AP Unit 3- Biological Psychology
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
lesion
tissue destruction. A naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue.
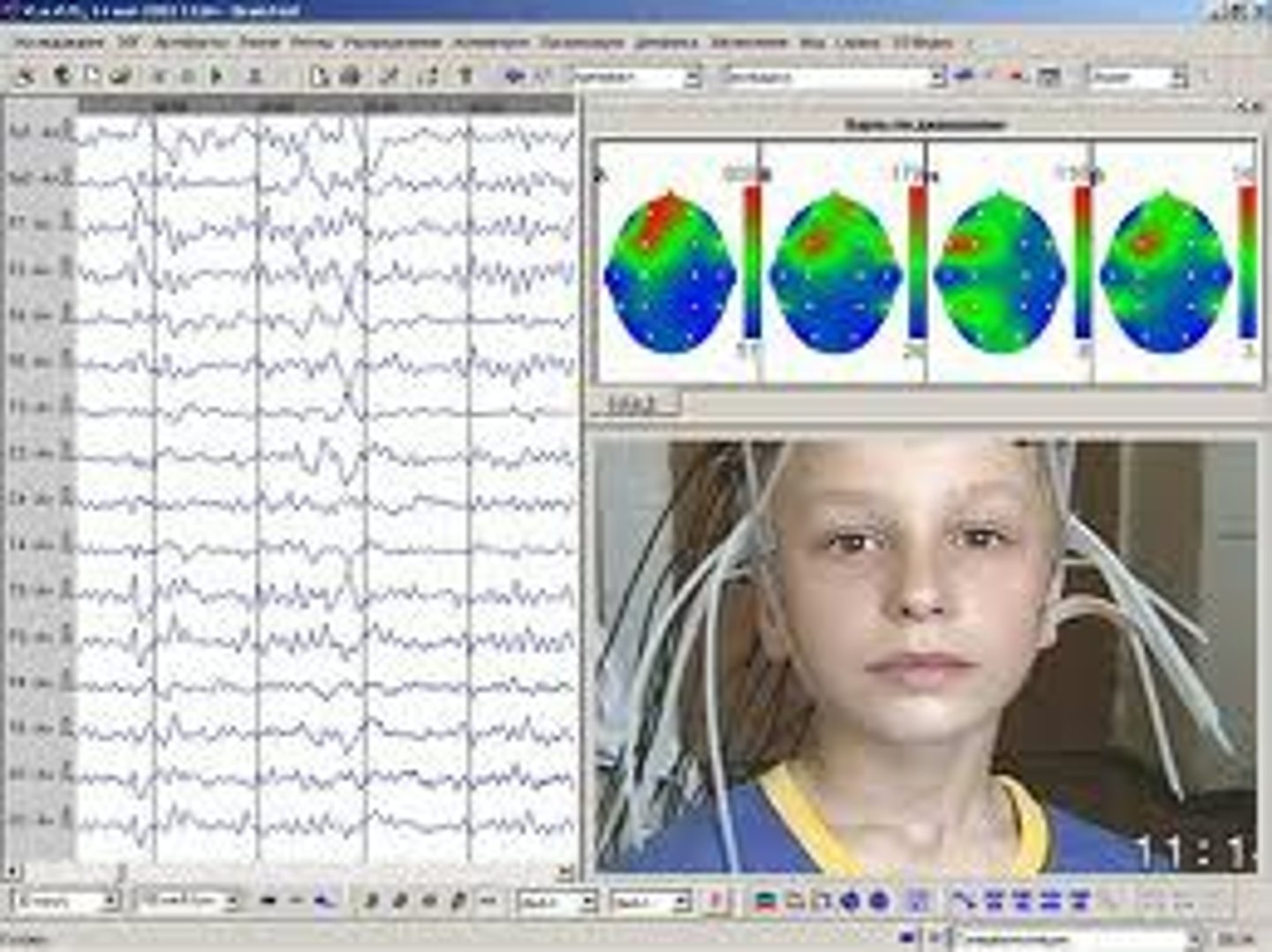
electroencephalogram (EEG)
an amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp. Used in sleep studies.
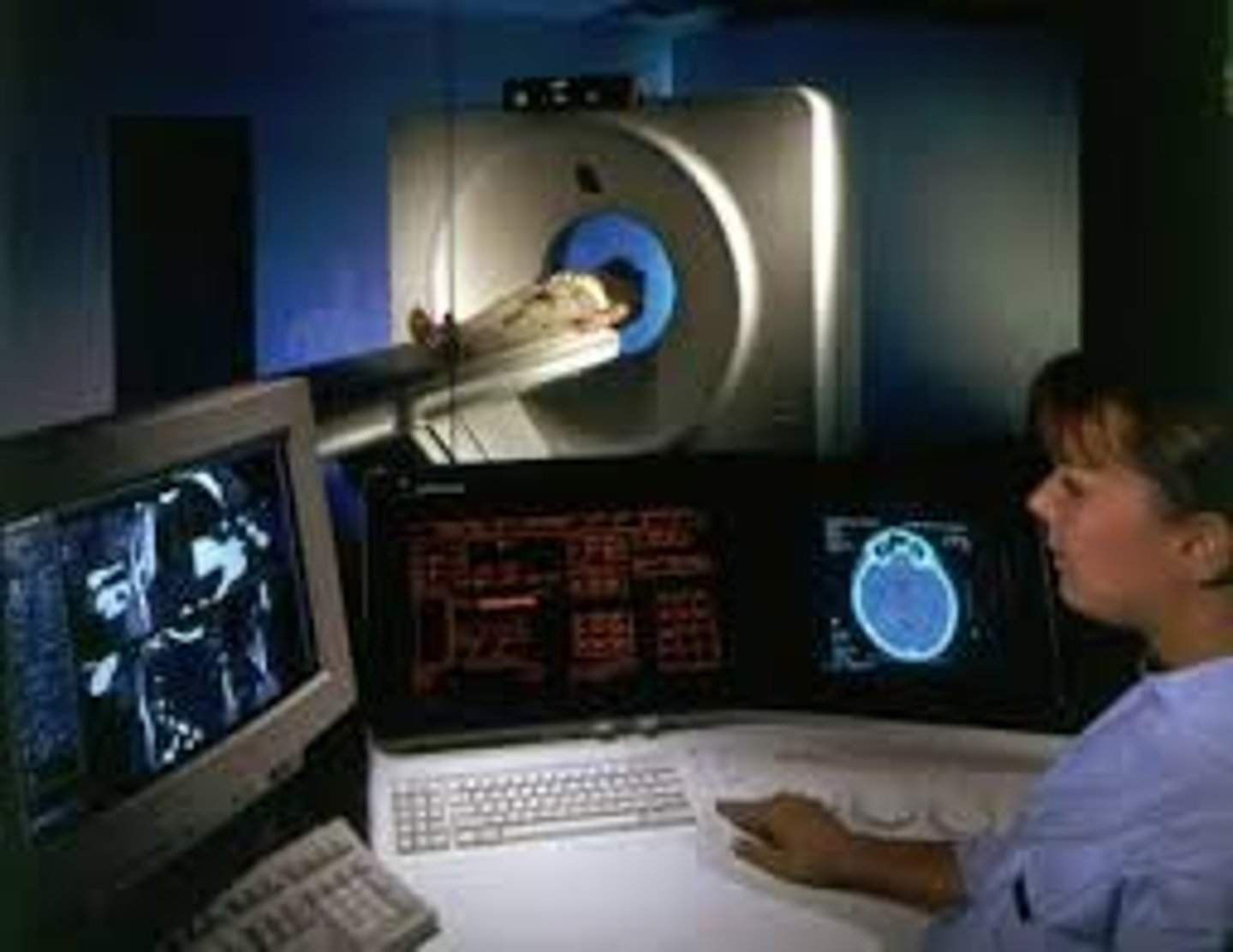
CT (computed tomography) scan
a series of X-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice through the body. Also called CAT scan.
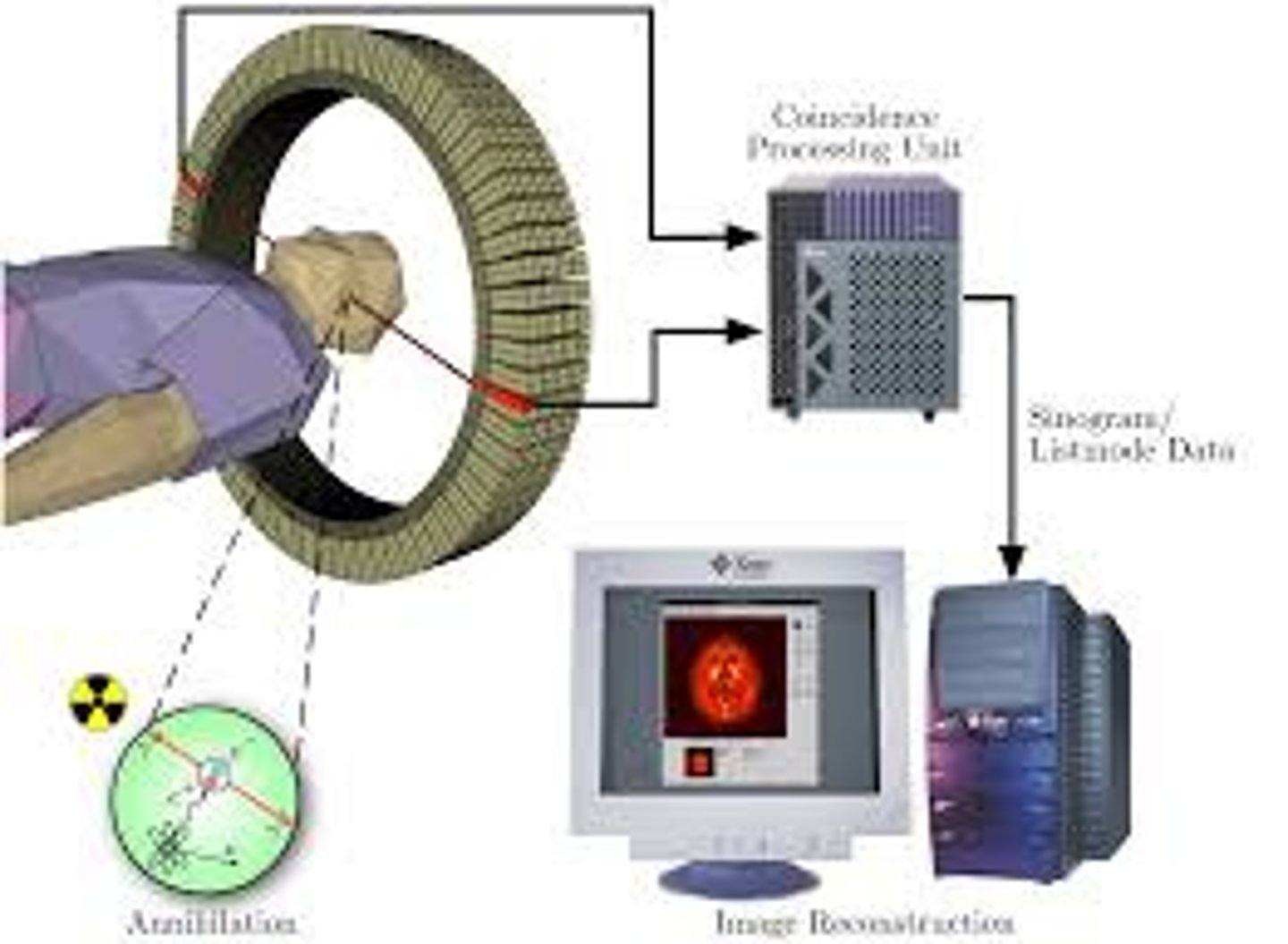
PET (positron emission tomography) scan
a visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue. They scans show brain anatomy.
fMRI (functional MRI)
a technique for revealing bloodflow and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans. These scans show brain function.
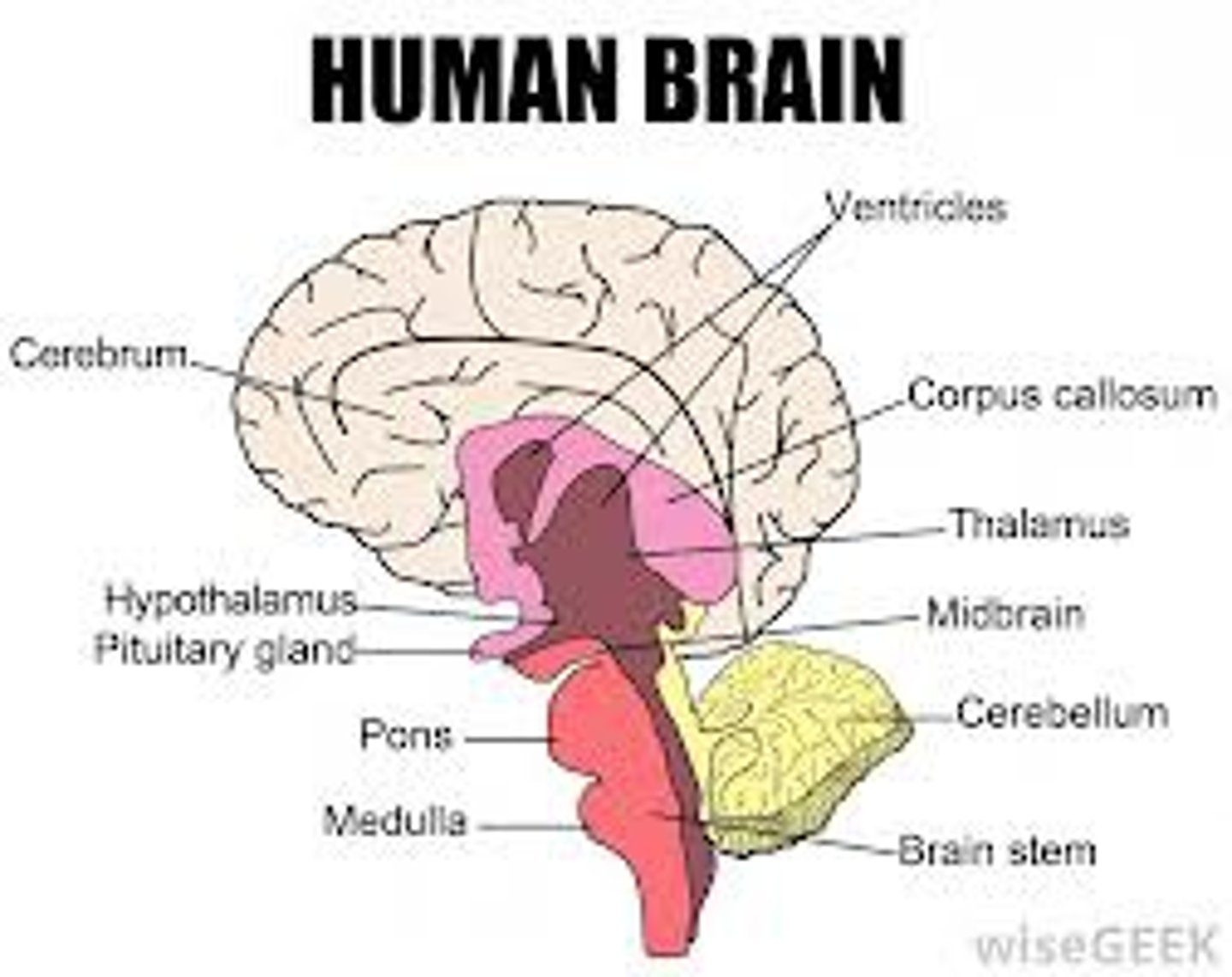
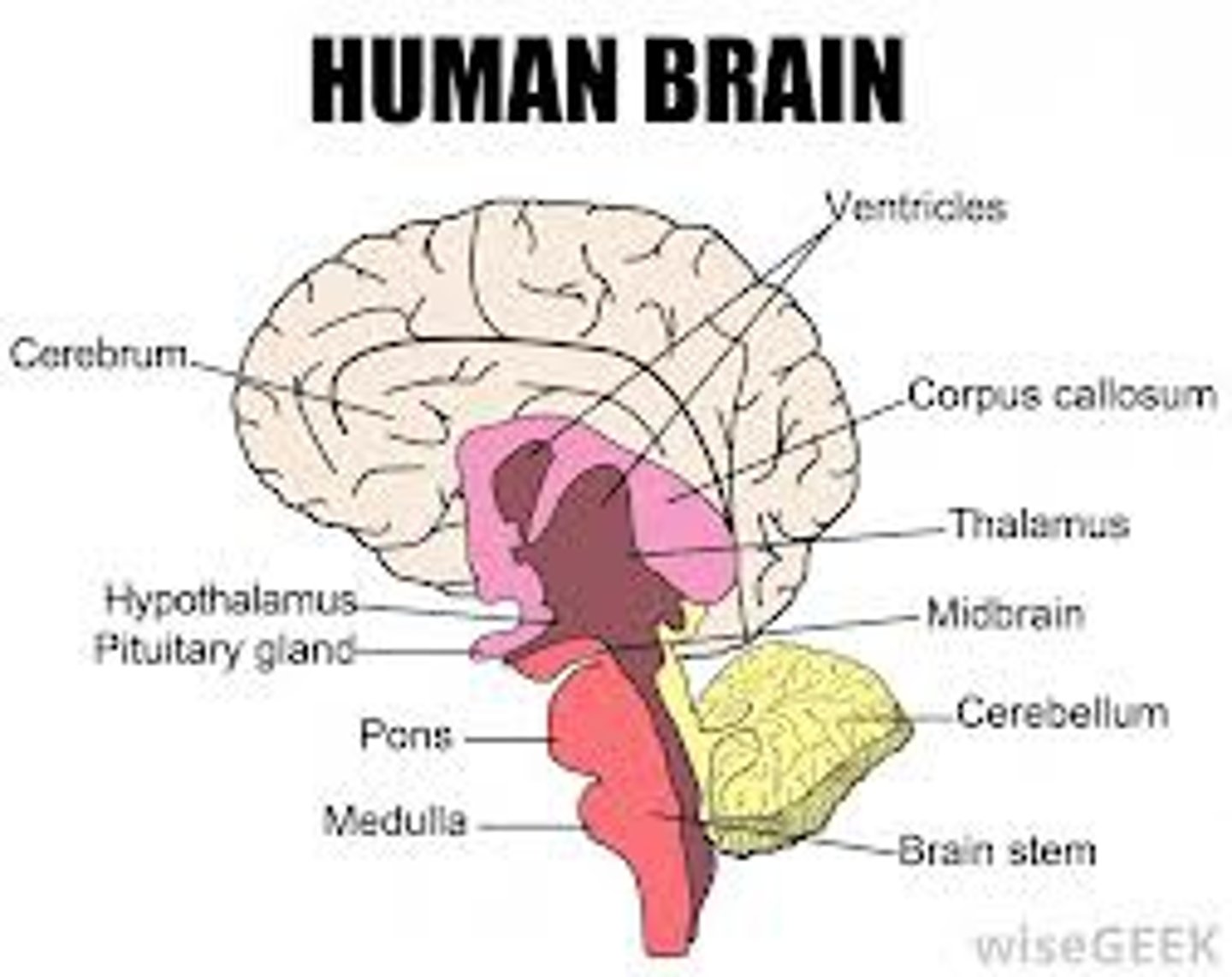
brainstem
the oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; It is responsible for automatic survival functions.
