Principles of chemistry
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Chemistry
The science of matter.
Matter
Any object that has mass and occupies space.
Pure Substance
A material with a definite, fixed composition that is either an element or a compound.
Element
A fundamental substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means.
Compound
A substance made of two or more elements chemically combined.
Homogeneous Matter
Matter that is uniform in appearance and has the same properties throughout.
Heterogeneous Matter
Matter consisting of two or more physically distinct phases.
Mixture
A combination of two or more pure substances.
Significant Figures
Digits that carry meaning contributing to their measurement accuracy.
Density (d)
The ratio of the mass of a substance to the volume occupied by that mass.
Thermal Energy
A form of energy involving the motion of small particles of matter.
Heat
The flow of energy due to a temperature difference.
Atomic Mass Unit (amu)
A unit of mass used to express atomic and molecular weights.
Ionic Compound
A compound formed from ions, which are charged atoms or groups of atoms.
Cation
A positively charged ion.
Anion
A negatively charged ion.
Reactants
Substances that start a chemical reaction.
Products
Substances formed as a result of a chemical reaction.
Physical Change
A change in substance that does not alter its chemical composition.
Chemical Change
A change that results in the formation of new chemical substances.
Potential Energy (PE)
Stored energy, the energy an object possesses due to its position.
Kinetic Energy (KE)
Energy possessed by matter due to its motion.
Scientific Notation
A method of expressing numbers as a value multiplied by a power of ten.
Volume
The amount of space occupied by matter, typically measured in liters or milliliters.
Significant Figures Rule 1
All non-zero digits are significant.
Solute
The smaller component in a solution, dissolved in the solvent.
Combination

Decomposition
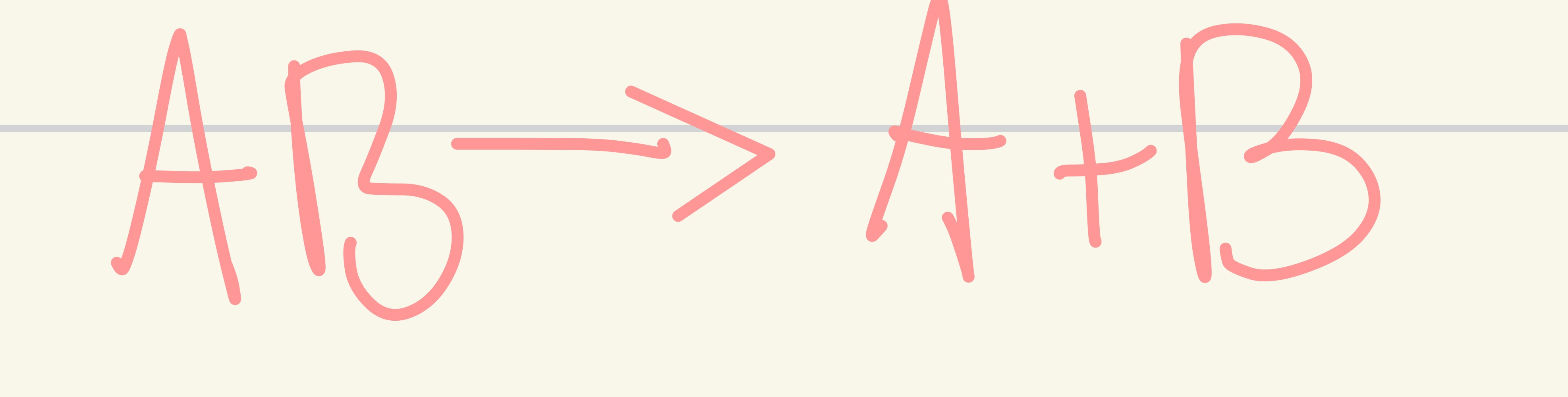
Single displacement

Double displacement

heat of reactions
quantity of heat actually produced during a chemical reaction
Exothermic Reaction
releases heat (heat can be treated as a product)
Endothermic Reaction
absorbs heat (heat can be treated as a reactant)
Photosynthesis
Converts energy in the form of light from the sun into chemical energy (bonds in gluclose)
Photosynthesis is a____
Endothermic (the needed energy is supplies by sunlight)
Fossil fuels
Petroleum,coal, and natural gas all release significant of energy during combustion.
Activation energy
Amount of energy needed to initiate a chemical reaction
mole
avogrado’s number (6.022 × 10²³) of units (atoms,molecules,ions etc.)
Molar Mass(MM)
sum of the atomic mass of the atoms in an element, compund, or formula unit.
Stoichiometry
area of chemistry that deals with quantitative relationships between products and reactants in chemical equations.
Mole Ratio
Ratio(conversation factor) betweenany two species in a chemical reaction.
Theoretical yield
maximum possible yield for a reaction, calculated based on the balenced chemical reaction
Actual Yield
Obtained from the reaction
Percent yield
Ratio of the actual and theoretical yield