BIOL 1410 Reproductive system
1/165
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LECTURE 17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
What are the two different gonads?
Testes (biological male), ovaries (biological female)
What 2 things do gonads produce?
Gametes + hormones
What do ducts in the reproductive system do?
Transport & store gametes
What do accessory glands in the reproductive system do?
Produce secretions that support gametes
The gonads/testes of the testicular reproductive system are located within what structure?
Scrotum
Testes are surrounded by what 2 tunics (outer → inner layer)?
Tunica vaginalis, tunica albuginea
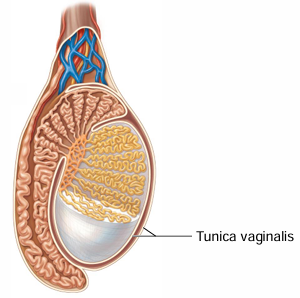
What type of membrane is the tunica vaginalis + what is it derived from?
Serous membrane derived from peritoneum
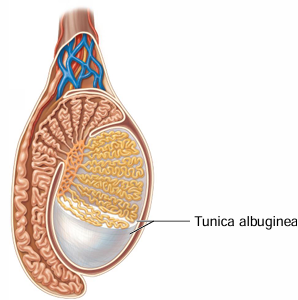
The tunica albuginea is an inner ______ CT capsule
“fibrous”
The tunica albuginea extends inwards to divided testis into what structure?
Lobules (small lobes)
What 2 things does each lobule contain (structure/type of cells)?
Seminiferous tubules, interstitial endocrine (Leydig) cells
What 2 cells are contained in the walls of seminiferous tubules?
Spermatogenic cells, sustentocytes (nurse cells)
What are spermatogenic cells + what do they develop into?
Germ cells (in various stages of development); become sperm
What do sustentocytes (nurse cells) do?
Surround, nourish and protect developing gametes
Where do sustentocytes (nurse cells) extend from/to?
Basement membrane → lumen
What are sustentocytes (nurse cells) connected by, therefore forming what structure?
Connected by tight junctions; form blood-testis barrier
What do sustentocytes (nurse cells) produce + for what purpose?
Produce testicular fluid; for sperm transport in lumen
Where are interstitial endocrine (Leydig) cells found?
In CT between seminiferous tubules
What do interstitial endocrine (Leydig) cells secrete?
Testosterone (hormone)
Material in the testicular reproductive system run from what 2 structures before reaching the duct system?
Seminiferous tubules → rete testis → then into duct system
What are the 4 components of the duct system?
Epididymis, vas (ductus) deferens, ejaculatory duct, urethra
Where is the epididymis?
Posterior border of testis
What occurs in the epididymis?
Sperm is stored and matures here (develops the ability to swim)
What is the function of the vas (ductus) deferens?
Transports sperm from epididymis during ejaculation
What is included in the spermatic cord?
Vas deferens, nerves, blood supply, and lymphatic vessels
The vas (ductus) deferens enters the anterior ______ wall
“pelvic”
The vas (ductus) deferens loops over the ________ wall of the bladder
“posterior”
What is the ejaculatory duct formed by?
Union of vas deferens + duct from seminal vesicle
What is the function of the urethra in the testicular reproductive system?
Transports urine + semen out of the body
What are the 3 regions of the urethra in the testicular reproductive system?
Prostatic, intermediate (membranous), spongy (penile)
Where is the prostatic region of the urethra?
Through prostate gland
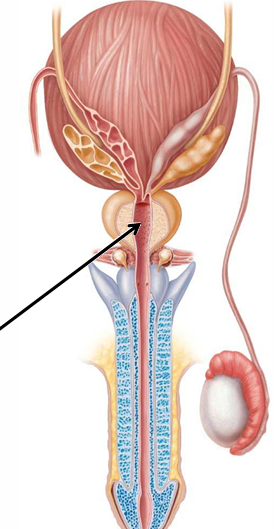
Where is the intermediate (membranous) region of the urethra?
Through urogenital diaphragm
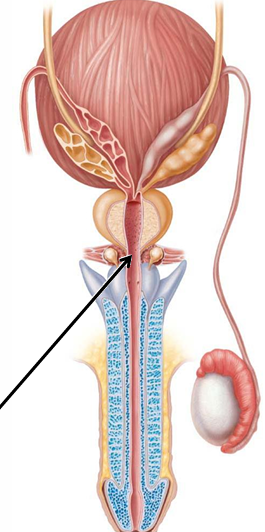
Where is the spongy (penile) region of the urethra?
Through corpus spongiosum of penis
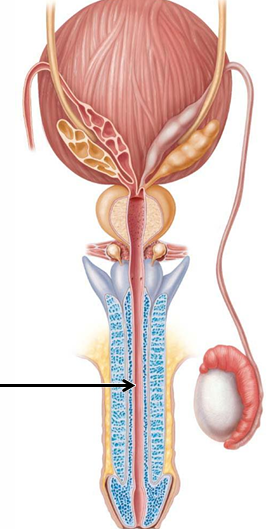
Where does the spongy (penile)/urethra open at?
