: Abx, maintain airway withendotrachealtube or tracheostomy