Chapter 2 - Rhythm, Meter, and Metric Organization
Notating Rhythm
Music notation - It shows how long one note lasts in relation to others.
Two half notes equal a whole note and two quarter notes equal the duration of a half note.
Note tree - Relationship of duration symbols

Rest tree - The relationship of the equivalent rests

The Dot and the Tie
- Dot and tie - Two symbols that extend the length or duration of a note.
- Dot - Used to extend the value of a single note by one-half of its original value.
- A dotted quarter note divides into three eighth notes.
- Double dot - Lengthens the dotted note value by half the length of the first dot.
- Tie - It combines the durational values of two or more notes of the same pitch using a curved line.
Metric Organization
- Duration - The length of time sound or silence occurs.
- Beat - A regular, recurring pulsation that divides music into units of time.
- Meter - The organization of musical time into recurring patterns of strong and weak beats.
- Duple (Strong weak) - Two beats per measure
- Triple (Strong weak weak) - Three beats per measure
- Quadruple (Strong weak less strong weak) - Four beats per measure
- Subdivision - The division of the beat into two or three equal parts.
- Rhythm - Series of durations, often varying, of sound and silence.
- Tempo - The speed of the beat.
- Meter signature - Establishes the grouping of the beats and the nature of the subdivision of the beat.
- Simple meter - Refers to the beat being divided equally into two parts.
- Compound meter - Refers to the beat being divided equally into three parts.
Simple Meter
The top number represents the number of beats per measure and the bottom number represents the fractional equivalent of the note that is the beat.
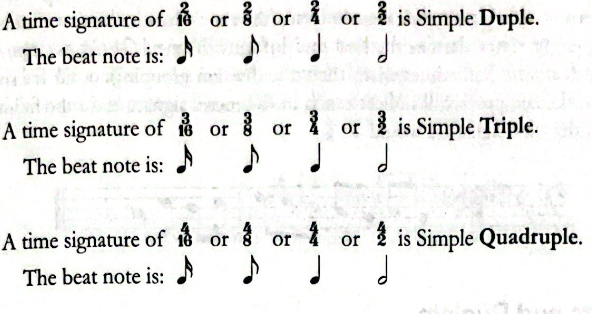
Common time - Represented by a lowercase c, it is used to represent 4/4.
Alla breve (Cut time) - Designated by a c with a line going through, is a substitute of 2/2.
Compound Meter
In compound meter, the time signature represents the subdivision, not the beat.
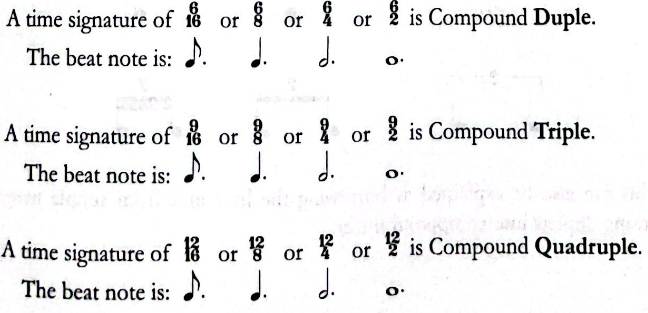
Asymmetrical Meters
- Asymmetrical meters - Meters that have beat units of unequal length.
- The most common ones have 5 or 7 as the top number.
Triplets and Duplets
- Irregular division - When a note is divided into an odd number of parts.
- Triplet - To divide a regular duration into three,
- Simple division of a dotted note (Duplet or Tuplet) - When two notes divide the beat.
Downbeats and Upbeats
- Downbeat - The first beat of the measure.
- Anacrusis - Songs that begin with one or more notes that precede the first full measure.
- Syncopation - The rhythmic displacement of the expected strong beat created by using dots, rests, ties, accent marks, rhythm, and dynamics.
- Hemiola - A special type of syncopation where the bead is temporarily regrouped into twos.
- Cross-rhythm - Metric device where the rhythmic relation of three notes occurs in the time of two.
Rhythmic Notation Guidelines
- For pitches on the middle line and above on the staff, the stems go downward.
- For pitches below the middle line, the stems extend upward.
- When drawing notes with single flags, the flag always goes on the right side of the note.
- Rhythmic patterns should be grouped with the beam to indicate beat units.