forensic microscopy final exam
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Mitochondrial DNA
transmitted only from mother to child
every cell in the body contains hundreds of mitochondria, which provides energy to the cell
Hundreds to thousands of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) compared to 2 copies of nuclear DNA in a single cell.
constructed in a circular or loop configuration
each loop contains enough (approx. 16,569 base pairs) A, T, G, and Cs to compose 37 genes involved in mitochondrial energy generation.
Hair Growth Rate
1/2in per month
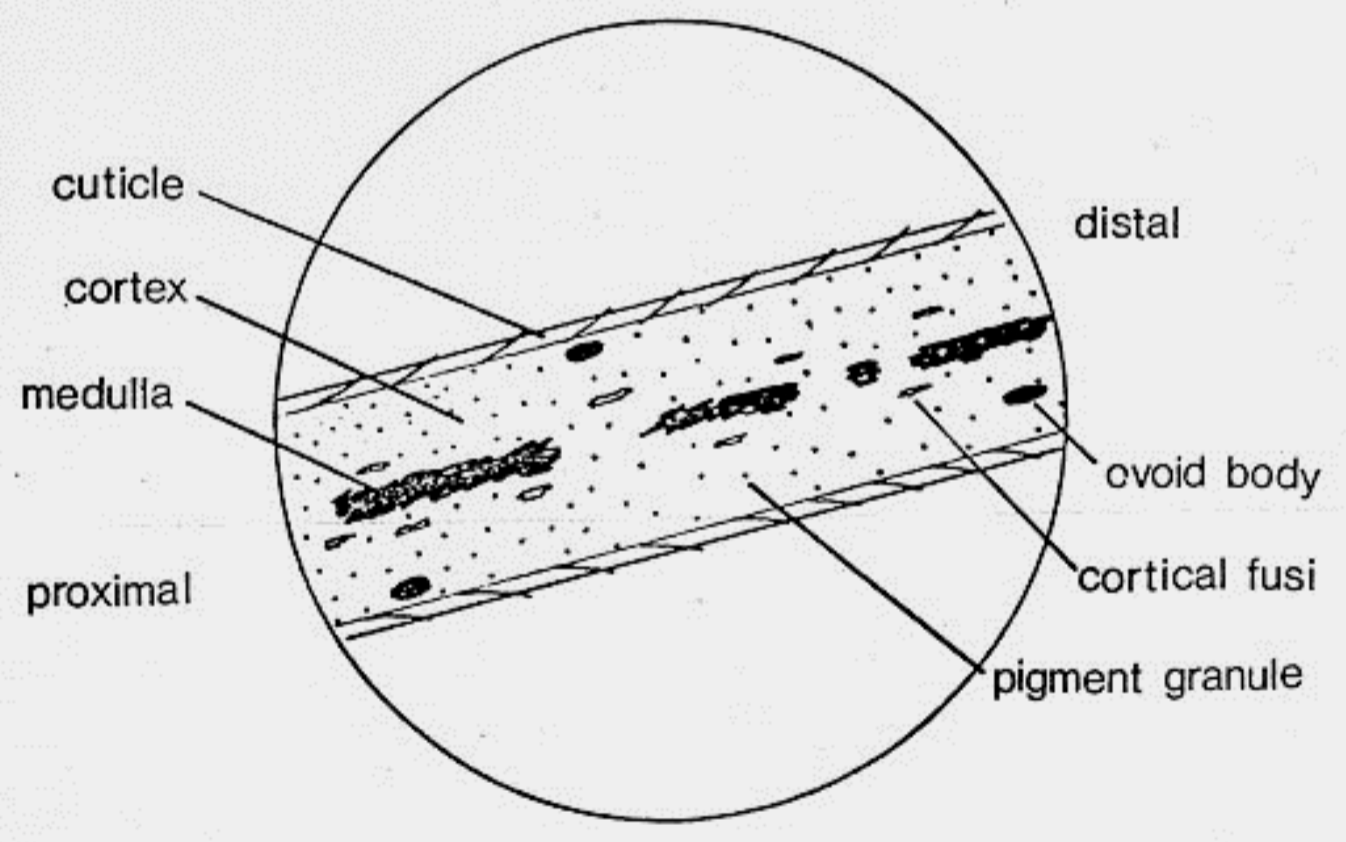
Basic hair structure
Cuticle
Cortex
Medulla
Cortical Fusi
Ovoid bodies
Pigment Granules
Medullary Index
Medulla /Hair Width
Negroid
diameter - 60-90 um
cross section - flat
pigmentation - dense & clumped
no info on cuticle
undulation - prevalent
Caucasoid
diameter - 70 - 100 um
cross section - oval
pigmentation - evenly distributed
cuticle - medium
undulation - uncommon
Mongoloid