At the glans penis (external urethral orifice)
What are the 3 parts of the penis?
Root, body (shaft), glans penis (enlarged tip)
The 3 cylindrical bodies of erectile tissue of the penis are blood _______ bound by ___
“sinuses,” “CT”
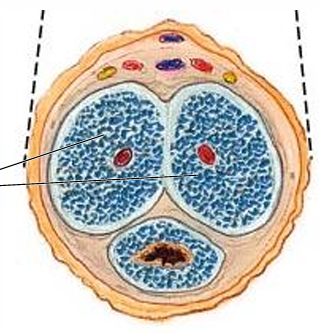
What are the 3 cylindrical bodies of erectile tissue of the penis?
(2) corpora cavernosa, (1) corpus spongiosum
Which of the 2 types of cylindrical bodies of erectile tissue of the penis are dorsal/posterior in erect position?
Corpora cavernosa
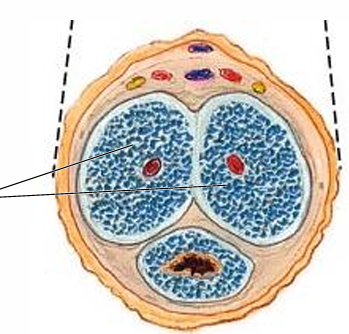
Which type of cylindrical bodies of erectile tissue of the penis form most of the root and shaft?
Corpora cavernosa
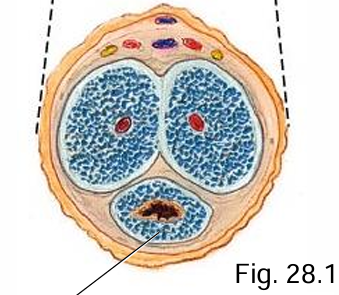
What does the corpus spongiosum surround and form?
Surrounds urethra, forms the glans penis
What do accessory glands in the testicular reproductive system contribute?
Secretions during sexual arousal
What glands do 95% of semen come from (highest → lowest contribution)?
Seminal vesicles (2), prostate gland, bulbourethral glands (2)
Where are the seminal vesicles (2) found?
Posterior to bladder
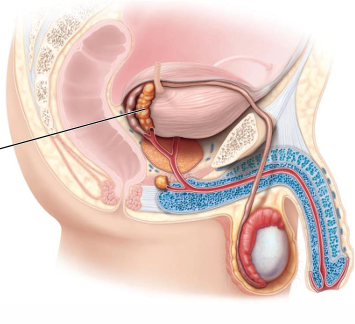
What do seminal vesicles (2) secrete?
Fluid that provides sperm with a source of nutrients
Where is the prostate gland found?
Inferior to the bladder
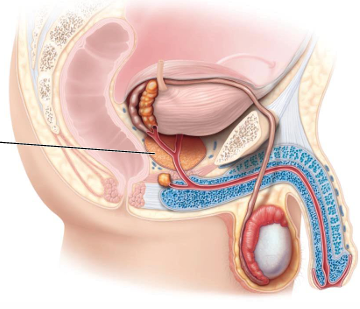
What does the prostate gland encircle?
Encircles the prostatic urethra
What is the function of the fluid the prostate gland secretes?
Nourishes + activates sperm motility
Where are bulbourethral glands found (+ what is it in contact with)?
Below prostate gland in urogenital diaphragm , contact with external urethral spincter
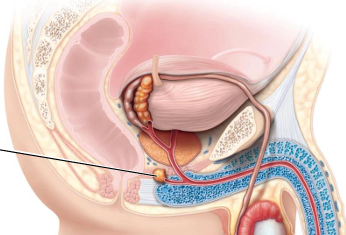
What do the bulbourethral glands secrete (+ function of the secretion)?
Thick mucus; lubricates urethra + glans penis
What is spermatogenesis?
Sperm production within seminiferous tubules
Spermatogenesis begins with spermatogonia, a 2n cell. It undergoes mitosis to become what 2 things?
1 primary spermatocyte (2n) + (another) spermatogonia (2n)
When spermatogonia (2n) undergoes mitosis, why does it produce another spermatogonia (2n)?
To maintain the cell line
From spermatogonia (2n) → 1 primary spermatocyte (2n), the primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis I to produce?
2 secondary spermatocytes (n)
The 2 secondary spermatocytes (n) undergo meiosis II to produce?
4 spermatids (n)
4 spermatids undergo spermiogenesis, the final stage of spermatogenesis. What is the final product?
4 spermatozoa (n)
Differentiation of spermatids = ?
Spermiogenesis
What are 3 major changes in cells as a result of spermiogenesis?
