Information processing
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is information processing?
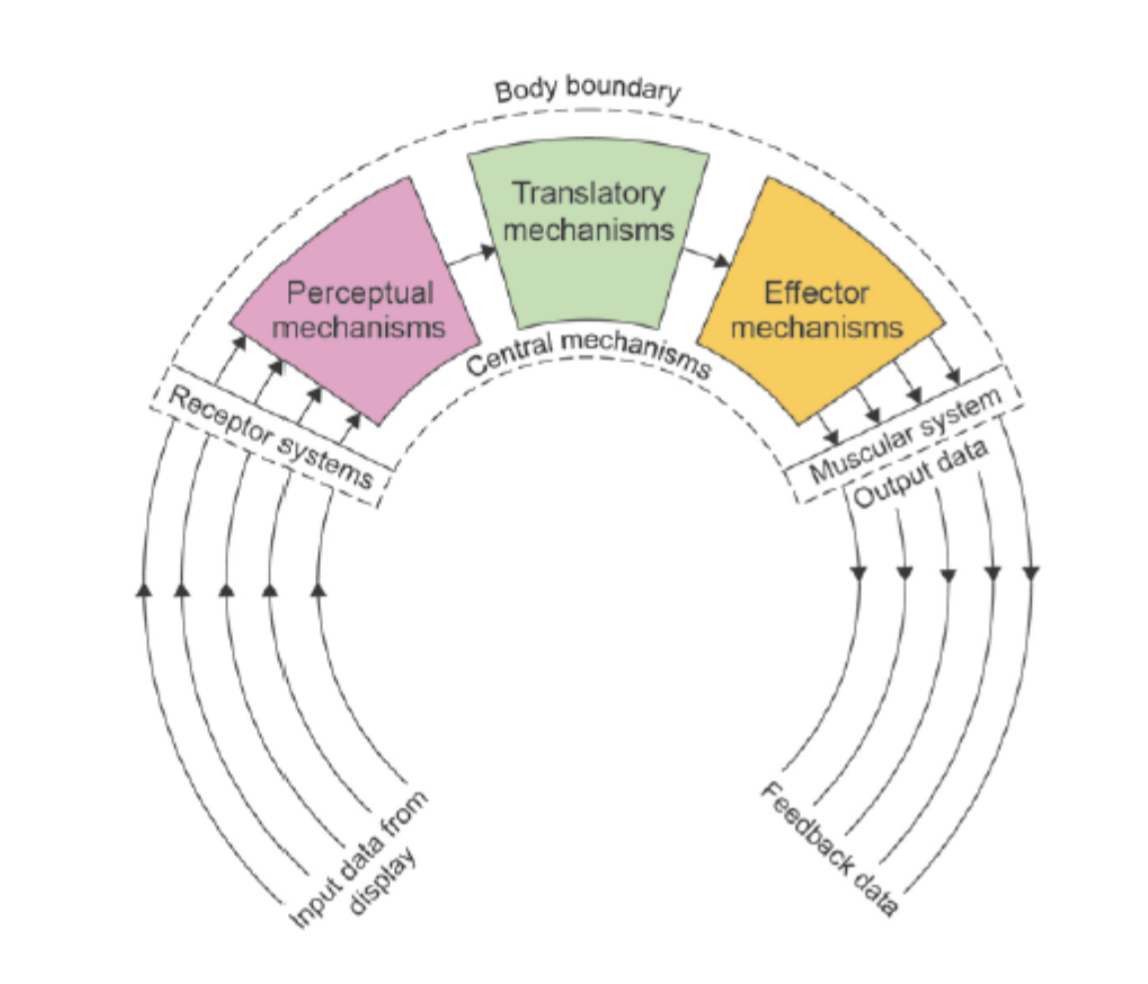
Methods by which data from the sporting environment is collected and utilised
What is the input stage of information processing?
The first stage of information processing. During this stage the performer uses the senses to pick up information from the display
What is the display?
Display - everything in the sporting environment
What are receptor systems and what are the different type of receptor system?
Receptor systems - the senses that pick up information from the display
External senses - information collected from the environment
sight & auditory
Internal senses (proprioceptors) - provide internal information from within the body
touch, balance & kinesthesis
kinesthsis - the inner sense that gives information about the body position and muscular tension)
What is the decision making stage?
The second stage of information processing. The performer must make a decision based on all the information collected by the senses, in order to make these decisions selective attention and the use of the memory system is important.
What is selective attention?
The performer can receive a host of information from the five senses and yet needs to make a decision based on only the important aspects of that information. Selective attentions is the process of filtering out the relevant information from irrelevant information.
How can a coach develop selective attention?
improved motivation - coach can enhance this by giving positive feedback and rewards, once the motivation is increased the performer may become more alert to important information
practice with distractions - in order to learn to ignore the irrelevant stimuli
mental practice - can help process of selective attention when the performer runs through the upcoming task in the mind before the movement starts, saving time and energy on the actual move
increase the intensity of the stimuli - stimuli is made more bright, intense or loud. It helps the performer to develop concentration
What are the benefits of selective attention?
improve reaction time significantly
improves the chances of the correct decision being made
helps speed up the decision making process as less information to focus on
What is perception?
The process of coding and interpreting sensory information
What are 3 elements of perception?
DCR process - detection, comparison, recognition
detection - the performer has picked up the relevant information using the senses and identified it as important, via the process of selective attention. Detection belongs in the input stage
comparison - match information identified as important to any information already stored in the long term memory
recognition - the performer has used information from the memory to identify an appropriate response. This response can then be put into action
What is the translator mechanism?
Adapting and comparing coded information to memory so that decisions can be made
What is the process of the translator mechanism?
helps to convert information so that decisions can be made. Once information has been filtered it is then adapted into an image that can be sent to the memory for comparison, similar actions that have been stored in the memory can be matched to information in the coded image an appropriate motor programme can be selected and used.
What is the output stage?
This stage involves the execution of a physical response or movement and is based on the decision made during the processing stage
What is the effector mechanism?
The network of nerves that is responsible for delivering decisions made during the perceptual process to the muscles so that those muscles can contract and perform the action
What is the feedback stage?
Is information used during or after the response to aid movement correction
Whiting’s information processing model