diameter - 90 - 120 um
cross section - round
pigmentation - dense auburn
cuticle - thick
undulation - never
Scalp somatic origin
100-1000 mm long, 25 - 125 um diameter, 0.4 mm/day growth; small root; tapered tip, little diameter variation; various medullation; often with cut tips; may be artificially treated
Pubic somatic origin
pudendal; 10 - 60 mm long; coarse diameter and prominent diameter variation and buckling; broad medulla; follicular tags common; asymmetrical cross section twisted and constricted; may be straight, curved or spirally tutted - root is very fleshy, the tip is abraided since it is rubbing against clothes
Vulvar somatic origin
secondary pubic hair; finer and shorter than pubic hair, may be abraided
Beard somatic origin
facial hair, very coarse: 50 - 300 mm long; large root, irregular structure: often triangular cross section; complex medullation; blunted or razor cut tips; 0.40 mm per day
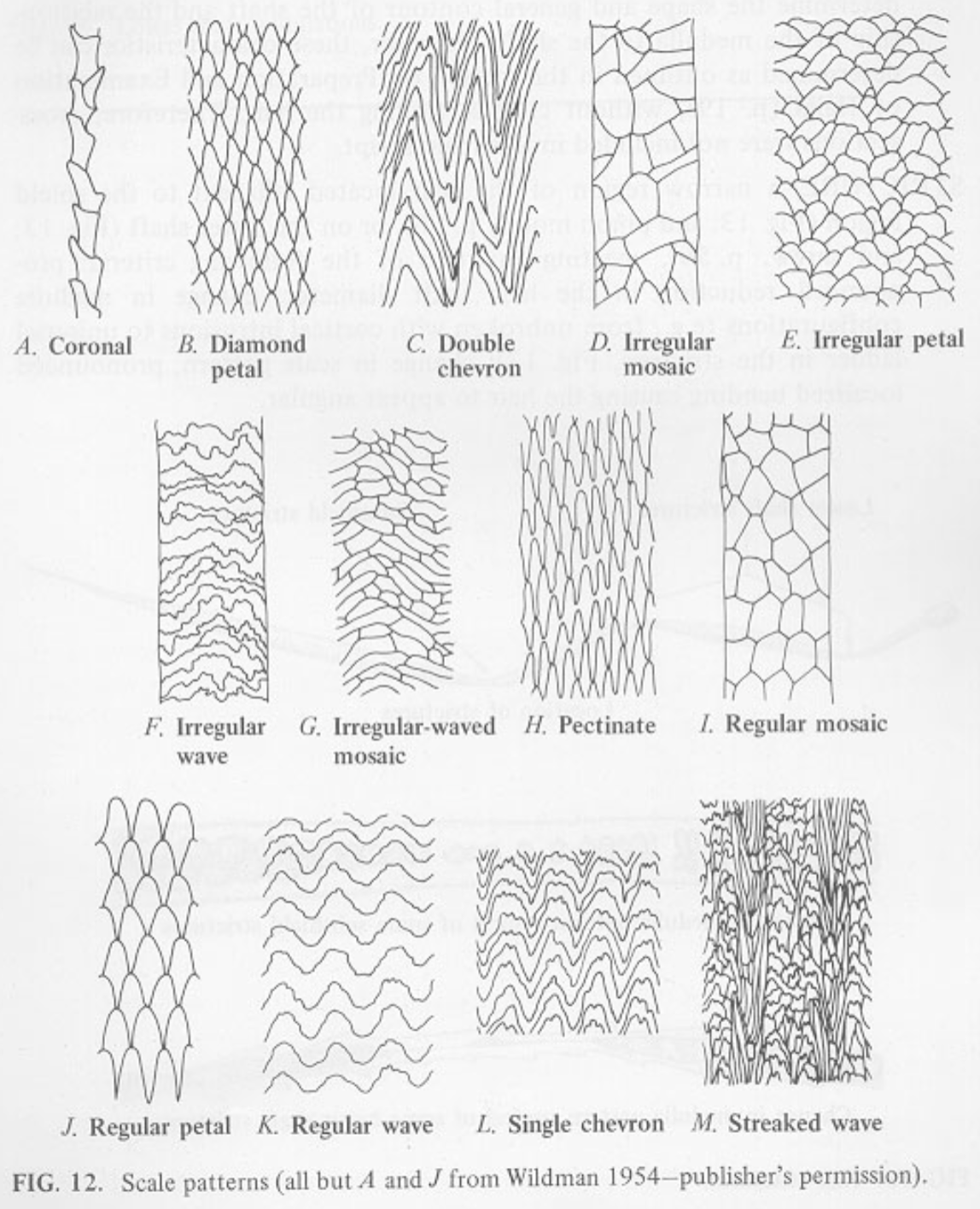
scales pattern
Mosaic
Petaloid
Double Chevron
Irregular wave