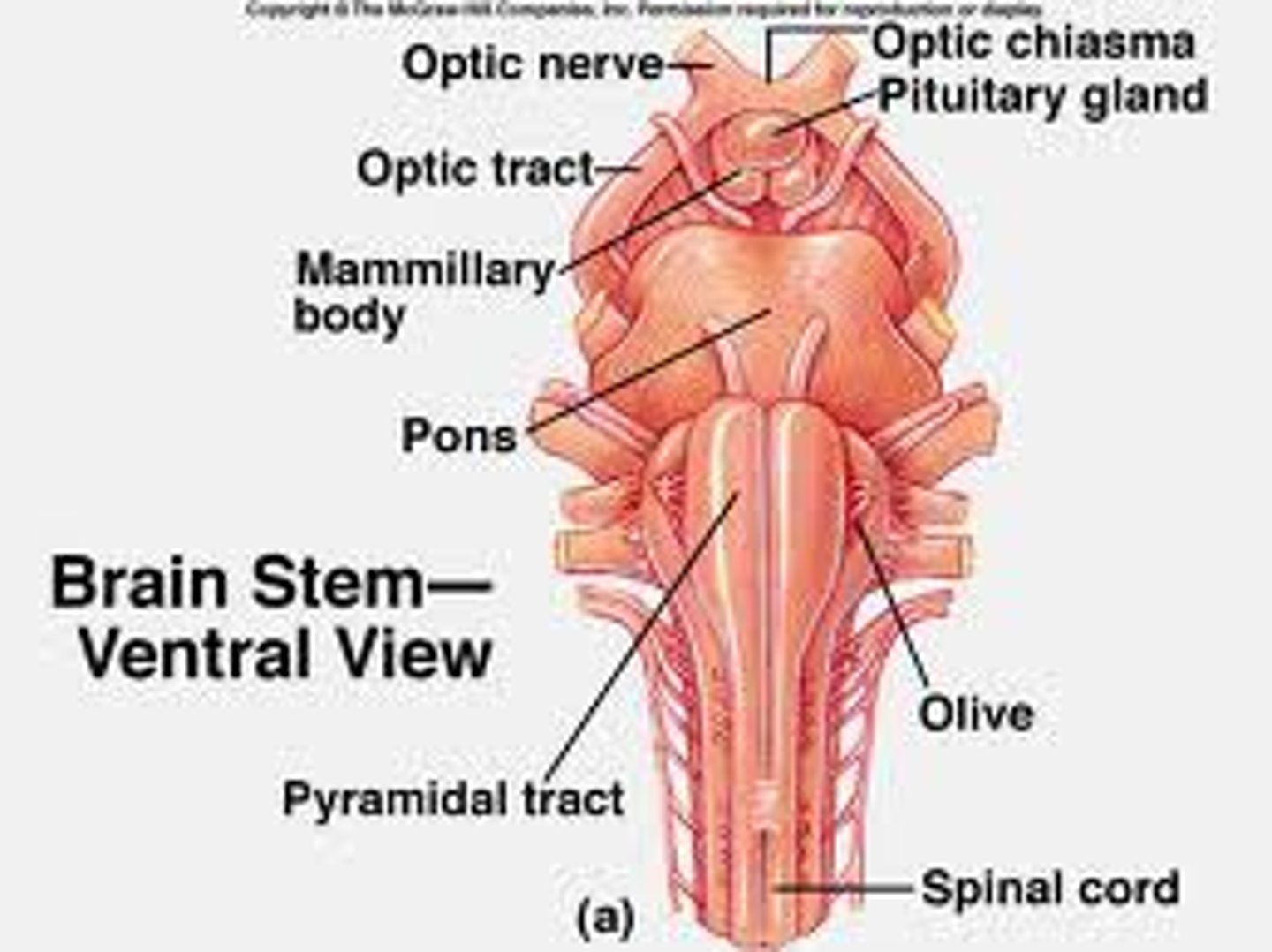
medulla
the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing, responsible for automatic survival functions.
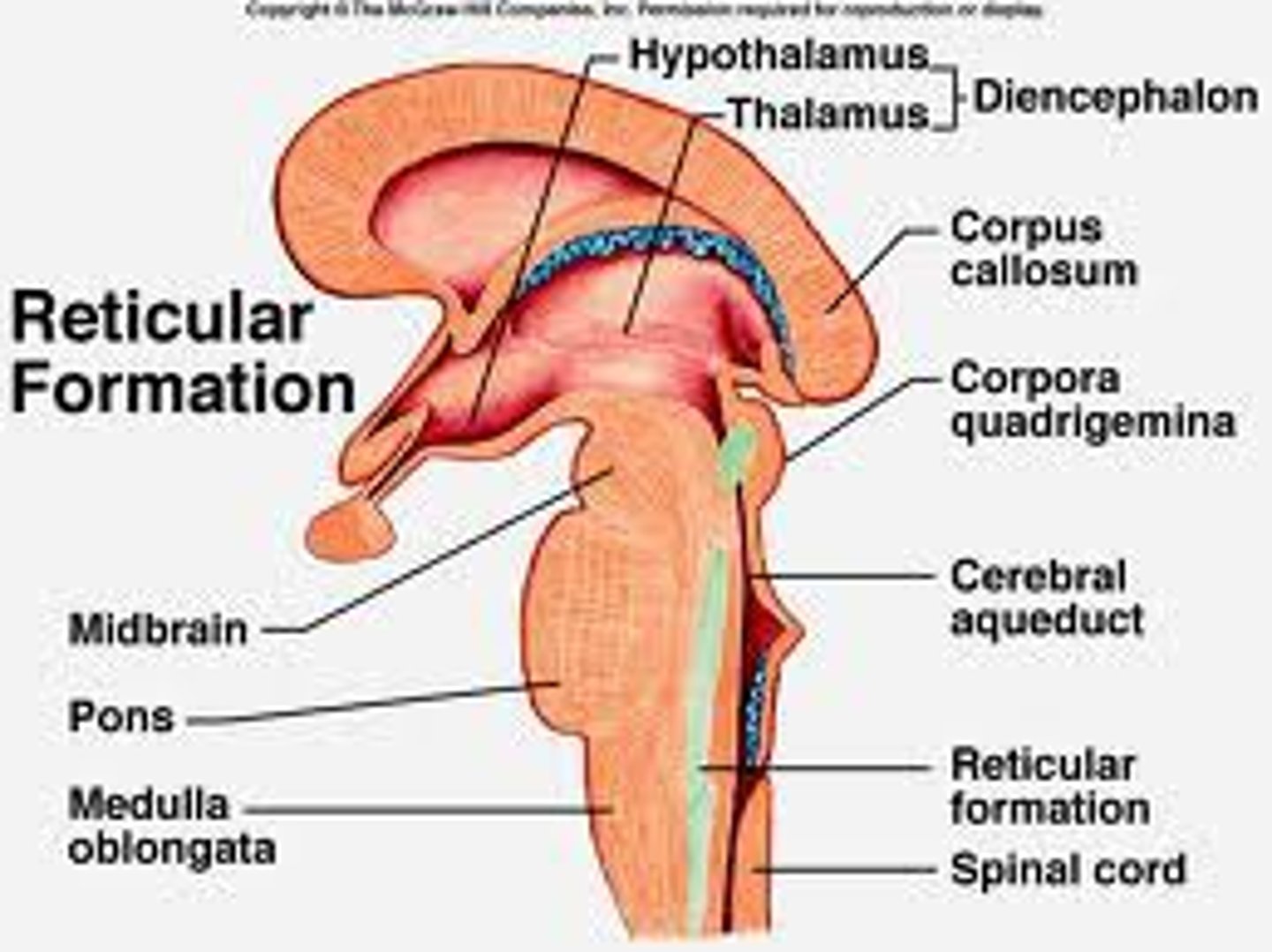
reticular formation
a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal, such as waking you up and alerting your attention.
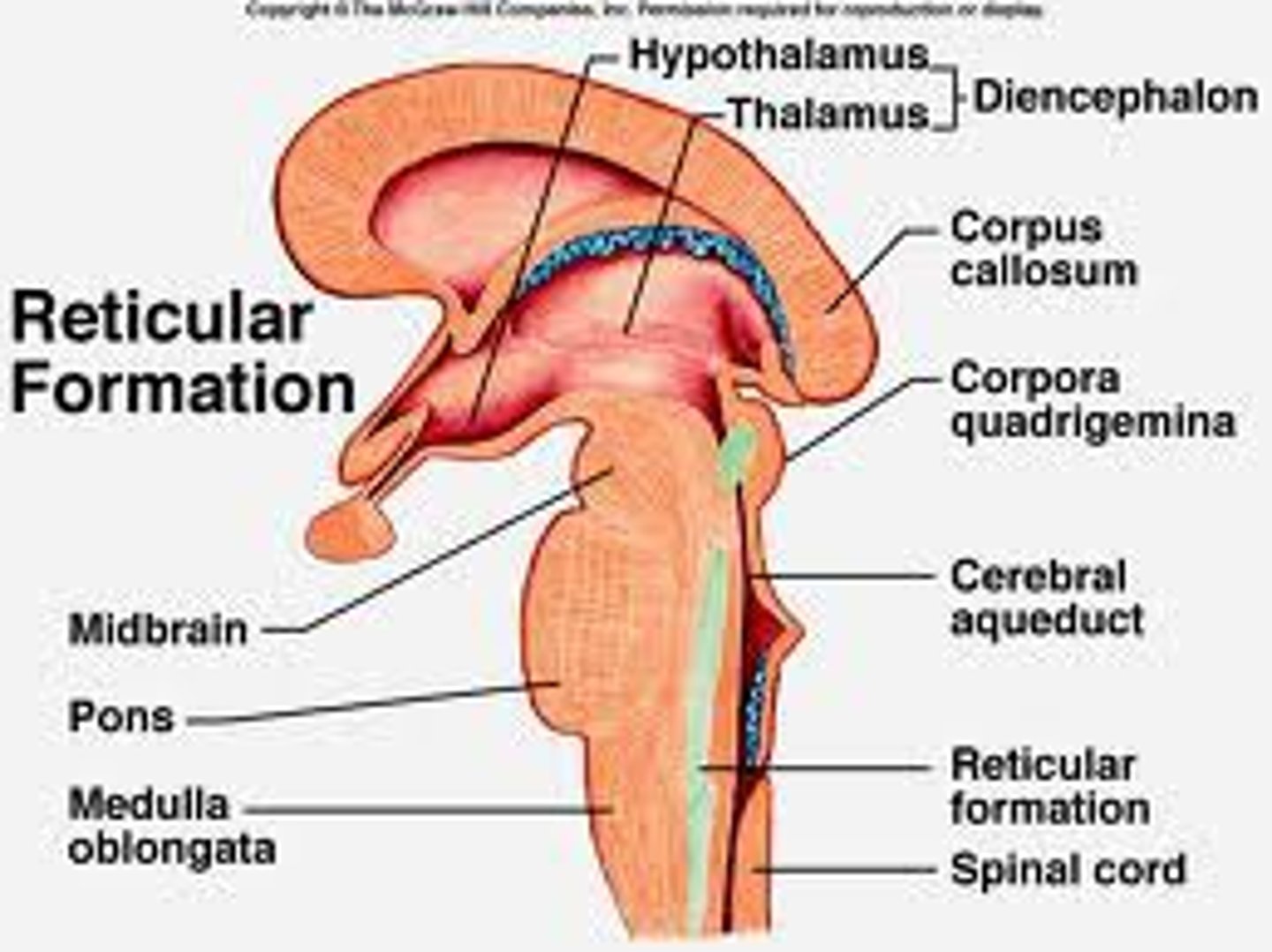
thalamus
the brain's switchboard for senses (all except smell), located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex.
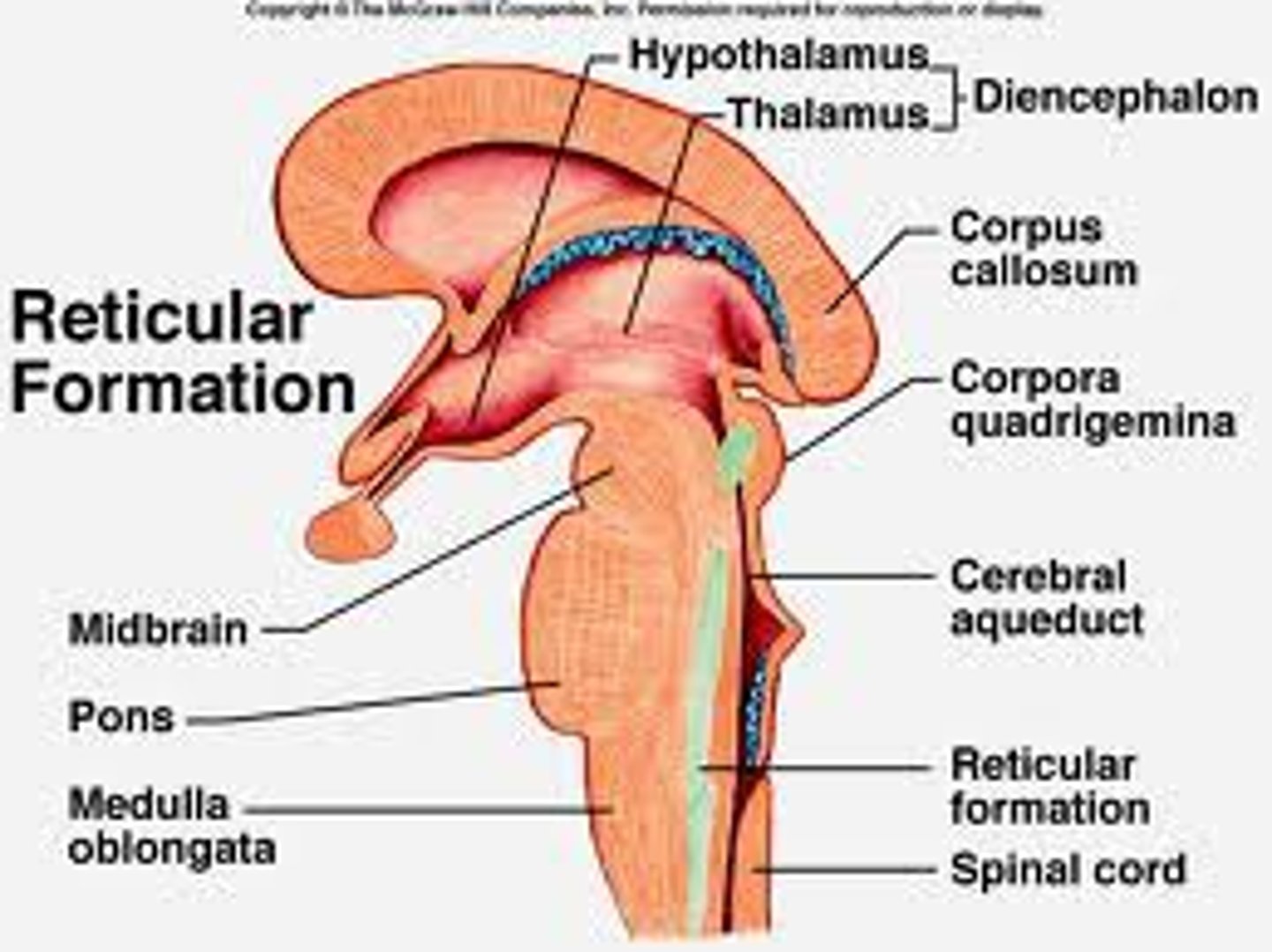
cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; it's responsibility is coordinating movement output and balance control.
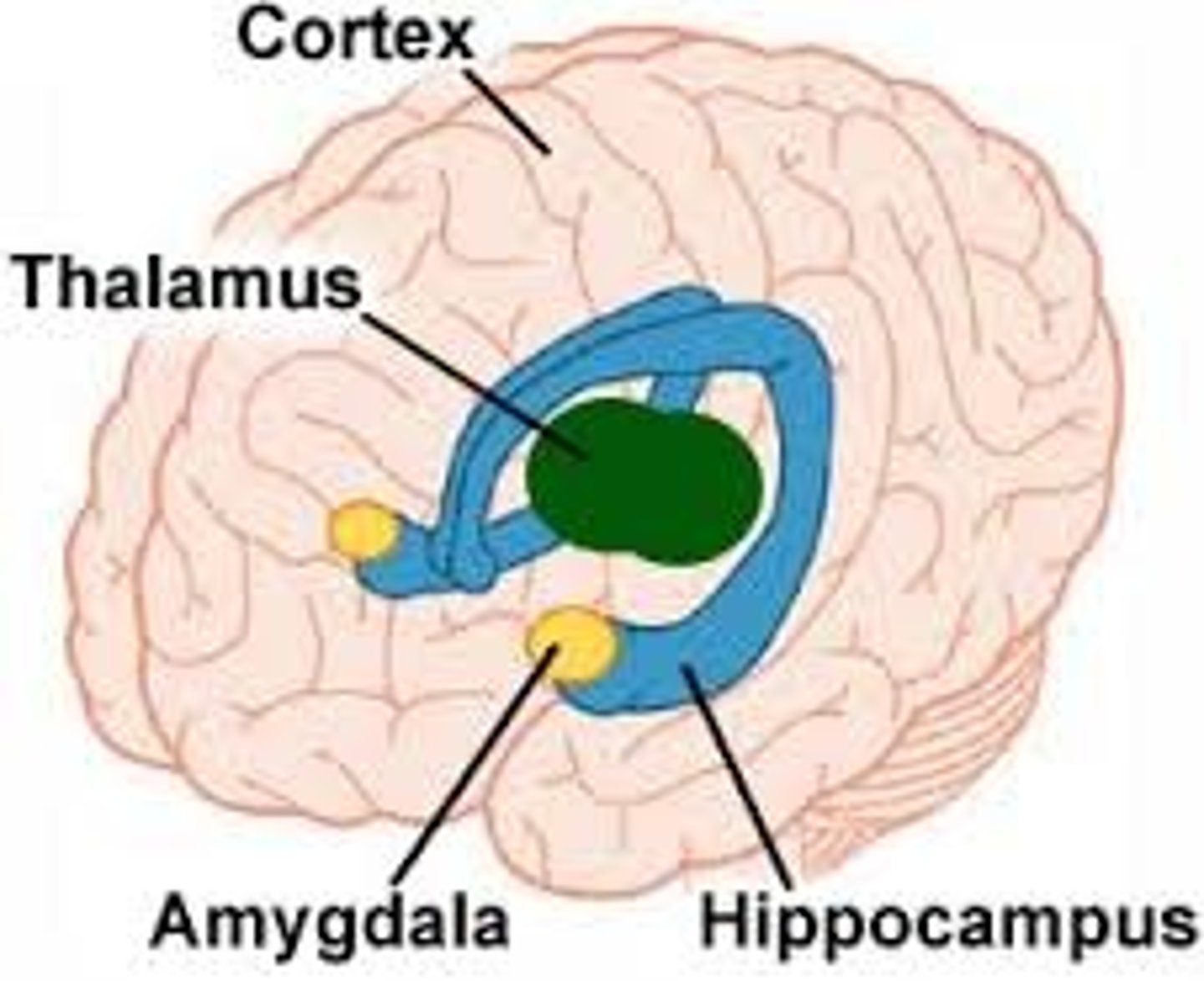
limbic system
doughnut-shaped neural system (including the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus) located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions, drives, and memory.
