CompTIA A+ 1101 SATA, SCSI, and PATA Device Cables
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment)
- uses a 1 meter cable
- internal
- 7-pin connector
- connects a storage device to the motherboard
- uses a 15-pin connector to connect to power
revision 1.0:
- SATA 1.5 Gb/s
revision 2.0:
- SATA 3.0 Gb/s
revision 3.0:
- SATA 6.0 Gb/s
revision 3.2:
- SATA 16 Gb/s
eSATA (External SATA)
- speeds match the (internal) SATA version
- uses a 2 meter cable
- similar in size to SATA, with a very different connector
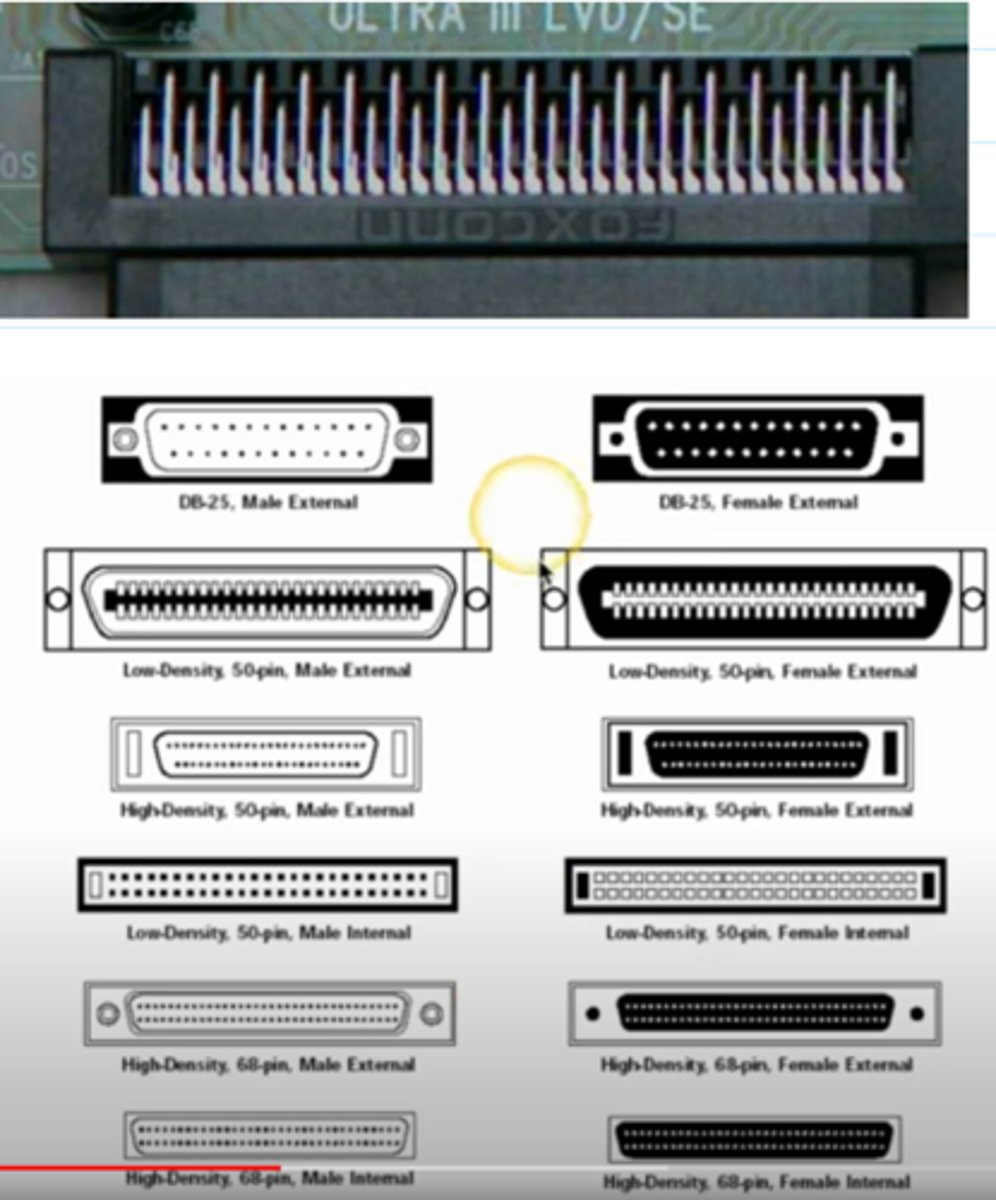
The SCSI (Small Computer Systems Interface) Standard
- originally designed to string many peripherals together on a single controller (up to 16 devices in an SCSI chain)
- parallel and serial connectivity, depending on the format
- not just for hard drives
Serial Attached SCSI (SAS)
- move from parallel to serial
- point-to-point connection
- no daisy chains or terminator required, unlike parallel SCSI

SCSI Interface and Connectors (Image)
The PATA (Parallel AT Attachment) Standard
- speeds from 16 MB/s through 133 MB/s
- a legacy technology
PATA Cabling
- 40-pin connectors on a ribbon cable
- the first device is "device 0", and the end device is "device 1" (swapped when using an 80-pin cable, which has minimized cross talk)

PATA Connector
- the missing pin allows us to properly orient the cable into the connector