Imbricate (human hair)
Medullary Configuration
Serial ladder
Amorphous cellular
Specific gravity
dry weight / loss of weight in water
Karat (K)
1/24 Pure Gold
Carat (C)
0.2 g or 100 points
1 point = 0.01 ct
Demarcation Line (Dyed Hair)
occurs when hair grows
the contrast between new hair growth and previously colored hair

Pigment aggregates
clumps of pigment irregularly distributed along hair shaft
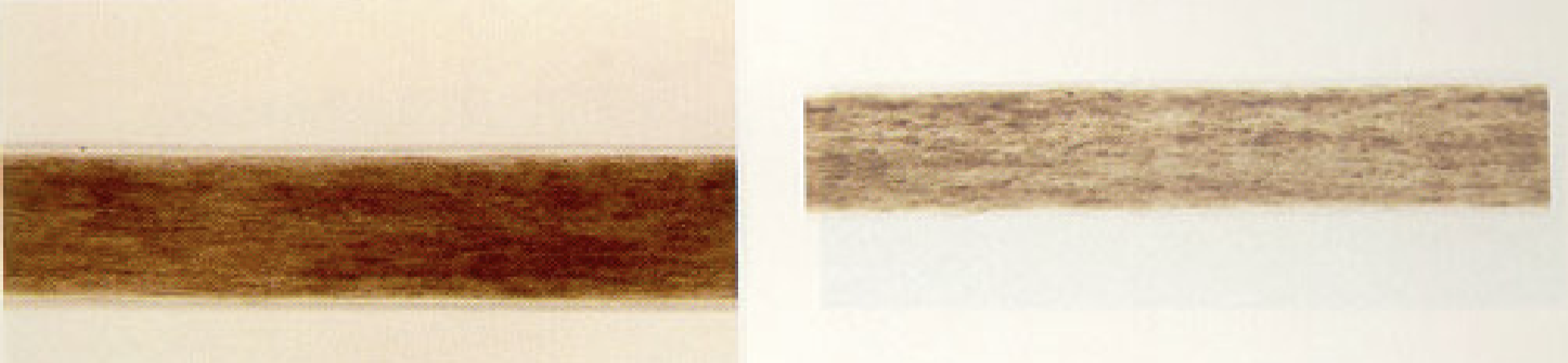
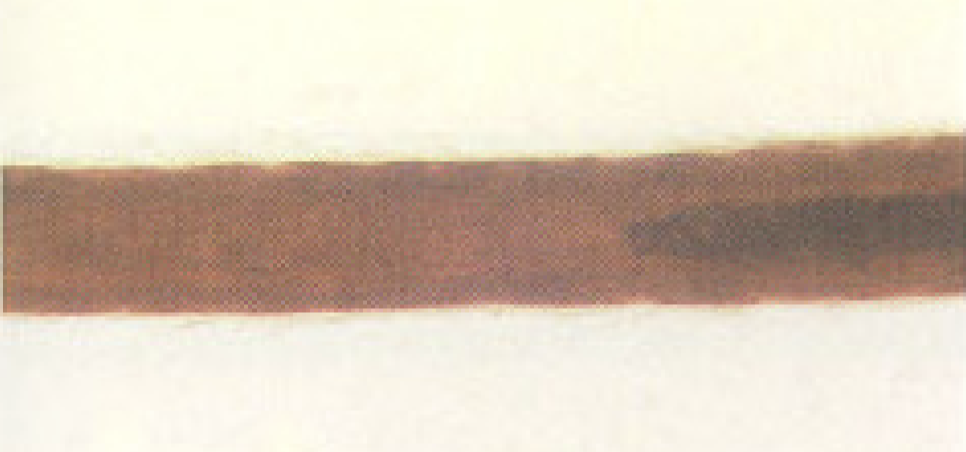
Discontinuous medulla
patchy and does not run through the entire hair fiber length
Continuous medulla
A medulla pattern where the medulla line is unbroken
Translucent medulla

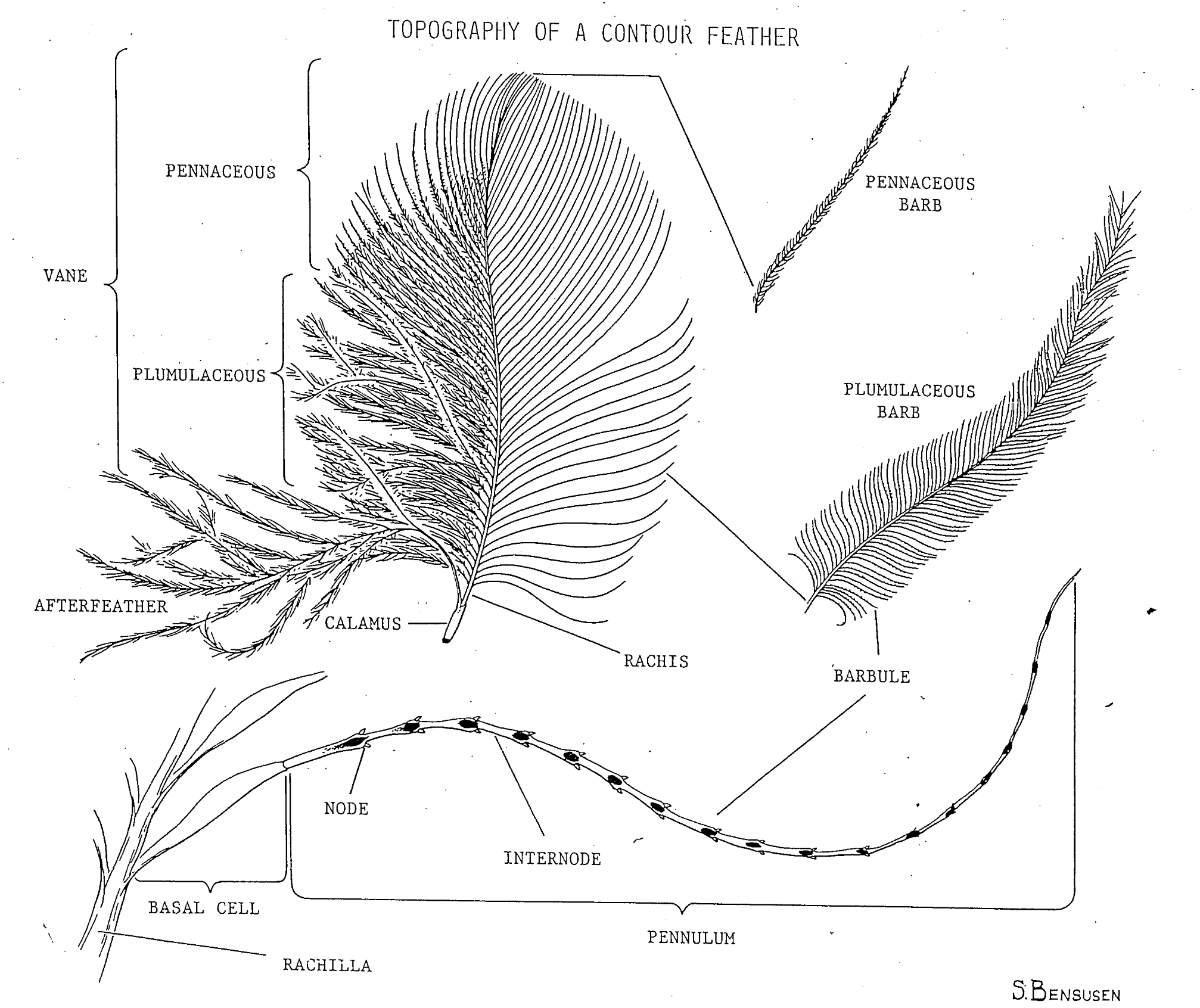
feather terminology
rachis - shaft of the feather
calamus - root portion of the feather
quill - some feathers don’t have a large shaft (rachis)
quill point - the point that the fiber feathers meet
down feather - has no shaft
barbs - coming off of the main shaft
barbules - coming off of the barbs