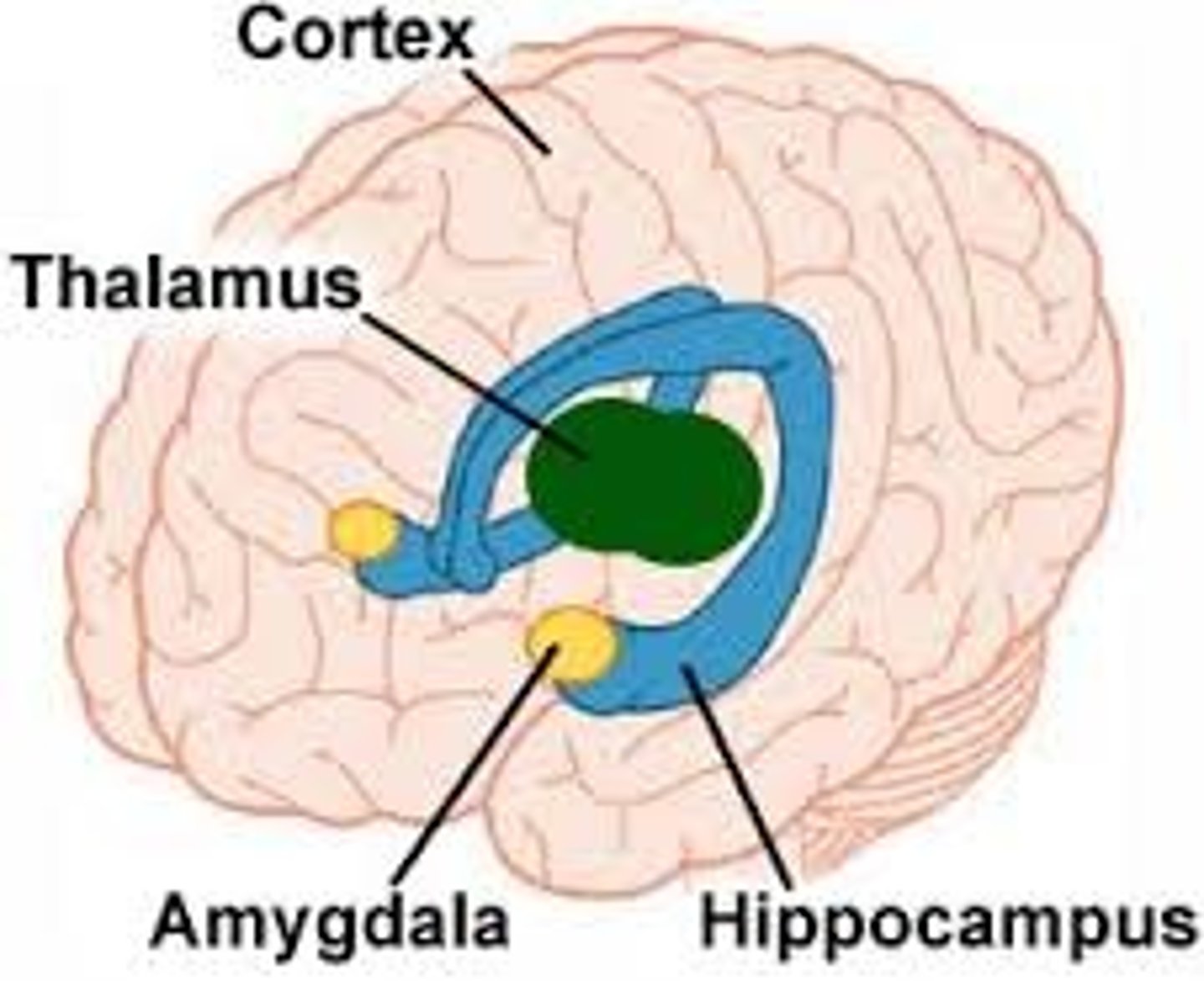
amygdala
lima bean-sized neural cluster in the limbic system; linked to fear and aggression.
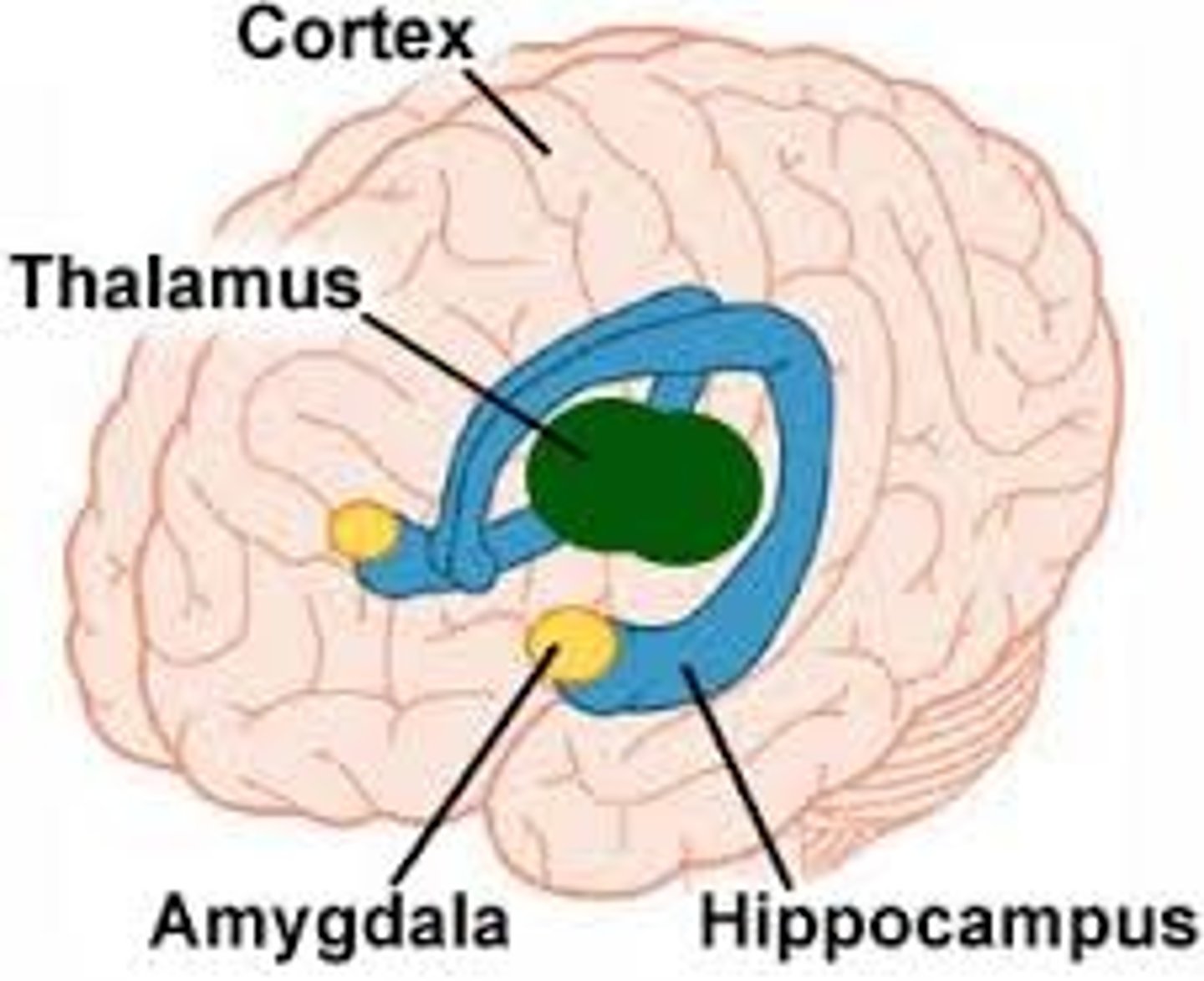
hypothalamus
a neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (hunger, thirst, sexual arousal, and temperature control) , and it is linked to emotion and reward.
cerebral cortex
1/4 inch fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebrum; the body's Ultimate Control and Information-processing center.
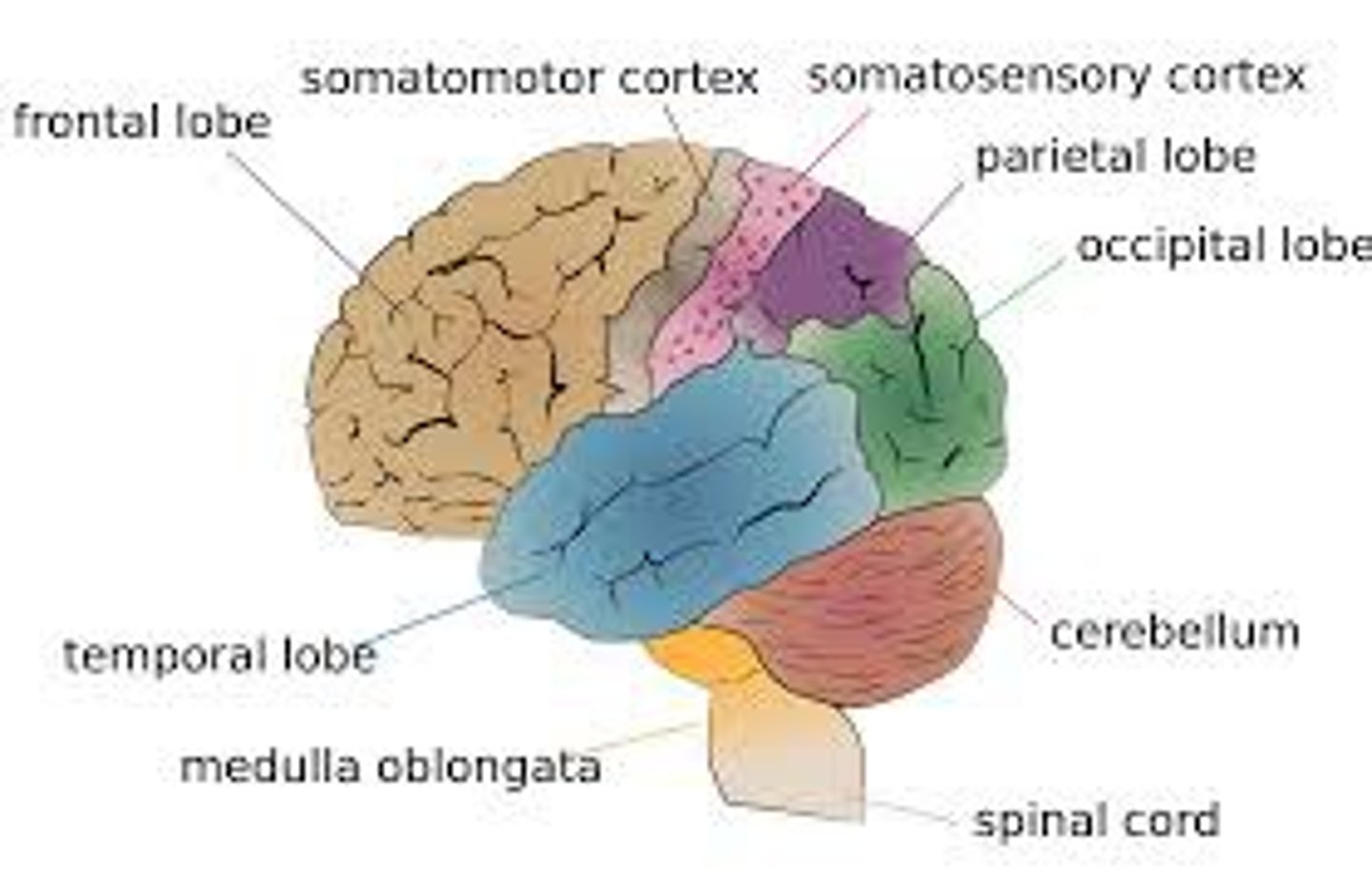
frontal lobes
portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead; involved in speaking and muscle movements and in making plans and judgments.
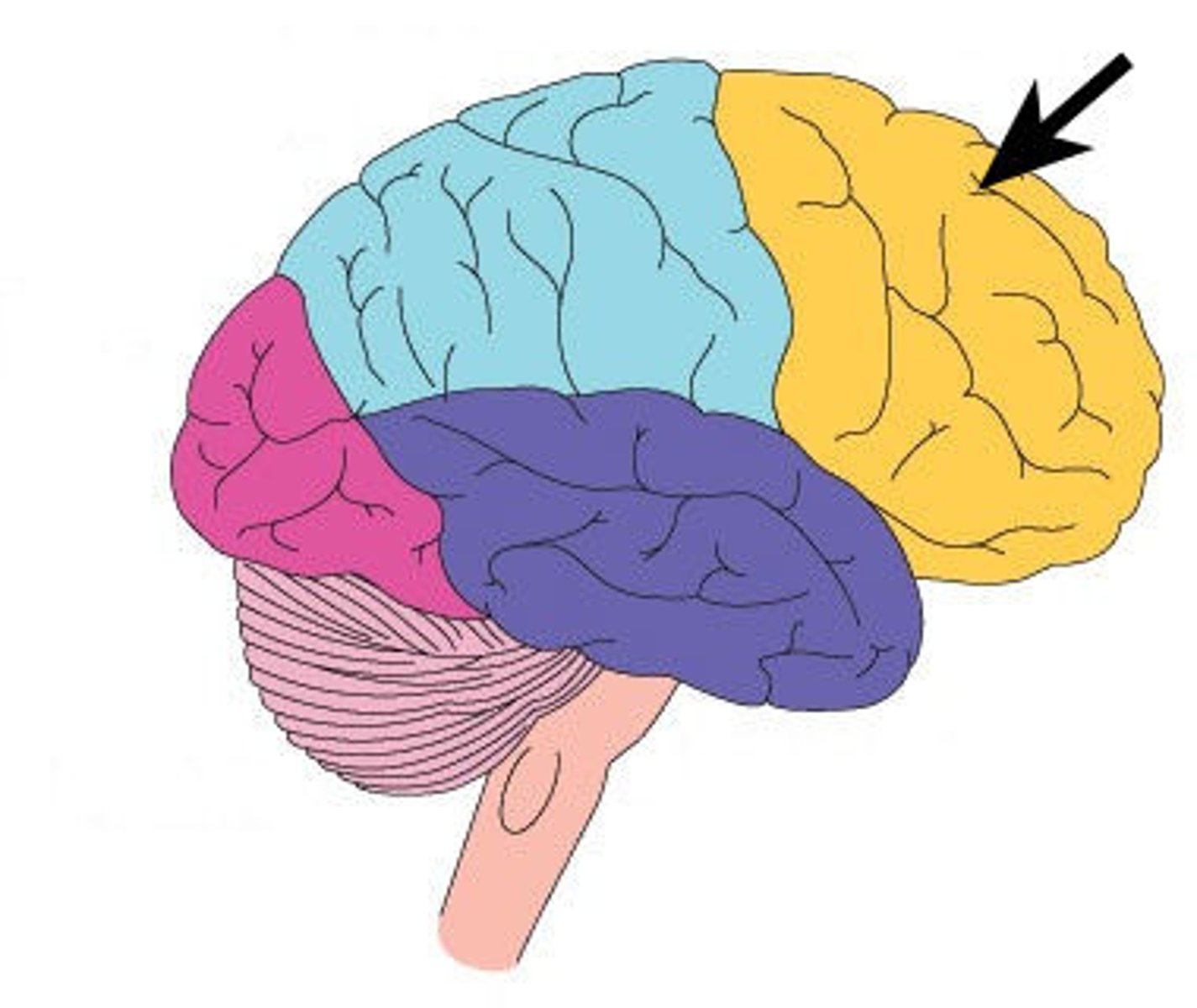
parietal lobes
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position.
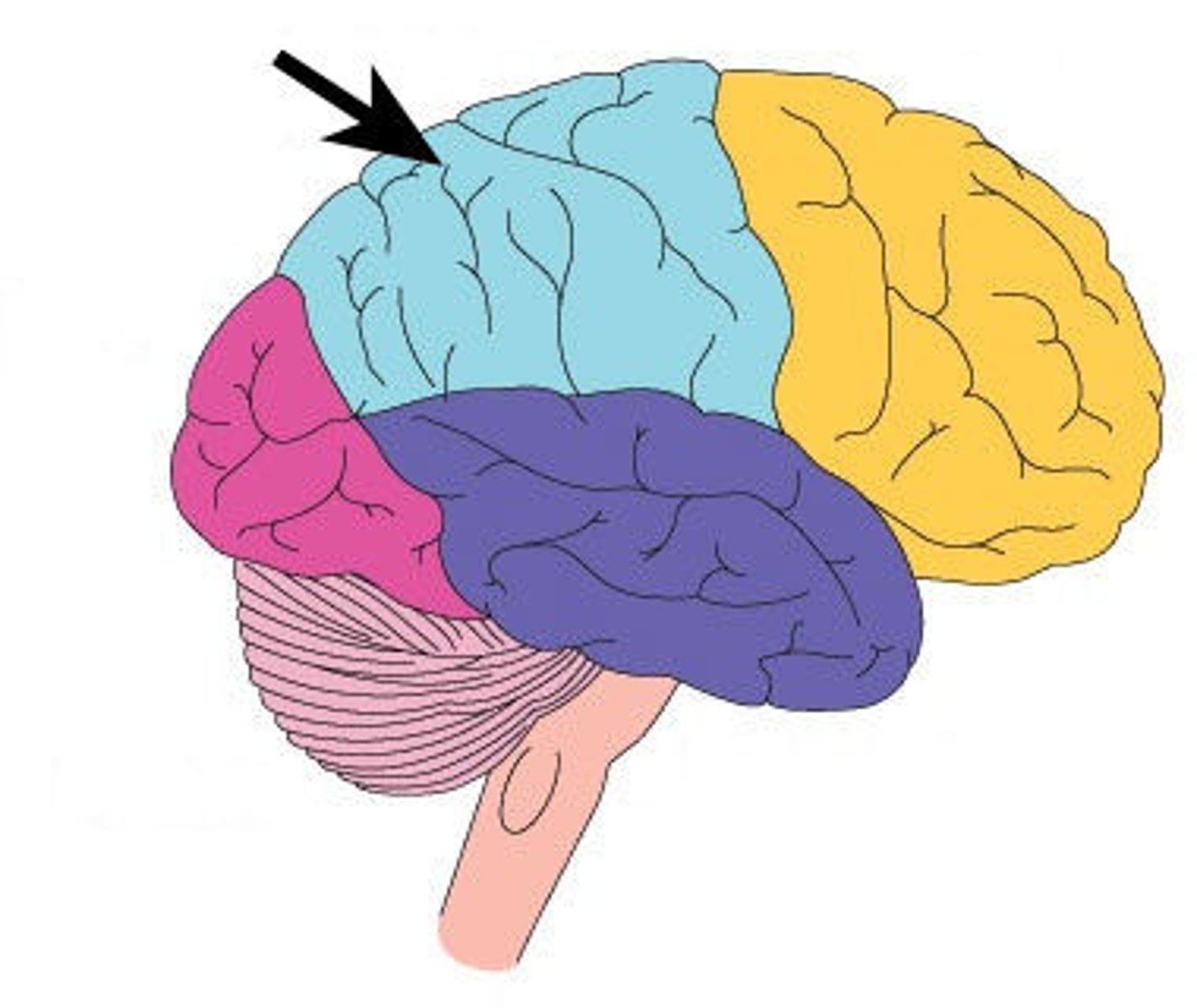
occipital lobes
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; includes areas that receive information from the visual fields.
