Prenatal development
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
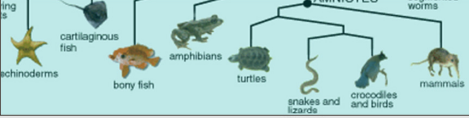
what is the shared feature of chordates?
all have spinal cords
when was the microscope invented?
1950s
what does scala naturae mean?
great chain of being (species are fixed and arranged hierarchally)
what did Nicolaas Hartsoeker do?
used a microscope to see a embryo/foetus and came up with preformation theory
what development occurred in the 19th century?
improvements in optics demonstrated that embryonic development did not involve simple processes of growth but also substantial differentiation
what is a teleological view?
what is recapitulation theory?
embryos took the form of a less evolved version of the species/the development of an animal from an embryo to an adult mirrors the evolution of that animal
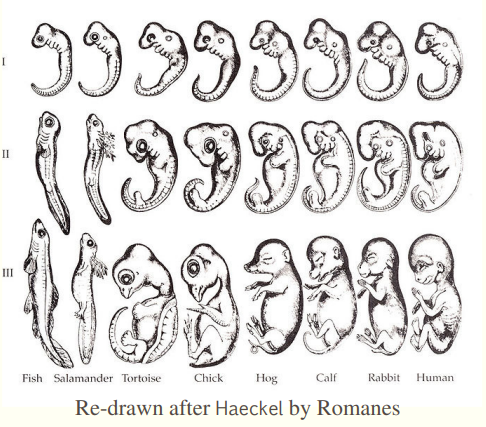
how did photographs change the previous understanding of prenatal development?
showed that early embryos are much more differentiated across species (disproves recapitulation theory)
what are the stages of prenatal (antenatal) development?
the germinal period (conception to implantation)
the embryonic period (implantation to approx. 2 months)
the foetal period (2 months to birth)
what is a morula (germinal period)?
the collection of cells formed in the first few days after conception
what is a blastocyst (germinal period)?
the mass of cells 5 days after conception
what occurs after the first two weeks of prenatal development?
cell differentiation
what are the layers of the nervous system?
ectoderm
mesoderm
endoderm
what is the ectoderm for?
nervous system
cornea and lens of eye
epidermis of skin
epithelial lining of mouth and rectum
what is the mesoderm for?
skeletal system
circulatory system
lymphatic system
muscular system
excretory system
reproductive system
dermis of skin
lining of body cavity
what is the endoderm for?
epithelial lining of the digestive tract, respiratory tract, reproductive tract and urinary tract
liver
pancreas
thyroid
parathyroids
thymus
what occurs at the third week of prenatal development?
eye is apparent
brain is beginning to bulge
heart and liver are forming
scaffolds for individual vertebrae
there is a rudimentary tail
‘buds’ where arms and legs will be
what occurs at 7 weeks of prental development?
individual fingers and toes are apparent
gut is developing
what occurs at 2 months of prenatal development?
limbs are well-formed
the brain has expanded substantially
what occurs at 4 months of prenatal development?
ears are taking their final form
eyelids are well-developed
foetus is capable of movement
can react to touch and sound (250-500 Hz)
what occurs at 8 months of prenatal development?
genitalia are nearly fully formed and apparent
what is aneuploidy?
the condition of having fewer or more than the usual number of chromosomes
what is trisomy 21?
extra 21st chromosome that causes Down’s syndrome
what is trisomy 18?
an extra 18th chromosome that causes Edwards syndrome
what is trisomy 13?
an extra 13th chromosome that causes Patau syndrome
what are teratogens?
any agent or substance which can cause malformation of an embryo/birth defects (includes drugs, alcohol, tobacco, and other environmental agents)
what was the thalidomide tragedy?
a drug developed to treat headaches, insomnia and morning sickness that caused babies to be born with severely misshapen limbs
what problems can be caused by foetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)?
microcephaly (the baby’s head is much smaller than expected)
vision and hearing problems
learning difficulties
describe the results of study by DeCasper and Spence
babies were able to differentiate between a story their mothers read during late pregnancy and a new stories (babies showed preference for familiar over new stories)