nodes - these are on barbs
specialized nodes - indicates what type of species a bird is, they have a certain shape and characteristic, or location to them to help with identification
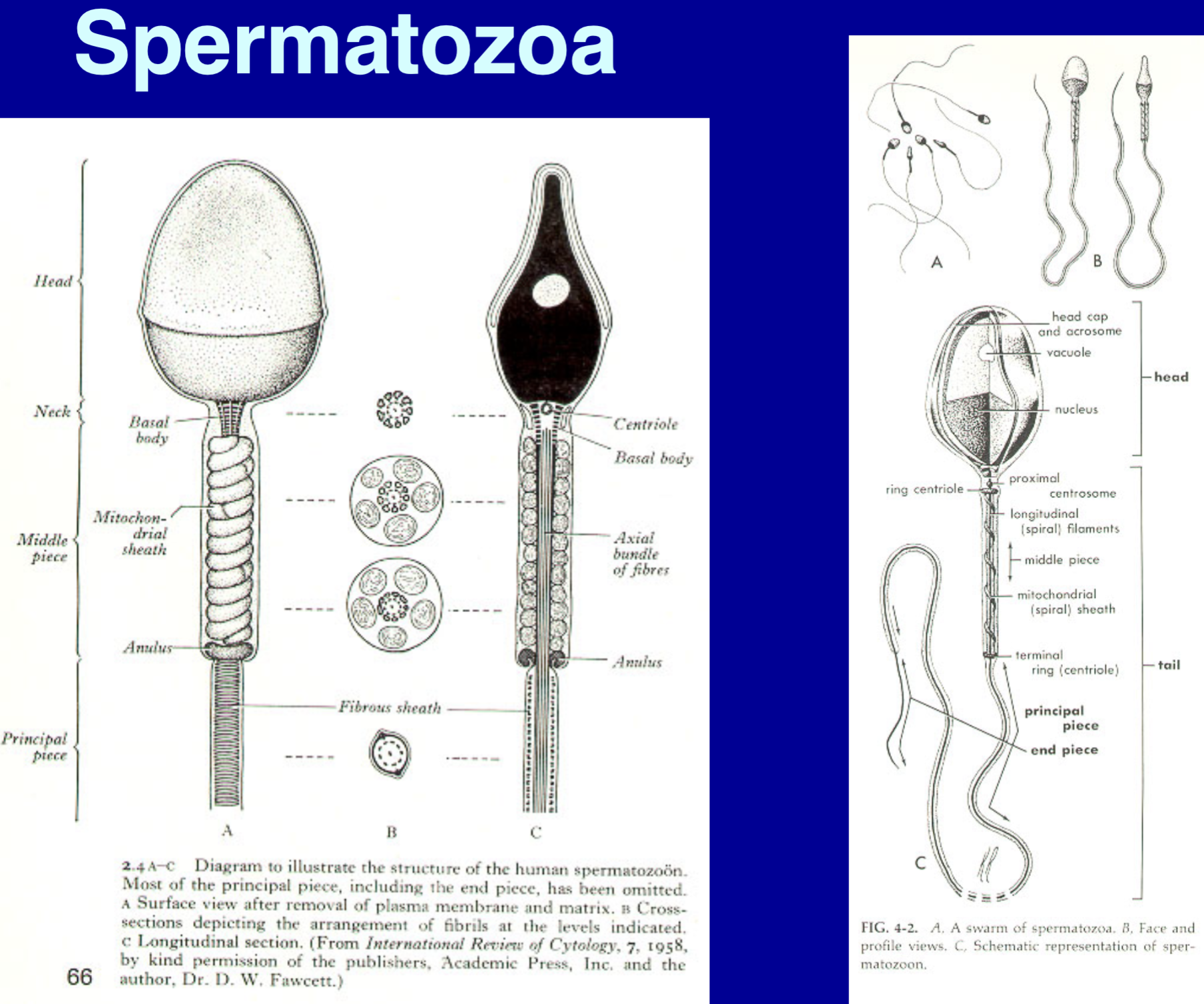
spermatozoa terminology
acrosome - top layer, part of the head
head - size - length 4.4 um, width 3.2 um
middle piece - size - length 4.0 um, diameter 1.0 um
mitochondrial sheath - in the middle piece
tail - the tail typically falls off, so the majority of the time forensics only has the head cells, there are no measurements for the tail
forensic use phase contrast to identify sperm cells
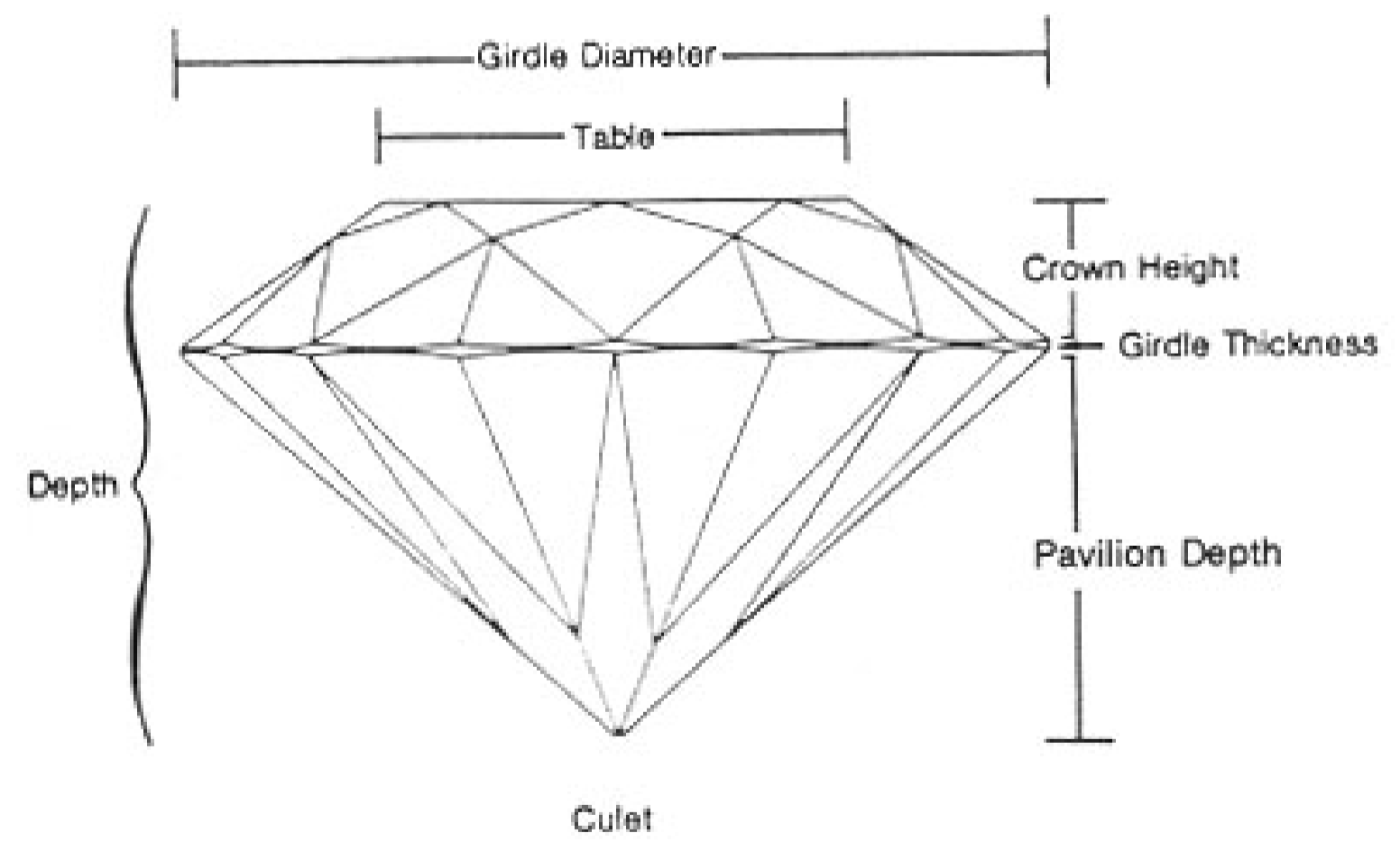
diamond terminology
crown (or bezel - from the girdle up)
girdle
pavilion (from the girdle down)
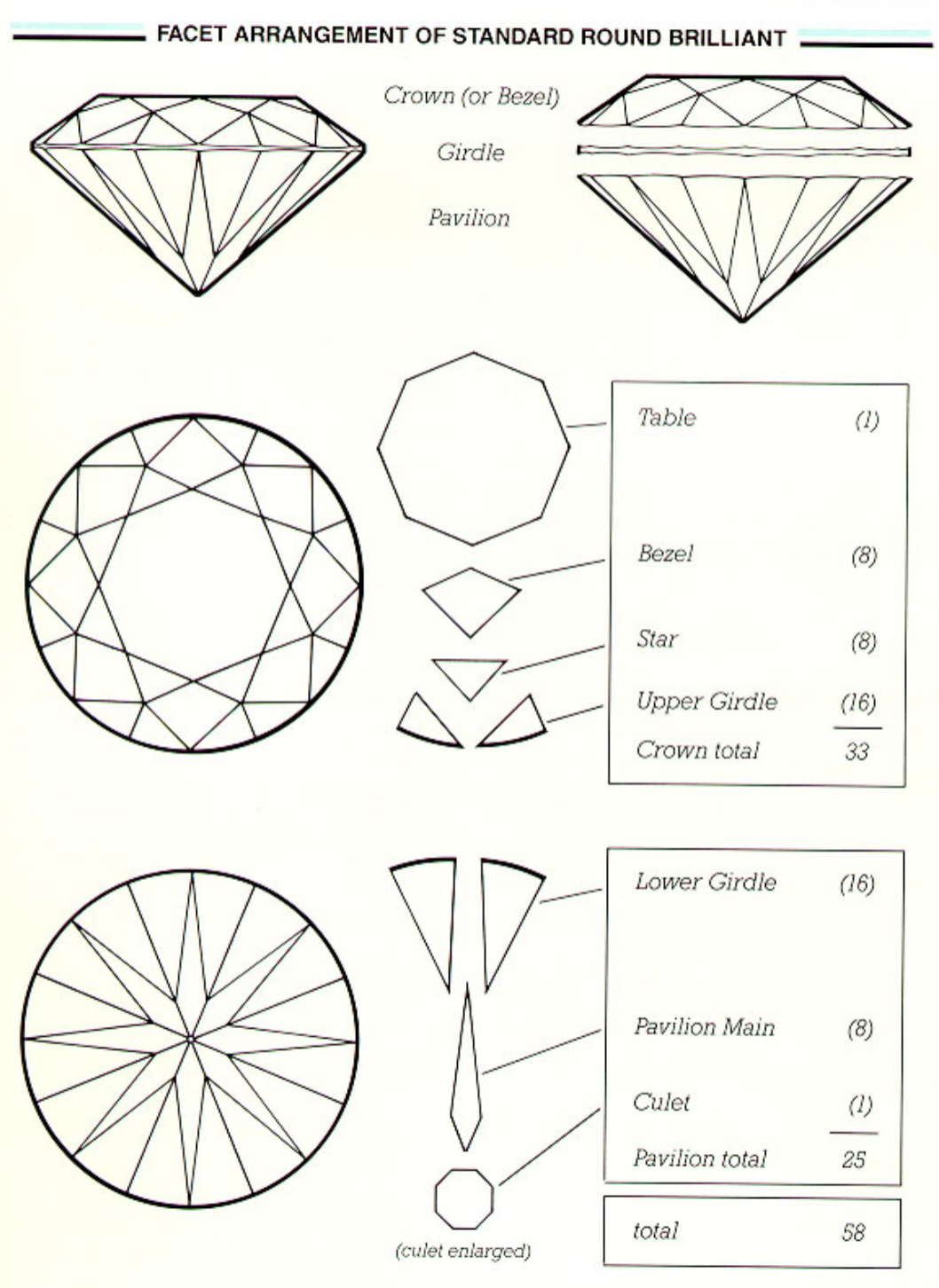
facet terminology
table - the largest facet (octagonal shape) on the top of the diamond - pretty important because if you have inclusions or blemishes that are on the table it is real obvious which devalues the stone
bezel