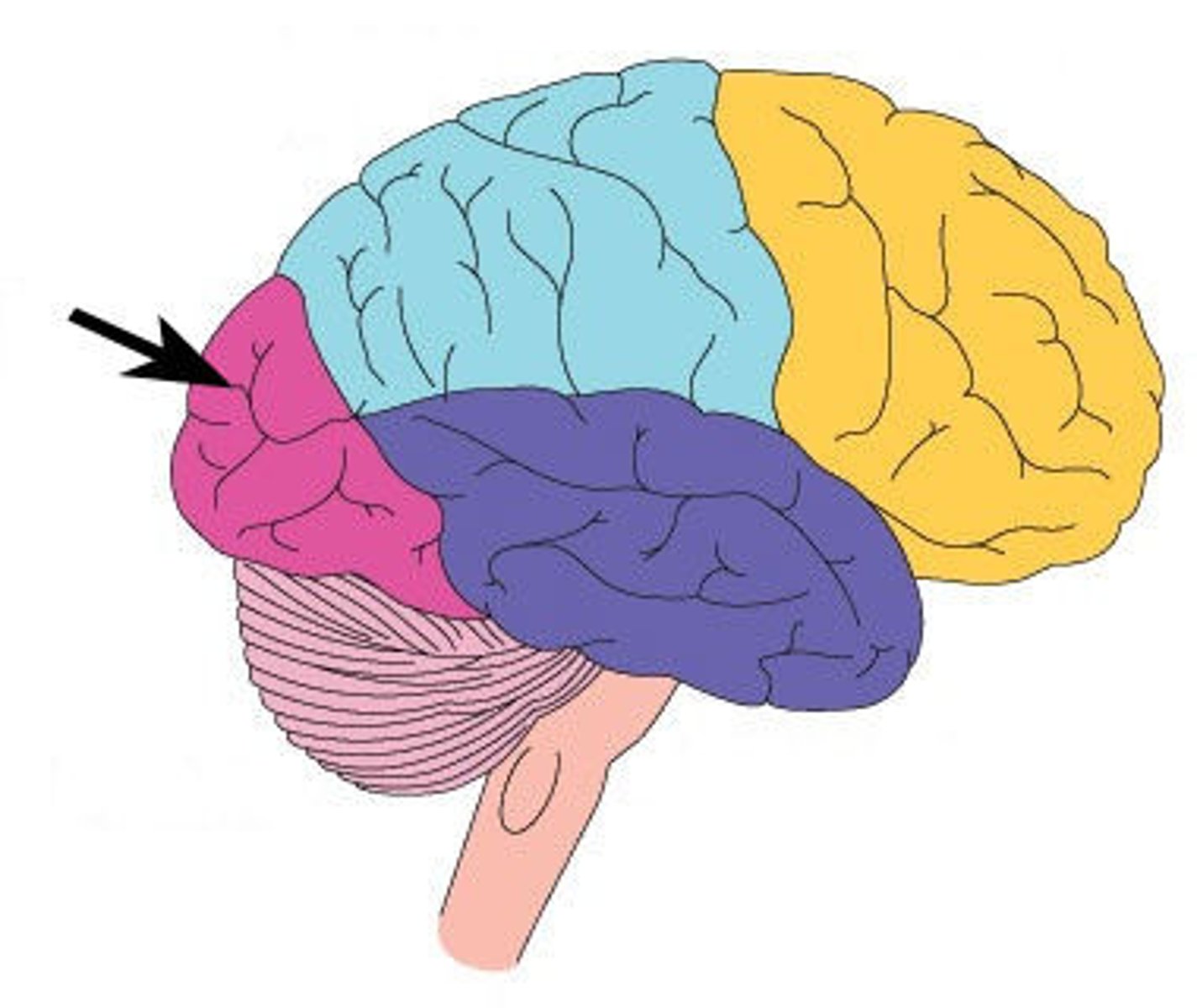
temporal lobes
portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear.
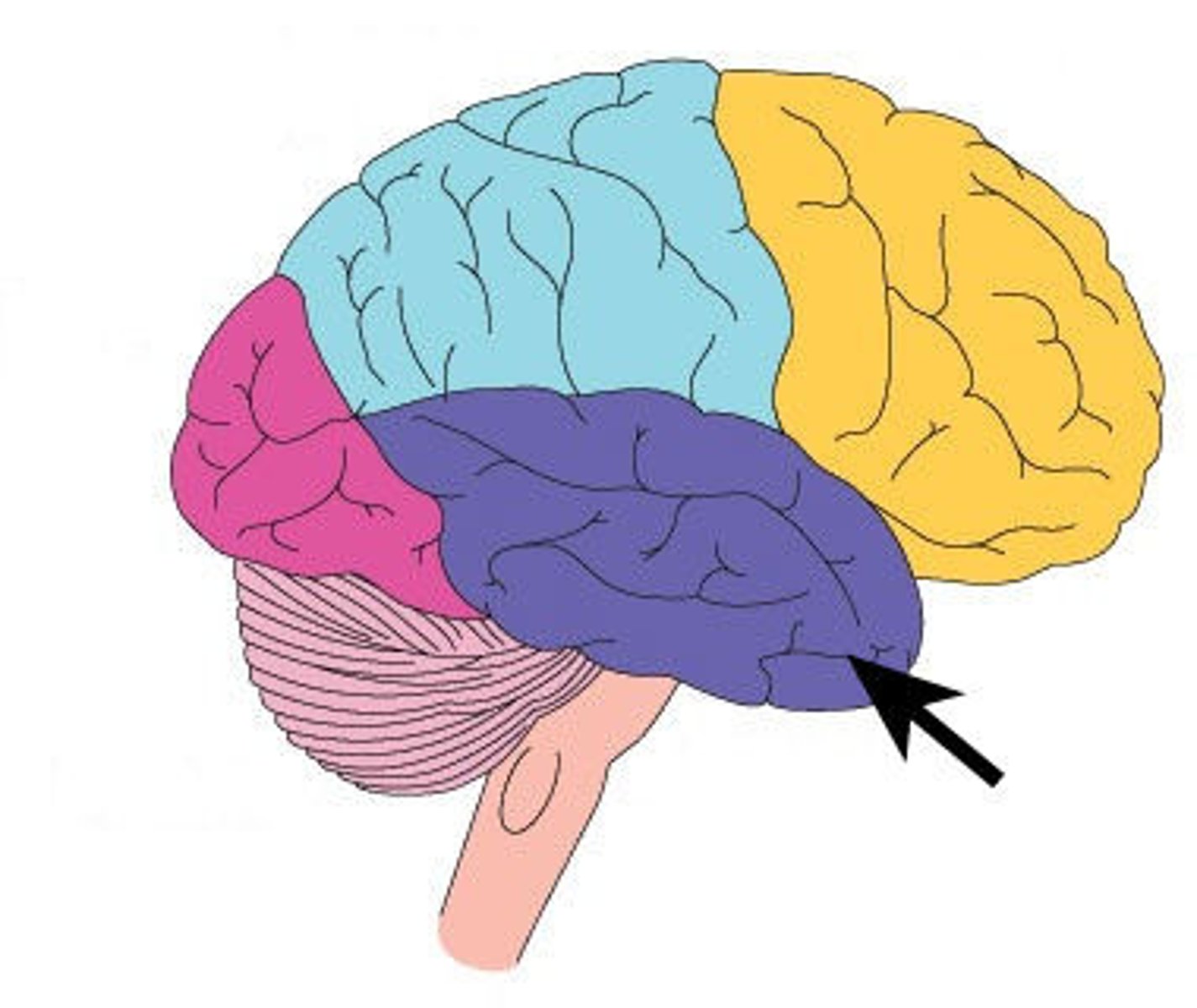
motor cortex
an area/strip at the rear of the frontal lobes (where you'd wear headphones) that controls voluntary movements.
sensory cortex
area/strip at the front of the parietal lobes (where you'd wear headphones) that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations.
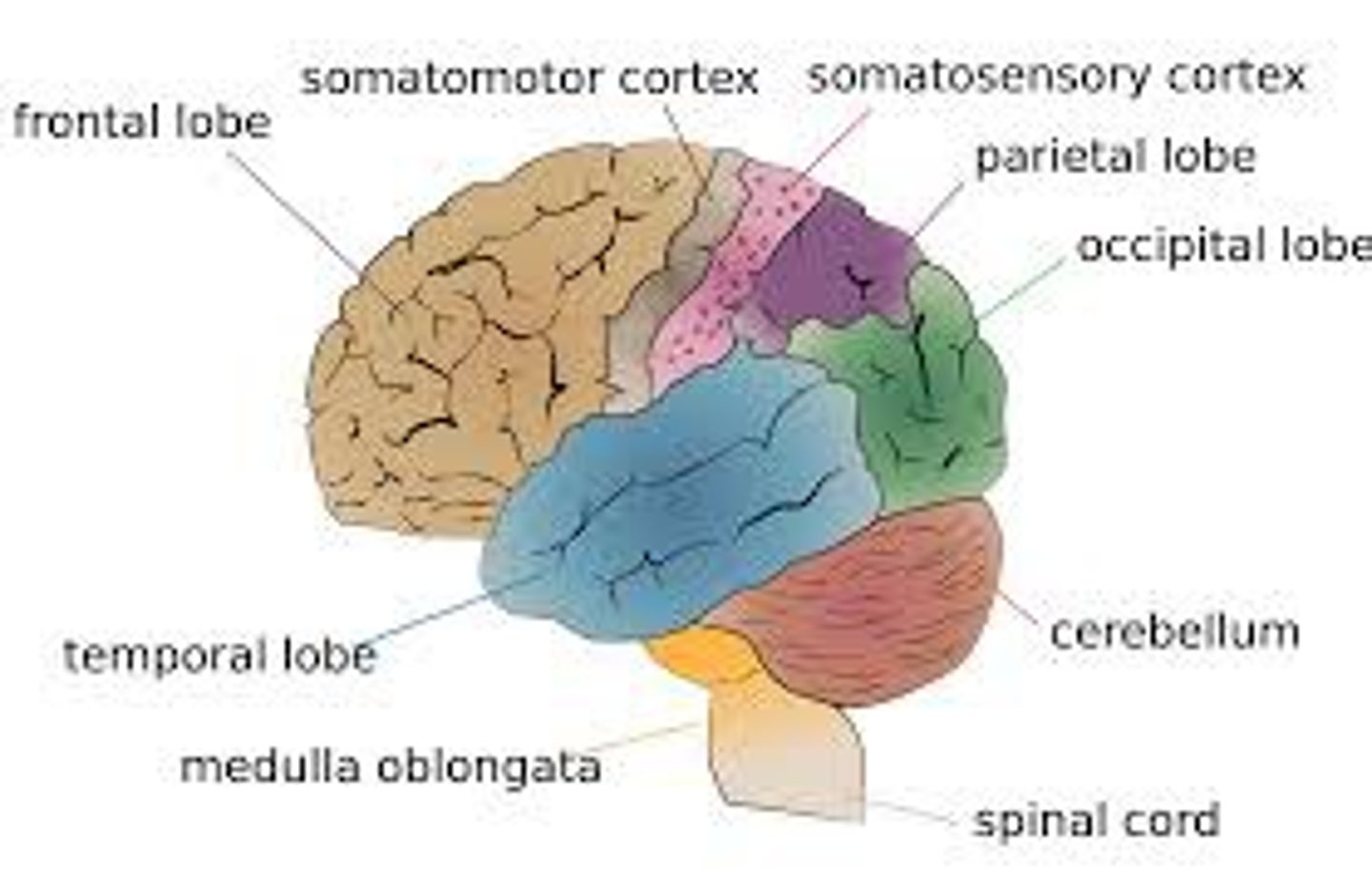
association areas
areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking.
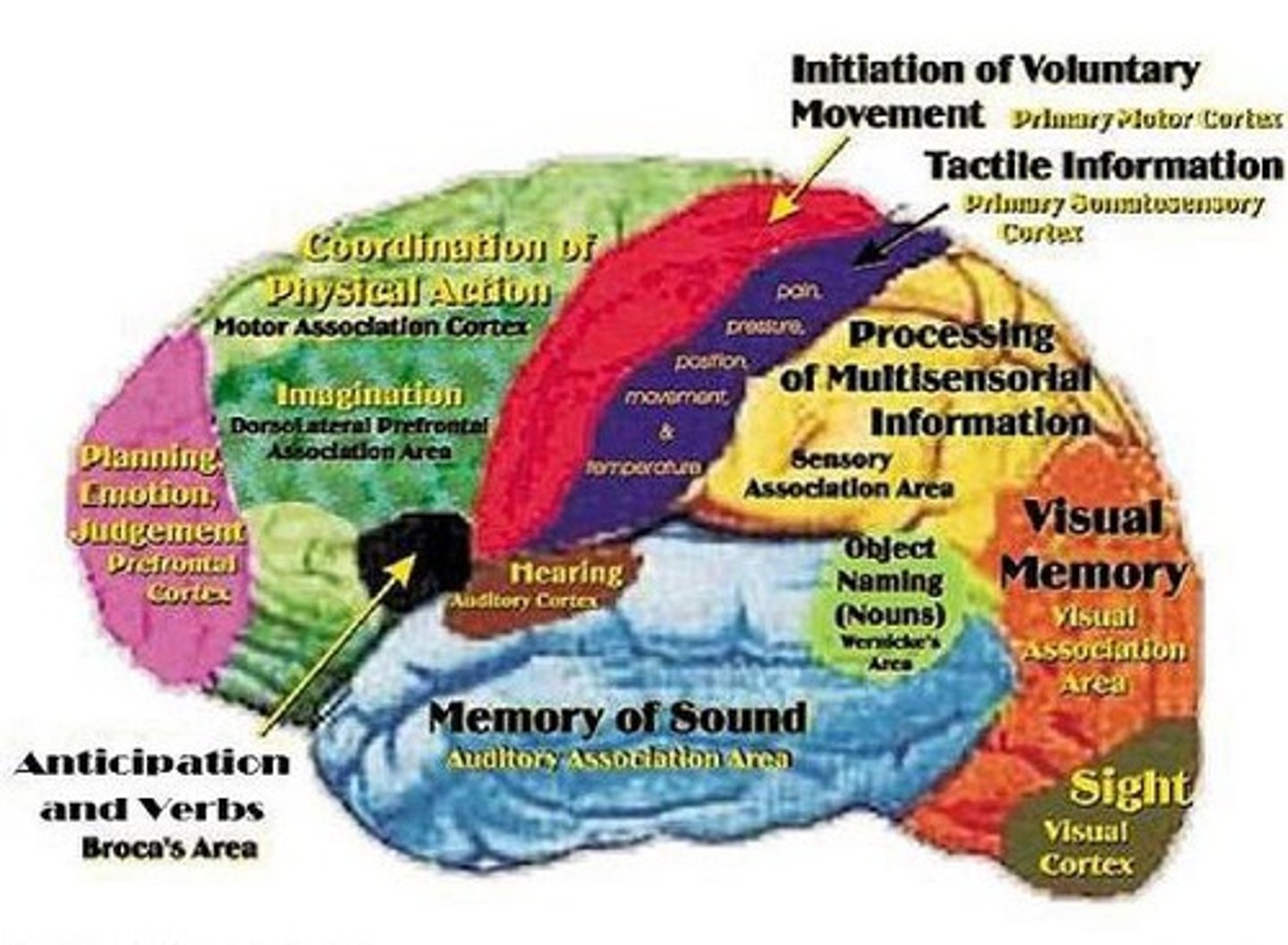
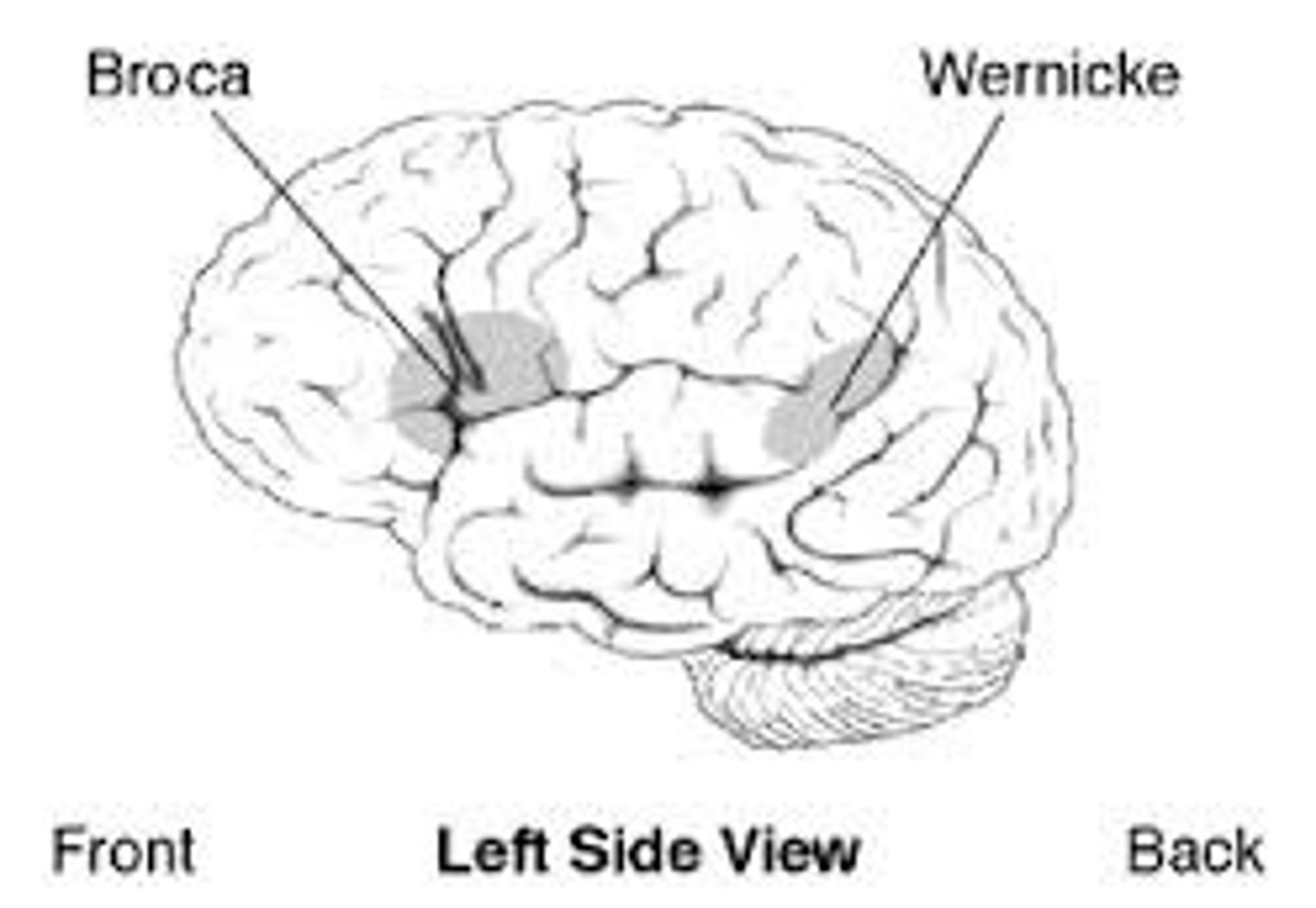
aphasia
impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca's area (impairing speaking) or to Wernicke's area (impairing understanding).
