UNIT 18: APPLICATION OF MOTORS
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:32 PM on 1/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
On any given motor, there will be the manufacturer and the model number. The manufacturer sticker will give most of the power supply information, including:
1. Voltage
2. Current capacity in amperes
3. Frequency in hertz/cycles per second
1. Phase
2
New cards
Every motor operates around +/- ____ % of its rated voltage
10%. Ie a 208 v motor can operate 228.8 to 187.2
3
New cards
Explain why a motor that is receiving too low of voltage would overheat
If the voltage is lower than expected, the motor’s current draw will go up, because its trying to do its job but lacks the power to do so. As the motor draws this high current it will eventually start to overheat
4
New cards
Explain why a motor that is receiving too high of voltage would break
If the motor is receiving too high of voltage, it will burn out because its windings are not able to take on such high amounts of voltage. Thus the windings will burn out and the motor will overheat
5
New cards
What does UL stand for?
Underwriters laboratories- its a type of approval stamped onto compressor motors
6
New cards
This is the reserve horsepower a motor can operate at if need be for a limited amount of time
Service factor
7
New cards
A service factor for a motor of 1.35% means:
That the motor can operate for a limited time at 35% higher than its specified rating
8
New cards
What is the main determination behind the phases a motor receives?
Its application
9
New cards
T/F: Three phase motors cannot run on one phase power, but single phase motors can operate on two phases of three-phase power
True
10
New cards
What type of application would require an explosion proof motor?
May be used in a room that contains explosive gases. Normal motors with centrifugal starting switches might accidently ignite the gas and blow up the motor. Thus, an explosion-proof motor enclosed in housing can be used
11
New cards
What type of application would require a TECM (totally enclosed electronically commutated) motor?
TECM motors are used in applications where the area is very dirty. This keeps the motor protected from unusually high levels of gunk
12
New cards
What type of application would require a drip-proof motor?
Applications where there is a danger of water falling on and damaging the motor may use drip-proof motors
13
New cards
What does a motor’s insulation class signal?
The insulation class determines how hot the motor can safely operate in a particular ambient temperature situation
14
New cards
What are the two main types of bearings?
1. Sleeve
1. Ball
15
New cards
What two factors largely determine bearing selection?
1. Load characteristics
1. Noise level
16
New cards
This type of bearing is used when the load is light and noise must remain low, such as for a fan motor that is on a residential furnace
Sleeve bearing
17
New cards
Residential and light commercial applications normally see this type of bearing
Sleeve
18
New cards
What is the difference between oil ports and permanently lubricated bearings?
Oil ports require oil to be added into the bearings periodically by hand, while permanently lubricated bearings require no maintenance. Perminately lubricated are phasing out the oil port types
19
New cards
This type of bearing is a little louder and used with larger fans/pumps which are far enough away from the conditioned space that the noise will not be noticed
Ball bearings
20
New cards
While sleeve bearings use oil, ball bearings use:
grease
21
New cards
This is what determines how a motor will be secured during its operation:
its mounting characteristics
22
New cards
This type of mounting includes bolted metal to metal to the frame of the fan or pump and will transmit any motor noise into the piping/ductwork. Thus have louder sound “issues”.
Rigid-mount motors
23
New cards
This type of mounting uses different methods of isolating the motor and bearing noise from the metal framework of the system so as to make the motor less noisey than the rigid-mount
Resilient-mount motors
24
New cards
What are the four basic mounting styles:
1. Cradle mount
2. Rigid base mount
3. End mount
4. Belly-band mount
25
New cards
These are devices that connect the motor (driving device) to the driven load (fan)
Motor drives
26
New cards
What are the two main ways driving devices (motors) drive their loads?
1, Belts
2. Direct drive
2. Direct drive
27
New cards
What is the purpose of a motor drive?
The function of a motor drive is to transfer the motor’s rotating power (energy) to the driven device (the fan or other thing that needs to be powered)
28
New cards
What is the biggest pro to using a belt-drive motor drive?
The strength of the belt drive is its versatility. Both its pulley size and the speed of the driven device can be changed, which makes it very easy if the capacity of a compressor or a fan speed must be changed after the system has already been installed
29
New cards
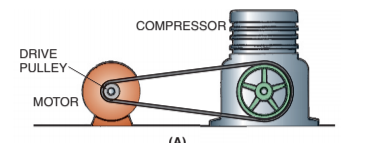
What is this a picture of ?
A belt-drive motor
30
New cards