star
upper girdle
lower girdle
pavilion main
culet
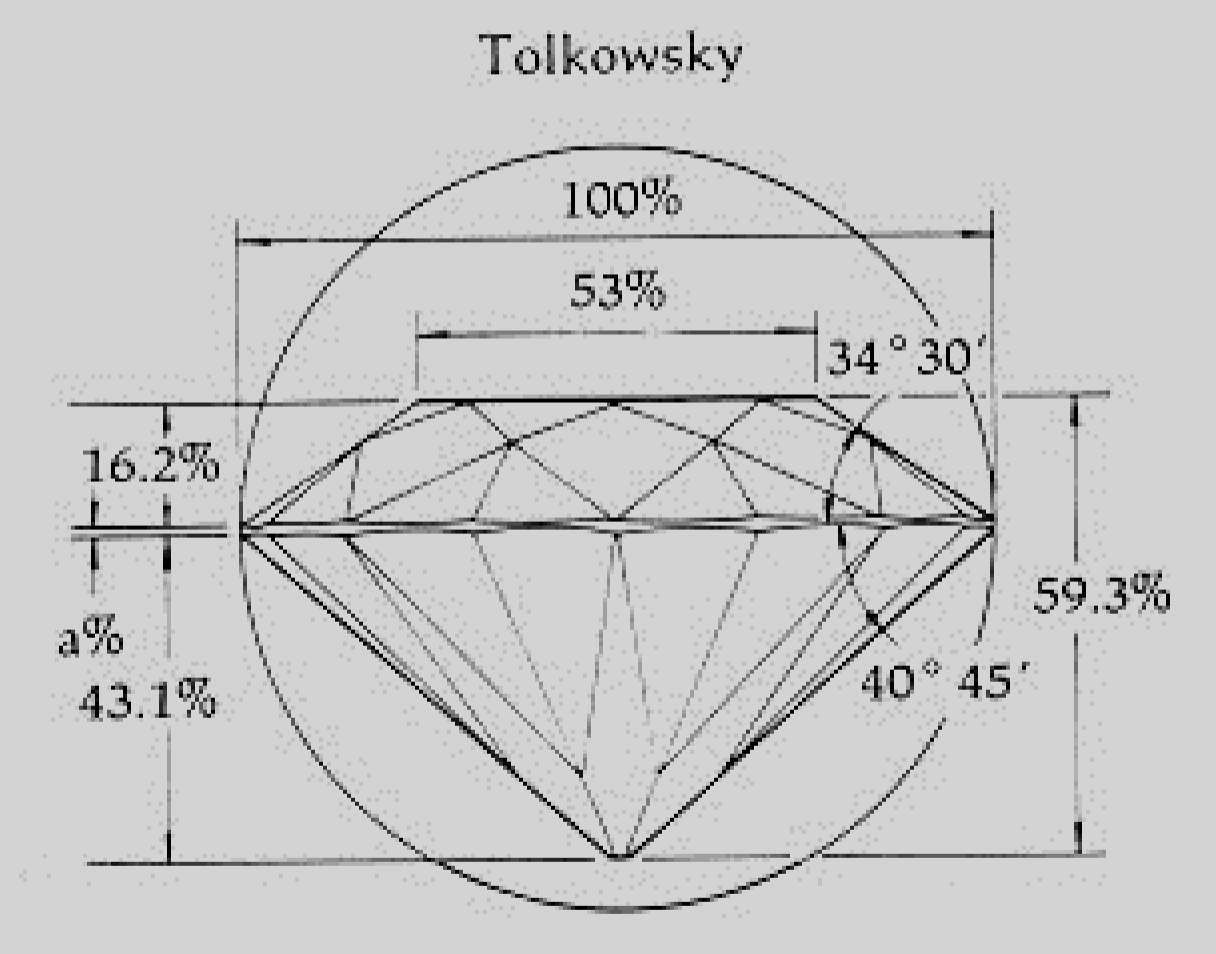
Tolkowsky
American Cut
this the standard round brilliant faceting cut
Single Cut
18 Facets
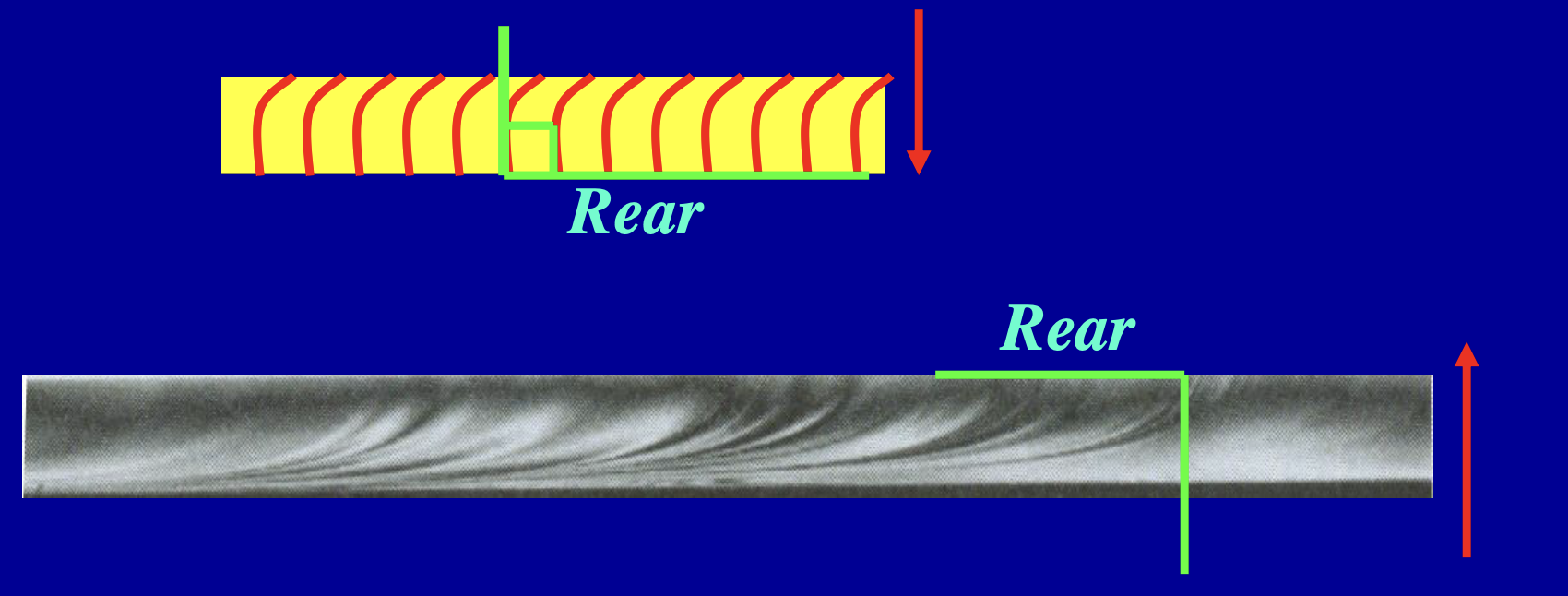
4R rule for glass fracture analysis
Ridges on Radial cracks are at Right angles to the Rear
• The “rear” is the side opposite the impact
SEM signals
With an electron microscope, the forensic microscopist bombard the gunshot residue particles with a electron beam and the result is different signals coming off from the particles
backscatter electrons - comes close to the nucleus of the material that they have, it typically gets backscatter back to the detector, doesn’t lose a lot of energy, most of the electrons that they sent down are coming right back
secondary electrons - the electron beam comes down and not so close to the nucleus of the atom but closer to the outer shells - knocks one of the outer shells out - typically loses some energy and give off some x-rays then goes down a lower orbital shell, the electrons you are getting are actually the electrons from the sample not from the beam