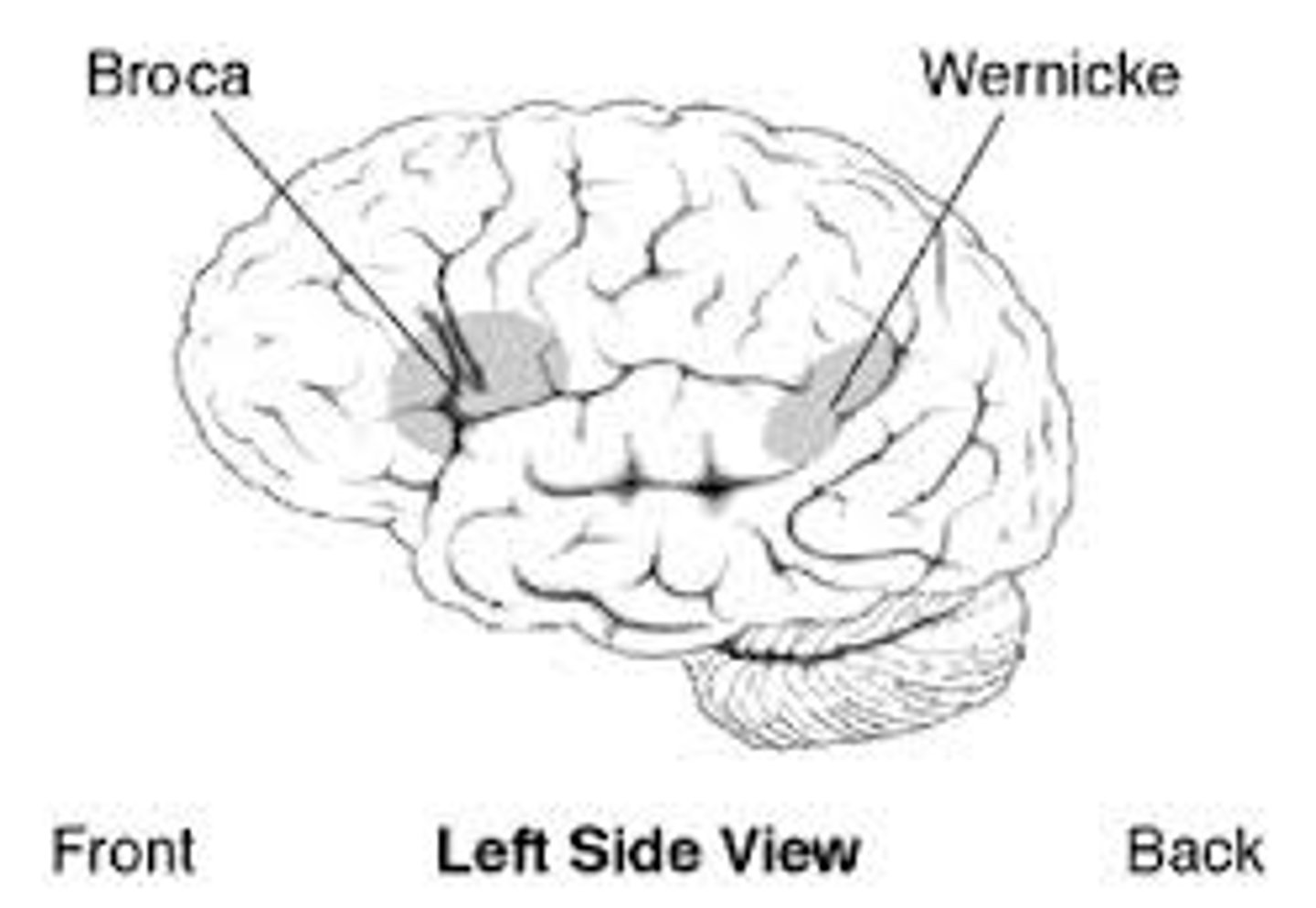
Broca's area
controls Language Expression—an area, usually in the left frontal lobe, that directs the muscle movements involved in speech.
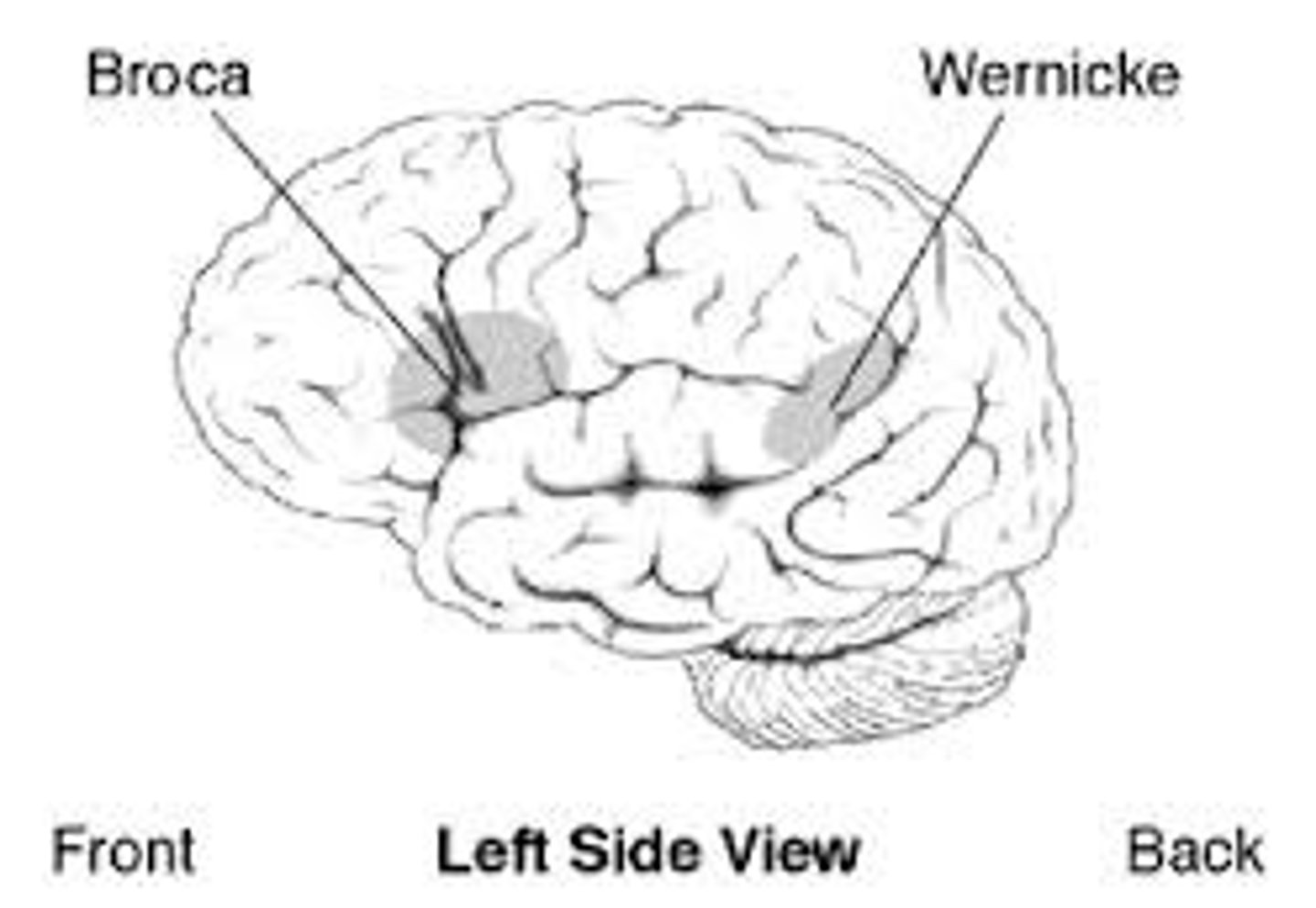
Wernicke's area
controls Language Reception—a brain area involved in language comprehension and expression; usually in the left temporal lobe.
plasticity
the brain's ability to change and adapt, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience.
neurogenesis
the formation of new neurons.

corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them, usually cut due to uncontrollable seizures
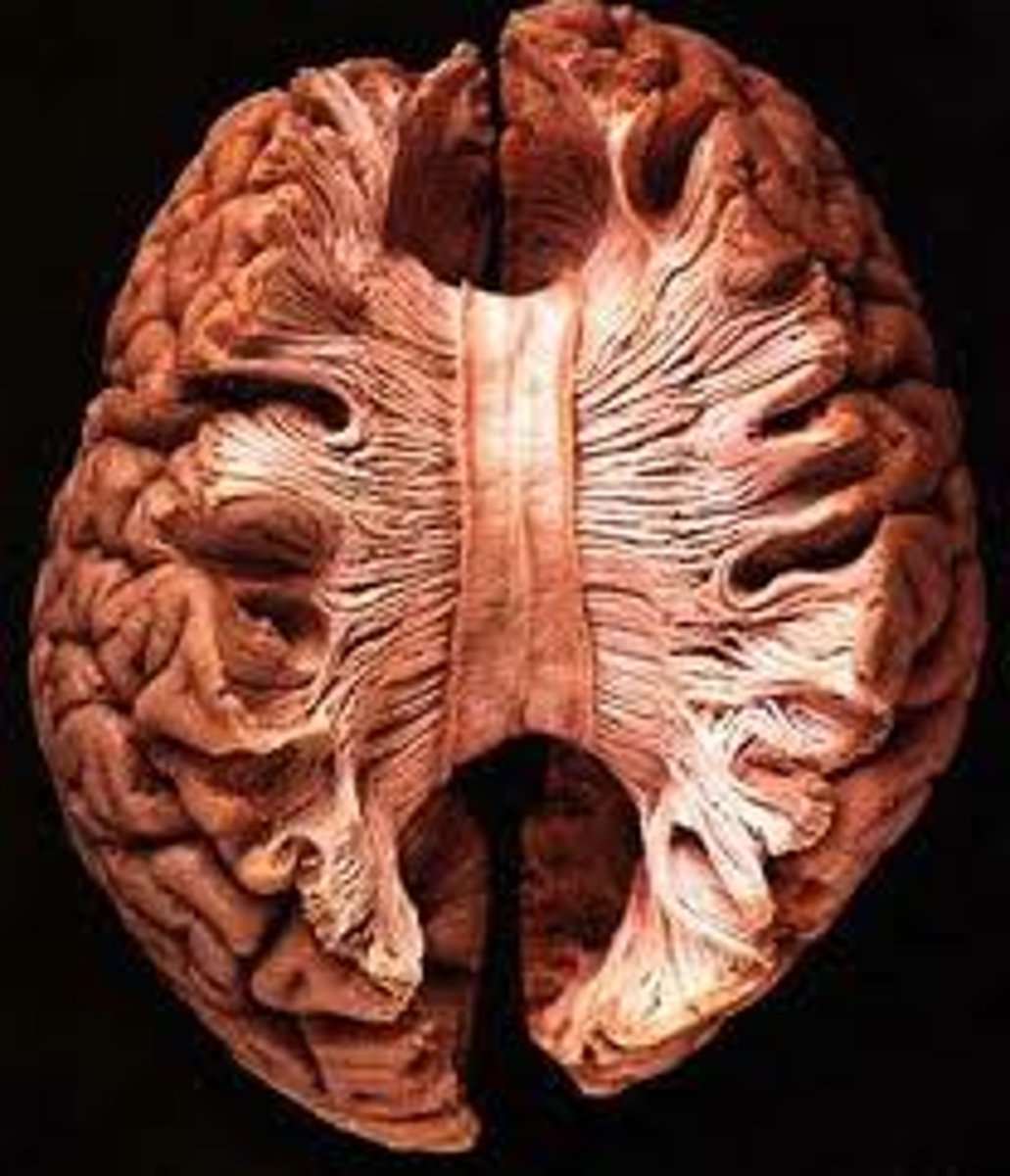
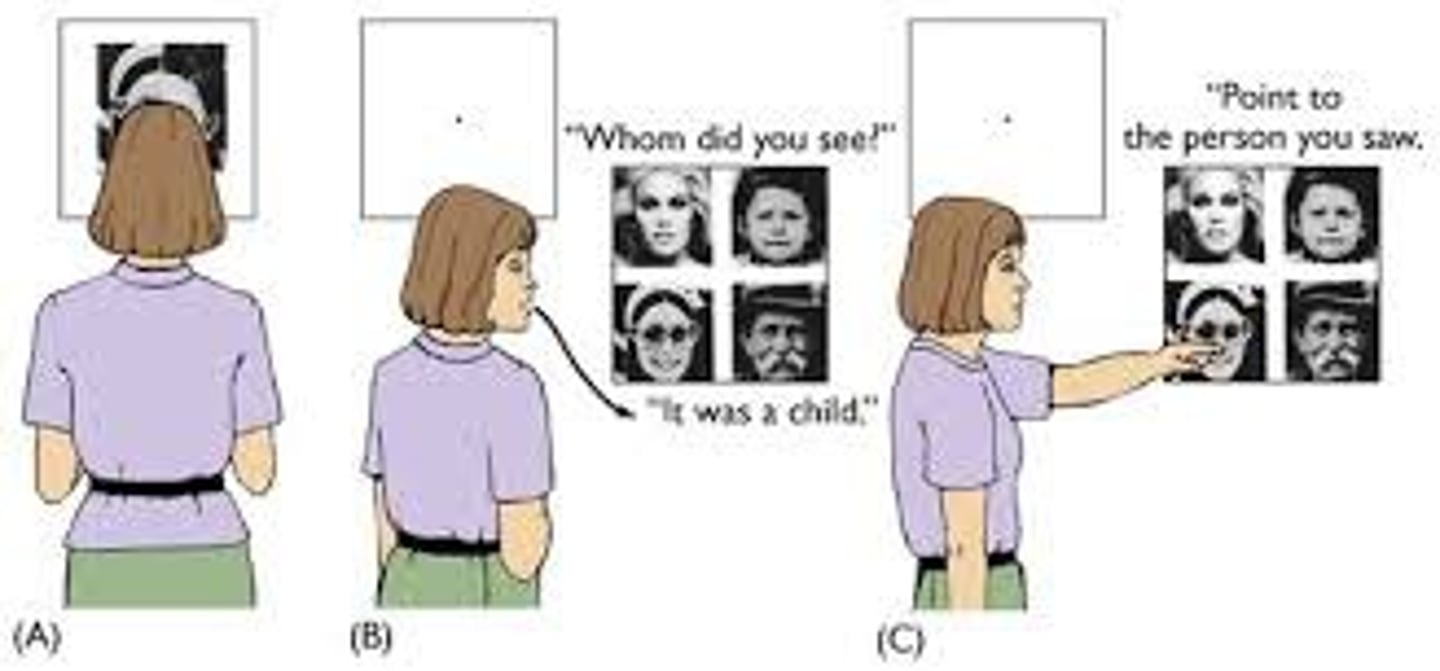
split brain
a condition resulting from surgery that isolates the brain's two hemispheres by cutting the fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) connecting them.
cognitive neuroscience
the interdisciplinary study of the brain activity linked with cognition (including perception, thinking, memory, and language).

dual processing
the principle that information is often simultaneously processed on separate conscious and unconscious tracks.
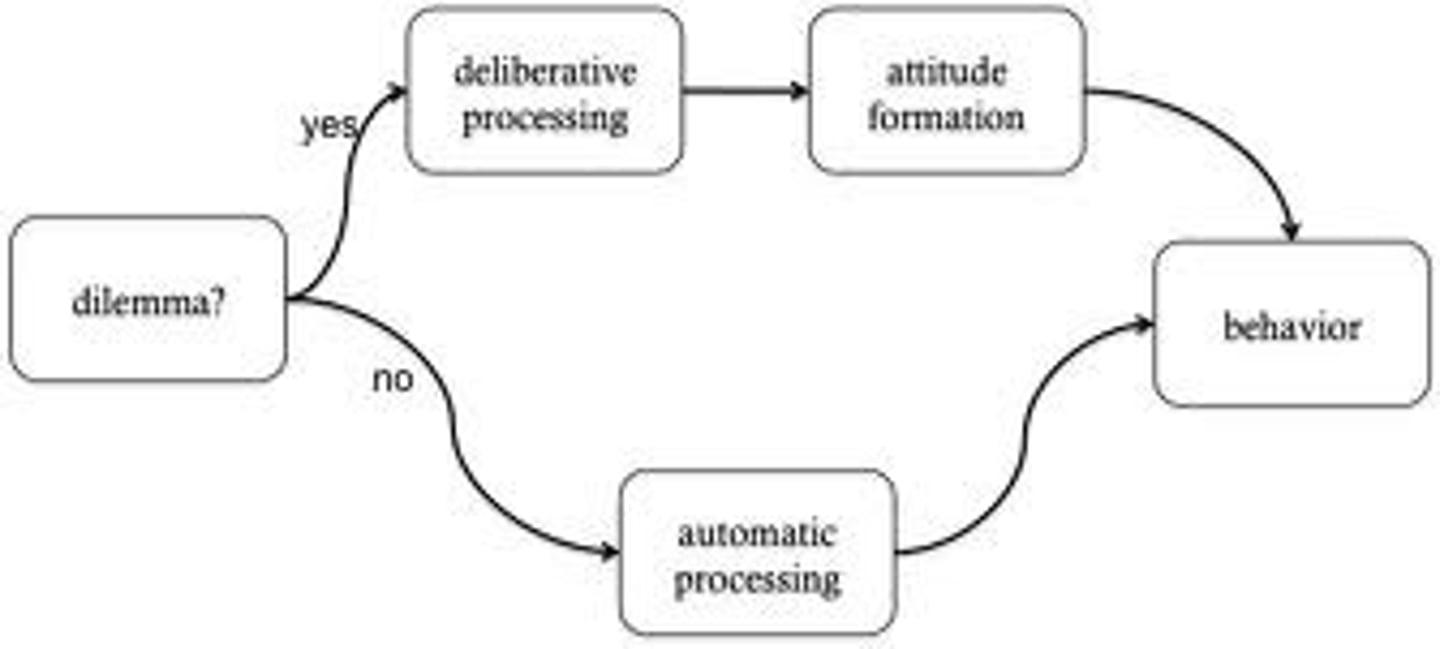
PET scan
a visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task such as movement or talking
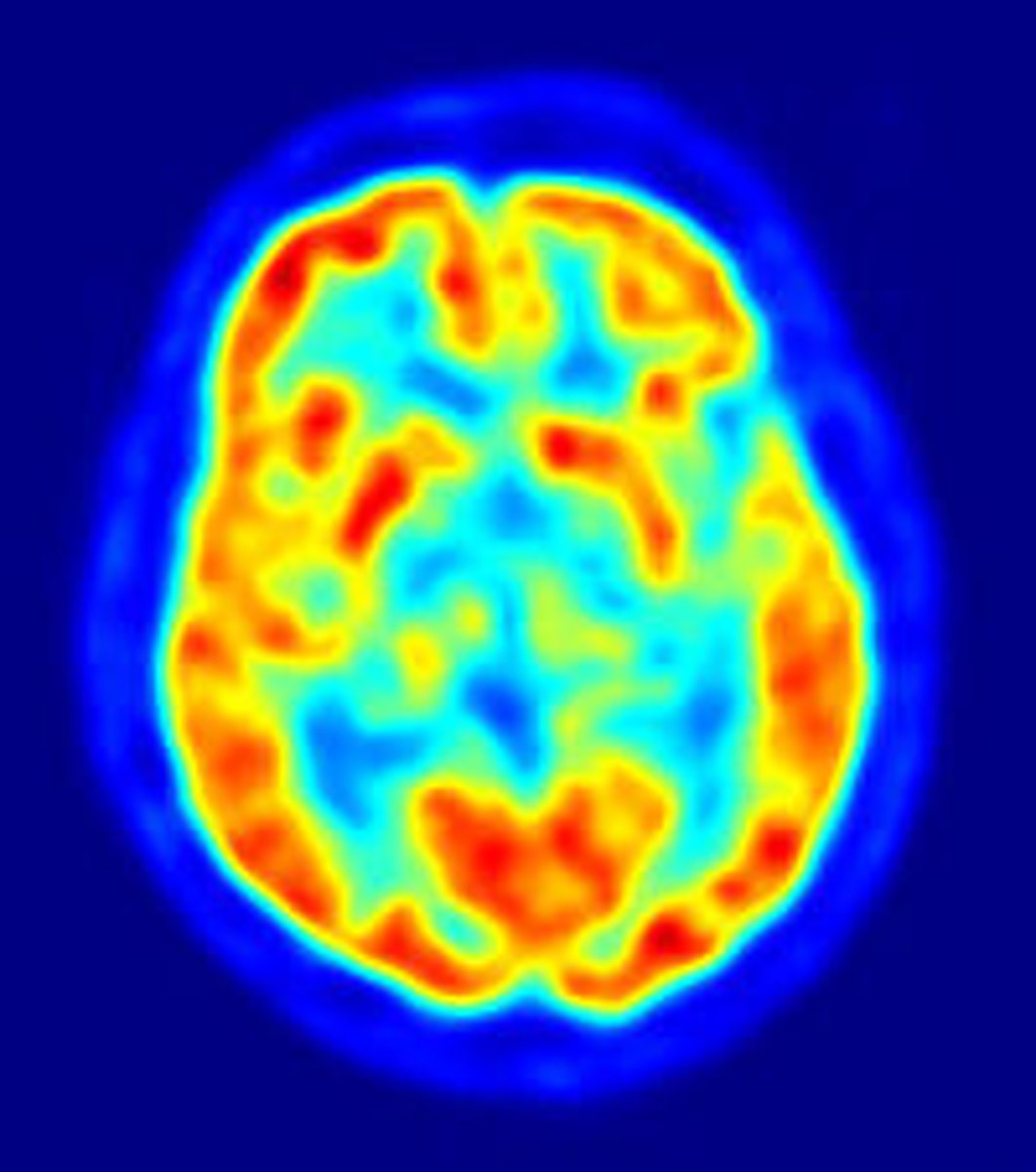
MRI
a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue. May be used to detect fluid in brain, for example.