Sperm cells develop flagella, acrosomes, and lose most of the cytoplasm
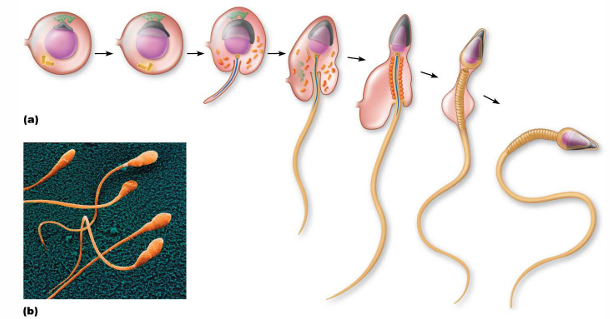
What things does the structure of a spermatozoa consist of?
Head, body (midpiece), tail (flagellum)
What 2 things are contained in the head of spermatozoa?
Nucleus (23 [n] chromosomes), top of nucleus covered by acrosome
The acrosome is a modified lysosome. What does this tell you it contains (+ function)?
Enzymes; penetrate secondary oocyte
The body of spermatozoa contains a large # of what organelle?
Mitochondrion
Why does the body of spermatozoa need so much mitochondrion?
To produce ATP for movement
What is the tail/flagellum of spermatozoa made of?
Microtubules
What does semen consist of?
Sperm + testicular fluid (5%), accessory gland secretions (95%)
How much semen is approximately released at ejaculation?
2-5mL
How much sperm/mL is approximately released at ejaculation?
20-150 million sperm/mL
What is the pH of semen?
7.2 - 7.6 (slightly alkaline)
What 3 things does semen provide sperm with?
Transportation medium, nutrients, protection
What are the gonads of the ovarian reproduction system?
Ovaries
Where are the ovaries located?
In pelvic cavity on lateral sides of uterus
How are the ovaries connected to the body wall?
Ligaments that are continuous with the peritoneum
The histology of the ovaries contained what 4 layers (outer → inner)?
Surface (germinal) epithelium, tunica albuginea, ovarian cortex, ovarian medulla
The surface (germinal) epithelium layer is made of what type of epithelial cells?
Simple cuboidal epithelial cells
The cuboidal epithelial cells of the surface (germinal) epithelial layer of the ovaries are modified of what structure?
Modified visceral peritoneum lacking CT
What is the tissue type of the tunica albuginea of the ovaries?
Dense CT
What 2 things are contained in the ovarian cortex?
Ovarian follicles + CT
The follicles of the ovarian cortex are a layer of cells surrounding what structure?
Developing oocyte
What 4 things are contained in the ovarian medulla?
Blood/lymph vessels, nerves, CT
What are the 3 sections of the uterine (fallopian) tubes?
Infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus
Where is the infundibulum section of the fallopian tubes?
Suspended over each ovary
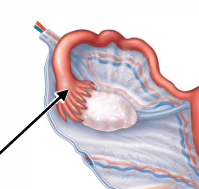
The infundibulum includes the opening of the uterine tube into what cavity?
Peritoneal cavity
What are fimbriae?
Finger-like projections of the infundibulum
What is the function of fimbriae?
Cover ovary during ovulation, help capture/move oocyte
In what section of the uterine (fallopian) tubes does fertilization usually occur?
Ampulla (middle section)
What does the isthmus section of the uterine (fallopian) tubes connect to?
Connects to uterus
What are the 3 components of the histology of the uterine (fallopian) tubes?
Mucosa, muscularis externa, serosa
What is the tissue type of the mucosa of the uterine (fallopian) tubes?
Simple columnar epithelium
What are the 2 cell types of the mucosa of the uterine (fallopian) tubes?
Ciliated + non-ciliated secretory cells w/ microvilli
What is the purpose of ciliated cells of the mucosa of the uterine (fallopian) tubes?
Help move oocyte/zygote/morula along the tube
What is the purpose of non-ciliated cells of the mucosa of the uterine (fallopian) tubes?
Secrete fluid that provides nutrients
What type of muscle is the muscularis externa of the mucosa of the uterine (fallopian) tubes made of (+ function)?
Smooth muscle; help movement
What is the serosa of the mucosa of the uterine (fallopian) tubes?
Visceral peritoneum
Is the uterus or the bladder superior to the other?
Uterus is superior to bladder
What are the 3 parts of the uterus?
Fundus, body, cervix
Where is the fundus part of the uterus?
Superior to isthmus of uterine tubes
What is the space within the body of the uterus called?
Uterine cavity
Most of what process occurs in the body of the uterus?
Where most embryo implantation/growth occurs
The cervix is a narrow passageway that opens into the _______
“vagina”
What are the 3 components/layers of the histology of the uterus?
Endometrium, myometrium (muscularis externa), perimetrium (serosa)
The endometrium is what kind of membrane?
Mucous membrane
What 2 tissue types is the endometrium made of + what does it line?
Simple columnar epithelium; lines inner surface of uterus.
Specialized lamina propria (consists of 2 highly vascularized layers)