auger electrons - typically emitted from the near-surface region of a material, providing information about the top few nanometers - a surface technique - we don’t do much with this in forensics
characteristic x -rays - you have a spectrometer (EDS & WDS) connected to the detector that will analyze x-rays from the particle -we use this in forensic so we can identify what the material is made out of, with gunshot residue we can go down to a half of micron size particle
Another signal is cathode luminescences signals
resolution limits of microscopy
d = 0.61 λo / n sin θo
Unaided Eye d = 0.1mm (at 25cm)
In LM d=0.2μm (200nm)
In TEM d=0.21nm (2.1Å at 50kV)
In SEM d=3nm (30Å)
Monte Carlo Diagrams
function of accelerating voltage and atomic number
it is a software program - when you hit a particle with a certain electron volts signal, depending upon the atomic number, what it is made out of, the computer program will calculate/extrapolate where those electrons would go and what kind of signal you get off
the smaller the particle, the higher chance you have went pasted the particle and are getting some of the background - the carbon peak gets bigger & the signal to noise ratio gets worse as you blow past the particle
^^ All of this tells the forensic world not to analyze gunshot residue particles smaller than half a micron size
when you have a gunshot residue particle and you want to hit it with an electron beam, analyze the characteristic x-rays to see what that particle is made out of, you don’t want to blow past that little particle because then you will be analyzing the background (stuff that is not part of the gunshot residue particle)
Soil analysis
color - dry it - get all the moisture out, prepare with a Munsell soil color charts
particle size
mineral ID - polarizing light work so we can identify minerals in the soil
(theoretically) instrumental work - x-ray diffraction.