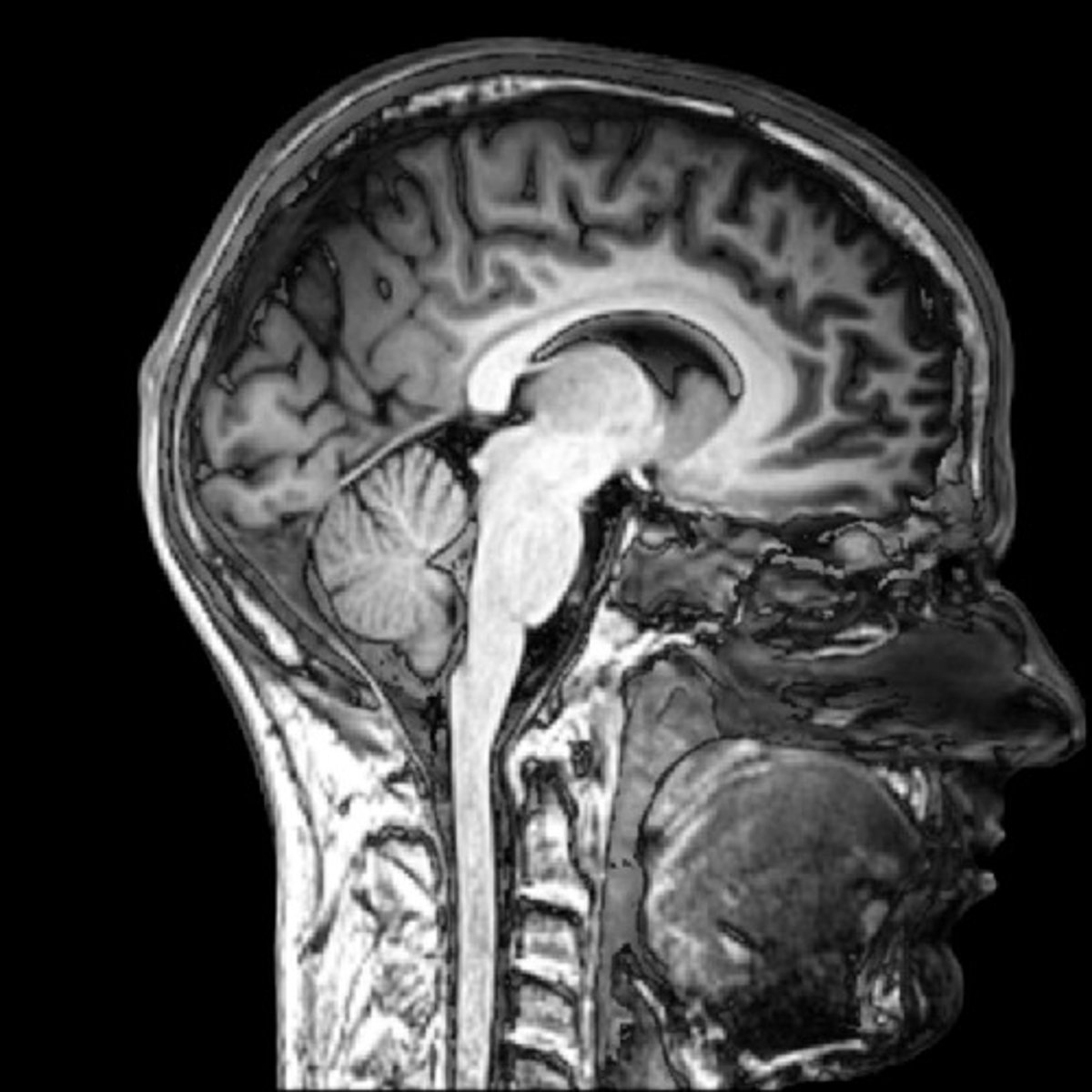
fMRI
a technique for revealing blood flow and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans, used to map pain centers.
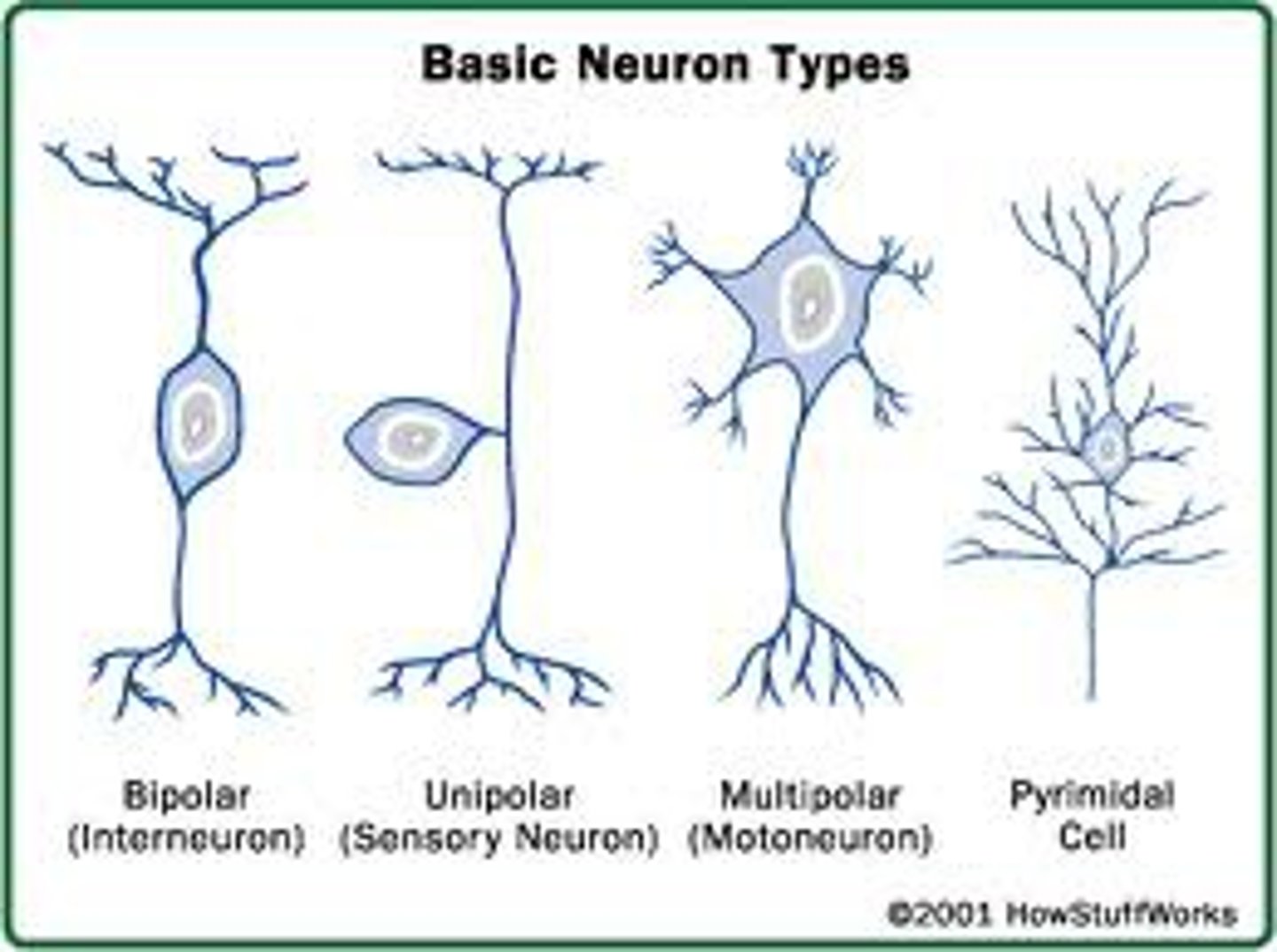
sensory neuron
type of neuron that carries information from sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
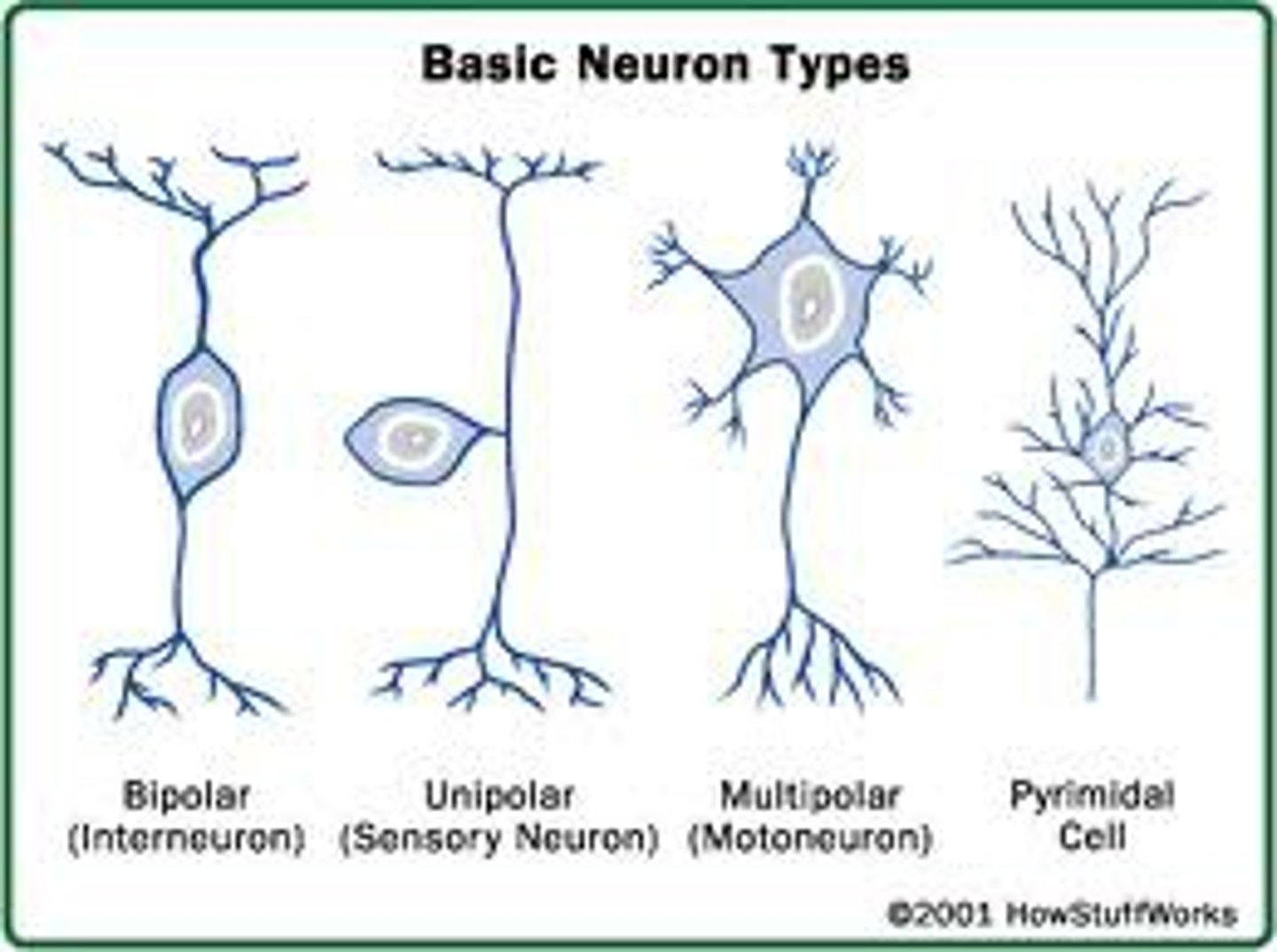
motor neuron
type of neuron that carries information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and joints
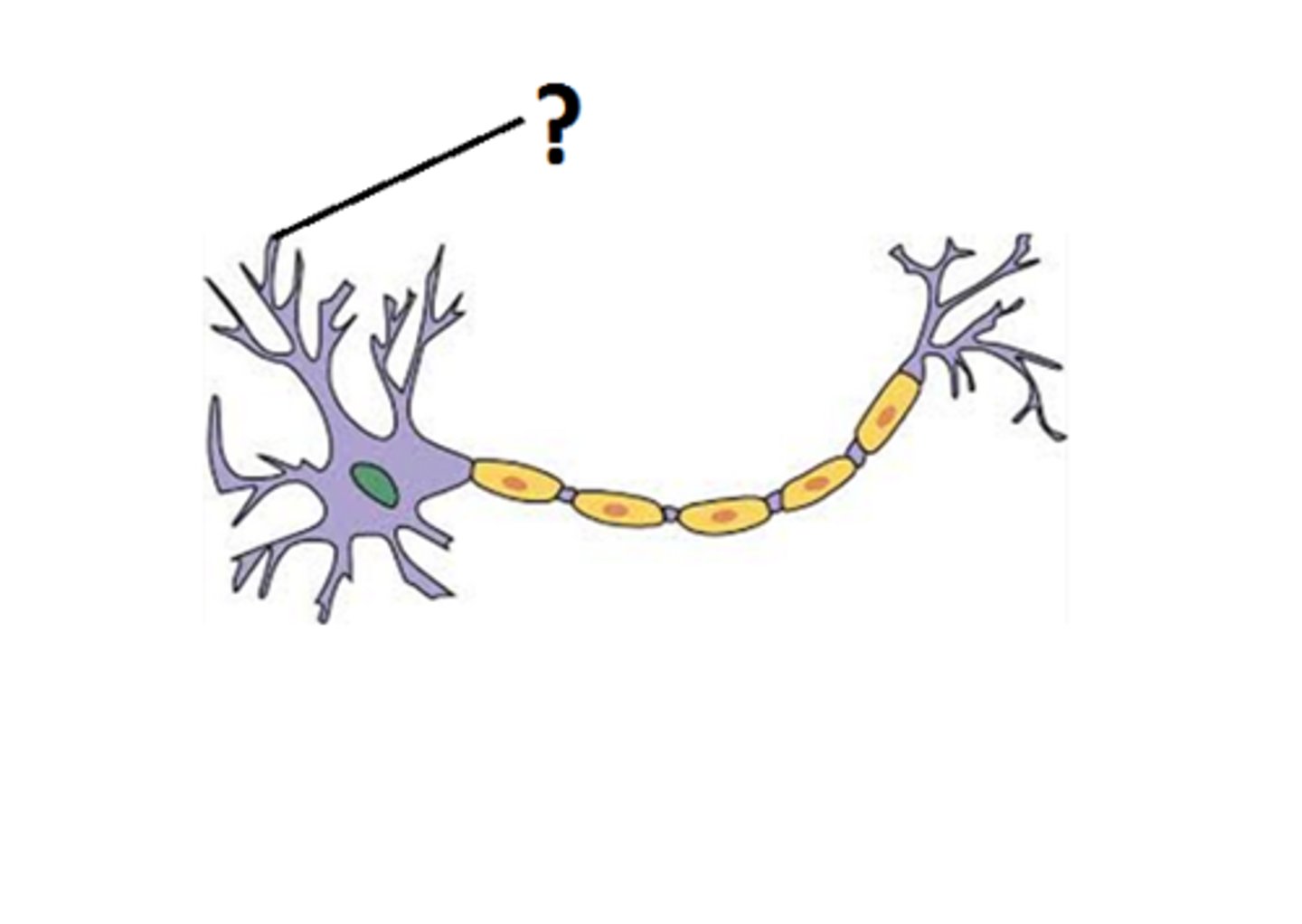
dendrite
branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
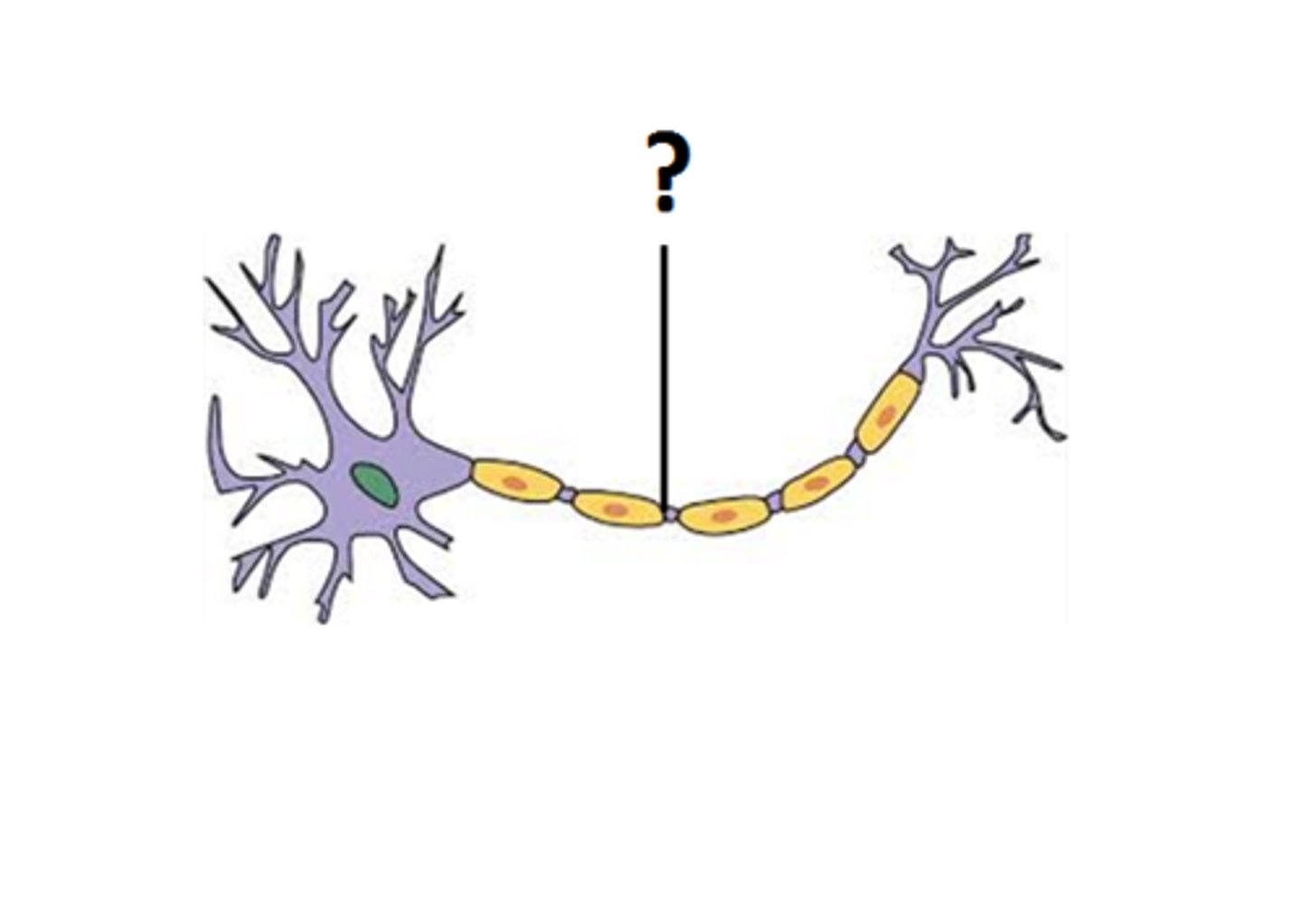
axon
extension of a neuron through which messages pass to other neurons (or muscles or glands), the longest part of the neuron
myelin sheath