most crime labs don’t get involved in the soil instead they look for artifacts (paint chips, glass, fiber, hair)
down feather/down cluster
the undercoating of waterfowl, approximately 20% of the total covering of the mature bird
a large number of slender filaments or barbs growing in all directions from a single quill point (much superior to feathers as a filling material)
feather fiber
loose barbs or fibers
EDS and WDS
Different types of spectroscopy when it comes to electron microscopy - attaching a spectrometer to an electron microscope
EDS - energy dispersive spectroscopy
cheaper and easier to use - meaning most crime labs do this for gunshot residue
WDS - wavelength dispersive spectroscopy
has a better resolution than EDS
some universities have wavelength dispersive spectroscopy
Everhardt-Thornley Detector
backscatter electron detector - classic one
if it gets to close to the nucleus of the material that they have, it typically gets backscatter right back to the detector, doesn’t lose a lot of energy, most of the electrons that they sent down are coming right back
Solid state backscattered detector
detects secondary electron signals
the electron beam comes down and not so close to the nucleus of the atom but closer to the outer shells - knocks one of the outer shells out - typically loses some energy and give off some x-rays then goes down a lower orbital shell, the electrons you are getting are actually the electrons from the sample not from the beam
X-Ray fluorescence
instead of hitting the particle with an electron beam, you hit the electron coming from the tungsten filament against a source (i.e. rhodium) in a tube which gives off x-rays (x-ray tube), so you can hit your sample with x-rays - which gives lower energy characteristic x-rays coming off
basically the same thing as SEM and electron beam characteristic x-rays - very similar process except that you are using an x-ray tube for the source
what limits gunshot residue analysis?
that the forensic microscopist can’t analyze any gunshot residue particle smaller than half a micron (0.5)
wood terminology
cross section - pretty important because you are trying to see how these wood looks like with a hand lens or a microscope (you can get different types of shapes & sizes to these cells based on how you cut it) - this will tell you if it is a softwood or a hardwood - trying to categorize it - how you cross section it really determines how it looks
bark - protects trees from harsh environmental conditions including weather, pests, disease, and physical damage from animals
cambium - the layer of cells in a plant that provides unspecialized cells to promote growth
sapwood - outer, living layers of the secondary wood of trees, which engage in transport of water and minerals to the crown of the tree
heartwood - the central, supporting pillar of the tree
pith - a tissue in the stems of vascular plants
softwoods - wood from conifers (cone-bearing plants), which usually remain green and do not yearly shed all their leaves, gymnosperms
hardwoods - a category of tree species (angiosperm) that have broad leaves and true flowers with the seed being enclosed
woody monocots - Monocotyledons - any of a group of flowering plants (as the palms and grasses) having an embryo with a single cotyledon and usually leaves with parallel veins and flower parts in groups of three (i.e palm trees)
resin cells - secretes or stores resin - resin protect plants from insects and pathogens
tracheid cells - a long and tapered lignified cell in the xylem of vascular plants
parenchyma cells - carry nutrients - performing metabolic functions such as carbohydrate storage in the growing stem
longitudinal cells - transporting nutrients/water up or down the wood (runs up & down the wood, in general)
ray cells - anything with “ray” comes from the center/middle moves out
ray, longitudinal, parenchyma, & tracheid cells - ALL different types of cells that transport nutrients/water in the plant material
vessel elements - the conducting pathways that constitute the major part of the water transporting system in flowering plants - largest cells in hardwoods, with thin walls and spacious cell cavities (sap conduction)
perforation plates - in tress, there are these long cells that kinda connect to each other - when the come together it is like a cell wall and the nutrients will go in between the two - IF THERE ARE SLOTS then it is scalariform plates
Hair papilla
(dermal papilla) - where the hair follicle is mitotically dividing/growing - part of your scalp, melanocytes that are in here and the melanocytes produce melanin - melanin is being dumped into the cortex of the hair and as it comes up out of that root sheath it becomes keratinized - keratinous dome - keratin hardens (no nucleus in these cells) most of the hair shaft is keratinized cells that do not have a nucleus
Anagen stage
when the cells are actively mitotically dividing (growing), there is a medullary cavity which are air voids in the center of the hair that gives the hair support
this is the type of hair that forensic would do conventional nucleic DNA work - because of the follicular tag & the root sheath
Catagen stage
transitional stage - the area of where the air voids are in (medullary cavity) stops producing the medulla, melanocytes start shutting down
last around a week - very short stage
Telogen stage
the hair is not mitotically dividing, being held in your head by the hair follicle’s club shaped base (can easily fall out), most of the hairs you shed will be this types of hairs
control samples of hair
the amount of control samples of hair is between 50-100
want to have hair from every area of the head (occipital, parietal, frontal)
sequencing glass fractures
observing the existing fracture lines and their points of termination
tempered, laminated, and thermal fractures
thermal fractures - is curved and has a smooth edge, no indication of point of origin
tempered fractures - cannot easily be reconstructed, dices without forming ridges
laminated fractures - 4R rule is not reliable because the two sheets of glass are restricted in movement, remains bulged
muzzle to large distance determinations
As the muzzle-to-target distance increases, the presence of nitrite residues becomes more important in determining distance
electron scattering
occurs when electrons are displaced from their original trajectory
This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present
GSR (gunshot residue) analysis
Automated Particle Analysis
• In control test firings, it has be shown that the concentration of gunshot residue significantly
declines on living subjects after approximately 4 hours.
How is GSR analyzed?
• Historical - Atomic absorption, ICP, NAA, SEM+EDS (manual+semi-automatic)
• These days - Atomic absorption & SEM+EDS (automatic)
• Current Equipment - Digital SEM with motor stage, BSD (backscattered electron detector) and integrated EDS
• Setting of white level thresholds
• Acquisition of BSE image
• Position and size of candidate particles are recorded