layer of fatty tissue encasing neuron fibers that enhances speed of neural transmission
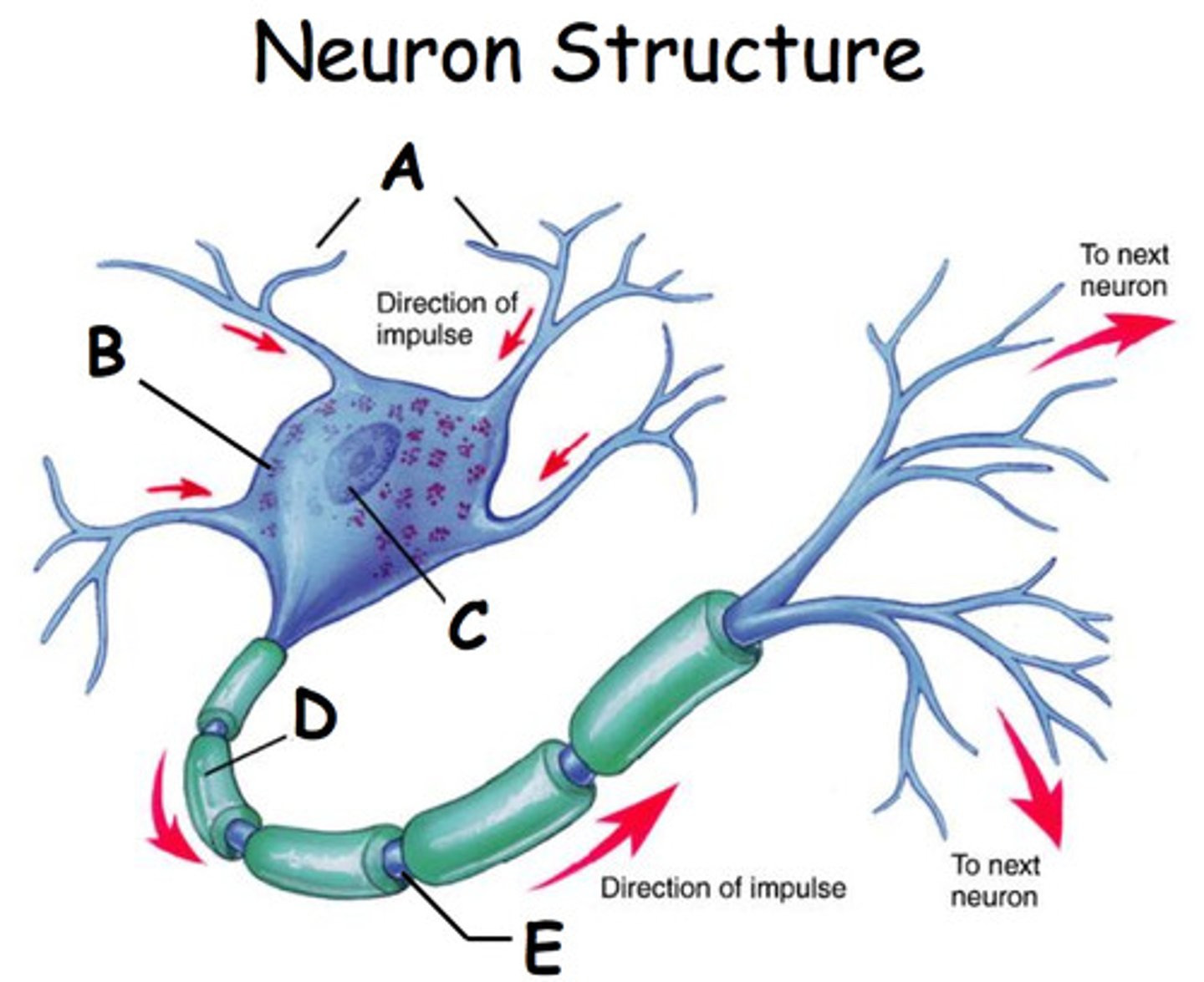
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
synapse
junction between the terminal branches of axon of the sending neuron and the dendrites of the receiving neurons
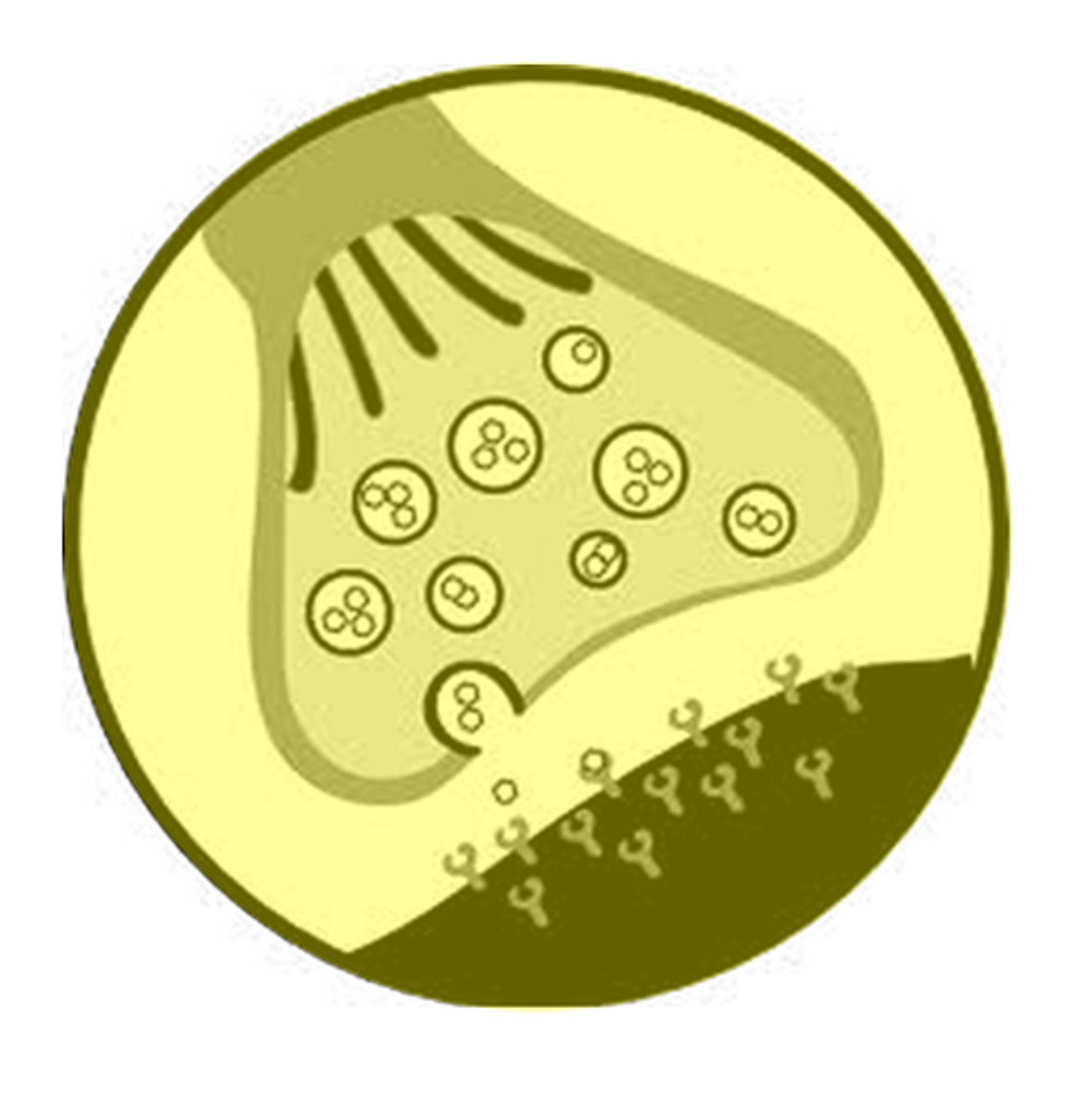
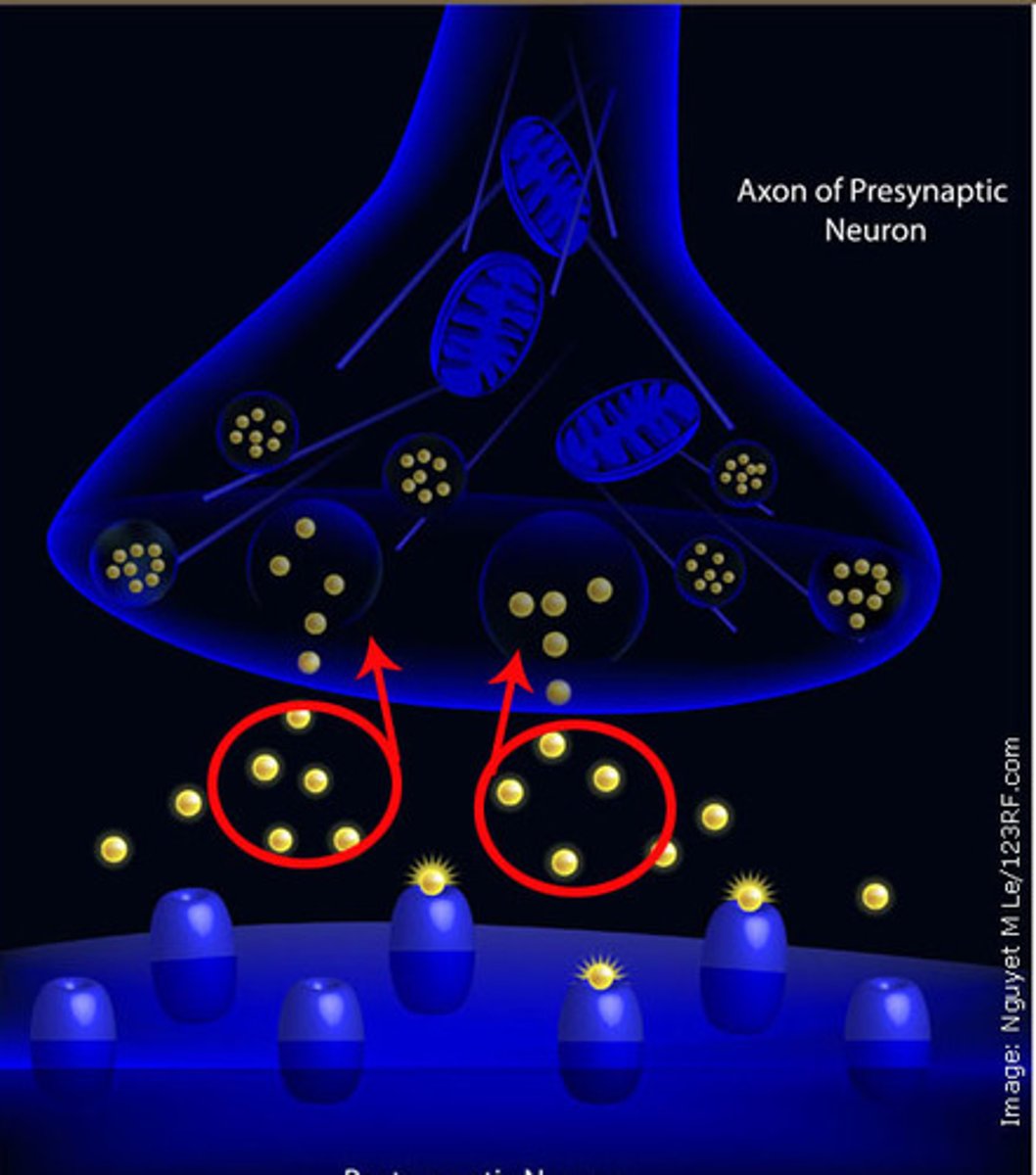
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gap between neurons
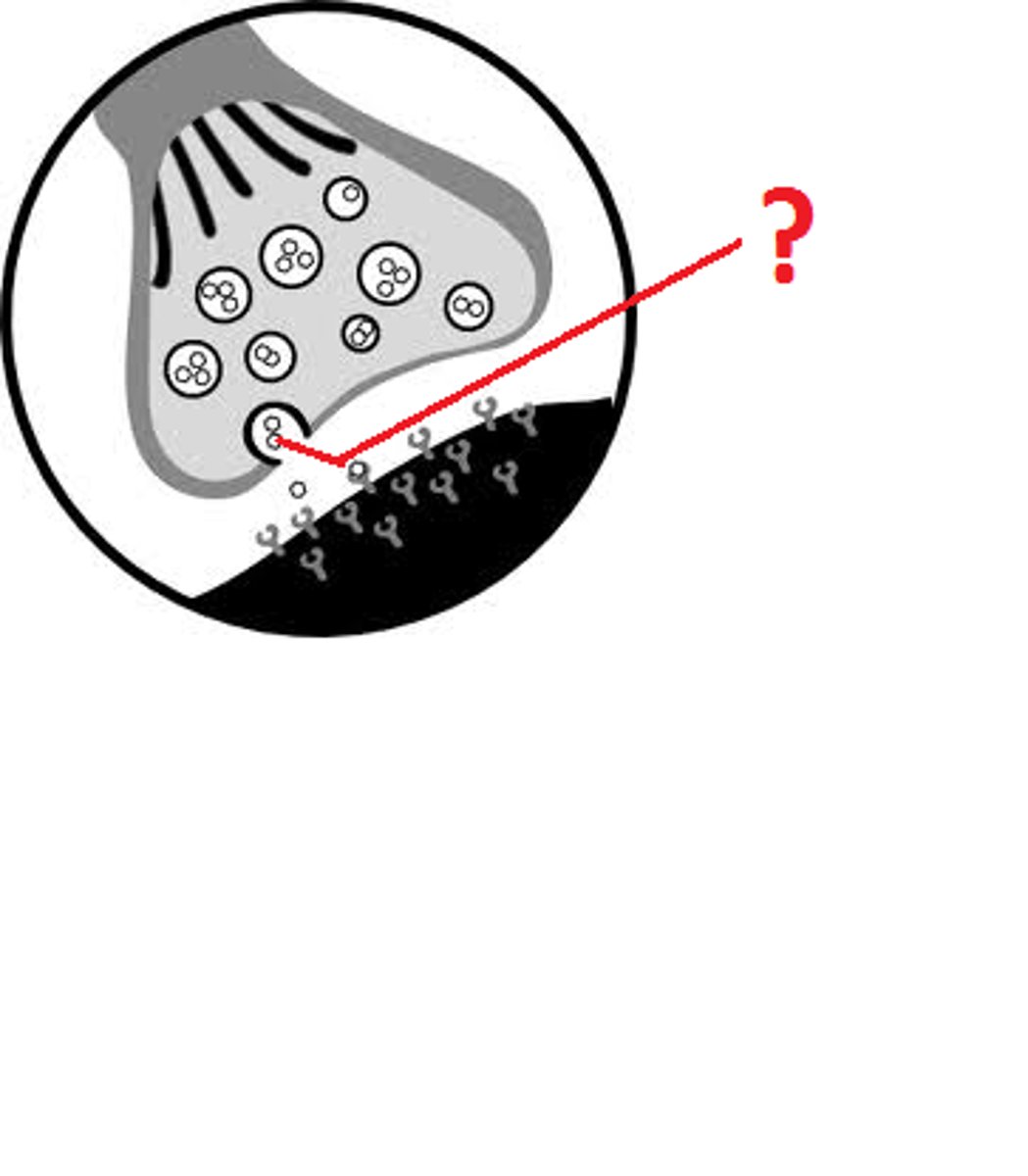
reuptake
a neurotransmitter's reabsorption by the sending neuron
nervous system
body's electrochemical communication network consisting of nerve cells
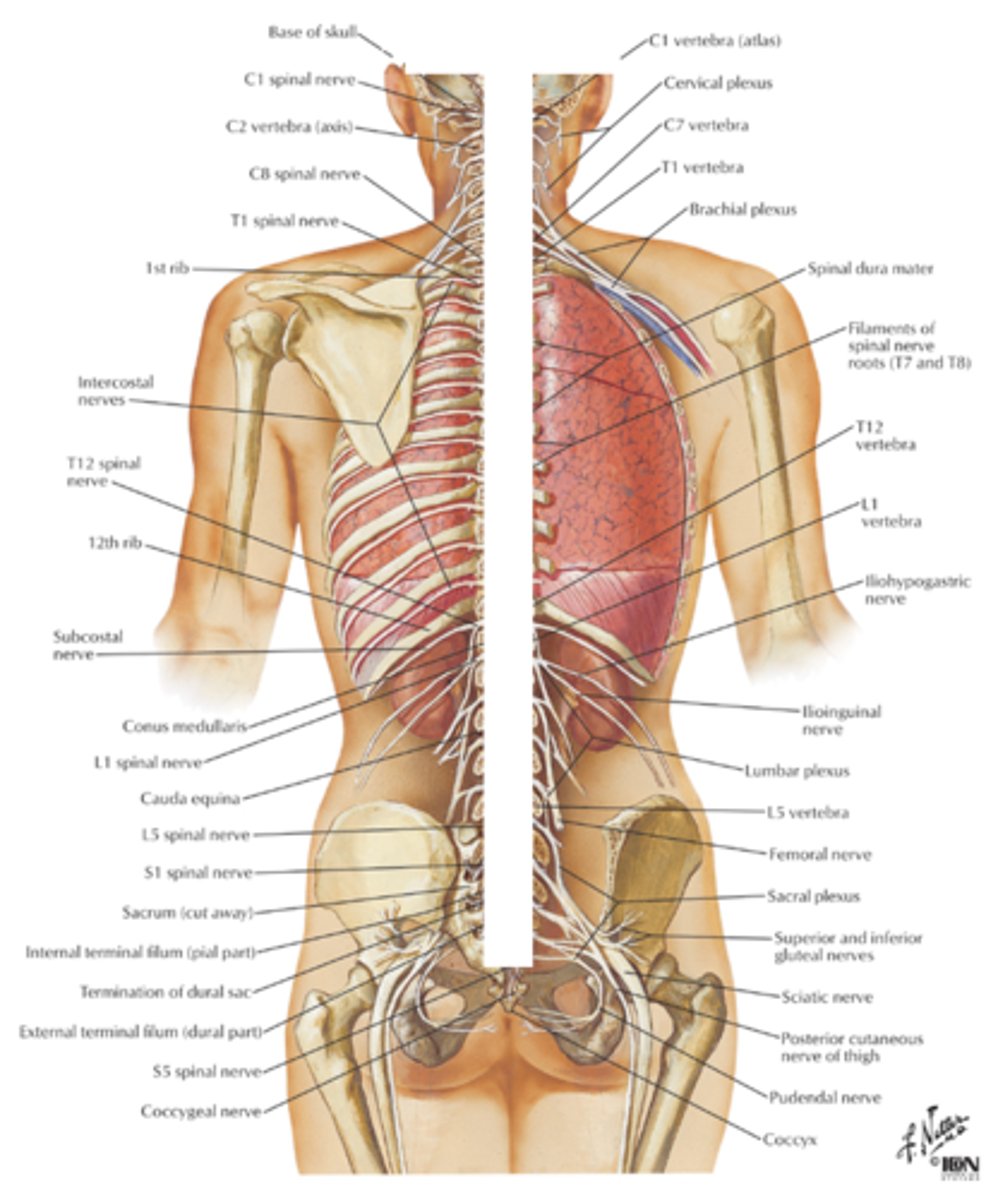
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord make up the __________.
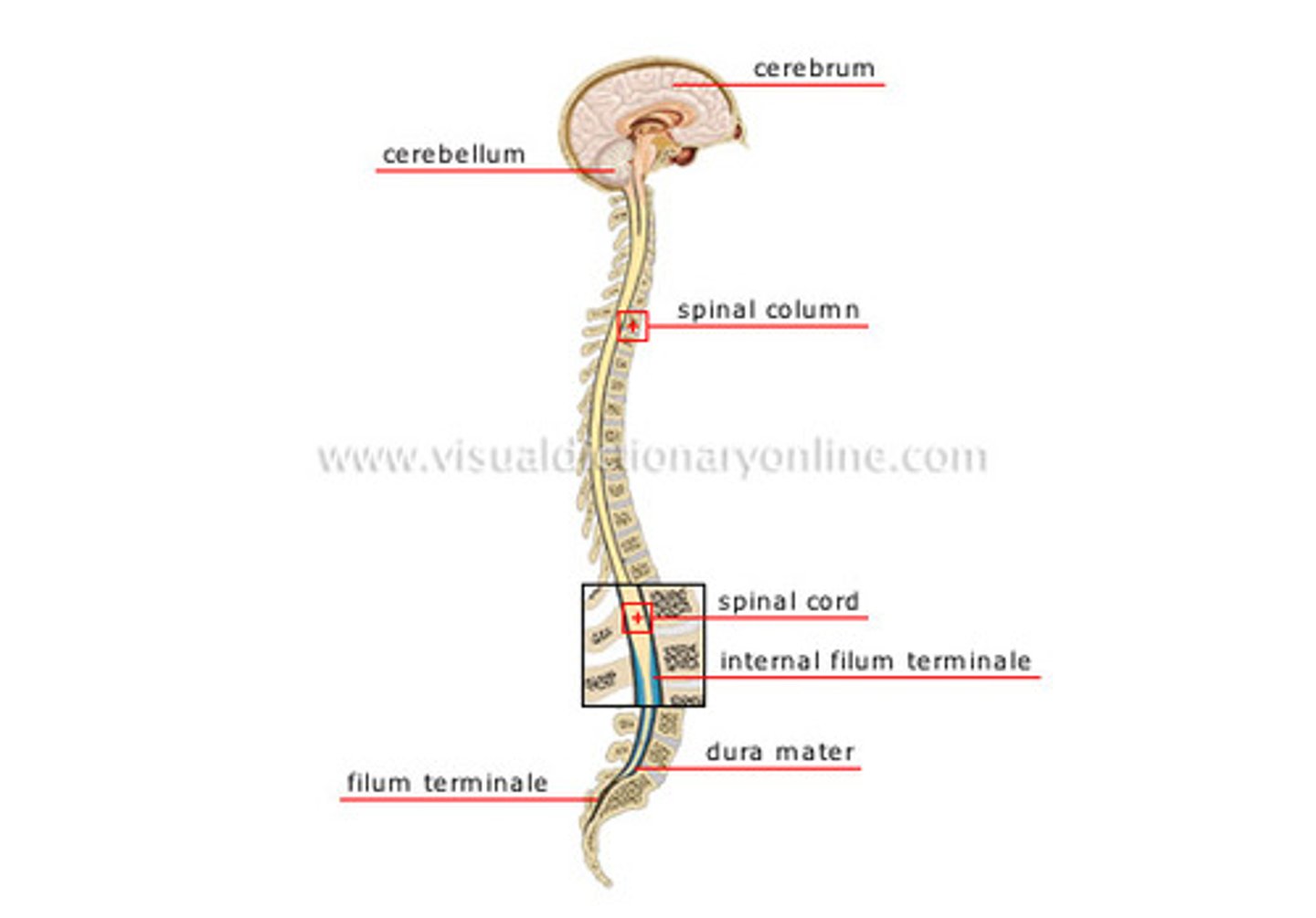
peripheral nervous system
sensory and motor neurons that connect central nervous system to rest of the body
somatic nervous system
part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles, voluntary movement
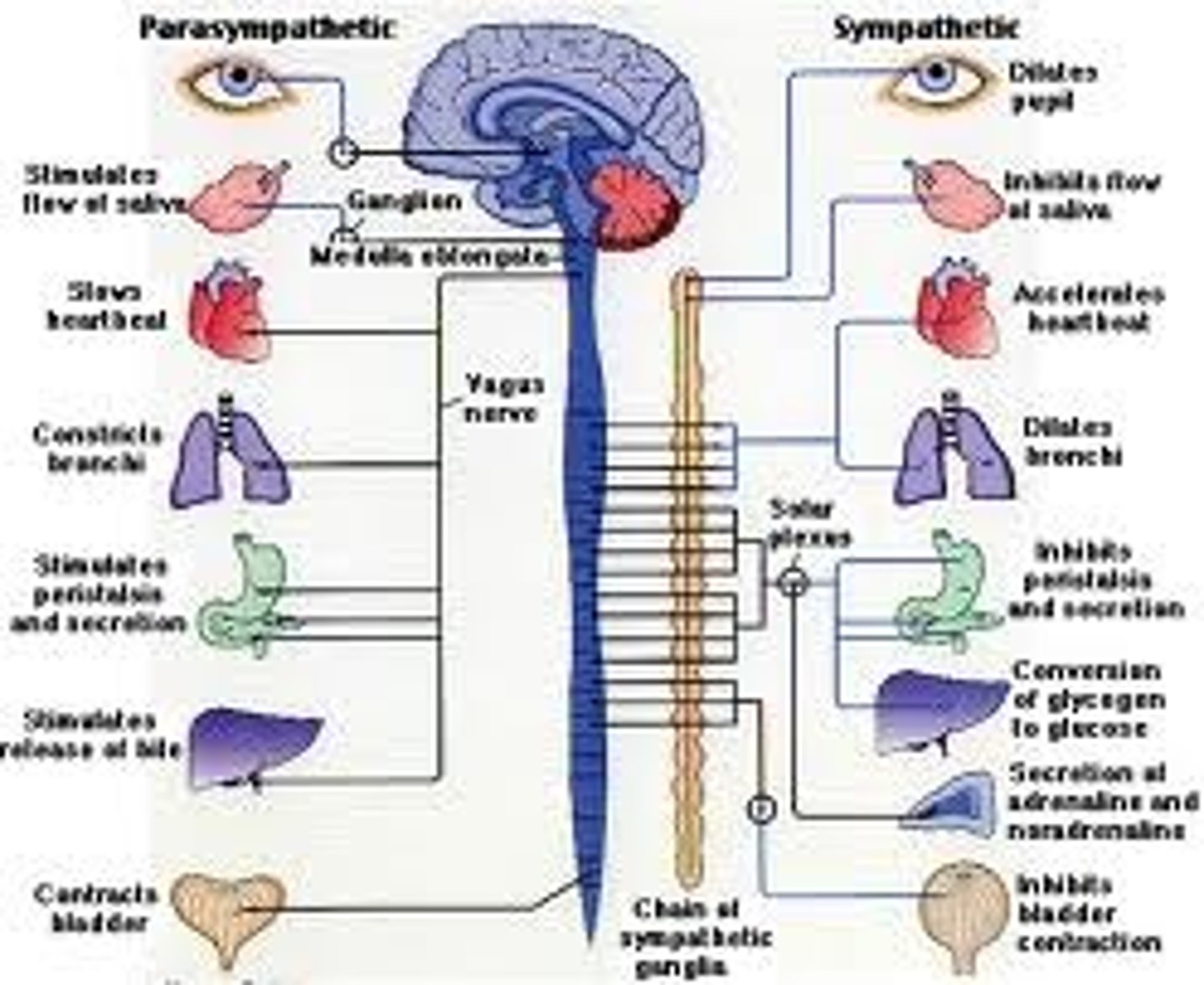
autonomic nervous system
part of the peripheral nervous system that controls glands and muscles of internal organs; involuntary
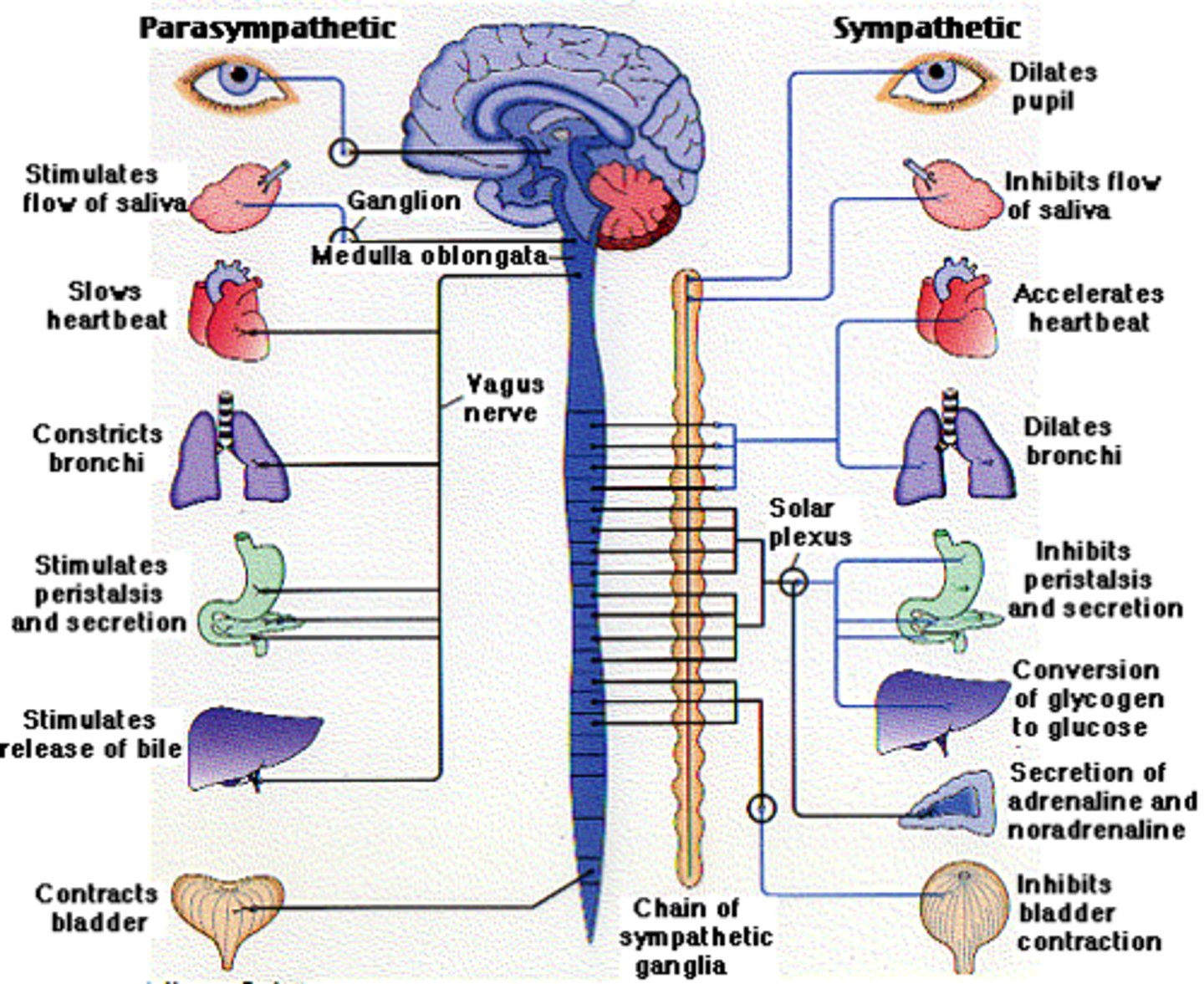
parasympathetic nervous system
branch of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body; rest and digest
sympathetic nervous system
branch of the autonomic nervous system that produces rapid physical arousal in response to perceived emergencies or threats; "flight or fight"
sympathetic and parasympathetic
what are the two subdivision of the automonmic nervous system?
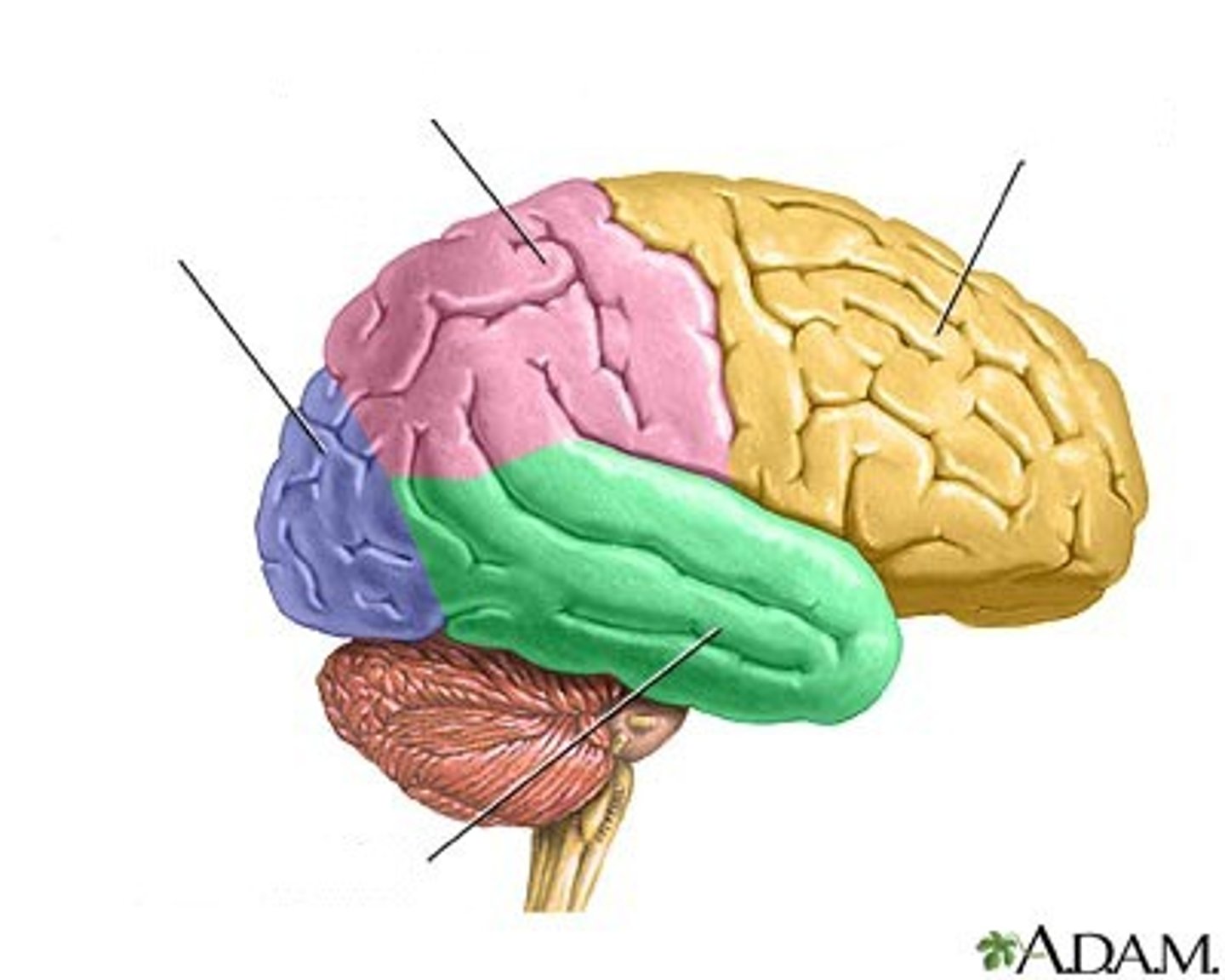
frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal
Names of the 4 lobes of the brain.
somatic and autonomic
what are the two categories in the peripheral nervous system?